-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Mining Engineering and Mineral Processing
2012; 1(2): 31-37
doi: 10.5923/j.mining.20120102.02
Effect of 25% Goethite on the Hydrophobicity and Oleate Flotation of Hematite
Keith Quast
Ian Wark Research Institute, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes, 5095, South Australia
Correspondence to: Keith Quast , Ian Wark Research Institute, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes, 5095, South Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Flotation tests conducted on the two Iron Duke samples using oleate showed that the presence of goethite adversely affected the flotation response of the hematite but contact angle measurements showed a higher hydrophobicity for the sample containing 25% goethite. Correcting the oleate addition for the changes in surface area still showed that the goethite reduced the flotability of the hematite. Aspects of processing iron ores containing goethite will need to be addressed as the high grade hematite ores are depleted, especially if flotation is employed in the beneficiation process.
Keywords: Contact Angle, Hematite, Goethite, Flotation
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The aim of this paper is to investigate some of the effects of the presence of goethite on the flotation behaviour of Iron Duke hematite, a high grade deposit in the southern Middleback Ranges of South Australia. With the depletion of higher grade iron ores, ores containing significant amounts of goethite will need to be processed. Contact angle measurements were also made on these two samples as an indication of their relative hydrophobicity. The two Iron Duke samples were also examined for the effect of associated goethite on the flotation behaviour of hematite using oleic acid.
2. Literature Survey
2.1. Middleback Range Hematite Ores
2.1.1. Historical
- Mining in the Middleback Ranges area has centred on three locations, comprising Iron Knob and Iron Monarch in the north, Iron Prince and Iron Baron in the centre, and Iron Duke in the south. Reid[1] reported on the then current mining operations in the Middleback Ranges. Iron Knob, Iron Baron and Iron Duke were producing 1.8 Mt/year iron ore for the Whyalla steelworks and 0.9 Mt/year for the Newcastle and Port Kembla steelworks. The Iron Duke mine was opened on 27 February, 1990 by BHP managing director, Mr. B.T. Loton. Production from the Iron Duke mine during 1993 was 1.5 Mt/year, with a planned mine life of 20 years. A fully integrated and automated crushing sampling and blending plant is used to crush ore that had previously been blended in run of mine stockpiles. Pellet ore grade is 64.7 % Fe, 4.0 % SiO2, 2.05 % Al2O3 and 0.037 % P.According to PIRSA in 2011, the Iron Duke mine currently produces more than 1 million tonnes of ore every year[2].
2.1.2. Geology and Mineralogy
- At the Iron Duke mine the high grade orebodies are dominantly hematite replacing magnetite; in the deeper unoxidised, metamorphosed ores, both magnetite and hematite occur and Catley[3] considered that a mixture of the two minerals was present in the primary sediments.In a detailed mineralogical study of the iron ores from the Middleback Ranges, Edwards[4] reported compositions of 67.2 % Fe and 0.20 % Mn for Iron Duke ore. Miles[5] gave weighted averages of ore computed from assays and samples cut from the surface exposures of the Iron Duke mine as 61.63 % Fe, 0.18 % Mn and 0.034 % P. A sample of hard hematite from the main orebody at the south end of the lease returned 69.18 % Fe, 0.06 % Mn and 0.05 % P; values also reported by Liddy[6].According to Owen and Whitehead[7], the Iron Duke orebody has a discontinuous hematite outcrop over a strike length of 5,500 feet (1700 m) and an irregular width not exceeding 600 feet (180 m). The hematite ore occurs only in the western limb of the syncline and generally to depths of approximately 400 feet (120 m) where it passes, in descending succession, into magnetite jasperlite, magnetite-talc ore, magnetite dolomite ore and hematite dolomite ore. Some of the surface hematite ore is superficial and is confined to a zone of surface enrichment 50 – 60 feet (15-18 m) deep below which it passes abruptly to jasperlite, and then to the sequences given above.
2.2. Flotation of Iron Ores
- A review article on the use of oleic acid for the flotation of hematite has been published by the author[8]. This review examined the flotation characteristics of a high grade (>98 % Fe2O3) specular hematite from a local source and a hematite ore containing 57 % Fe2O3 using oleic acid. The maximum recovery of the specular hematite occurred at neutral pH and the highest hematite grades were obtained at pH 5-6 for low additions of oleic acid rising to pH 9-10 as the amount of collector was increased. The interaction between hematite and oleate was confirmed as chemisorption in a more recent paper by the author[9]. It is the purpose of this paper to investigate the flotation characteristics of goethite in more detail since the flotation characteristics of hematite with oleate have been well documented.Sun[10] used bubble pick-up as a means of examining the flotation properties of goethite. He identified a pH range of 4 to 8 for the interaction of oleic acid with goethite.The classic study on the flotation characteristics of goethite was published by Iwasaki, Cooke and Colombo[11]. They measured the isoelectric point of their natural goethite sample at 6.7 using streaming potential. The critical pH curves for the flotation of goethite were determined using vacuum flotation tests. At 10-4 M sodium oleate, flotation was possible between pH 2 and 11.5, very similar to the range previously reported by Cooke and Nummela[12]. These data were confirmed using Hallimond tube testing where the region of flotability was established as pH 2.5 – 10.5 using the same addition of sodium oleate. Iwasaki, Cooke and Choi[13] found a region of good goethite flotation using 10-4 M oleic acid over the pH range 3-11. They also reported that the isoelectric points of hematite and goethite occurred at pH 6.7.The goethite-oleic acid-oleate system has been investigated in detail and reported by Jung et al[14]. Detailed adsorption isotherms were constructed using radiochemical analyses of oleate on synthetic goethite. The zero point of charge of the goethite used was 8.75, and the isoelectric point was 9.1. Adsorption was controlled by coulombic plus hydrophobic effects together with a specific adsorption component that was considered to be neutral oleic acid co-adsorption with oleate ions, or acid soap dimer adsorption. The electrokinetic data also indicated a specific contribution beyond coulombic plus hydrophobic effects. This system was modelled, and the dominant surface oleate species were (FeOHOl)2H- at lower pH values giving way to FeOHOl- as the pH was raised[15].The only comparative study on the flotation of hematite and goethite located by the author to date has been reported by Abeidu[16]. The results obtained using 100-150 µm mineral particles have been scaled from his article and reproduced as Figure 1, showing that hematite floats over a slightly wider pH range using 100 mg/l oleic acid than goethite but the curves are very similar.
2.3. Measurement of Contact Angles
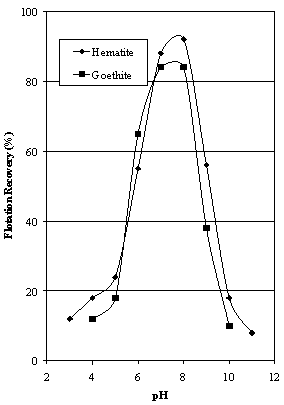 | Figure 1. Comparative Flotation Data for Hematite and Goethite using 100 mg/l Oleic Acid (data of Abeidu[16] |
 | Figure 2. Sketch of equipment used to determine contact angles on solid particles |
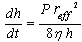 | (1) |
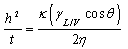 | (2) |
 tortuosity factor
tortuosity factor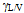 - liquid/vapour surface tension of the penetrating liquid
- liquid/vapour surface tension of the penetrating liquid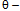 contact angleIf the effective pore radius is known the tortuosity factor can be approximated and hence a contact angle can be obtained from the rate of penetration. If a liquid known to have a contact angle of zero with a solid is used to measure the rate of penetration of a packed column of that solid, we can write.
contact angleIf the effective pore radius is known the tortuosity factor can be approximated and hence a contact angle can be obtained from the rate of penetration. If a liquid known to have a contact angle of zero with a solid is used to measure the rate of penetration of a packed column of that solid, we can write. | (3) |
 - surface tension for the non-wetting liquid
- surface tension for the non-wetting liquid - surface tension for the wetting liquid
- surface tension for the wetting liquid - viscosity of the non-wetting liquid
- viscosity of the non-wetting liquid - viscosity of the wetting liquidThen it follows that:
- viscosity of the wetting liquidThen it follows that:  | (4) |
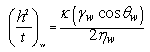 | (5) |
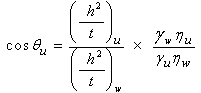 | (6) |
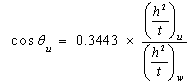 | (7) |
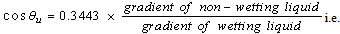 | (8) |
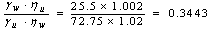 | (9) |
 - cyclohexane
- cyclohexane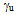 =72.75 mNm-1 - water
=72.75 mNm-1 - water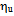 =1.002 mNm-2s- water
=1.002 mNm-2s- water =1.02 mNm-2s- cyclohexaneThe cosine of the contact angle is thus given by substituting the rates of rise of the wetting and non-wetting liquids into equation (7).
=1.02 mNm-2s- cyclohexaneThe cosine of the contact angle is thus given by substituting the rates of rise of the wetting and non-wetting liquids into equation (7).3. Materials Examined
- Two samples of high grade iron ores from Iron Duke in the Middleback Range area were investigated in this study. These samples were received as lump ore from BHP Long Products Division, Whyalla, South Australia. According to Kirk[19], these represent end-members of material at the Iron Duke deposit. Sample # 1 was described as well bedded blue hematite, typically specular with well-defined bedding planes. The crystals are elongated parallel to the bedding planes and mechanical breakage is listed as ‘easy”. Sample # 2 is massive brown goethitic hematite, very hard and showing a good preservation of lump. Mechanical breakage is listed as “difficult”. X-ray Diffraction suggests that sample # 2 contains approximately 25 % goethite and 75 % hematite, whereas sample #1 was only composed of hematite. Chemical analysis gave acid insolubles of 0.1 % for sample # 1 and 1.9 % for sample # 2 (see 4.1 below).
4. Procedure
4.1. Characterisation of Minerals
- The Iron Duke samples were received as large, hand-picked lumps. They were crushed and pulverised in a ring mill until they were all finer than 150 µm prior to analysis and testing.Iron assays were determined using the method of Kolthoff et al[20] which involved digestion using stannous chloride and hydrochloric acid followed by titration with potassium permanganate solution. Acid insolubles (primarily silica) were determined gravimetrically on the insoluble residue from the digestion process by filtration on ashless filter paper followed by drying and combustion at 800℃.Specific Gravity (S.G.) was measured by displacement of nitrogen in a Quantachrome Stereopycnometer and the surface areas of the pulverised samples were measured using a Fisher Sub-sieve Sizer model 95 as per ASTM B330-88[21]. Results are given in Table 1.
|
4.2. Measurement of Contact Angle
- A diagram of the apparatus used is given in Figure 2. Four graduated capillary tubes with the same weight and length were selected. A small plug of Kleenex tissue was inserted in one end. Small amounts of the iron ore powder were scooped into the tube and tapped 20 times. This process was repeated until the powder reached the 40 mm mark on the tube. The four tubes were packed with tapped powder. A Washburn tube was placed vertically in a glass vial containing a small amount of water. The rate of rise of the water past the marks on the tube was recorded. This procedure was repeated for the second tube. The two other tubes were placed in a small amount of cyclohexane in other vials and the rate of rise of the cyclohexane recorded. The contact angle was calculated by substituting the gradients in equation 7.
4.3. Flotation Testing
- The natural hematite samples (at all finer than 150 µm) were riffled into 100 g charges for testing by flotation. A sample was placed in a one litre flotation cell and demineralised water was added to bring the pulp level to 20 mm below the overflow weir giving a pulp density of approximately 10 % solids by weight. The cell was placed on a Galigher Agitair laboratory flotation machine model LA-500. The pH of the pulp was adjusted to the desired value using a dilute solution of either hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide. The oleic acid (10 µL Ajax Chemicals, technical grade) was added to the cell using a microlitre syringe. The pulp was conditioned for 5 minutes at 1000 rpm. Strict pH control was maintained throughout the testwork. After 5 minutes, one drop of Yarmor pine oil (approximately 25 mg) was added and conditioning continued for a further 5 minutes.The pulp was aerated at two litres/minute for three minutes, during which time the froth layer was removed using a spatula. The froth product was filtered, dried and weighed, and the recovery calculated as the weight per cent of hematite floated for an addition of 3x10-5M oleic acid corresponding to 100 g/t.
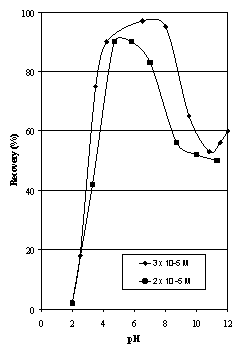 | Figure 3. Flotation Recovery as a Function of pH for Iron Duke #1 samples |
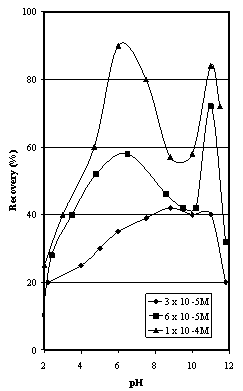 | Figure 4. Flotation Recovery as a Function of pH for Iron Duke #2 samples |
5. Results and Discussion
- The selection of two samples of relatively pure, naturally-occurring hematites from the same general area but containing different amounts of goethite should give an indication of the sensitivities of the various techniques used to study their flotation and hydrophobicity properties in respect to changes in mineralogy. In order to compare hydrophobicities and flotation behaviour with other surface properties, values of isoelectric points and zero points of charge for these two samples have been measured previously by the author, and have been submitted in another manuscript to this journal[22]. Isoelectric points were measured by microelectrophoresis and zero points of charge using a modified titration technique. A summary of the surface characteristics of the two samples of hematite are given in Table 2.
|
6. Conclusions
- The natural hematite samples have similar mineralogical characteristics, being formed under similar processes. The hematite sample had a high iron content, but the iron content of sample # 2 was much lower suggesting different mineralogy due to the presence of 25% goethite.The contact angles measured in this study show a different trend to that expected from the literature. Normally the presence of goethite would reduce the contact angle of hematite, but the results obtained in this study show a higher contact angle associated with the presence of 25% goethite. This may well be due to differences in surface chemistry, particle porosity and surface roughness.The results of the flotation testing show that pure hematite floats more readily than when goethite is absent, probably due to the much higher surface area and porosity associated with the goethite. Even increasing the collector addition in proportion to the measured surface area failed to produce as high a recovery as for the purer hematite sample. This has consequences when lower grade iron ores containing goethite as well as hematite are processed using flotation or some other form of beneficiation process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author is grateful to BHP Long Products Division (now Onesteel), Whyalla for providing the Iron Duke samples investigated in this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML