-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Mining Engineering and Mineral Processing
2012; 1(2): 21-30
doi: 10.5923/j.mining.20120102.01
Biobeneficiation of Iron Ores
H. Sarvamangala 1, K. A. Natarajan 2, S. T. Girisha 1
1Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology, Bangalore University, Bangalore , 560056, India
2Department of Materials Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore , 560 012, India
Correspondence to: K. A. Natarajan , Department of Materials Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore , 560 012, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Utilization of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms in iron ore beneficiation is discussed. Microorganisms such as Paenibacillus polymyxa, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (SRB) are capable of significantly altering the surface chemical behavior of iron ore minerals such as hematite, corundum, calcite, quartz and apatite. Differing mineral surface affinities of microbial cells and metabolic products such as proteins and polysaccharides can be utilized to induce their flotation or flocculation. Mineral-specific bioreagents such as proteins are generated when bacteria and yeast were grown in the presence of hematite, corundum, calcite, quartz and apatite. This study has demonstrated the utility and amenability of microbially-induced mineral beneficiation of iron ores through bacterial and yeast cells and their metabolic byproducts.
Keywords: Paenibacillus Polymyxa, Bacillus Subtilis, Saccharomyces Cerrevisiae, Desulfovibrio Desulfuricans, Biobeneficiation, Iron Ores, Bioreagents
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Ever-increasing world demand for iron ores has led to exploitation of even lean-grade ores. However, acceptable specifications on the quality of iron ore concentrates necessitate close control of impurities such as alumina, silica, alkali and phosphates. Besides the availability of lean grade ores, significant tonnages of iron ore fines and even high iron containing processed wastes accumulated in various mining sites around the world call for immediate action. Under the circumstances, it becomes necessary to develop efficient mineral processing techniques which areenvironment-friendly, cost-effective and energy-efficient. Use ofmicroorganisms to bring out microbially-induced flotation or flocculation of the desirable mineral constituents could prove to be a novel alternative to existing physico-chemical methods.Several microorganisms which are present ubiquitously in many iron ore deposits act as reagents, collectors or modifiers, to bring about selective mineral separation. Microbially-induced beneficiation of iron ores is a new concept having potential industrial applications in iron ore mining industries, worldwide. In this paper, biotechnological aspects of environmentally benign iron ore beneficiation are discussed with respect to biomineralisation,miningmicroorganisms, surface chemical aspects of microbe-mineral interactions and role of mineral-specific bioreagents.Hematite is the most abundant and important iron bearing mineral relevant to iron and steel industries. But hematite is generally associated with oxide gangue minerals such as quartz, clayey matter, alumina and calcite. Various physico-chemical methods such as froth flotation and electrostatic separation used to separate the gangue minerals from hematite are considered to be expensive and are not environment friendly. Utility of microorganisms in iron ore beneficiation was understood and developed only in the last decade[1-4]. Smith and co workers have reported extensive studies on the relevance and promise of microorganisms in mineral bioprocessing[5-9].Utility of Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans in the beneficiation of hematite ores has been recently studied[10-12]. More detailed studies involving microbiological and surface chemical aspects are needed to understand basic mechanisms governing microbially induced iron ore beneficiation. Considering the above scenario, a system of hematite along with quartz, corundum, calcite and apatite was chosen to separate hematite from rest of the oxide gangue minerals. In this paper, the role of bioreagents secreted by Paenibacillus polymyxa in altering the surface chemistry of some iron ore minerals, such as hematite, corundum, calcite and quartz is discussed. The consequences ofmicrobe–mineral interactions of relevance in mineral beneficiation are brought out in terms of iron ore flotation and selective flocculation. Paenibacillus polymyxa[13] is a Gram-positive neutrophilic, periflagellated heterotroph, occurring indigenously associated with several mineral deposits. It secretes exopolysaccharides, proteins and several organic acids such as acetic, formic and oxalic acids. The utility of corundum-adapted bacterial cells in the removal of alumina from iron ores is discussed. Another bacterium namely, Bacillus subtilis was used to demonstrate separation of hematite from calcite, silica, corundum and apatite. Bacillus subtilis is a Gram-positive neutrophilic periflagellated aerobic, catalase-positive capsulated bacterium commonly found in soil[14]. Saccharomyces cerevisiae are unicellular and chemoorganotrophic, eukaryotes classified in the kingdom of fungi. Cells and metabolic products of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Saccharomyces cerrevisiae were successfully used to separate quartz from hematite through environmentally benign microbially induced flotation and flocculation. Desulfovibrio desulfuricans is a Gram negative sulfate reducing, facultative anaerobe, occurring indigenously associated with iron ore deposits and is implicated in the biomineralization of several iron oxides. It is essential to understand the mechanisms and resulting consequences of microbe-mineral interactions before the utility of microorganism in the processing of minerals could be established. Since mineral beneficiation processes such as flotation and flocculation depend on the surface chemical properties of the minerals, any changes in the surface chemistry brought about by biotreatment would be of significance.
2. Biomineralisation and Biogenesis of Iron Oxides
- A prior knowledge of indigenous microorganisms associated with natural iron ore deposits will not only enable an understanding of iron oxide-bacteria cycle in nature, but also would facilitate the right choice of mining bacteria for biobeneficiation. The formation of various iron oxides under the earth’s crust are due to both biological and abiotic reaction mechanisms[15-19]. Involvement of various microorganisms in extracellular and intracellular iron oxide formation is a definite indication of biogenesis of iron ores. In natural sediments, iron oxide particles often occur in intimate association with bacterial cell envelopes and their exopolymers. Biogenesis of oxyhydroxides such as goethite, lepidocrocite and limonite as well as oxides such as magnetite and hematite is likely in natural environments. From iron-rich seepage neutrophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria could be isolated. Anaerobic microorganisms such as Sulphate Reducing Bacteria (SRB) present in anoxic mining environments facilitate formation of ferrihydrite and magnetite. Microbial iron oxidation and reduction are involved in natural bacteria-iron cycles following various mechanisms and conditions of varying pH, oxygen availability, temperature and ionic concentrations. For example, Gallionella spp and Leptothrix spp are invariably associated with biogenic iron oxides at neutral pH in oxygen rich zones. In acidic environments, Acidithiobacillus spp. brings about ferrous iron oxidation. Iron oxidizing archea such as Thermoplasmales could be identified in extreme acidic environments. Bioreagents such asexopolysaccharides and proteins are secreted by iron-bacteria during the process of iron biogenesis and conversion. Microorganisms capable of producing polyphosphate granules, sulfur granules and other intra-cellular and inter-cellular inorganic polymers have also been located in mining environments. Many iron-bacteria exhibit magnetotaxis and are implicated in the biosynthesis of magnetite[20]. An iron-reducing bacterium, such as Shewanella putrefaciens is capable of production of intracellular particles of iron-minerals[21]. With reference to banded iron formations, it is possible for iron oxidizing bacteria to produce and precipitate iron-rich sediments on a large scale. Different metabolic activities, redox reactions and internal biomineralisation processes are thus involved in biological iron oxide formation.
3. Microorganisms Useful in Iron ore Beneficiation
- Diversity of microbial life in iron ore deposits can be established through molecular biology tools. It will be useful to isolate and identify microbes which are indigenously present in an iron ore deposit for a beneficiation process. For example, mine-isolated phosphorous solubilising microbes could be utilized for dephosphorization of iron ores. Mineral specific organic and inorganic biopolymers secreted by microbes inhabiting a mining environment can find use in selective mineral separation. Close association between bacteria and precipitated silica as well as iron and alumina-silicates could pave the way for development of processes to separate clay and alumina particles from iron oxides. Bacteria with enhanced iron reducing properties include: Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Bacillus circulans, Bacillus pumilus, Paenibacillus polymyxa, Pseudomonas spp, Bacillus acidocaldarius, Bacillus mesentericus, Shewanella putrefaciens and Sulfate Reducing Bacteria (SRB). Many of the above microorganisms could be utilized to reduce ferric iron (present in iron oxides) to metallic iron.Many types of microorganisms including autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria, fungi, yeast and algae which inhabit iron ore deposits find use in iron ore beneficiation[22-24] Morphological features of some microorganisms useful in iron ore beneficiation are illustrated in Figure 1. Possible use of microbial cells and bioreagents as flotation, flocculation and dispersion reagents in iron ore beneficiation need be understood. For example, yeast cells can be used to agglomerate iron oxide fines. Bacteria such as Mycobacterium phlei, Bacillus subtilis and Rhodococcus opacus have been used to demonstrate their utility in iron ore beneficiation[25-26]. Mycobacterium phlei and their surface active products have been shown to function as flotation collectors and flocculation agents for hematite[5-9]. Best flotation was found to be at acidic pH of 2.5. Hematite can be selectively flocculated from silicates.Utility of bacteria, metabolites, and other bioreagents in iron ore beneficiation has been reported[27-31].Pure strains of Paenibacillus polymyxa (NCIM 2539), Bacillus subtilis (NCIM 2655), Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (NCIM 2047) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (NCIM 3309) used in our studies were procured from National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms, National ChemicalLaboratory, Pune, India.
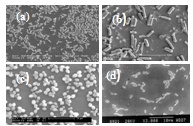 | Figure 1. Some microorganisms useful in iron ore processing (a) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (b) Bacillus subtilis (c) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (d) Paenibacillus polymyxa |
3.1. Bioseparation of Quartz from Hematite
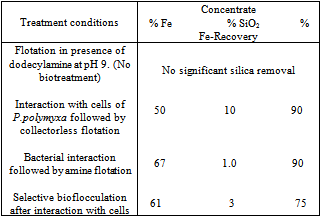
- Microbially–induced separation of quartz from hematite is demonstrated through the use of the following microorganisms, namely, Paenibacillus polymyxa, Bacillus subtilis, Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Among the microorganisms used, Paenibacillus polymyxa and Bacillus subtilis are aerobic neutrophilic bacteria, Desulfovibrio desulfuricans is an anaerobic sulphate reducing bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an yeast (Figure 1).Kinetics of bacterial and yeast cells adsorption was obtained by estimating their adsorption density onto quartz and hematite as a function of time. Adsorption behavior with respect to time was investigated in a 10-3 M KNO3 electrolyte solution at different pH values. In case of all the bacterial and yeast cells, adsorption was found to be significantly higher on hematite compared to that on quartz. Interaction with microbial cells, metabolites and proteins resulted in enhanced hydrophobicity for quartz unlike hematite which was rendered more hydrophilic after similar treatment. Microbial metabolites contain exopolysaccharides and many proteins and their preferential adsorption on the minerals are responsible for the above observations. Predominant adsorption of polysaccharides would render the mineral more hydrophilic and of proteins confer enhanced hydrophobicity. Proteins were observed to be predominantly adsorbed onto quartz, while hematite exhibited enhanced affinity towards polysaccharides. It has also been observed that when microbial cells were grown in the presence of minerals, amounts of protein and polysaccharide secretions differed depending on the mineral as illustrated in Table 1 below.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
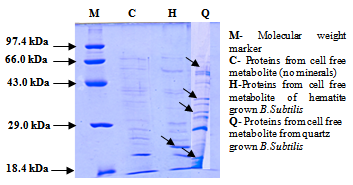 | Figure 2. SDS-PAGE of proteins isolated from cell free metabolite of B.subtilis [10] |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.2. Role of Paenibacillus Polymyxa and Bacillus Subtilis in Hematite-Corundum Separation
- The beneficial aspect of using corundum-adapted cells has been demonstrated with respect to efficient separation of alumina from hematite using Paenibacillus polymyxa[30]. Unadapted cells could not bring about hematite-alumina separation. Corundum-adapted cells were shown to secrete additional mineral specific proteins besides otheralumina-specific bio-surfactants unlike unadapted cells. Whilecorundum-adapted cells enhanced the flocculation of alumina particles, hematite-adapted cells selectively flocculated hematite. Significant changes in the surface chemistry of iron oxides and associated minerals are brought about when cells and metabolic products of Paenibacillus polymyxa are interacted [27-31]. Cells of Paenibacillus polymyxa were grown in the presence of corundum with repeated subculturing for six months.Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) in the presence of an anionic detergent, namely, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) by which proteins can be characterized in terms of molecular weight of the constituent peptides was carried out to reveal alumina-specific bioproteins generated due to bacterial growth and adaptation in the presence of the mineral. Presence of new proteinaceous bands with positively charged NH3+ functional groups could be readily identified on alumina-grown bacterial cell walls as well as in metabolic products. Bacterial cells grown and adapted in presence of alumina secreted mineral-specific proteins which were not present in unadapted bacterial cells. The new protein secreted during alumina adaptation is a cytoplasmic protein.The molecular weight of this alumina-specific protein which is present in both cytoplasm and the extracellular metabolite was found to be 31 kDa. It has also been observed that when microbial cells were grown in the presence of corundum and hematite, amounts of protein and polysaccharide secretions also differeddepending on the mineral. Relatively higher amounts of proteins were generated by both types of bacterial cells when interacted with corundum.Percent adsorption of ruthenium red onto bacterial cells before and after interaction or adaptation with minerals is given in Table 5.
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.3. Role of Bacillus Subtilis in Hematite-Calcite Separation
- Role of B.subtilis in separation of calcite from hematite has been studied. Typical scanning electron micrographs depicting adhesion of Bacillus subtilis onto calcite and hematite are illustrated in Figure 3. As could be readily seen, profuse and significant adhesion of bacterial cells could be seen on hematite when compared to calcite.
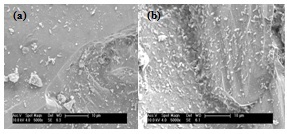 | Figure 3. Scanning electron micrographs of B. subtilis attached onto (a) calcite and (b) hematite |
|
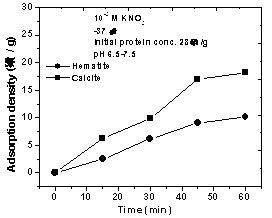 | Figure 4. Adsorption behavior of proteins secreted by B.subtilis cells onto calcite and hematite |
3.4. Protein, Genomic DNA and RAPD-PCR Fingerprinting Profiles of Bacillus Subtilis
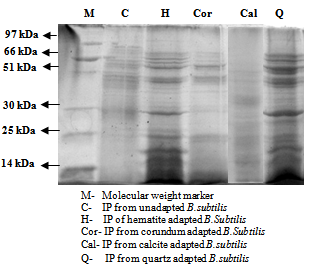 | Figure 5. SDS-PAGE of intracellular proteins isolated from cell free metabolite of B.subtilis in absence and presence of minerals |
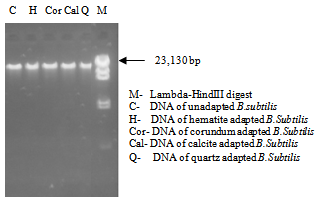 | Figure 6. Agarose gel showing genomic DNA of B.subtilis in absence and presence of different minerals |
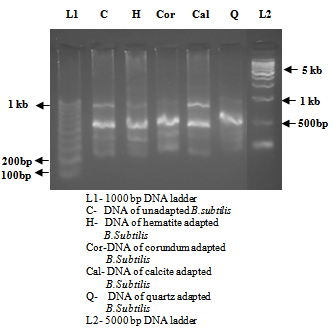 | Figure 7. RAPD amplification patterns of PCR products of B.subtilis in absence and presence of different minerals |
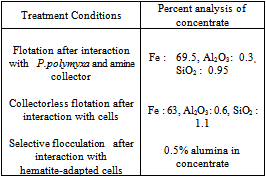
3.5. Biobeneficiation of Iron Ores for Removal of Silica and Alumina
- Having studied the amenability of microbially – induced flotation and flocculation using pure mineral samples, the investigations were extended to demonstrate potential of biobeneficiation to real iron ore samples. Removal of silica and alumina from two typical Indian iron ore deposits using biobeneficiation is demonstrated.The Kudremukh iron ore deposits situated in Karnataka, India have high silica (mainly as quartz) content. The Bolani iron ores used by Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) have high alumina content (present as alumina and clays). High alumina: silica ratios (>1) in the processed ore burden (sinter) create problems in blast furnace smelting and therefore, there is an urgent need for reducing the alumina content (and thereby reducing the alumina: silica ratio in the blast furnace feed) in such high alumina iron ores.
|
|
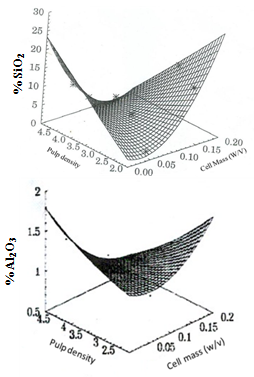 | Figure 8. Selective bioflocculation of iron ore slimes using alumina-adapted strains of P. polymyxa. (a) Silica separation, (b) Alumina separation [37] |
3.6. Role of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae in Hematite-apatite Separation
- The attachment of yeast cells onto hematite and apatite was first compared. As illustrated in Figure 9, profuse attachment of yeast cells could be seen on apatite unlike onto hematite surfaces at neutral pH range, while attachment onto apatite was lower than that on hematite as the pH increased.
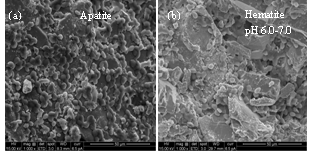 | Figure 9. Scanning electron micrographs of S. cerevisiae attached onto (a) apatite and (b) hematite |
3.7. Environmental Aspects
- Biobeneficiation processes are more environment-friendly than physico-chemical alternatives. For example, many of the microorganisms reported to be useful in iron ore beneficiation are also implicated in bioremediation through degradation of organic reagents. Efficient biodegradation of various amines and oleate collectors used in iron ore flotation could be brought about by Paenibacillus polymyxa[28]. Bacteria such as Bacillus spp, Pseudomonas spp and Sulphate Reducing Bacteria (SRB) could also be used to degrade residual collector concentrations present in mill process effluents before environmental disposal. Similarly, the above organisms were also found to be useful in biological stripping of adsorbed reagents from mineral surfaces subsequent to flotation. Such biological surface removal of hydrophobic reagents from mineral particle surfaces would be very useful and beneficial in subsequent processing of a flotation concentrate. A case in point is pelletization of iron ore fines after beneficiation through flotation. Metabolic activity of iron-reducing bacteria could enhance the natural or engineered remediation of waste tailing disposal sites. Iron ore fines and slimes present in tailing dams can be efficiently agglomerated and stabilized using native microorganisms from an environmental angle. Also, such bioprocess would pave the way for recovery of valuable minerals from wastes and for reharvesting and recirculation of process water.
4. Summary
- Many microorganisms such as Paenibacillus polymyxa, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans can be efficiently used for removal of silica, alumina and apatite from iron ores through microbially-induced flotation or selective flocculation. When microorganisms were grown in the presence of hematite, corundum, calcite and quartz mineral-specific bioproteins and exopolysaccharides were generated. Bacteria such as Paenibacillus polymyxa can be used for biodegradation of flotation collectors such as amines and oleates and also to strip residual collector reagents from floated concentrates. Microbially-induced iron ore beneficiation is thus environment-friendly and cost-effective. However, large scale tests using real ores need be carried out using real ore systems to establish techno-economic feasibility of the biobeneficiation process for commercial applications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are thankful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India, New Delhi for financial support, Indian Institute of Science and Bangalore University for the infrastructure. Thanks are due to the National Academy of Sciences (India) for Platinum Jubilee Senior Scientist Fellowship to the corresponding author (K.A. Natarajan).
References
| [1] | Deo, N and Natarajan, K. A, 1997, Interaction of Bacillus polymyxa with some oxide minerals with reference to mineral beneficiation and environmental control, Minerals Engineering, 10:1339-1354. |
| [2] | Deo, N and Natarajan, K. A., 1998. Studies on interaction of Paenibacillus polymyxa with iron ore minerals in relation to beneficiation, Int. J. Miner. Process, 55:41-60. |
| [3] | Partha Patra and Natarajan, K. A., 2004, Microbially induced flocculation and flotation for separation of chalcopyrite from quartz and calcite, Int. J. Miner. Process, 74:143-155. |
| [4] | Partha Patra and Natarajan, K. A., 2006, Surface chemical studies on selective separation of pyrite and galena in the presence of bacterial cells and metabolic products of Paenibacillus polymyxa, J. Colloid and Int Sci, 298:720-729. |
| [5] | Dubel, J, Smith, R. W, Misra, M and Chen. S., 1992, Microorganisms as chemical reagents: the hematite system, Minerals Engineering, 5, 547-556. |
| [6] | Misra, M., Chen, S, Smith. R.W, Raichur, A.M., 1993, Mycobacterium phlei as a flotation collector for hematite. Minerals and Metallurgical Processing 10, 170–175. |
| [7] | Smith, R. W, Misra, M and Chen, S., 1993, Adsorption of a hydrophobic bacterium onto hematite: Implications in the froth flotation of hematite, 11, 63-67. |
| [8] | Scheider, I. A. H, Misra, M and Smith, R. W., 1994, Bioflocculation of fine hematite suspensions with products from yeast cell rupture, Chemical Engineering and Mineral Processing, 4, 248-252. |
| [9] | Smith, R. W and Miettinen, M., 2006, Microorganisms in flotation and flocculation:Future technology or laboratory curiocity?, Minerals Engineering, 19, 548-553 |
| [10] | Sarvamangala, H and Natarajan, K. A., 2011, Microbially induced flotation of alumina, silica/calcite from hematite, International Journal of Mineral Processing, 99:70-77. |
| [11] | Usha Padukone, S and Natarajan, K. A., 2011, Microbially induced separation of quartz from calcite using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J.Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 88:45-50. |
| [12] | Sabari Prakasan, M.R., and Natarajan, K.A., 2010, Microbially-induced separation of quartz from hematite using sulfate reducing bacteria, Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, Vol. 78, pp. 163-170. |
| [13] | Ash, C., Priest, F.G., Collins, M.D., 1993, Molecular identification of rRNA group of 3 Bacilli using a PCR probe test. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 64, 253–260. |
| [14] | Madigan, M, Martinko, J, 2005. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 11th ed., Prentice Hall, New York. |
| [15] | Arakaki, A, Nakazawa, H, Nemoto, M, Mori, T and Matsunaga,T., 2008. Formation of magnetite by bacteria and its application, J.R.Soc.Interface, 5, 977-999. |
| [16] | Bonneville, S, Van Cappellen, P and Behrends, T., 2004, Microbial reduction of iron (III) oxyhydroxides; Effect of mineral solubility and availability, Chemical Geology, 212, 255- 268. |
| [17] | Fortin, D and Langley, S., 2005. Formation and occurrence of biogenic iron-rich minerals, Earth-Science Reviews, 72, 1-19. |
| [18] | Gilbert, P U P A, Abrecht, M and Frazer, B H., 2005. The organic-mineral interface in biominerals, Rev. Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 59, 157-185. |
| [19] | Williams, P J and Cloete, T E., June 2008, Microbial community study of the iron ore concentrate of the sishen iron mine, South Africa, World J. Microbiology & Biotechnology, (on-line publication). |
| [20] | Liu, Y, Gao, M, Dai, S, Peng, K and Jia, R., 2006. Characterization of magnetotactic bacteria and their magnetosomes isolated from Teishan iron ores, in Huber province of China, Materials Science and Engineering, 26, 597-601. |
| [21] | Roberts, J. A, Fowle, D A, Hughes, B. T and Kulczycki, E., 2006. Attachment behavior of Shewanella putrefaciens onto magnetite under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, Geomicrobiology Journal, 23, 631-640. |
| [22] | Botero, A E C, Torem, M L and Mesquita, L M S., 2007, Fundamental studies of Rhodococcus opacus as a biocollector of calcite and magnesite, Minerals Engineering, 20, 1026-1032. |
| [23] | Delvasto, P, Ballester, A, Munoz, J A, Gonzalez, F, Blazquez, M L, Igual, J M, Valverde, A and Garcia-Balbua, C., 2008, Mobilization of phosphorous from iron ore by the bacterium Burkholderia caribensis FeGLO3, Minerals Engineering, 22, 1-9. |
| [24] | Fortin, D and Langley, S., 2005, Formation and occurrence of biogenic iron-rich minerals, Earth-Science Reviews, 72, 1-19. |
| [25] | Zheng, X, Arps, P J and Smith, R W., 2001, Adhesion of two bacteria onto dolomite and apatite: their effect on dolomite depression in anionic flotation, Int. J. Miner. Process, 62, 159-172. |
| [26] | Mesquitaa, de, L.M.S, Linsb. F.F, Torem, M.L., 2003, Interaction of a hydrophobic bacterium strain in a hematite–quartz flotation system, Int. J. Miner. Process, 71, 34-44 |
| [27] | Namita Deo and Natarajan K A., 1997, Interaction of Bacillus polymyxa with some oxide minerals with reference to mineral beneficiation and environmental control, Minerals Engineering, 10, 1339-1354. |
| [28] | Namita Deo and Natarajan K A., 1998a, Biological removal of some flotation collector reagents from aqueous solutions and mineral surfaces, Minerals Engineering, 11, 717-738. |
| [29] | Namita Deo and Natarajan. K. A., 1998b, Studies on interaction of Paenibacillus polymyxa with iron ore minerals in relation to beneficiation, Int. J. Miner. Process, 55, 41-60. |
| [30] | Namita Deo and Natarajan K A., 1999, Role of corundum-adapted strains of Bacillus polymyxa in the separation of hematite and alumina, Minerals & Metallurgical Processing, No.4, 16, 29-34. |
| [31] | Namita Deo and Natarajan. K. A., 2001, Role of bacterial interaction and bioreagents in iron ore flotation, Int. J. Miner. Process, 62, 143-157. |
| [32] | Phalguni Anand, Modak, J.M., Natarajan, K.A., 1996, Biobeneficiation of bauxite using Bacillus polymyxa:calcium and iron removal. Int. J. Miner. Process. 48, 51–60. |
| [33] | Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T., 1989, Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor LaboratoryPress, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y. |
| [34] | Baars, J.K., Dissertation, University of Delft, 1930. |
| [35] | Gunasekaran.P., 1996, Laboratory manual in microbiology, New Age International Publishers (New Delhi), India. |
| [36] | Natarajan, K.A and Usha Padukone. S., 2012, Microbially-induced separation of quartz from hematite using yeast cells and metabolite, Minerals and Metallurgical Processing, No.2,29:81-87. |
| [37] | Natarajan, K.A., Microbial aspects of environmentally benign iron ore beneficiation, in: Proc. Iron Ore Conference, July 27–29, AUSIMM, Perth, WA, 2009, p.27. |
| [38] | Natarajan, K.A., Biotechnological innovations in the biobeneficiation of iron ore and coal fines with environmental protection, in: Proc. International conference on biobeneficiation of fines and its technology, Dec 10-11, 2007, Jamshedpur, India. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML