-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2020; 10(3): 59-70
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20201003.01
Received: Oct. 8, 2020; Accepted: Nov. 13, 2020; Published: Nov. 28, 2020

Invitro Interactive Toxicities of Quaternary and Quinary Mixtures of SDS and Metal Ions to Serratia marcescens (SerEW01)
Reuben N. Okechi 1, Edna I. Chukwura 2, Christian O. Nweke 3
1Department of Biotechnology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria
2Department of Applied Microbiology and Brewing, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Anambra State, Nigeria
3Department of Microbiology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Reuben N. Okechi , Department of Biotechnology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The toxicities of some metal ions (Pb2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Co2+ as individuals and in quaternary and quinary mixtures with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) to Serratia marcescens (SerEW01) isolated from Otamiri river, Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria were assessed, using dehydrogenase activity as an endpoint. The EC50S observed ranged from 0.046 ± 0.003 mM for Zn2+ to 2.329 ± 0.092 mM for SDS and Duncan tests indicated that the EC50S of the toxicants were significantly different from each other. Among the individual toxicants, the increasing toxicities ranking were SDS> Pb2+> Ni2+> Co2+> Cd2+> Zn2+. The responses of the bacterium to the toxicities of the toxicants were dose-dependent, and the toxicants also progressively inhibited the dehydrogenase activity as the concentration increased. Fixed ratio mixtures (Arbitrary concentration ratio (ABCR) and equieffect concentration ratio (EECR) mixtures) were designed to evaluate the combined toxicities of these toxicants. All the dose-response relationships of the ABCR and EECR mixtures and the individual toxicants could be described by 2-parameter logistic function. All quaternary and quinary mixtures were strongly synergistic against the organisms. Within each mixture ratio, experimental, CA and IA-predicted EC50S were statistically different from one another for both mixtures. The quinary mixtures were generally more toxic to the bacterium than the quaternary mixtures. Both CA and IA models greatly underestimated the toxicities of the quaternary and quinary mixtures against S. marcescens (SerEW01). The synergistic effects of the both the quaternary and quinary mixtures of the toxicants indicates potential deleterious effects of the mixtures to the aquatic bacteria of the river.
Keywords: Metal ions, Otamiri river, SDS, Dehydrogenase activity, Quaternary, Quinary mixtures
Cite this paper: Reuben N. Okechi , Edna I. Chukwura , Christian O. Nweke , Invitro Interactive Toxicities of Quaternary and Quinary Mixtures of SDS and Metal Ions to Serratia marcescens (SerEW01), Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2020, pp. 59-70. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20201003.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) is an anionic surfactant which has taken up an enormous piece in our lives as humans, especially in households [1]. SDS usually gets into water sources through outfalls of waste or by direct application such as spraying of agricultural chemical like pesticides, where it serves as dispersant [2,3]. SDS is used for cell lysis in biochemical research, DNA extraction via SDS-PAGE, and as viral biocide [4]. It was formally thought to be environmental friendly, based on its relatively non-persistence properties in the surroundings [5]. Studies however showed that severe exposure to SDS can be toxic. According to Kegley et al. [6], SDS is neither monitored in water treatment facilities at present nor regarded as one of the contaminants of underground water sources unlike other surfactants with similar uses. Heavy metals are another set of environmental pollutants that are also common in aquatic ecosystems. Though they can occur naturally both in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, human activities are however responsible for a considerable level of metals in the environment. Heavy metals such as copper, cobalt, iron, nickel, and zinc are necessary for microbial growth and are therefore termed trace elements, while the likes of cadmium, lead, mercury, silver and gold have no known biochemical functions and are therefore toxic to living organisms [7]. Some of the trace metals function as bio-catalysts, osmo-and-gene expression regulators, and by stabilizing proteins in microbial membranes [8].Exposure to chemicals in the environment mostly involves concomitant exposure to chemical mixtures. According to Borgert et al. [9], the fate and behaviour of chemical mixtures has raised concerns both in clinical and environmental risk evaluation, and is increasingly an active field in scientific study. This concern is as a result of possible mixtures interaction, thus resulting in mixture effects on the biological systems that might be less or greater than the sum of the effects of the single chemicals. There is growing interest in interactions that might take place at low concentrations of chemicals, as these might be necessary in the establishment of tolerable environmental exposure standards. [10]. The microbiological, physicochemical and heavy metal contents of Otamiri River water and sediment have been investigated extensively by many researchers [11,12]. Similarly, bacterial isolates from Otamiri river have been reported to be resistance to heavy metals and some antibiotics, as well as biodegrade some commercially available detergents [13,14]. Furthermore, anionic surfactants content of Otamiri river water and sediment have been evaluated by Okechi and Chukwura, [12]. To date, no study on the joint toxicities of some heavy metals and an anionic surfactant to the bacterial isolate from the river have been reported. This work therefore aims at accessing the in vitro toxicities of quaternary and quinary mixtures of an anionic surfactant (SDS) with some of the heavy metals to a preponderant bacterial isolate from Otamiri river water.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection/Isolation of Test Bacterium
- The study area, sample collection and isolation techniques have been described elsewhere [12]. The preponderant river water bacteria (33.33% occurrence) identified through morphological, biochemical and molecular (16S rRNA partial gene sequencing) characterization as Serratia marcescens (SerEW01) was selected for the toxicity assay.
2.2. Culturing of the Bacterium
- S. marcescens (SerEW01) cells were grown in nutrient broth on a rotary incubator (150 rpm), at 26 ± 2°C for 24 hours. The cells were collected by centrifugation at 3000 rpm (Newlife Centrifuge, NL80-2) for 15 minutes [15]. Collected cells were washed twice and suspended in sterile deionized water. The cell density was adjusted to 1.1x108 cells/ml according to Mac-Falland turbidity standards.
2.3. Quaternary and Quinary Mixture Ratios
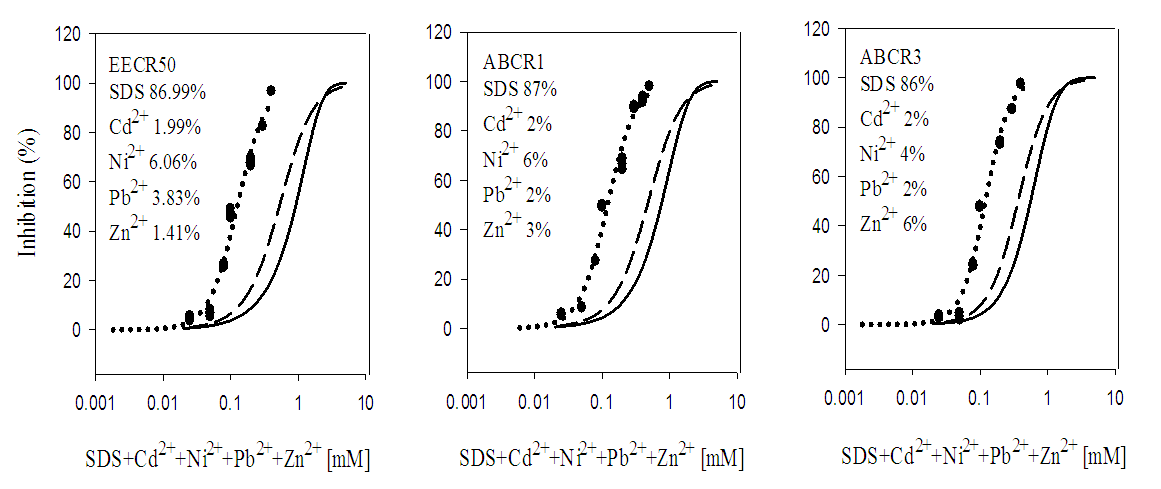
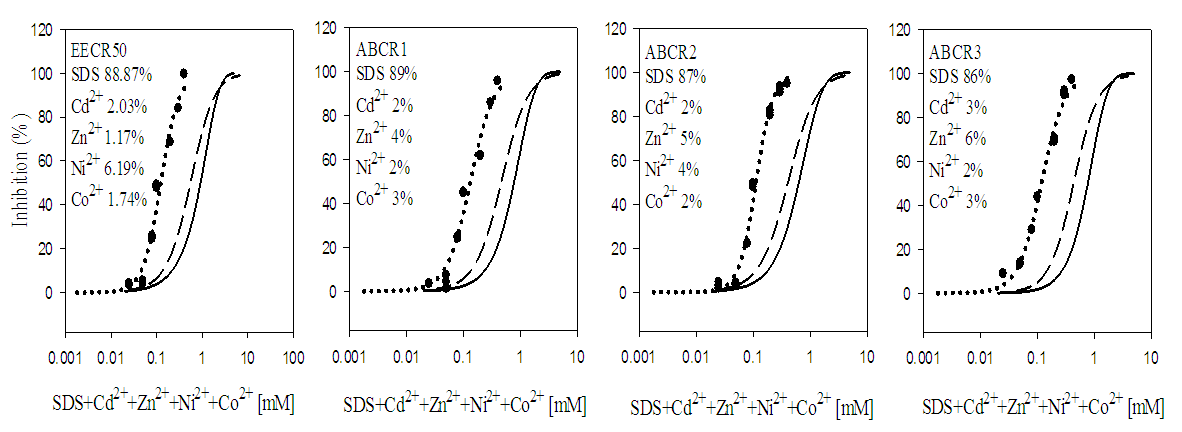
- Quaternary and quinary mixtures which consisted of SDS and three or four of the five metals ions (Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Co2+ and Ni2+) respectively were studied using fixed ratio designs [15]. The concentration ratios of the mixtures are shown Table 1. The mixtures were prepared as 10 and 50 mM stock solutions for the metal ions and SDS, by mixing required volumes of 10 and 50 mM stock solution of each metal ion and SDS to give a specific concentration ratio. Every mixture was treated as a solution of a single toxicant during toxicity testing.
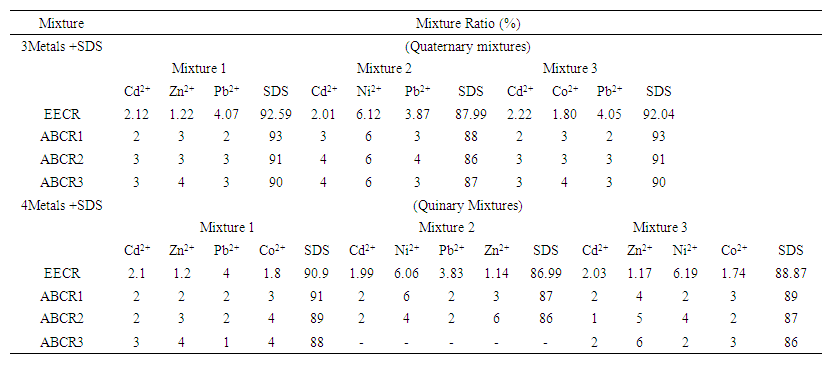 | Table 1. Quaternary and Quinary Mixture Ratios for the Toxicants |
2.4. Dehydrogenase Activity Assay
- Dehydrogenase activity was determined using 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) as the artificial electron acceptor. The assay was done in 2-ml volumes of nutrient broth-MTT medium (pH 7.0) supplemented with varying concentrations of SDS and metal ions in separate 15-ml screw-capped culture tubes. A 0.5 ml portion of x4-strenght nutrient broth and required volumes of sterile deionized distilled water and stock solutions (10 or 50 mM) of the particular heavy metals and SDS were added into culture tube in triplicates to obtain varying total concentrations of SDS and metal ions in each mixture ratio. Thereafter, 0.1 ml each of 0.05% aqueous solutions of MTT and bacterial inoculum were added into each tube. The final total concentrations of the toxicants ranged from 0.05 to 3.0 mM. The controls consisted of the medium without SDS or heavy metals. The cultures were incubated at 26 ± 2°C for 24 h. After incubation, 4 ml n-butanol was added into each tube and shaken for 1 min to extract the purple MTT-formazan that was produced by enzymatic reduction of MTT. The absorbance of each extract was determined in a spectrophotometer (VIS Spectrophotometer 721D) at 590 nm.
2.5. Determination of EC50
- The response for each test concentration was normalized relative to the mean of controls as inhibition (%) of dehydrogenase activity which ranged from 0 to 100% (Eq 1). The mean and standard deviations of inhibitions (%) were generated from triplicate determinations.
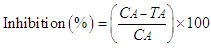 | (1) |
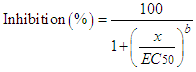 | (2) |
2.6. Toxic Index (TI)
- The TI of a given mixture was calculated as the summation of the toxic units of every component in the mixture (Eq. 3).
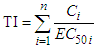 | (3) |
2.7. Prediction of Mixture Toxicities
- The joint effects of both quaternary and quinary mixtures on the dehydrogenase activity of S. marcescens (SerEW01) were predicted according to concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) models. Based on CA model, the EC50 of the mixture can be estimated as shown in the equation 4 [17].
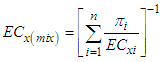 | (4) |
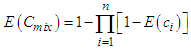 | (5) |
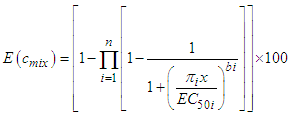 | (6) |
2.8. Model Deviation Ratio (MDR)
- The MDR values were calculated as shown in equation 7, using the predicted and experimental EC50 [20,21]. MDR > 1 indicates underestimation of the toxicity by the model (synergism) whereas MDR < 1 indicates overestimation of the toxicity by the model (antagonism).
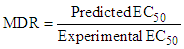 | (7) |
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Individual Toxicants
- The response of the bacterium to the toxic effect of the toxicants was dose-dependent. The toxicants increasingly repressed the dehydrogenase activity as the concentration increases, giving percentage inhibitions greater than 95% at 1 mM for Zn2+ and Ni2+, 0.5 mM for Pb2+, Cd2+ and Co2+, as well as 8 mM for SDS (Figure 1). Table 2 shows the Experimentally-derived and predicted toxicity thresholds (EC50) of individual toxicants, as well as their Quaternary and Quinary mixtures against S. marcescens (SerEW01) The EC50S of the individual toxicants showed Zn2+ to be the most toxic toxicant (0.046 ± 0.003 mM) while SDS was the least (2.329 ± 0.092 mM). The Duncan test indicates that the individual EC50S of the toxicants differed significantly from one another (P < 0.05).
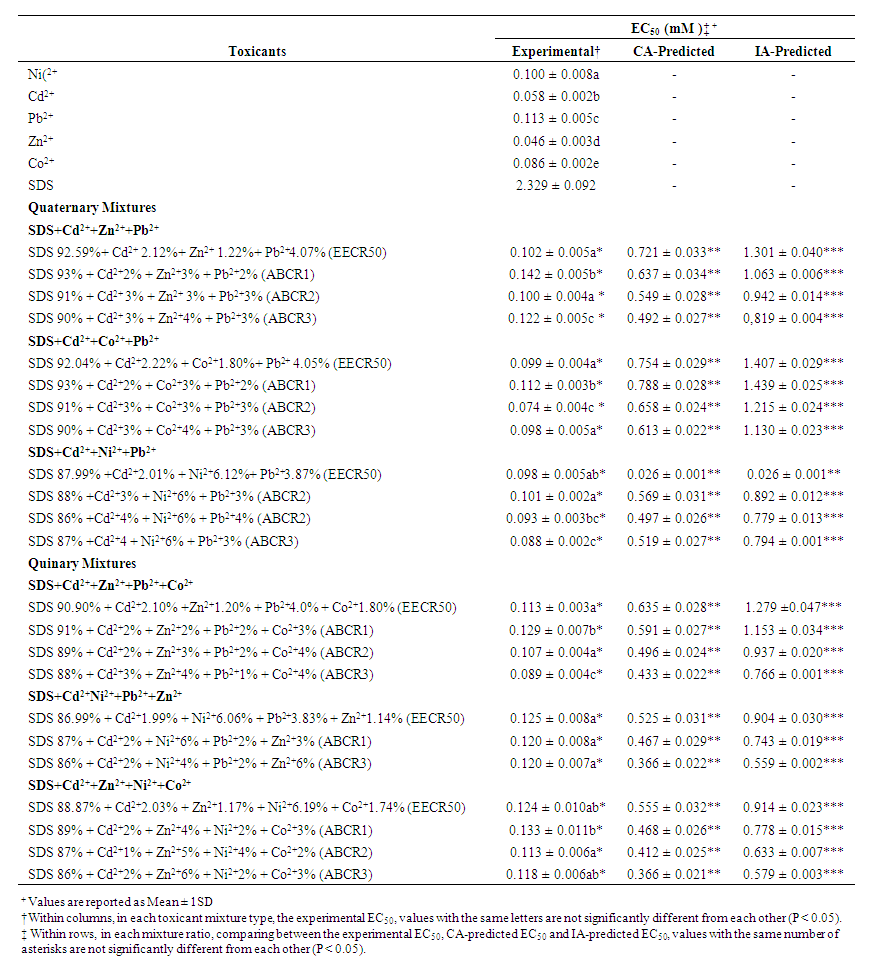 | Table 2. Experimentally-Derived and Predicted Toxicity Thresholds (EC50) of Individual toxicants, as well as their Quaternary and Quinary Mixtures against S. marcescens (SerEW01) |
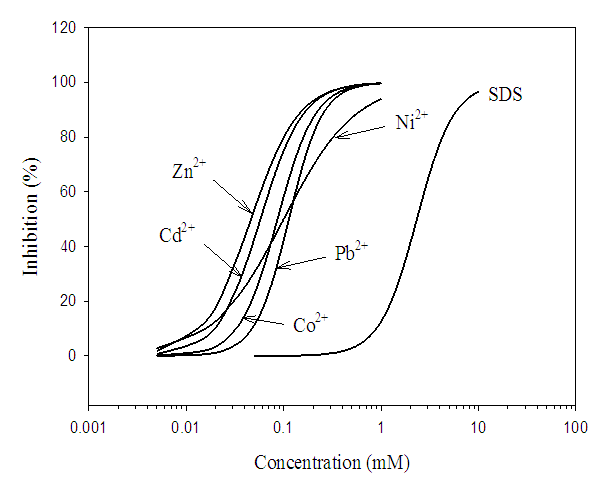 | Figure 1. Inhibition of dehydrogenase activity of S. marcescens (SerEW01) by the individual metal ions and SDS |
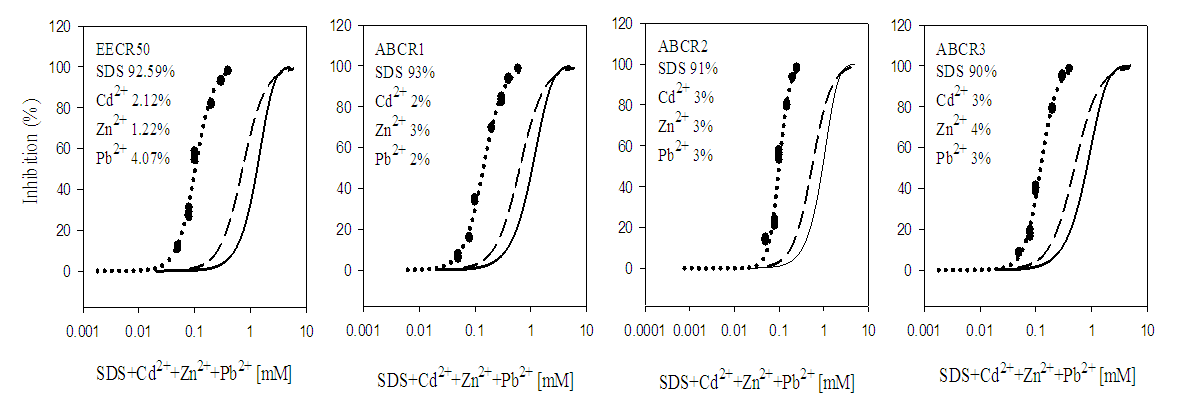
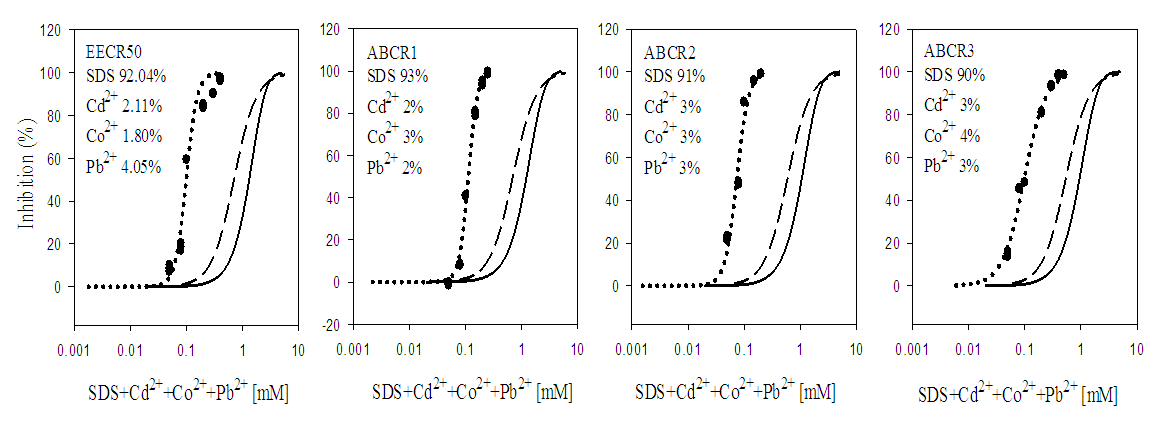
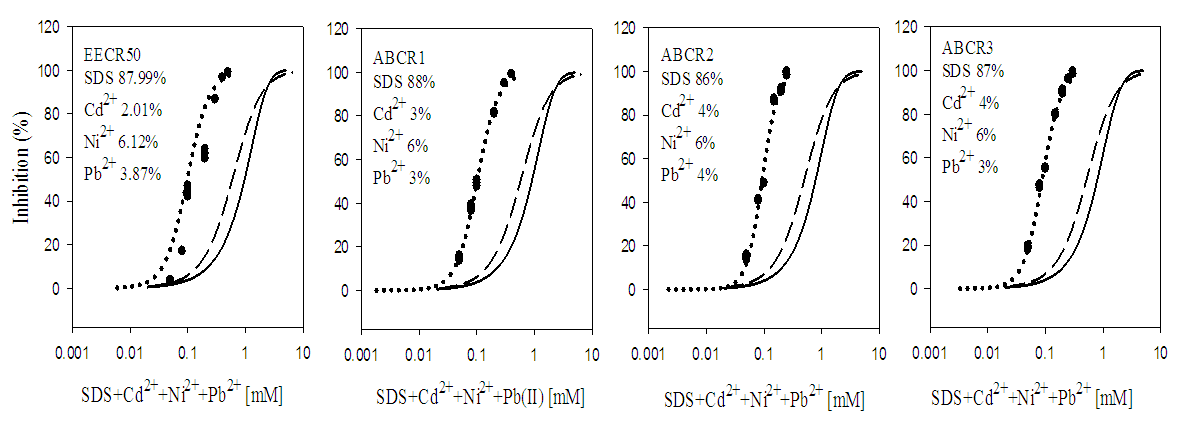
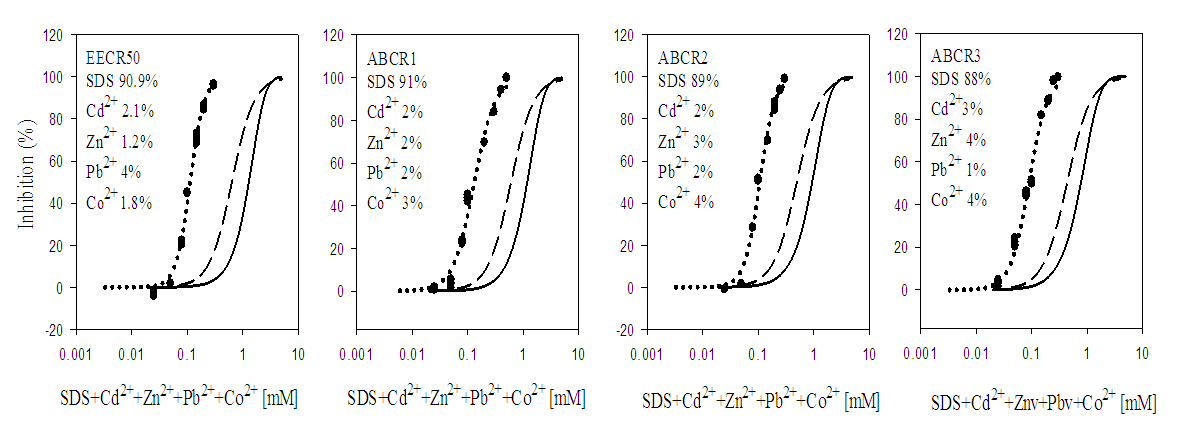
3.2. Toxicity of Mixtures
- In quaternary mixtures, the experimentally-derived EC50S in SDS + Cd2+ + Zn2+ + Pb2+ ranged from 0.100 ± 0.04 mM for ABCR2 to 0.142 ± 0.005 mM for ABCR1 mixture ratios. Mixture ratios ABCR1 and ABCR3 EC50S were significantly different from those of EECR50 and ABCR2. In SDS + Cd2++ Co2++ Pb2+ mixtures, ABCR2 mixture ratio was the most toxic with EC50 of 0.074 ± 0.004 mM, while ABCR1 mixture ratio was the least with EC50 of 0.112 ± 0.003 mM. The experimentally-derived EC50S, for ABCR1 and ABCR2 mixture ratios were statistically different from those of EECR50 and ABCR3. In SDS + Cd2++ Ni2++ Pb2+ mixtures, the experimentally-derived EC50S showed that only ABCR3 mixture ratio was statistically different from EECR50. Generally, in all quaternary mixtures, except EECR50 mixture ratio of SDS + Cd2++ Ni2++ Pb2+ mixture, experimentally-derived EC50, CA- and IA-predicted EC50S were all statistically different from one another (P < 0.05).In quinary mixtures, the experimentally-derived EC50S of SDS + Cd2+ + Zn2+ + Pb2++ Co2+ quinary mixture ranged from 0.089 ± 0.004 mM for ABCR3 to 0.129 ± 0.007 mM for ABCR1 mixture ratios. The EC50S for ABCR1 and ABCR3 mixture ratios were significantly different from the rest. In SDS + Cd2+ + Ni2+ + Pb2+ + Zn2+ quinary mixtures, the experimentally-derived EC50S showed that ABCR2 mixture ratio was the most toxic of the mixtures (0.120 ± 0.007 mM), while EECR50 mixture ratio was the least (0.125 ± 0.008 mM). The experimentally-derived EC50S showed no statistical difference from one another. In SDS + Cd2+ + Zn2+ + Ni2+ + Co2+ quinary mixtures, the experimentally-derived EC50S showed that ABCR1 was significantly higher than ABCR2. In all quinary mixtures however, the experimentally-derived EC50S, CA- and IA-predicted EC50S were also statistically different from one another (P < 0.05). Toxic index, model deviation ratio and effect of metals and SDS quaternary and quinary mixtures on S. marcescens (SerEW01) are shown in Table 3. In quaternary mixtures, the toxic index (TI) values ranged from 0.092 ± 0.068 to 0.247 ± 0.004, while MDR ranged from 4.041 ± 0.071 to 8.854 ± 0.215 for CA and 6.738 ± 0.270 to 16.394 ± 1.312 for IA. In all the mixture ratios tested, the metals and SDS quaternary mixtures were synergistic in their action. Similarly, in quinary mixtures, the TI values ranged from 0.178 ± 0.003 to 0.386 ± 0.002, while MDR ranged from 3.105 ± 0.023 to 5.620 ± 0.098 for CA and 4.739 ± 0.299 to 11.331 ± 0.717 for IA. At all the mixture ratios tested, the metals and SDS quinary mixtures were synergistic in their actions on the bacterium.
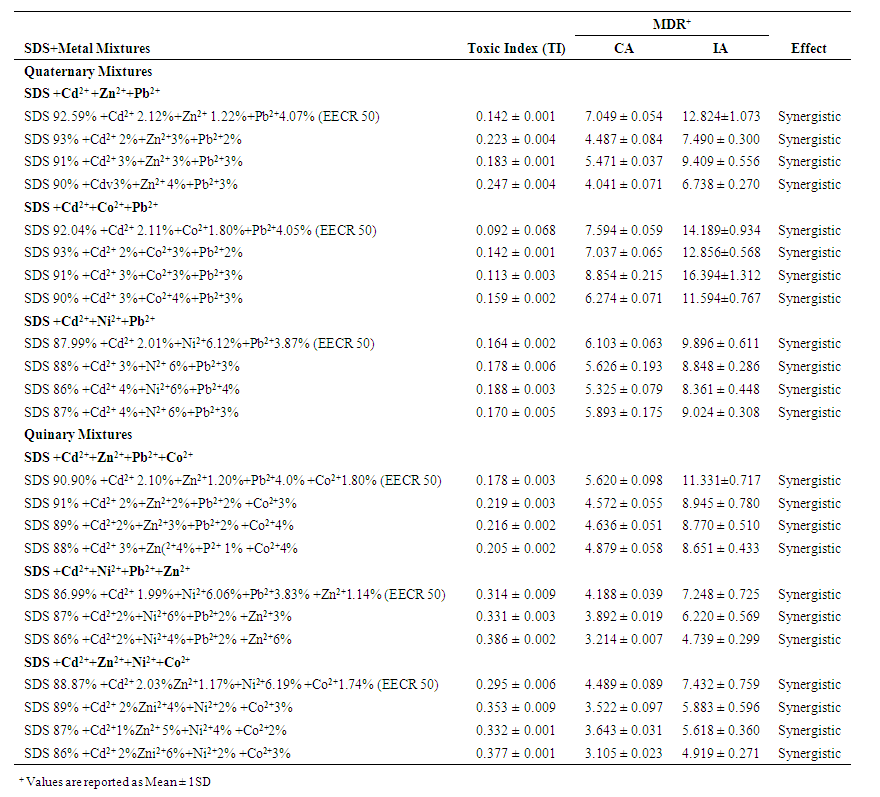 | Table 3. Toxic Index, MDR and Effect of SDS+Metals Quaternary and Quinary Mixtures on S. marcescens (SerEW01) |
4. Discussion
- Trace metals such as zinc, cobalt, copper and nickel are some of the essential elements required for the growth and enzyme activity of heterotrophic bacteria. Excess levels of these metals can however be toxic and inhibit some microbial processes. According to Bong et al. [24], heavy metals can change the structural configuration of nucleic acids and proteins, and subsequently form complexes with protein molecules, and thus inactivate them. In the present study, these heavy metals and SDS were inhibitory to S. marcescens (SerEW01) dehydrogenase activity at high concentrations. Inhibitions of enzymes activities and other microbial processes at high and low concentrations by heavy metals have been reported [20,23,24]. Zinc for example, was reported to severely inhibit microbial community diversity at high concentrations, with the survival of only limited number of resistant bacteria [25]. In the present study, 0.046 ± 0.003 mM of zinc inhibited dehydrogenase enzyme activity in the bacterium by 50% as against 0.328 ± 0,015 mM reported by Nwanyanwu et al. [26] for bacterial consortium. Similarly, a 50% toxicity threshold of 0.180 ± 0.010 mM zinc was recorded against Pseudomonas fluorescens dehydrogenase activity by Nweke et al. [20] (2018). In addition, embryonic toxicity and spermitoxicity of zinc at 3.09 µM and 5.55 µM respectively to Sea urchin have been reported by Xu et al. [27] Although tolerance of Serratia to zinc and other heavy metals has been reported [28,29], better tolerance of Gram negative bacteria to heavy metals toxicity than Gram positive bacteria have been reported [30]. The differences observed in toxicity thresholds in these studies could be attributed to the different bacteria employed. Nickel and cobalt are also co-enzymes required in various physiological processes by microorganisms. They were however toxic to S. marcescens (SerEW01) at EC50S of 0.100 ± 0.008 mM and 0.086 ± 0.002 mM respectively, in the present study. Toxicities of these metals at higher doses to microorganisms have been reported. For instance, toxicity thresholds of 0.265 ± 0.015 mM Ni and 0.142 ± 0.001 mM Co were reported to inhibit the dehydrogenase activity in aquatic microbial community [15]. Similarly, a 15 min EC50 of 45.9 ± 4.59 mg/l Co (≈ 0.35 mM) was reported to reduce the intensity of light emission in Vibrio fischeri by 50% [31] (Fulladosa et al., 2005). Although the mechanisms of cobalt toxicity to bacteria are poorly understood, toxicity of nickel to microorganisms is by replacing the essential metals of metalloproteins, binding to enzymatic residues of non-metalloenzymes; as well as by indirectly causing oxidative stress [32]. Cobalt has been reported to be a more potent growth inhibitor than nickel [33]. The same assertion could be made for the present study, with respect to their toxicity thresholds. Lead and cadmium are known to be cytotoxic to microorganisms even at low concentrations and are therefore termed non-essential elements. In the present study, both heavy metals inhibited dehydrogenase activity in S. marcescens (SerEW01) at EC50S of 0.113 ± 0.005 mM and 0.058 ± 0.002 mM respectively, for lead and cadmium. In a study on the combined toxicity of heavy metals to Photobacterium phosphoreum T3S, Zeb et al. [34] reported 15 min EC50S of 1.231 mg/l (≈ 0.004 mM) and 0.537 mg/l (≈ 0.002 mM) for lead and cadmium respectively. Similarly, 15 min toxicity thresholds (EC50S) of 4.47 mg/l (≈ 0.02 mM) and 5.83 mg/l (≈ 0.02 mM) were reported for cadmium and lead by Mansour et al. [35] against Vibrio fischeri. Furthermore, 24 hours EC50 values of 0.254 mg/l (≈ 0.001 mM) and 0.413 mg/l (≈ 0.001 mM) were recorded for cadmium and lead respectively, against Daphnia magna in the same study. The differences observed in the toxicity thresholds could be due to variations in test organisms, responses monitored and the durations of the studies.SDS has been reported to denature proteins by binding to folded proteins; its charged counter ion will upset the balance of the inherent charges of the protein and eventually unfold the protein with its negative charge [36]. Information regarding the effects of SDS on the activities of dehydrogenase enzyme in aquatic bacteria is scarce in literature, however, its toxicity to other aquatic organisms has been reported. For instance, at a concentration range of 0 -15 mg/l (≈ 0.05 mM), SDS enhances morphological changes in such organs as kidney and spleen of gilthead (Sparusaurata L.). Alteration in metabolic rates and swimming ability, as well as changes in growth and death rates in Cyprinus carpio L have also been reported [37,38]. Similarly, inhibitory effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on the fluorescent ability of E. coli was reported by Ooi et al. [39]. In addition, the acute toxicity of SDS to Daphnia magna increased with growing alkyl chain length of Alcohol Sulfates [40]. However, Masakorala et al. [41] reported no measurable toxicity by SDS to the marine macroalga, Ulva lactuca over a concentration range of 0-10 mg/l (≈ 0 – 0.04 mM). In the present study, sodium dodecyl sulfate recorded an EC50 of 2.329 ± 0.092 mM. The decreasing toxicity ranking for individual toxicants as recorded in this study is Zn2+> Cd2+> Co2+> Ni2+> Pb2+> SDS. Similar order of sensitivity (Zn > Cd > Cu >Pb) for dehydrogenases, acid and alkaline phosphatases in naturally and artificially contaminated soils was reported by Wiatrowska et al. [42].The higher toxicity of zinc as against cadmium, as well as relative tolerance to lead by this bacterium is quite unusual, although S. marcescens high tolerance to lead and cadmium has been reported [43]. Pollutants in aquatic environment usually occur as mixtures of different compounds, not a single compound. There is also paucity of information regarding the toxic effects of quaternary and quinary mixtures of SDS and divalent metals on aquatic bacteria. In the present study however, the mixture toxicities seem to increase as the proportions of the more toxic components (metal ions) increased, with the corresponding decrease in the proportions of the least toxic component (SDS) in both quaternary and quinary mixtures. Similar result was reported by Nwanyanwu et al. [26] in their study on the quaternary mixture of metals and chlorophenols to bacterial consortium. This shows that the modulating effects of SDS on the mixture components tend to decrease with increasing number heavy metal components in the mixture and could also vary with the proportions of those components in the mixture. This high toxicity of SDS and metal ions mixtures could be as a result of the remobilization of metals by SDS or reduced rates of SDS biodegradation, owing to the presence of more metal ions in the mixture. Similar results have been reported elsewhere [44,45].On the basis of TI analysis, the joint action of the quaternary mixtures was synergistic. Similarly, in the present study, MDR values ranged between 4.041 ± 0.071 and 16.394 ± 1.312 for both CA and IA, indicating strong synergistic interaction between components of the mixtures. Hagopain-Schlekat et al. [46] reported equi-toxic mixture of Pb+Cu+Zn+Ni to be synergistic to estuarine meiobenthic harpacticoid copepod Amphiascus tenuiremis, in their study. Similarly, Nwanyanwu et al. [26] reported the effects of quaternary mixtures of metals and chlorophenols to be synergistic against bacteria consortium. In addition, a quaternary mixture of benzo[a]pyrene + As + Cd + Pb showed a strong synergistic response at lower effect levels against HepG2 cells [47]. According to Chen et al. [48], possibilities of synergistic effects tend to increase with the complexity of any given mixture. Concentration addition and independent action models were used to predict the toxicities of chemical mixtures on the basis of the concentration-response relationship of the mixture components by Nweke et al. [20]. In the present study, both CA and IA models greatly underestimated the joint effect of SDS and metal mixtures to S. marcescens (SerEW01), even at low concentrations. Such underestimation by both models has been reported against Vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 by Ge et al. [49].The toxic index and model deviation ratios in all the quinary mixtures showed strong synergistic interactions for the joint mixtures of the toxicants. This result also lends credence to the assertion that the relevance of synergistic effects usually increases with the complexity of the mixture [48]. Similarly, quinary equi-toxic mixture of Cd+Cu+Ni+Pb+Zn was also reported to be synergistic against Amphiascus tenuiremis [46]. In addition, synergistic effect was also reported in a study on the quinary mixture of Cd-Atrazine-Chlorpyrifos-Lambda-cyhalothrin-Abamectin against Eisenia fetida [50]. However, Otitoloju [51] reported mainly antagonistic toxicity in his studied on the fixed-ratio of Pb+Cd+Hg+Cu+Zn mixture in Lagos lagoon sediment against benthic animal. In all quinary mixtures in the present study, both models grossly underestimated the joint toxicities of SDS and heavy metal mixtures to S. marcescens (SerEW01). Such underestimation of toxic effects of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, biocides and organic contaminant multicompound mixtures on the marine algae Skeletonema pseudocostatum by CA has been reported by Petersen et al. [52].
5. Conclusions
- This study evaluated the joint effects of quaternary and quinary mixtures of SDS and metal ions to S. marcescens (SerEW01) from Otamiri River, in Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria. Inhibition of dehydrogenase activity in this preponderant bacterium increased with increasing concentrations and number of the toxicants in the mixtures, thus quinary mixtures were more toxic than the quaternary mixtures. Although some researchers have reported SDS to be safe, the results of this study has however suggested that in combination with some heavy metals in aquatic environment, the mixtures could interact synergistically, thus giving room for possible hazardous effect to the microbiota of Otamiri River ecosystems.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are grateful to Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TET-fund), Abuja, Nigeria, for the financial sponsorship of this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML