-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Mining Engineering and Mineral Processing
2012; 1(2): 73-83
doi: 10.5923/j.mining.20120102.09
Some Surface Characteristics of Six Hematite Ores from the Middleback Range Area, South Australia
Keith Quast
Ian Wark Research Institute, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes, 5095 South Australia
Correspondence to: Keith Quast , Ian Wark Research Institute, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes, 5095 South Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Surface chemical techniques were used in an attempt to characterise eight samples of hematite. The hematites studied were six samples from the Middleback Ranges (Iron Knob (2 samples), Iron Monarch, Iron Prince, Iron Princess and Iron Baron) and two high purity, synthetic sa mples. The isoelectric points of the hematite samples showed a wide variation in value (from <2 to 8) whereas the zero points of charge were in the range 5.5 to 7.5. Using a simple mathematical calculation it was possible to estimate the surface charge characteristics of these hematite samples which gave a much better picture of the true surface properties of these samples in an aqueous environment. It was hoped that this study would contribute to a better understanding of the interaction between different hematite samples and water, a mechanism that is important in many industrial applications e.g. slurry pumping, agglomeration and granulation.
Keywords: Zeta Potential, Hematites, Isoelectric Points, Zero Points of Charge
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The aim of this report is to investigate several aspects of the surface chemistry of samples from five high-grade hematite deposits in the Middleback Range area of South Australia. It was hoped that these surface properties could be used to characterise ores from the different deposits and provide additional techniques to identify or “fingerprint” these materials. These deposits are all located in the northern area of the Middleback Ranges (see Figure 1). The surface characteristics of these hematite samples were investigated using conventional microelectrophoresis techniques as well as a modified form of potentiometric titration that allowed the estimation of surface charges using an innovative mathematical calculation.
2. Literature Survey
2.1. Middleback Range Hematite Ores
- According to the Resources and Energy Group of the Department for Manufacturing, Innovation, Trade, Resources and Energy of the Government of South Australia, the mines currently operating in the Middleback Ranges of South Australia are (from North to South) Iron Knob, Iron Baron, Iron Queen, Iron Cavalier, Iron Chieftain, Iron Knight, Iron Duchess and Iron Duke (DMITRE,[1]). Iron Monarch, Iron Baron and Iron Duke have collectively yielded more than 200 million tones of iron ore in almost100 years of mining. High grade ore has been mined from three areas: Northern Iron Knob area that includes Iron Knob, Iron Monarch and Iron Princess deposits, Central Iron Baron area comprising the Iron Baron, Iron Prince, Iron Queen and Iron Cavalier deposits and the South Middleback Ranges which includes the Iron Duke, Iron Duchess, Iron Knight and Iron Chieftain deposits (see Figure 1). Iron Duke, Iron Magnet, Iron Knight (North and South) and Iron Chieftain quarries are all currently (2012) being mined. Iron Baron (East) mining commenced at the beginning of 2012. The Iron Baron ore beneficiation plant is currently being commissioned in order to beneficiate both old stockpiled and newly mined low grade ores.
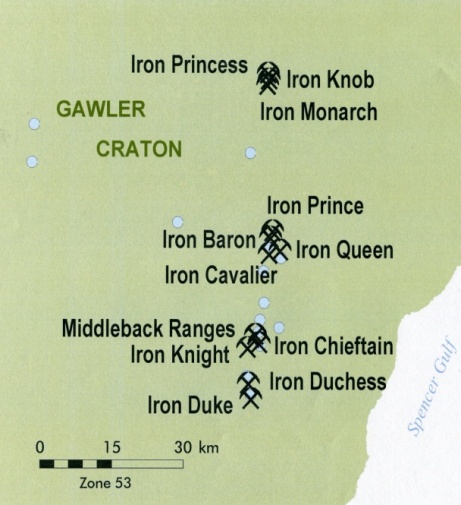 | Figure 1. Location map for iron ore mines in the Middleback Range area of South Australia (after DMITRE,[1] |
2.1.1. Historical
- The Iron Baron mine was developed in 1930 and closed in 1989. During 1986 the Iron Baron mining area produced approximately 1.1 Mt of ore averaging 60.2 % Fe, 3.8 % SiO2 and 1.8 % Al2O3, while the Iron Knob mining area produced 0.85 Mt averaging 66.8 % Fe, 1.95 % SiO2 and 0.76 % Al2O3 (Yeates,[3]). Reid[4] reported on the then current mining operations in the Middleback Ranges. Iron Knob, Iron Baron and Iron Duke were producing 1.8 Mt/year iron ore for the Whyalla steelworks and 0.9 Mt/year for the Newcastle and Port Kembla steelworks. Lump ore from the Iron Knob area assayed 66.5 % Fe, 2.0 % SiO2, 0.8 % Al2O3 and 0.8 % P at the time of the article.
2.1.2. Geology and Mineralogy
- The iron ores of the Middleback Range were formed by supergene enrichment. This process involved selective dissolution of gangue material and partial or total replacement by ore forming minerals. The iron formations were originally magnetite-rich (c.f. Lake Superior type banded iron formations (Liddy,[5]) with the magnetite being of diagenetic origin. The source of the iron was either primary sedimentary hematite or basin fluids. Carbonate minerals within the orebodies were almost completely replaced with iron but relic carbonate textures were retained. Silicates, however, were much less soluble and therefore mineralisation in the silicate facies iron formation is more patchy (Yeates,[3]). The diagenetic magnetite was recrystallised and remobilised during metamorphism and deformation. Uplift followed by several periods of intense erosion and weathering led to the oxidation of magnetite to hematite and martite by supergene processes.In a detailed mineralogical study of these iron ores, Edwards[6] reported the average compositions given in Table 1.
|
|
3. Hematite Surface Chemistry
- When a relatively insoluble oxide e.g. hematite is placed in an aqueous electrolyte solution, rearrangement of ionic species at the solid-liquid interface occurs and an electrical double layer forms. This double layer consists of one layer of surface charge and another layer of counter ions. The net surface charge may be positive, negative or zero, and since the system as a whole must remain electrically neutral, the medium surrounding the oxide must contain an equivalent number of counter ions with opposite charges. These will be attracted to the charged surface sites and adsorbed at the oxide/solution interface. However, because of thermal agitation, this adsorbed layer extends as a diffuse layer over a finite distance from the particle surface.The electrical double layer that develops at the hematite/solution interface is the result of hydrolysis of the surface species, followed by pH-dependent dissociation of surface hydroxyls. A general equation for this process is:
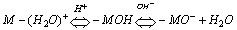 | (1) |
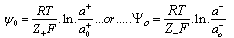 | (2) |
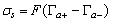 | (3) |
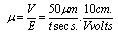 | (4) |
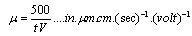 | (5) |
4. Materials Examined
- Four samples of high grade iron ores from the Middleback Range area were investigated in this study. These samples were received as lump ore from BHP OneSteel, Whyalla, South Australia. The synthetic hematite sample of Analytical Reagent (A.R.) grade was supplied by J.T. Baker Pty. Ltd and the Precipitated Hematite sample was from BDH.
5. Procedure
5.1. Characterisation of Minerals
- Hematite samples from Iron Knob, Iron Princess, Iron Monarch, Iron Baron and Iron Prince were examined in this study. The samples were crushed and pulverised in a ring mill prior to analysis.Iron assays were determined using the method of Kolthoff et al[18] which involved digestion using stannous chloride and hydrochloric acid followed by titration with potassium permanganate solution. The amount of acid insolubles (primarily silica) was determined gravimetrically on the residue remaining by filtration after acid digestion.Specific Gravity (S.G.) was measured by displacement of nitrogen in a Quantachrome Stereopycnometer and the surface areas of the pulverised samples were measured using a Fisher Sub-sieve Sizer model 95 as per ASTM B330-88 (1988)[19].
5.2. Measurement of Zeta Potential
- Suspensions of 1 g of hematite in 50 ml of distilled water, with the pH adjusted using dilute solutions of either hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide were centrifuged for 30 seconds at 2000 rpm. Substituting the centrifugal force acting in Stoke’s Law equation for free settling reveals that the largest hematite particle remaining in suspension after centrifuging was 1.5 μm, and the largest quartz particle was 2.3 μm. The supernatant liquid containing sub-micron particles was transferred to the flat cell of a Rank Bros. Microelectrophoresis Apparatus Mark II.Particles were timed in moving a distance of 50 μm under a known potential gradient which was chosen to give timings between 5 and 10 seconds. At least 10 separate particles were timed, followed by another 10 after the electrode polarity had been reversed. The average of the 20 timings was used in the calculation of mobility as given in equation (5). Zeta potentials were calculated from mobility data using the rationalised Smoluchowski equation which is applicable for this system. Under normal operating conditions, zeta potential (ζ) in mV is given by equation (6).
 | (6) |
5.3. Measurement of Zero Point of Charge (zpc)
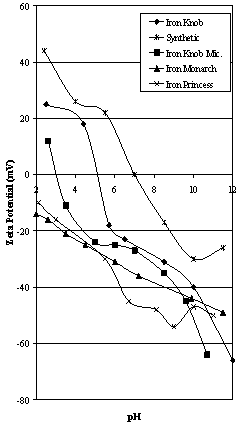 | Figure 2A. Zeta Potential Characteristics of Iron Knob area ores compared to synthetic hematite |
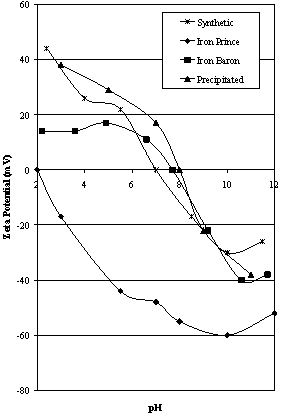 | Figure 2B. Zeta Potential Characteristics of Iron Prince area ores compared to synthetic hematites |
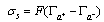 | (3) |
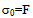 | (7) |
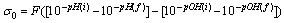 | (8) |
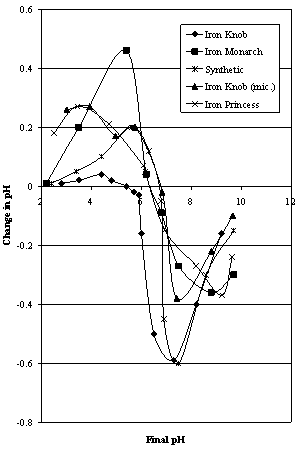 | Figure 3A. Mular and Roberts plots for Iron Prince area ores compared to synthetic hematites |
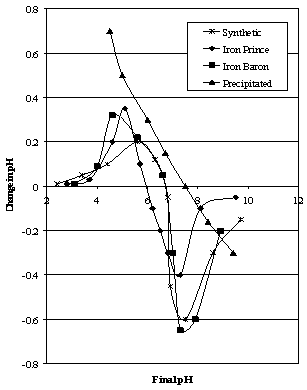 | Figure 3B. Mular and Roberts plots for Iron Prince area ores compared to Synthetic Hematites |
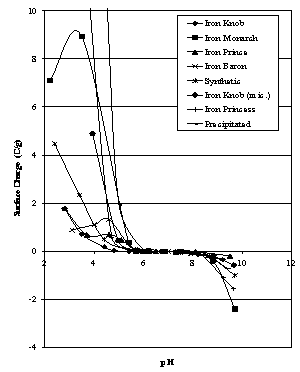 | Figure 4. Surface Charge estimates for hematites |
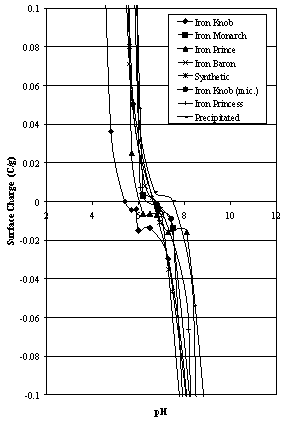 | Figure 4A. Surface Charge estimates for hematites (low surface charge area) |
6. Results and Discussion
- A summary of the physical and chemical characteristics of the pulverised hematite samples is given in Table 4.
|
|
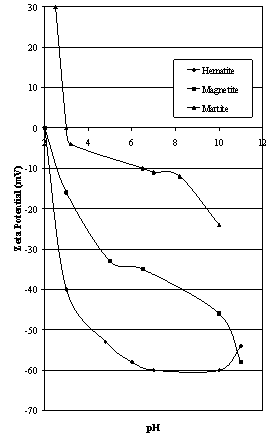 | Figure 5. Zeta Potential of iron oxide minerals as reported by Chuanyao and Yongxin[38] |
7. Conclusions
- Different samples of hematite exhibit different surface characteristics depending on such factors as colour, purity (and S.G.) and surface area. The natural hematite samples have very similar mineralogical characteristics, being formed under similar processes. All the hematites examined have high iron contents. Of the natural hematites examined, the Iron Knob sample had the highest purity.Hematite surface chemistry was investigated using two techniques: microelectrophoresis and a modified form of potentiometric titration. These techniques allowed the determination of the isoelectric point and zero point of charge respectively. Isoelectric points for the samples examined showed a wide range of values due to the presence of fine silica in the ore strongly influencing the values of iep for some samples.Using a simple potentiometric titration technique allowed the determination of the zero point of charge for these samples, but a simple mathematical calculation allowed an estimation of the surface charge characteristics. It is recommended that this technique be conducted on many different and well-characterised hematite samples to determine its suitability as a rapid method of characterisation, especially as it could point to the development of micaceous habit.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author is grateful to BHP Long Products Division, Whyalla for providing the original hematite samples investigated in this study and for Onesteel for the Iron Princess sample. Informative discussions with Professor Tom Healy, former Director, Advanced Mineral Products Research Centre, University of Melbourne are gratefully acknowledged.
References
| [1] | DMITRE, 2012, South Australian Earth Resources Information Sheet M20, Iron Ore Deposits in South Australia, published February, 2012, 5p. |
| [2] | Quast, K.B., 2012, Effect of 25% Goethite on the Surface Chemistry of Hematite, Manuscript submitted to International Journal of Mining Engineering and Mineral Processing.. |
| [3] | Yeates, G., 1990, Middleback Range Iron Ore Deposits, in “Geology of the Mineral Deposits of Australia and Papua New Guinea” ed. F.E. Hughes, The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, p. 1045-1048. |
| [4] | Reid, R.B., 1993, Iron Ore Mining by BHP Steel-Long Products Division at Iron Knob and Iron Duke, S.A. in “Australasian Mining and Metallurgy (Sir Maurice Mawby Memorial Volume) 2nd. Ed. Vol. 1, ed. J.T. Woodcock and J.H. Hamilton, Monograph 19, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, p. 245-246. |
| [5] | Liddy, J.C., 1968, The Jaspilite Iron Ores of Western and South Australia, Australian Mining, 60(10), 21-29. |
| [6] | Edwards,A.B., 1936, The Iron Ores of the Middleback Ranges, South Australia, Proceedings, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, No. 102, 155-207. |
| [7] | England, B.M. and Turner, K.E., 1983, A Morphological and Mineralogical Study of Selected Ores from the Middleback Range, South Australia. Part 1- Iron Knob, Iron Monarch, Iron Prince, Iron Baron, Iron Queen, Cavalier and Racecourse Orebodies, BHP Central Research Laboratories Report No. CRL/R/27/83. 96p. |
| [8] | Edwards, A.B., 1953, Mineralogy of the Middleback Range Iron Ores, in, “Geology of Australian Ore Deposits”, Vol. 1, Proceedings of the Fifth Empire Mining and Metallurgical Congress, ed. A.B. Edwards, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, p. 464-472 |
| [9] | Miles, K.R. 1954, The Geology and Iron Ore Resources of the Middleback Range Area, Geological Survey of South Australia Bulletin No. 33, 245 p. |
| [10] | Owen H.B. and Whitehead, S., 1965, Iron Ore Deposits of Iron Knob and the Middleback Ranges in “Geology of Australian Ore Deposits” 2nd. Ed., Eighth Commonwealth Mining and Metallurgical Congress, Vol. 1, ed. J.McAndrew, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, p. 301-308. |
| [11] | Newton, W. Davies, M. and Morris, B., 1997, Emerging New Resources for World Class Iron and Steel Production in South Australia, MESA Journal, 7, p. 6-11. |
| [12] | Rudd, E.A. and Miles, K.R. 1953, Iron Ores of the Middleback Ranges, South Australia, Proceedings, Fifth Empire Mining and Metallurgical Congress, Vol. 1, “Geology of Australian Ore Deposits” ed. A.B. Edwards, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, p. 449-463. |
| [13] | Owen, H.B., 1963, The Geology of the Iron Monarch Orebody, paper No. 6, Annual Conference of the AusIMM, Whyalla, S.A. p. 1-8. |
| [14] | Owen, H.B., 1964, The Geology of the Iron Monarch Orebody, Proceedings of the Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 209, 43-67. |
| [15] | Jack ,R.L., 1922, The Iron Ore Resources of South Australia, Geological Survey of South Australia Bulletin No. 9, p. 38. |
| [16] | Thomson, I.A., 1974, BHP Raw Materials Operations in South Australia, Mineral Resources Review (Dept. of Mines, South Australia) 140, p. 7-20. |
| [17] | Ashworth, K.L. and Furber, D.V., 1976, Middleback Iron Ore, Mining Magazine 134, 170-179. |
| [18] | Kolthoff, I.M., Sandell, E.B., Meehan, E.J. and Bruckenstein, S.,1969, Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 4th. Ed., Macmillan, New York, p. 832-834. |
| [19] | ASTM B330-88, 1988, Standard Test Method for Average Particle Size of Powders of Refractory Metals and their Compounds by the Fisher Sub-Sieve Sizer, 3p. |
| [20] | Mular, A.L. and Roberts, R.B., 1966, A Simplified Method to Determine Isoelectric Points of Oxides, Canadian Mining and Metallurgical Bulletin 59(655), 1329-1330. |
| [21] | Woods, R., 1990, The Electrical Double Layer Properties of Oxides, M. App. Sc. Thesis, S.A. Institute of Technology, 199 p. |
| [22] | Kulkarni,R.D. and Somasundaran, P.,1976, Mineralogical Heterogeneity of Ore Particles and its Effects on their Interfacial Characteristics, Powder Technology,14, 279-285. |
| [23] | Lyklema, J., 1975, cited in Yariv, S. and Cross, H.,1979, Geochemistry of Colloid Systems for Earth Scientists, Springer-Verlag, p.218. |
| [24] | Joy, A.S., Watson, D. and Cropton, R.W.G., 1964, Collector Adsorption and Surface Charge Density, Trans. AIME, 229, 5-7. |
| [25] | Smith G.W. and Salman, T., 1971, The Adsorption of Dehydroabietylamine Acetate on Mineral Oxides, Canadian Mining and Metallurgical Bulletin, 64(709), 70-75. |
| [26] | Mwaba, C.C., 1991,Surfactant-Enhanced Dewatering of Graphite and Hematite Suspensions, Minerals Engineering, 4(1), 49-62. |
| [27] | Das, B. and Naik, P.K., 2003, Electrokinetic and Flotation Studies of Hematite using di(2-ethyl hexyl) Phosphoric Acid, J. South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 103, July/August, 397-401. |
| [28] | Pugh, R.J. and Lundstrom,H.,1987, The Surface Characterization and Flocculation of Hematite Fines, in “Flocculation in Biotechnology and Separation Systems” ed. Y.A.Attia, Elsevier, p. 673-694. |
| [29] | Joy, A.S. and Watson, D., 1963, Occurrence and Properties of Hematite Slimes, in “Mineral Processing” (Proceedings of the Sixth Mineral Processing Conference, Cannes, France) ed. A. Roberts, paper 24F, Pergamon Press, p 355-368. |
| [30] | Parks, G.A., 1965, The Isoelectric Points of Solid Oxides, Solid Hydroxides and Aqueous Hydroxo Complex Systems, Chemical Reviews, 65, 177-198. |
| [31] | Fuerstenau, D.W., 1970, Interfacial Processes in Mineral/Water Systems, Pure and Applied Chemistry, 24(1), 135-164. |
| [32] | Winer, A.A. and Wright, I.F., 1966, Practical Problems in Particle Size and Surface Area Measurements, J. Canadian Ceramic Society, 35 68-75. |
| [33] | Smith, G.W. and Salman, T., 1966, Zero Point of Charge of Hematite and Zirconia, Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 5(2), 93-97. |
| [34] | Smith, R.W. and Trivedi, N., 1974, Variation of Point of Zero Charge of Oxide Minerals as a Function of Ageing Time in Water, Trans. AIME, 255, 69-74. |
| [35] | Montes, S., Atenas, G.M. and Valero, E., 2007, How fine Particles on Haematite Mineral Ultimately Define the Mineral Surface Charge and Overall Floatability Behaviour, Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 107, 689-695. |
| [36] | Kosmulski, M., 2001, Chemical Properties of Mineral Surfaces, Marcel Dekker, New York |
| [37] | Kosmulski, M., Maczka, E., Jartych, E. and Rosenholm, J.B., 2003, Synthesis and Characterisation of Goethite and Goethite-Hematite Composite: Experimental Study and Literature Survey, Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 103, 279-285. |
| [38] | Chuanyao, S. and Yongxin, L., 1992, Effect of Trace Elements Occurring on Mineral Surface on Floatability. Part 11: Effect of Surface Characteristics of Aegirine and Hematite on their Floatability, in “Proceedings of the First International Conference on Modern Process Mineralogy and Mineral Dressing”, International Academic Publishers, p. 213-218. |
| [39] | Gibb, A.W.M. and Koopal, L.K. 1990, Electrochemistry of a Model for Patchwise Heterogeneous Surfaces, J. Colloid and Interface Science, 134(1), 122-138. |
| [40] | Sadowski, Z. and Laskowski, J., 1980, Hindered Settling-a New Method of the iep Determination of Minerals, Colloids and Surfaces, 1, 151-159. |
| [41] | Kanungo, S.B. and Mahapatra, D.M., 1989, Interfacial Properties of Two Hydrous Iron Oxides in KNO3 Solution, Colloids and Surfaces, 42, 173-189. |
| [42] | Torrent, J. and Barron, V., 2002, Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy of Iron Oxides, in "Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science", Marcel Dekker, p. 1438-1446. |
| [43] | Alvarez-Silva, M., Uribe-Salas, A., Mirnezami, M. And Finch, J.A., 2010, The Point of Zero Charge of Phyllosilicate Minerals using the Mular-Roberts Titration Technique, Minerals Engineering, 23, 383-389. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML