-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2020; 10(2): 23-44
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20201002.01

Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever, an Emerging Viral Infection, Epidemiology, Transmission, Pathogenesis and Control - The Nigerian Experience
1Department of Microbiology, School of Life Sciences, Modibbo Adama University of Technology, Yola, Nigeria
2Department of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Technology, Federal Polytechnic, Mubi, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Doughari J. H., Department of Microbiology, School of Life Sciences, Modibbo Adama University of Technology, Yola, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Ebola haemorrhagic fever (EHF) is a zoonosis affecting both humans and none-human primates (NHP). The fever is caused by Ebola virus, a highly pleomorphic virus of the filovirus family. The virus is a non-segmented negative-stranded RNA virus. Five species of the virus including Zaire ebolavirus, Bundibugyo ebolavirus, Tai Forest ebolavirus (formerly known as Cote d’Ivore), Sudan ebolavirus, and Reston ebolavirus (found in Western Pacific, highly pathogenic in nonhuman primates) have been identified. The recent West African outbreak, which is the biggest since the virus was discovered in 1976, is caused by a new strain, the Zaire ebolavirus. The most recent outbreak of Ebola haemorrhagic fever, the worse ever recorded in the history of the disease was recorded in 2013 in Gueckedou prefecture in Guinea and spread across the bordering Liberia and Sierra Leone. Nigeria, Senegal, Mali and U.S.A recorded imported cases of EVD with the epidemic spanning through 2014, 2015 to early 2016. The onset of the disease is abrupt after an incubation period of two to 21 days followed by clinical manifestations of influenza–like syndrome, persistent fever not responding to antimalarial drugs or to antibiotics (acute phase), and the a brief improved condition of pseudo-remission and then the aggravation stagecharacterized by various symptoms including respiratory disorders such as dyspnoea, throat, chest pain, cough and hiccups, bloody diarrhoea, hematemesis, conjunctival bleeding, gingival bleeding, nose bleeding and bleeding at the site of injection which consistent with disseminated intravascular coagulation and eventually, death. Transmission cycle of Ebola virus include endozootic, epizootic and human to human transmission Though just like other viral diseases, Ebola has no cure, antiretroviral drugs recommended for treatment but still undergoing clinical trials include; Favipir, Zmapp, interferons with or without Ribavirin and TKM-10082. A clear understanding of the virus and its molecular composition will be of immense help in developing more effective therapies as and preventive measures.
Keywords: Antiviral, Ebola, Interferon, Haemorrhagic, Zoonosis, Transmission
Cite this paper: Doughari J. H., Abubakar I., Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever, an Emerging Viral Infection, Epidemiology, Transmission, Pathogenesis and Control - The Nigerian Experience, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 23-44. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20201002.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The current outbreak of Ebola virus (EBOV) in West Africa can be described as most severe public health emergency in modern times [1]. The number of potential cases ranges from thousands to millions with mortality rate up to 74% compared to the very first outbreak of Ebola which infected about 284 people, with a mortality rate of 53% [2]. The initial source of the current outbreak appears to be a tiny village called in Guekedou prefecture called Meliandou in the Southern Guinea forest where an index-case, a two-year old boy name Emille developed a haemorrhagic fever and died on 6th December 2013 [3]. On March 23, 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) notified of an outbreak of EVD in Guinea [4]. Soon after that, the infection spread to Liberia and Sierra Leone. Imported cases have occurred in Nigeria, but also in European countries and USA. An unrelated outbreak was also reported in Democratic Republic of Congo [5]. Infection among healthcare workers in developed countries has showed that we are not properly prepared for care of patients with highly communicable diseases, such as Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) and these among others are the major reasons for the enamours challenges posed by the outbreak of the Ebola to both the Health and scientific community. The objective of this seminar paper is to review the recent Ebola outbreak in West Africa and Nigeria in particular, to assess its challenges on the Health and Scientific community so as to proffer solutions for future occurrences.
1.1. History of Ebola Disease Outbreaks
- Ebola haemorrhagic fever (EHF) is a zoonosis affecting both humans and none-human primates (NHP). The first southern African centre for infectious disease surveillance (SACIDS) conference on one Africa one health was inspirational for complete review to illustrate the concept through a typical emerging infection of Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever (EHF) which is caused by any of the five genetically distinct member of the filoviridae family: Zaire Ebolavirus (ZEBOV) Sudan Ebola Virus (SEBOV), Bundibugyo Ebola virus (BEBOV) and Reston Ebola Virus (REBOV). Interestingly cote d’Ivoir Ebola Virus has been associated with only one human case [6].Reston Ebola Virus (REBOV) has only caused disease in non-human primates (NHP) and was found in swine suffering from porcine reproduction and respiratory disease syndrome (Barret et al., 2009). Zaire, Sudan and Bundibugyo Ebola Virus have been found to be responsible for most EHF outbreaks [7,8,9] but ZEBOV constitutes particularly serious threat to both human and NHPs. In sub-Saharan Africa, Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever has been associated with large human outbreaks, with case fatality rate of ZEBOV as high as 90%. The case fatality rate of EBOV in non-human primates (NHPs) is unknown but some ecological data suggests that it has contributed to declines of up to 98% of local great ape populations in Gabon and the republic of Congo [10].Currently there are no approved antiviral drugs against filoviruses this is one amongst numerous challenges of EHF. The prevention of EHF is still key in mitigating against the disease. The prevention of EHF requires improving our understanding of the epidemiology of the disease, especially the role of wildlife, inches bats, in the transmission of Ebola virus to human. Different fundamental aspects of the outbreak of EHF, which Gonzalez and Baize [11] reviewed the major advances in our understanding of the ecology, host interactions, and control of Ebola and Marburg viruses.In this present review, important features related to the recent Ebola outbreaks in the continent as well as the success and challenges to the scientific and health committee is the main focus. The challenges of the Ebola virus outbreak are huge ranging from natural to manmade challenges such as hygiene, tradition and religion, while other challenges such as inadequate funding and staff training has been the major challenges of the health communities, although successes have also been recorded in certain areas.The first documented outbreaks were generally regarded as causing a mysterious disease, dramatic in its effects that it inspired novelists and film producers. In most of the cases, the disease has appeared suddenly out of exclusive natural environment and dissipated slowly during the outbreaks. The first outbreak of Ebola virus disease occurred almost simultaneously in 1976 in Southern Sudan and north western Zaire (now Democratic Republic of the Congo DRC). Initially it was thought that the DRC outbreaks was due to the dissemination of the Sudan outbreak but in fact, the outbreaks were caused by two antigenically and biologically distinct species names SEBOV and ZEBOV. The index case in Sudan was a worker in cotton factory in Nzara who subsequently was the source of nosocomial transmission in Maridi hospital. The mortality rate amongst the 284 notified cases was 53% [12]. The index case in the Zaire or DRC outbreak was a 44 years old male instructor at the Yambuku catholic mission school who fell all after extensive travels in northern equatorial province. He bought fresh and smoked antelope and monkey meat on his way to Yambuku. He was treated for presumptive malaria at the Yambuku hospital.In 1979, Nzara and Maridi in Sudan were again stroke by a small outbreak, with 34 cases and 22 deaths [13] whereas a single case was described in a child at Tandala hospital in DRC [14]. Apparently, none of the cases had contact with wild animals. After an absence from 1980 to 1993, several independent foci of Ebola virus transmission were recorded most of them were caused by ZEBOV and SEBOV but some were caused by the newly discovered species, namely CEBOV (cold or Ebola virus) BEBOV. In the year 1994, a large Ebola virus outbreaks occurred amongst Chimpanzees living in Tai national park in Cote d’ Ivoire. An etiologist was infected whilst performing an autopsy on a dead chimpanzee. The patient was treated for presumptive malaria case in Abidjan hospital, without success. There were no secondary cases. This was the first documented outbreak of Ebola virus amongst NHP in nature and the first in West Africa. The outbreak led to the discovery of a new species of Ebola virus namely CEBOV [15].In 1994, 1996, and 1997 and between 2001-2002, several viral haemorrhagic fever outbreaks, caused by ZEBOV, were associated with the hunting of NHP. The 1994 outbreaks involved from gold diggers in the Minkibe forest who had killed a sick Gorilla for food; the illness was initially confused with yellow fever [16,17,18,19,20]. There were also outbreaks of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in the republic of the Congo between the years 2001-2002.In the year 1995, ZEBOV re-emerged in the city of Kikwit, with 400,000 inhabitants, 1000km south of the location of the 1976 outbreak in total 315 cases and 250 deaths were recorded. A 31 years old female Ebola patient travelled during the early stage of her disease to Kinshasa, where she was isolated in a private clinic. No secondary transmission occurred [21]. A further outbreak occurred in 2007 in Nweka health zone, west Kasai province, involving 264 cases and 187 deaths with a case fatality rate of 71% Kampungu city was the epicentre of the outbreak with 47% of cases, followed by the city of Kaluamba (42% of cases). The index case was the chief of the village and a hunter. The outbreak was apparently associated with a massive fruit bat migration through this region [22] during this outbreak; the fatalities amongst health care workers were fewer. However, several human-to-human transmissions had occurred in churches where patients had been taken for prayers and nursing presented in data compiled by doctors without borders in the same year. The risk factors for secondary human to human infection were mainly working in Kikwit General Hospital or preparing corpses for burial. Almost 20% of the 250 victims were health care workers [23].In 2003, ZEBOV re-emerged, affecting 143 individuals in Mbomon (17 cases) and Kelle (126 cases) and 128 deaths were recorded in all [24]. Three independent index cases were identified in relation to hunting episodes and contact with gorillas. During this outbreak intra-familiar transmission was more important than nosocomial transmission. However, three (3) health care workers were infected. In the same year, another small Ebola outbreak, involving 35 cases and 29 deaths, had occurred other documented outbreaks in Sudan was reported in 2005, with 11 cases and 9 deaths [25].In the 2008 Ebola outbreak in DRC Kaluamba was affected again, with a record of 32 cases and 14 deaths making case fatal rate of 43.8%. The index case was believed to be an 18 years old girl who had died of a post abortion haemorrhage. However, the source of exposure remains unknown. This outbreak was reported to the national and provincial health authorities 21 days after the disease onset, compared to a period of four months in the 2007 epidemic. The observed low fatality rate (CFR) in Kaluamba outbreak is considered to be due to the early recognition of the disease on the prompt response of the national team.In the year 2000, 2007 and 2011 respectively, outbreaks of Ebola haemorrhagic fever were recorded in Uganda. An outbreak of SEBOV occurred in Gulu in 2000 and spread to the cities of Mbarara and Maridi, with a total of 425 cases and 224 deaths with a case fatality rate of 52% recorded [26] this was the largest epidemic caused by SEBOV. The outbreak was recognised from a cluster of human cases and was amplified by nosocomial transmission. Uganda was again affected in 2007 when a new Ebola species, BEBOV killed 30 people out of a total 116 cases with case fatality rate of 26% (Towner et al., 2008). An isolated case of EHF caused by SEBOV was reported from Uganda in 2011 [27].Sudan recorded a small outbreak of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in 2004. The epicentres of the small outbreak of 17 cases and seven deaths with case fatality rate of 41.2% was the town of Yambio, near the two previous Ebola sites (Nzara and Maridi) [28]. The outbreak started with the admission of a 27 years old man to Yambio hospital with fever and haemorrhagic manifestations. The onset of symptom started on 15 April, 2004. The outbreak was rapidly contained with proper infection control measures, upon the really recognition and confirmation of the outbreak by the Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI).The most recent outbreak of Ebola haemorrhagic fever was recorded in 2013 in Gueckedou prefecture in Guinea and spread across the bordering Liberia and Sierra Leone. Nigeria, Senegal, Mali and U.S.A recorded imported cases of EVD. The epidemic spanned through 2014, 2015 to early 2016. This recent outbreak is the worse ever recorded in the history of the disease.
1.2. Structure of Ebola Virus
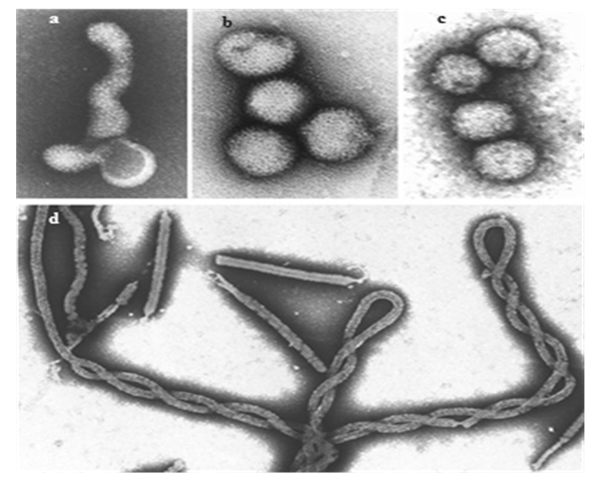
- Ebola virus is highly pleomorphic and can assume different shapes (Fig 1a, 1b and 1c). EBOV is zoonotic filovirus, comprised of envelope, non-segmented negative-stranded RNA. Up to now five species have been identified: Zaire ebolavirus, Bundibugyo ebolavirus, Tai Forest ebolavirus (formerly known as Cote d’Ivore), Sudan ebolavirus, and Reston ebolavirus (found in Western Pacific, highly pathogenic in nonhuman primates) [29]. Current West African outbreak, which is the biggest since the virus was discovered in 1976, is caused by a new strain Zaire ebolavirus [30]. Like all filoviruses Ebolavirus are membrane enveloped filamentous particles that may appear in the shape of a shepherd’s crook or in the shape of a ‘U’ or a ‘6’, and they may be coiled, toroid, or branched [31]. In general, Ebola virions are 80mn in width, but vary somewhat in length, in general, the median particle length of Ebola viruses ranges from 974 – 1,086 nm (in contrast to Marburg virion whose median particle length was measured at 795-828 nm), but particles as long as 14,000nm have been detected in tissue culture [32].
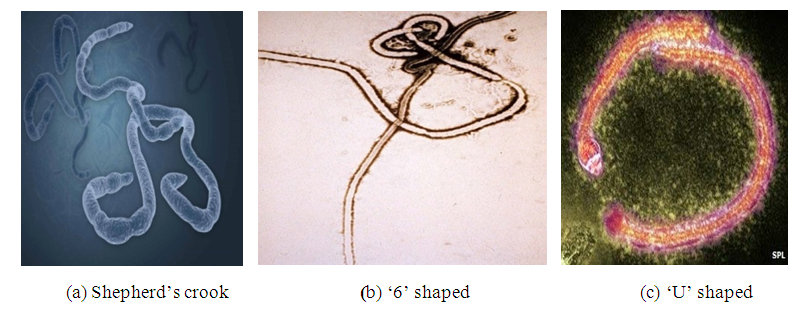 | Figure 1. The various shapes of Ebola virus as can be viewed using an electron microscope (Source: [33]) |
1.3. Ebola Genome
- Like all mononegative virus, ebolavirus has linear non-segmented, single strand, non-infectious RNA genomes of negative polarity that possesses inverse complementary 3 and 5 termini, do not possess a 51 cap, are not polyadenylated and are not covalently linked to a protein [34]. Ebolavirus genomes are approximately 19 kilo base pairs long and contain seven genes in the order [31]. Ebola does an incredible job being composed of only seven genes coding for eight proteins. The seven genes are nucleoprotein (NP), the viral proteins VP24, VP30-VP35-VP40, L (polymerase) and glycoprotein (GP) [35] The surface glycoprotein (GP) is coded by the GP gene and is expressed in two molecular forms (GP1 and GP2) that are generated by an RNA surface editing mechanism and it plays an important role in virus infection and pathogenesis, and its expression is tightly regulated during virus replication. It has been recently demonstrated that the level of GP1and GP2 expression regulates the virus production and release. The NP embeds the genetic material, forming with proteins VP35, and a large complex that is involved in synthesizing virus RNAs. Separate genes code for proteins VP40 and VP 24 localized in virus matrix space [36].
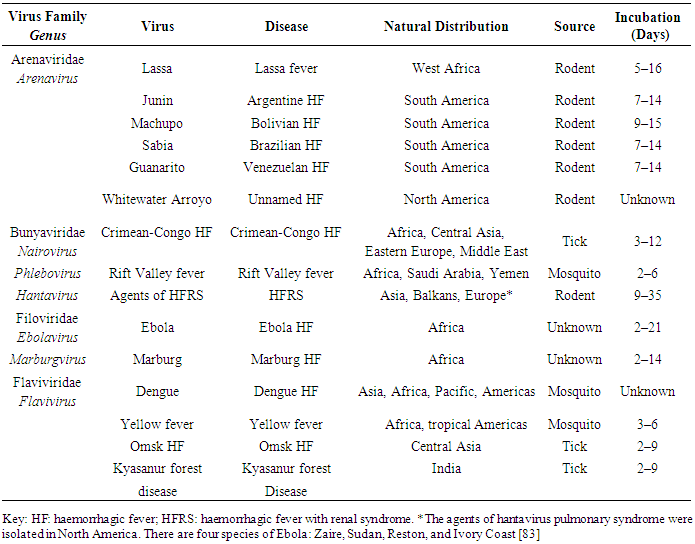
1.4. Epidemiology of Ebola Virus Disease
- The first outbreak of Ebola (Ebola-Sudan) infected over 284 people, with a mortality rate of 53%. A few months later, the second Ebola virus emerged from Yambuku, Zaire, Ebola-Zaire (ZEBOV), with the highest mortality rate of any of the Ebola viruses (88%), infected 318 people. Despite the tremendous effort of experienced and dedicated researchers, Ebola’s natural reservoir was never identified. The third strain of Ebola, Ebola Reston (REBOV), was first identified in 1989 when infected Monkeys were imported into Reston, Virginia, from Mindanao in the Philippines. Fortunately, the few people who were infected with REBOV (Seroconverted) never developed Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever (EHF). On the 22nd March 2014, the Ministry of Health in Guinea notified WHO about a rapidly evolving outbreak of Ebola viral disease (EVD) [37]. The first cases occurred in December 2013. The outbreak was confirmed have been caused by a clade of Zaïre ebolavirus that is related but distinct from the Ebola viruses that have been isolated from previous outbreaks in central Africa, and clearly distinct from the Taï Forest ebolavirus that was isolated in Côte d’Ivoire 1994–1995, this in itself was a major challenge to the scientific community as a strange strain need to be vigorously studied. The first cases in this latest outbreak in West Africa were reported from south-eastern Guinea and the capital Conakry in Gueckedu prefecture. An update documented by WHO on the 9th June 2016 revealed that Liberia recorded 10,666 cases, 4806 deaths and outbreak ended 9th June, 2016. Sierra Leone Recorded 14,122 cases, 3955 deaths and was officially declared free of Ebola on the 17th March, 2016, Guinea Recorded 3804 cases, 2536 deaths and officially declared free of Ebola on the 1st June, 2016. Nigeria Recorded 20 cases and 8 deaths and was officially declared Ebola free on the 18th January, 2014. Mali recorded 8 cases and 6 deaths and was officially declared free of Ebola on the 21st December, 2015 and United States of America recorded 4 cases with 1 death. Italy, United Kingdom, Senegal, and Spain recorded 1 case each and were declared Ebola free between 2014 and in the first quarter of 2014. The total cases recorded stood at 28,616 and 11,310 as of 8th May, 2016. The case fatality rate reported stood at 70% [38]. Donald (2015) reported that current estimates suggests that between 17% and 70% of Ebola cases were unreported as published in the New York times of 16th December, 2015.
1.5. The Nigeria Experience of Ebola
- As of October 13, 2014, the world Health Organisation declared Nigeria free of Ebola, a victory in a region where Ebola has claimed over 5000 lives already (Edwin, 2014). Out of the 20 confirmed cases in Nigeria, 8 infected persons have d and there are 12 survivors. Despite these dark times in the most populous nation of this continent, there are already notable lessons worthy of emulation by other countries [39]. The first case in Nigeria was a traveller who came into Nigeria by flight named Patrick Sawyer arrived Lagos on the July 20th 2014. Lagos state with an estimated population of 21 million) is a regional hub for economic, industrial, and travel activities [40] and a setting where communicable diseases can be easily spread and transmission sustained. The index patient died on July 25; as of September 24, there were 19 laboratory confirmed Ebola cases and one probable case in two states, with 894 contacts identified and followed during the response. Nigeria’s response to the Ebola epidemic in West Africa has been robust and decisive which attracted commendation from several international partners.
1.6. The Successful Containment of the Ebola Outbreak by Nigeria
- How Nigeria was able to contain the Ebola outbreak is the question that most countries of the world are interested in. This will not be better appreciated without mentioning the great Dr. Ameyo Stella Adedevoh of blessed memory, who spotted and tracked the Nigeria’s first case of Ebola in July, 2014 but unfortunately died of the disease in August, 2014. Dr. Ameyo is a UK trained endocrinologist took the crucial first step to spot and diagnose the first case of Ebola in Nigeria [41]. The crucial step in the Nigeria’s response was as a result of the combined vigilance of the aviation and Health authorities in Lagos state who identified and promptly isolated the first case of transported EVD Liberia into Nigeria and a crucial contact tracing team swiftly sprang into action [39].Following the isolation of the first case, the Nigerian Government was proactive to swiftly approve a special intervention plan to contain and prevent the spread of the Ebola outbreak. The plan was propped up with the release of USD 11.5 million to support implementation. An additional USD 1.2 million was also provided by the Federal government to support an already aggressive and successful response from the Lagos state Government and its Emergency Operation Centre (E.O.C). Effective coordination of Ebola containment and prevention interventions has remained vital in Nigeria’s war against the outbreak in the country [39].The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control has worked in close partnership with state government, the World Health Organisation, UNICEF, Medicins Sans Frontiers and U.S Centre for Disease Control and Prevention to establish the Emergency Operations Centre at the central public Health Laboratory in Yaba, Lagos and another in Rivers state [39]. Additionally, there have been other specific Ebola containment intervention by the Nigerian government and its partners. These include, banning of transportation of corpses both internationally and within Nigeria and the establishment of an Ebola treatment and research group with a mandate to carry out an extensive research into the Ebola virus, establishment of six testing centres nationwide, with plans to expand this further, training of Nigerian Health workers in Ebola containment related courses, delaying the reopening of schools, subject to the status of Ebola epidemic and private sector players like the Dangote Foundation significantly contributed towards the Ebola eradication by donating the sum of USD 1million to the Lagos state Government. With this aggressiveness and funding Nigeria was able to fight the epidemic successfully to a standstill, with valuable lessons learnt from the challenges encountered in the fight against the Nigerian outbreak. On the 20th October, 2014, WHO officially declared Nigeria free of Ebola virus transmission [12].
1.7. Aetiology of Ebola Virus
- Ebola virus belongs to the family filoviridae, in the order mononegavirales which includes Rhabdoviridae and Paramyxoviridae. The virus is pleomorphic, producing U-shaped, 6-shaped, or circular forms but the predominant forms of the virus most frequently seen by electron microscope are long tubular structures. It contains one molecule of linear, single-standard, negative sense RNA of 4.2x10 Da. The virus was first recognised in 1976 when two unrelated Ebola haemorrhagic fever (EHF) outbreaks occurred 800km apart in northern Zaire (Yambuku) and southern Sudan (Nzara or Maridi) [12,37].It was named ‘Ebola’ after the small river near the catholic mission of Yambuku, the epicentre of the 1976 EHF outbreaks. Ebola virus is not only restricted to Africa a new species, REBOV was described in Cynorio as Gus monkey (Macaque fascicularis) imported from the Philippines (Manilla) to quarantine facilities in Reston, USA in 1989. Subsequently REBOV has been re-isolated from cynomolgus monkeys and domestic pigs in the Philippines [42].
1.8. Ecology of the Tropical Rain Forest in Africa a Common Ecosystem for Ebola Virus Emergence and Transmission
- In most outbreaks, Ebola virus is introduced into human population via the handing of infected animal carcasses. Outbreaks could be traced to the first source of transmission. Most of these outbreaks could either be linked to animals found dead in the hunted areas in the tropical rain forest, followed by person-to-person transmission from index case to family members or health care staff [20]. It was established that the Transmission of Ebola virus in the Cote d’Iviore in 1995 was traced to the etiologist who was infected through handling of an infected, dead chimpanzee in the Tai forest and it was confirmed that the deaths of chimpanzees were indeed due to Ebola virus [15].In Gabon and the Republic of Congo, outbreaks in humans were associated with extensive deaths of Chimpanzees and Gorillas (Rouquet et al., 2005). In contrast the animal source of infection during the DRC, Uganda and Sudan outbreaks has never been detected, although the recent outbreaks in West Africa with onset in early February 2014 in Guinea and Liberia was linked to the forested region of south-eastern Guinea [43]. This is not entirely unexpected as Guinea shares an ecological system known to be associated with Ebola virus outbreaks. However, when analysing the risk factors for primary transmission of Ebola from a broad ecological point of view, it is observed that the increase in Ebola outbreaks since 1994 is frequently associated with drastic changes in forest ecosystems in typical Africa. The perturbation of their ecosystems due to extensive deforestation and human activities in the depth of the forest may have prompted direct or indirect contrast between human and a natural reservoir of the virus. Ebola infection has therefore been related to human economic activities like hunting (the young hunters infected by chimpanzees in the forest near Mayibout Gabon in 1996, farming (the charcoal makers in the forest near kikwit, DRC in 1995) and gold digging (in Minkebe forest, Gabon in 1994). In some cases, as in Mweka (DRC), EHF outbreaks seemed to be linked to the hunting of bats for bush meat [20]. These has demonstrated that it is in rare case that scientific activities primarily resulted in Ebolavirus infection, for example, in the case of etiologist who was involved in wild life studies in the Tai forest in 1994. The examples show clearly that certain economic activities, which many populations depend on for their survival in the tropics, were the risk factors for Ebola virus infection.Regarding human-to-human transmission, infection occurs in community and hospital settings through direct contact with infected fluids (blood, secretions and excretions) from tissues of an acute patient of through direct contact with contaminated materials. Any clustering of deaths in the same family pointed to EHF during the longer outbreaks. In the community settings new infections have been associated with the ministration of funeral rites such as ritual cleaning of the cadaver and removal of hair, finger nails, toe nails and clothing before burial. Most importantly people visiting or taking care of infected persons in their homes or in hospitals are also at the risk of being exposed to Ebola infections.However, major differences in EBOV transmission cycles between community –based outbreaks and hospital based outbreaks have been observed from the trends in the previous outbreaks. When Ebolavirus is introduced into a village, the outbreaks seems to end spontaneously, with limited generations of cases, this is the case with the DRC epidemics in Yambuku in 1976 when the virus was introduced into 55 villages and 25 villages around Kikwit in 1995, where the majority of the affected villages reported less than 10 cases each. Similarly, the chain of transmission of EHF in the village of Ekata in Gabon was also very short after the exposure of four (4) brothers to dead animals in 2001. In contrast, a hospital setting with low standards of hygiene and sanitation rapidly becomes a source of epidemic amplification, especially if barrier nursing techniques and universal hygiene measures are not observed by health workers. As a consequence of these nosocomial outbreaks are characterised by a relatively high proportion of deaths amongst health care workers [44].It is important to also state that it is possible that isolated cases may frequently happen in the community without being reported. In support of this hypothesis, several epidemiological sero-surveys reported high prevalence of Ebola antibodies in communities in the absence of reports of Ebola outbreaks [15,44] Experimental studies to identify candidates an animal reservoir that promotes the transmission Ebola virus was varied out. The study involved 33 varieties 24 species of plants and 19 species vertebrate and invertebrate experimentally infected with Ebola virus revealed the first evidence that both insectivorous and frugivorous bats can support the replication and circulation of EBOV [45]. This evidence along with reports of bats exposure for some of the Ebola wild cases directed the research towards the bats as potential reservoirs that promotes and supports the transmission of Ebola virus.Pourrut et al. [46] reported that six (6) bat species Epomops fraqueti, Hypsignatur monstrosus, Myonycteri’s torquata, Micropteropus pusillas, Mops condylurus and Rousettus aegyptiacus caught in the field for studies in an ecological survey revealed the presence of ZEBOV specific of fruit bats, during the 2001-2003 outbreaks in Gabon and Republic of Congo [47]. Swanepoel et al. [48] reported that such reservoir has been confirmed to be responsible for the repeated occurrences of short transmission chains arising in workers in Goroumbwa mine where large numbers of bats roosted.
1.9. General Overview of the Different Families of Haemorrhagic Fever Viruses
1.9.1. Arenaviridae
- Arenavirus particles (Fig 2a) range in morphology from highly pleomorphic as shown in this field to mainly spherical. Virion sizes range from 50 to 300 nm with a mean of 100 to 130 nm. Arenavirus particles contain a genome consisting of two ambisense single-stranded RNA molecules, designated S (small) and L (large), of about 3.4 kb and 7.2 kb in length, respectively [49]. The S segment contains two genes that encode three structural proteins: the nucleoprotein (NP or N), and the envelope glycoproteins (GP1 and GP2). The L segment contains two genes that encode two proteins: the viral polymerase (L protein) and the Z protein.NP and L associate with the genomic RNA in a ribonucleoprotein complex or nucleocapsid structure. Z protein functions as a matrix protein and is responsible for the formation of viral particles [50]. GP1 and GP2 are initially synthesized as a precursor molecule, GPC, which is posttranslational cleaved [51]. GP2 homotetramers bind by ionic interactions with GP1 homotetramers, which make up the globular head of the glycoprotein spikes [52]. GP1 is the portion of the surface glycoprotein spike that is the effector for receptor binding [53], [54] whereas the GP2 is the viral fusion protein [55].
1.9.2. Bunyaviridae
- Bunyavirus particles (Fig 2b) are roughly spherical and range in diameter from 90 to 120 nm. Bunyavirus particles contain three single-stranded RNA genome segments designated large (L), medium (M), and small (S), which vary in size among the genera. The L segment encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L), the M segment encodes two virion glycoproteins (G1 and G2) and in some viruses a non-structural protein (NSm), and the segment encodes a nucleoprotein (N) and in some viruses a non-structural protein (NSs) [57,58,59]. The structural proteins (L, N, G1, G2) are encoded in viral cRNA. NSs are encoded in the M segment cRNA and the S segment vRNA of phleboviruses. Hantaviruses and Nairoviruses use negative-sense coding strategies, whereas phleboviruses use ambisense coding strategies. The functions of the NSs have not been fully delineated; NS protein may control the activity of the viral polymerase and was proposed to block interferon (IFN) production [60].
1.9.3. Flaviviridae
- Flaviviral particles are essentially isometric and consistent in size (Fig 2c), ranging from 40 to 50 nm in diameter. Flavivirus particles contain an approximately 11-kb, single, positive-stranded RNA genome. A single open reading frame is flanked by 5’ and 3’ noncoding regions and produces a large polyprotein that is co-translationally and post-translationally processed by cellular proteases into three structural proteins and seven non-structural proteins in the order C-prM/M-E-NS1-NS2ANS2B-NS3-NS4A-NS4B-NS5 [61,62]. The nucleocapsid is composed of a single capsid protein (C). In infected cells, the prM protein is cleaved by furin to form a small, non-glycosylated membrane protein (M) and an N-terminal “pr” segment that is secreted. E protein is a large glycosylated type I membrane protein. The remaining proteins are non-structural proteins. The NS1 protein secreted from infected mammalian cells is thought to play a role in RNA replication [63]. The function of NS2A is unknown, but some data suggest that it may function in the recruitment of RNA templates to the membrane bound replicase, or it could be involved in the inhibition of IFN [64,65] NS2B is a small membrane-associated protein that forms a complex with NS3 and is a required cofactor of the serine protease function of NS3. NS3, a large cytoplasmic protein that associates with membranes by interacting with NS2B, is thought to play a role in polyprotein processing and RNA replication [65]. NS4A and NS4B are membrane-associated proteins; NS4A appears to be involved in RNA replication [64,66,67] and NS4B is also localized to sites of RNA replication and may be involved in inhibiting IFN signalling [68]. NS5 contains sequence homology similar to RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of other positive-stranded RNA viruses and also with methyltransferase enzymes involved in RNA cap formation [56,69].
1.9.4. Filoviridae
- Filoviral particles (Fig 2d) are mostly filamentous and vary in length up to 14,000 nm with a uniform diameter of 80 nm. Mean unit length is about 1,000 nm. Other forms of filoviral particles include U-shaped, “6”-shaped, or circular configurations; branching of filamentous particles can also occur. Ebola and Marburg virus which belongs to the family filoviridae are viral particles that contain an approximately 19-kb, single, negative-stranded, linear RNA genome that is non-infectious. The genome encodes seven structural proteins with the following gene order: 3’ leader, nucleoprotein (NP), virion protein (VP) 35, VP40, glycoprotein (GP), VP30, VP24, polymerase L protein, and 5’ trailer [70,71]. Four of these proteins, NP, VP30, VP35, and L, associate with the genomic RNA in a ribonucleoprotein complex, whereas the three remaining proteins, GP, VP24, and VP40, are associated with the membrane. GP is the surface glycoprotein that forms the spikes on the virion and is the effector for receptor binding and membrane fusion [72,73]. GP is synthesized as a precursor molecule, GP0, which is postranslationally cleaved by furin or a furin-like endoprotease into two subunits, GP1 and GP2; these subunits are linked by disulfide bonding to form a heterodimer [74,75]. Homotrimers of GP1-GP2 comprise the virion spikes. The unique organization of the GP gene of Ebola virus provides an important distinction between Marburg and Ebola viruses. The Marburg virus GP gene encodes a single product, the GP, is in a conventional open reading frame, whereas all of the Ebola viruses encode the GP in two open reading frames that are expressed through transcriptional editing [76,77]. The primary gene product of the Ebola GP gene is not the GP, but rather a smaller, non-structural, secreted glycoprotein (sGP), which is efficiently secreted from infected cells. VP40 functions as a matrix protein and is responsible for the formation of the filamentous particles [78]. VP24 is a minor viral protein whose functions remain unknown, but recent data indicate that VP24 possesses structural features consistent with viral matrix proteins and that it might have a role in viral assembly and budding. VP24 and VP35 have been shown to play a role in interfering with type IIFN signalling [79].
2. General Overview of Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers and Their Clinical Manifestations
- The clinical manifestation of all VHFs cannot be separated from their incubation periods (Table 1). Patients infected with these viruses may experience a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations with varying degrees of severity, yet not all patients develop classic VHF syndrome. The exact nature of the disease depends on the viral virulence and strain characteristics, routes of exposure, dose, and host factors. For example, Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever (DHF) and Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS) typically develops only in patients previously exposed to heterologous dengue serotypes [80]. As another example, for Ebola HF, the Zaire species is clearly more pathogenic in humans and nonhuman primates than the Sudan species, yet the incubation period reported for person-to-person transmission in Ebola-Zaire infections greatly exceeds the incubation period for injections or needle stick accidents [81].
|
2.1. Transmission of Ebola Virus Disease
- The transmission cycle of Ebola virus is divided into three main cycles, namely Endozootic, Epizootic and Human to human transmission (Fig 3). EVD is believed to occur after an Ebola virus is transmitted to a human index case via contact with an infected animal’s bodily fluids. Human to human transmission occurs via direct contact with blood or bodily fluids from an infected person (including embalming of an infected dead person) or by contact with contaminated medical equipment, particularly needles and syringes [37]. Medical workers who do not wear protective clothing, such as gloves and surgical masks, may also contract the disease [33]. In the past, explosive nosocomial transmissions have occurred in under equipped African hospitals due to the reuse of needles and lack of implementation of Universal precautions. Aerosol transmission has not been observed during natural EVD outbreaks. The potential for widespread EVD epidemics is considered low due to the high case fatality rate, the rapidity of demise of patients, and the often remote area where infections occur is of great significance.
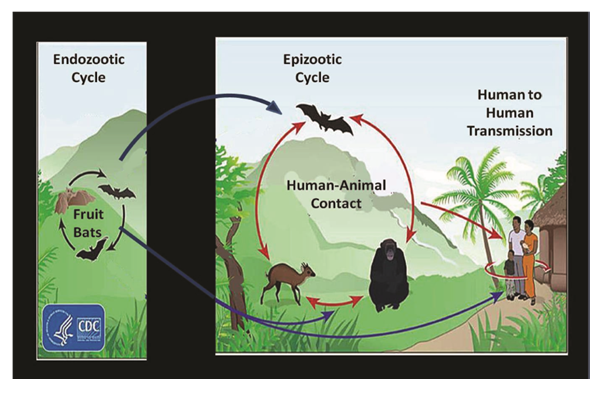 | Figure 3. The transmission cycle of Ebola virus [33] |
2.2. Immuno-pathogenesis of Ebola Virus
- Although the clinical course is well known, the species, mechanisms underlying the pathogenicity of Ebola virus have not been clearly delineated (Fig 4). Isolation of the viral cDNAs and the development of expression systems have allowed the study of Ebola virus gene products under less restrictive conditions and facilitated an understanding of the mechanisms underlying virally induced cell damage even at that, the pathogenesis of the disease is still not completely known. EBOV can enter the host body mostly via mucosal surfaces, or injuries in the skin [89]. Also infection through the intact skin cannot be excluded, although it is considered unlikely. Aerosol infection has been demonstrated in non-human primates under experimental conditions in dispersion chambers [90]. EBOV infection is characterized by immune suppression and a systemic inflammatory response, which could cause damage of the vascular, and immune systems that can lead to multi-organ failure and shock [91]. Geisbert et al. [90] presented study in non- human primates and showed that EBOV replicates in monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells; however, in situ hybridization and electron microscopy have also shown the presence of virus in endothelial cells, fibroblasts, hepatocytes, and adrenal cells [90]. Del Rio et al. [89] demonstrated, the EBOV disseminates to the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
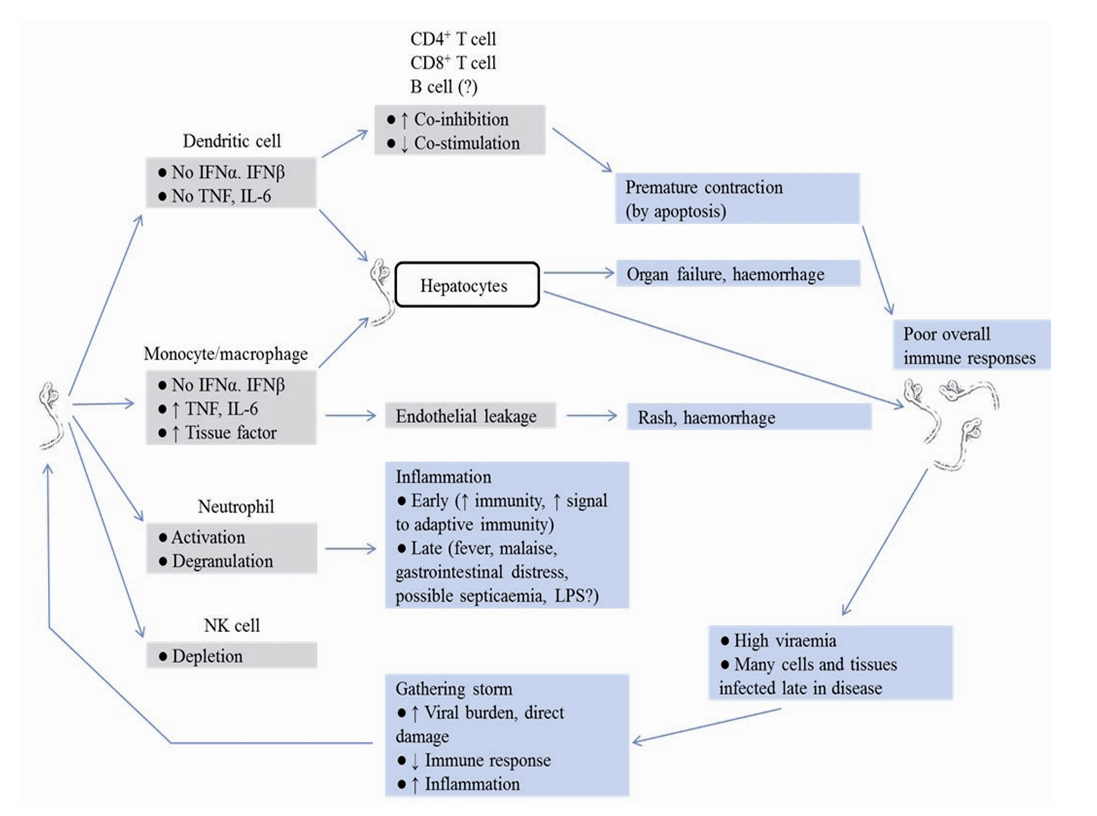 | Figure 4. Schematic representation of the pathogenesis of Ebola Virus Disease [89] |
2.3. Clinical features of Ebola Virus Disease
- The onset of the disease is abrupt after an incubation period of two to 21 days. The clinical features can be divided into four main phases. Phase one is a manifestation of influenza–like syndrome. The onset is abrupt with non-specific symptoms or signs such as high fever, headache, arthralgia, myalgia, sore throat, and malaise with nausea. Phase two is the acute stage which spanned 1–6 days. This stage is symptomatic, characterised by persistent fever not responding to antimalarial drugs or to antibiotics, headache, and intense fatigue, followed by diarrhoea, abdominal pain, anorexia and vomiting. In phase three pseudo-remissions occurs and spanned between 7–8 days. During this phase the patient feels better and seeks food. The health situation presents with some improvement. Some patients may recover during this phase and survive from the disease. Phase four is the aggravation stage starts from day 9 spanning through 21 days. In many if not most cases, the health status gets worse. This phase is associated with various symptoms which may include respiratory disorders such as dyspnoea, throat, chest pain, cough and hiccups. Symptoms of haemorrhagic diathesis such as bloody diarrhoea, hematemesis, conjunctival bleeding, gingival bleeding, nose bleeding and bleeding at the site of injection which consistent with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Other symptoms that come with the aggravation stage include cutaneous manifestations such as petechiae (not so obvious on black skin), purpura (morbiliform skin rash), maculopapular rash, and ecchymosis [30].Neuro-psychiatric manifestations have also been observed in many patients to include prostration, delirium and confusion. These manifestations indicate that the central nervous system is affected as judged by the development of severe headaches, agitation, confusion, fatigue, seizures and sometimes coma. In general development of haemorrhagic symptoms is indicative of a negative prognosis however, contrary to popular belief, haemorrhage does not lead to hypovolemia and is not the major cause of death because total blood loss is low except during labour) instead, death occurs due to Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MDDS) due to fluid re-distribution, hypotension, disseminated intravascular coagulation and focal tissue necrosis. In the end, cardio-vascular distress and hypovolemic shock leads to (death). The average time between contracting the infection and the onset of symptoms is 13-14 days, but can be as long as 21 days [92]. From these clinical manifestations it is obvious that EHF may mimic many other tropical diseases like malaria, typhoid fever or yellow fever at the start of the disease. In most outbreaks, recognition of the disease is delayed because physicians are not accustomed to this new illness and the symptoms are generally non-specific. Outside the epidemic context, it appears quite impossible to recognise the first Ebola case in an outbreak on clinical grounds only. Suspicion of EHF is mostly possible later during the aggravation phase.However, it should be stressed that in the 2014 West African outbreak, number of cases with rash and other haemorrhagic complications were less frequent (19%), and primary clinical manifestation was gastrointestinal [93]. In severe cases patients are developing hypovolemic shock and multi-organ failure, including hepatic damage, kidney and respiratory failure which may lead to Seizures and coma [94]. Analysis of cases during the current outbreak revealed that most of the patients died 7 to 11 days after the onset of symptoms (median 8 days). In previous outbreaks mortality rate ranges from 30 to 90%. In 2014 in Guinea case fatality rate was 43% and in Sierra Leone 74% [95].
2.4. Diagnosis of Ebola Virus Disease
- There are various methods of diagnosis of Ebola virus. The European Centre for Disease prevention and Control (ECDC) has laid down an international Algorithm for Ebola diagnosis for obtaining reliable results in the diagnosis of EVD (Fig 5). Early laboratory confirmation of suspected clinical haemorrhagic fever cases is essential to implement appropriate control measures. Definitive diagnosis of suspected cases of EHF is usually made by PCR detection and virus isolation on Vero cells. As a class-4 pathogen, Ebola virus culture requires a maximum containment facility and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) must be worn by the laboratory scientist or virologist [92].
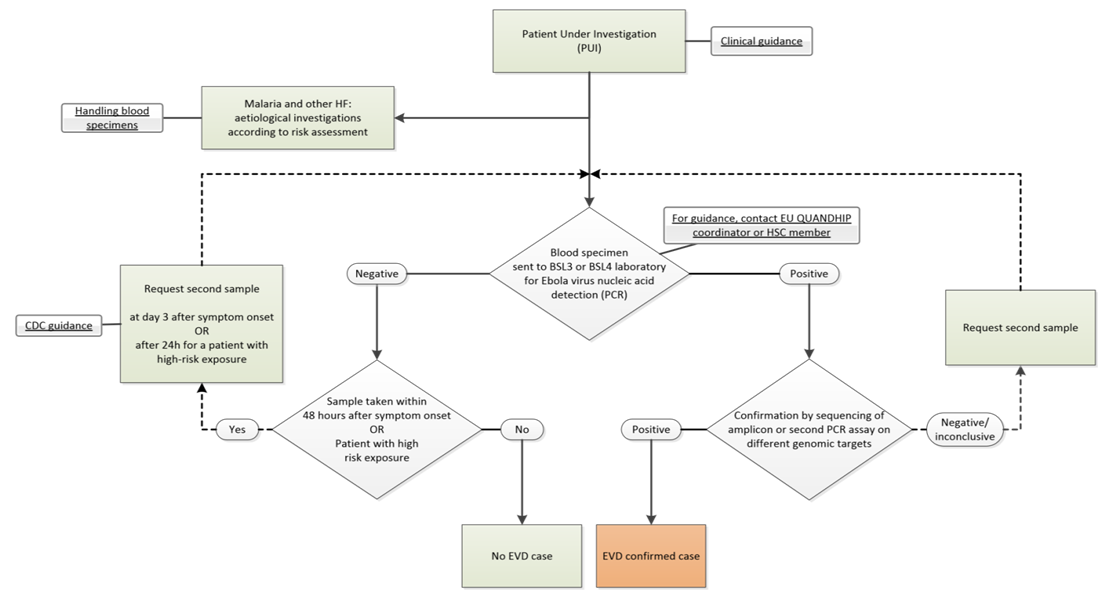 | Figure 5. Algorithm for Ebola virus disease laboratory diagnosis [95] |
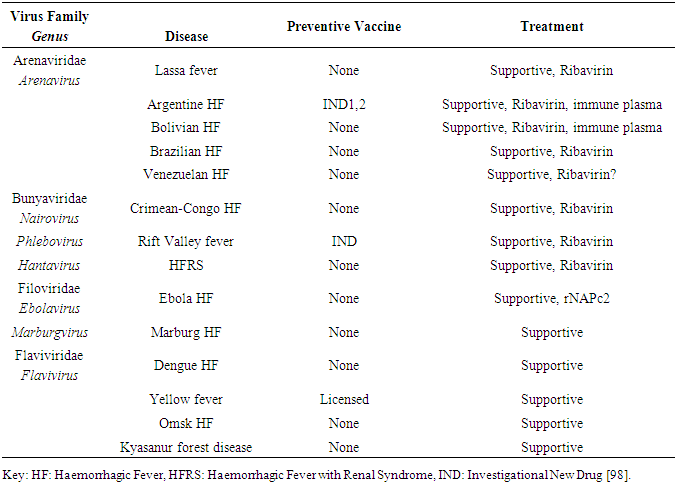
2.5. Treatment of Ebola Virus Disease
2.5.1. Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapeutic agents are available for clinical management of EVD but have not been fully certified (Table 2). Interestingly the WHO has published a document which is subject to review on categorization and prioritization of drugs for consideration for testing or use in patients infected with Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever [97]. Like every other HFs, supportive care is very important in the treatment of EVD. For an effective and complete treatment of Ebola Virus Disease, superinfections are treated using antibiotics and other conditions as they occur. Antiretroviral drugs recommended for treatment but still undergoing clinical trials include; Favipir produced by Fuji/Toyama in Japan which are small molecule antiviral therapy, with activity against many RNA virus functions through inhibiting viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Zmapp by MappBio, USA are monoclonal antibodies produced in tobacco plants, it has 100% survival rate when administered 5 days after virus challenge. Another valuable product is the interferons which can be administered with or without Ribavirin. It acts as immune modulator with antiviral activity. It has also been approved for the treatment of hepatitis B and C and multiple sclerosis. TKM-10082 produced by Tekrim, Canada is a small inhibitory RNA which cleaves Ebola RNA once inside the host cell. Interestingly TKM-10082 is Table 2. Available therapeutic agents and preventive vaccines for Viral Haemorrhagic fevers in humans particularly sequence specific to the strain of Ebola confirmed in this recent West African Ebola outbreak [97].
|
2.5.2. Supportive Care
- Patients with VHF syndrome generally benefit from rapid, traumatic hospitalization to prevent unnecessary damage to the fragile capillary bed. Transporting these patients, especially by air, is usually contraindicated because of the effects of drastic changes in ambient pressure on lung water balance. Frequently patients manifest restlessness, confusion, myalgia, and hyperesthesia; these conditions should be managed by reassurance and other supportive measures, including the judicious use of sedatives, pain relief, and amnestic medications. Secondary infections are common and should be sought and aggressively treated. Concomitant malaria should be treated aggressively with a treatment regimen known to be effective against the geographical strain of the parasite; however, the presence of malaria, particularly in immune individuals, should not preclude management of the patient for VHF syndrome if such treatment is clinically indicated.Intravenous lines, catheters, and other invasive techniques should be avoided unless they are clearly indicated for appropriate management of the patient. Attention should be given to pulmonary toilet, the usual measures to prevent superinfection, and the provision of supplemental oxygen. Treatment with steroids or other agents that causes generalized immunosuppression has no empirical basis and is contraindicated, except possibly in treatment of HFRS. The diffuse nature of the vascular pathological process may lead to a requirement for support of several organ systems. Myocardial lesions detected at autopsy reflect cardiac insufficiency ante mortem.
2.5.3. Treatment of Bleeding (Haemorrhage)
- The management of bleeding in VHF cases is controversial. Uncontrolled clinical observations support vigorous administration of fresh frozen plasma, clotting factor concentrates, and platelets, as well as early use of heparin for prophylaxis of DIC. In the absence of definitive evidence of VHF disease or DIC, mild bleeding manifestations should not be treated. More severe haemorrhage requires appropriate replacement therapy. When there is definitive laboratory confirmation of DIC, heparin therapy may be considered if appropriate laboratory support is available. Supportive strategies directed toward inhibiting coagulation activation may be warranted and have been shown to be beneficial in experimental and initial clinical studies [99]. Many new modalities to manage the pronounced coagulopathy that typifies many VHFs are being evaluated, most notably in nonhuman primate models of Ebola HF.
2.5.4. Treatment of Hypotension and Shock
- Management of hypotension and shock is difficult. Patients often are modestly dehydrated from heat, fever, anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhoea, in any combination. There is extensive loss of intravascular volume through haemorrhage and increased vascular permeability [100]. Nevertheless, these patients often respond poorly to fluid infusions and readily develop pulmonary oedema, possibly from myocardial impairment and increased pulmonary vascular permeability. A sanguineous fluid (either colloid or crystalloid solutions) should be given, with caution. Although it has never been evaluated critically for VHFs, dopamine might be the agent of choice for patients with shock who are unresponsive to fluid replacement. Alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction agents have not been clinically helpful except when emergent intervention to treat profound hypotension is necessary. Vasodilators have not been systematically evaluated. Pharmacological doses of corticosteroids (e.g. methylprednisolone 30 mg/kg) provide another possible, but untested, therapeutic modality in treating shock.
2.5.5. Isolation and Containment
- Patients with VHF syndrome (with the exception of dengue and classical hantavirus disease) generally have significant quantities of virus in their blood, and perhaps in other secretions as well. Secondary infections among contacts and medical personnel not parenterally exposed are well documented. Thus, caution is needed when evaluating and treating patients with suspected VHF syndrome. Overreaction by medical personnel is inappropriate and detrimental to both the patient and staff, but it is prudent to provide isolation measures as rigorous as feasible [101]. At a minimum, isolation measures should include restricted access to the patient and use of stringent barrier nursing methods such as the correct and consistent use of mask, gown, glove and observing needle precautions. Proper hazard labelling of all specimens submitted to the clinical laboratory with notification of appropriate clinical personnel is also crucial. All material within the isolation room must be properly kept after autoclaving or liberal disinfection of contaminated materials using such disinfectants as hypochlorite or phenols prior to their disposal.For more intensive care, however, increased precautions are recommended. Members of the patient-care team should be limited to a small number of selected, trained individuals, and special care should be directed toward eliminating all parenteral exposures. Use of endoscopy, respirators, arterial catheters, routine blood sampling, and extensive laboratory analysis increases opportunities for aerosol dissemination of infectious blood and body fluids. For medical personnel, wearing flexible plastic hoods equipped with battery-powered blowers provides excellent protection of the mucous membranes and airways [102].
2.6. Control measures of Ebola Virus Disease
- Social mobilisation and health education are critical for controlling an Ebola outbreak since resistance from the community to freely provide information on patients, deaths and contacts for effective control is a big challenge. The corner-stone for controlling an outbreak of EHF is to interrupt the viral transmission chain. In order to reduce transmission, several strict public health measures must be implemented as quickly as possible, including isolation of patients, barrier precautions and identification and tracking of all contacts. Most of the time, outbreaks are managed by a core structure called the International Committee on Scientific and Technical Coordination, under the aegis of the World Health Organisation (WHO). This committee is in charge of implementing control measure activities on a daily basis facilitated by different committees and working subgroups such as the Co-ordination committee, which is responsible for all epidemic response activities, chair daily meetings and write reports for public health authorities and health partners. The patient management team which is involved in the isolation of clinical cases in a quarantine ward, training of medical and relief personnel on the proper use of protective equipment (gloves, gowns, masks etc.), and providing medical care based on symptomatic therapy to maintain the vital respiratory, cardio-vascular and renal functions.The non-governmental organisation, Doctors without Borders and (MSF), has developed expertise in this field from involvement in outbreak responses. The hygiene and sanitation team is in charge of disinfection and burial of all Ebola and non-Ebola dead bodies under safe conditions. Local Red Cross volunteers usually perform these activities. The epidemiological surveillance team is in charge of active and passive case finding, contact tracing and rumour- verification of suspect cases or deaths in the community. Ebola haemorrhagic fever outbreaks have many socio-cultural aspects that need to be studied deeply as communities can reject the anti-epidemic control measures imposed by the international scientific and technical committee. The existence of rumours and legends related to the outbreaks could obscure the viral nature of the disease. Sometimes the anti-epidemic control measures needed to be adapted to the local culture, for example, funeral practices as in the 2003 Ebola outbreak in Republic of the Congo [103]. The members of this team should include medical anthropologists, local Red Cross volunteers and opinion leaders such as teachers, religious groups, etc., for public sensitisation, education and information. The logistic support team is in charge of providing any administrative, logistic and technical support to the other teams, such as coordination of secretariat, transport and communication. The laboratory and research team is in charge of collecting, storing and shipping of clinical samples for diagnostic confirmation. This team is also responsible for ecological studies to determine the origins of an outbreak. Psychosocial support for the affected family or families has been neglected during previous outbreaks, but this issue has become more and more important due to stigmatisation of survivors and their families by the community. In the past Ebola is usually sporadic, with high case fatality rates (up to 90%), the deadly Ebola haemorrhagic fever outbreaks are becoming more and more frequent in Africa, mostly in relation to increasing contact with infected wildlife. Previous epidemics were detected after a long delay, especially because of the remoteness of the epidemic focus, the lack of laboratory facilities and the poor knowledge of the disease by doctors and nurses, who confused Ebola disease with malaria or typhoid fever.
3. Challenges of the Recent Ebola Outbreak to the Health and Scientific Community
- Like every other outbreak of Epidemic diseases, the 2014 EVD outbreak in West Africa had its own challenges that are enormous and has led to many setbacks in different sectors, especially the Health and Scientific community. Inadequate basic information on EVD by trained community educators at the beginning of the outbreak worsened the epidemic as community members were not quite equipped with the relevant information needed to prevent the spread of the Ebola virus.The transmission chain of EVD remain a big concern for the scientific and health communities till date, since the inability to break the chain of transmission during the recent outbreak was a big challenge during the episode of the Ebola outbreak. Religious and cultural practices such as ritual baths and other cultural rights for burial which promote the spread of Ebola virus leading to new cases of EVD in the affected communities was highly challenging and it was highly responsible for the emergence of new cases.To further worsen the situation in West Africa is the delay in the intervention to stop the spread of the virus by the international bodies and as well treat the infected persons including the infected Health care workers worsened the epidemic situation in the recent outbreak. Insufficient international response in terms of funding of researches to help contain the epidemic was a big challenge in the fight against the recent outbreak which claimed many lives. The re-emergence of new cases and bizarre number of new cases reported on almost weekly bases was also big concern for the Health and Scientific community. The World Health Organization reported 132 new confirmed cases of EVD in Guinea and Sierra Leone in the week ending on March 1st, 2015, this created more fear amongst health care workers [104]. Western urban and western rural Chester of Sierra Leone continue to generate new EVD cases as some contacts are fleeing Rural districts. CDC staff reported tracing some EVD transmission chain in Bombali and Tonkoli districts back to the Western and Chester [33]. Repeated resurgence of new cases in Guinea prolonged the first outbreak in December 2013 and this was mainly due to community resistance to control measures such as contact tracing of unknown or suspected cases and safe burials. The challenges of sensitive organs such as eyes were also recorded bases on survey conducted by Medecins Sans Frontieres (MSF) among survivors of EVD which reported that 55% (n=48) of the patients with diagnosed eye conditions had uveitis [96]. On the 23rd of September 2014, a study published by the WHO Ebola response team forecasted challenge of more than 20000 cases (5740 in Guinea, 9890 in Liberia, and 5000 in Sierra Leone) by the beginning of November, 2014.The same study estimated the doubling time of the epidemic at 15.7 days in Guinea, 23.6 days in Liberia, and 30.2 days in Sierra Leone. This further raised fears among the Health care workers and lowering their moral [105].The moral of the health care workers was lowered due to the none payment of salaries of researchers and health care workers which mitigated against the fight to stop the spread of the disease in the affected communities. The morale of the health care workers in the affected countries continued to lower due to a number of reasons including a massive loss of their colleagues. In addition, they were being stigmatized by members of their community. These communities experienced shortage of labour supply, increased strikes and lowered productivity of health care workers and researchers which further worsened the situation of the epidemic in West Africa.Even U.S.A had an imported case of the disease. The US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced the first imported case of EVD in the USA linked to the current outbreak in West Africa on the 30th of September 2014 [106]. Subsequently a new case linked to the imported case was identified when a healthcare worker at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital who cared for the first imported EVD patient tested positive for Ebola on the 10th of October, 2014 [104]. The US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a new case in New York City. The case is a medical aid worker who volunteered in Guinea and recently returned to the United States [107]. This challenge further prompted the WHO to re-confirmed that the outbreak continued to constitute a Public Health Event of International Concern on the 23 October [108].Food chain supply was disrupted by the inadequate Regular updates on the performance of local markets (prices, food availability, supply chain, market integration, etc.) hindered the assessment of the severity of food insecurity in the affected communities for prompt response by international agencies, this challenges has led to the general inability of affected community members to perform optimally due to increased food crisis as a result of food insecurity posed a great challenge for all sectors and not only the Health and Scientific community [104].Degenerated relationship between health care workers and the people of the affected communities due to lack of trust, leading to assault on research team of MSF (Medicins Sans Frontiere) and in February, 2015, MSF reported throwing stones at its staff members and setting fire on MSF vehicles [104].The Education of students also suffered a big blow as schools in Nigeria, Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia were closed down for about three to fifteen months in other to curtail the rate of spread but this was a major setback for Educational sector as well as contact tracing. Inadequate and ineffective diagnostic equipment and approach was responsible for the poor acceleration of case ascertainment which was one of the major challenge that led to the increased spread in the recent Ebola outbreak in West Africa, as most patients with Ebola remain undiagnosed in their communities leading to high mortality and morbidity since average delay between symptom on set, to diagnosis is five days. On the 14th of October 2014 in the US, a second healthcare worker at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital who also provided care for the imported EVD patient from Sierra-Leone tested positive for Ebola [106].On the 22nd March 2014th the Ministry of Health in Guinea notified WHO about a rapidly evolving outbreak of Ebola viral disease (EVD). The outbreak is caused by a clade of Zaïre Ebola virus that is related but distinct from the viruses that have been isolated from previous outbreaks in central Africa, and clearly distinct from the Taï Forest Ebola virus that was isolated in Côte d’Ivoire 1994-1995, this in itself was a major challenge to the scientific community as a strange strain need to be highly studied and understood for effective therapy and management [109].Despite the overwhelming challenges faced by the Health and Scientific community, some successes were also recorded. The long awaited response by the International bodies since the announcement of the first case in 2013 was gained on the 8th of August 2014 when the WHO declared the Ebola outbreak in West Africa a Public Health Event of International Concern (PHEIC). This was a major success that result in the international willingness and commitment to jointly fight this danger disease called Ebola Virus Disease which prompted, the United Nations Security Council to recognised the EVD outbreak as a 'threat to international peace and security' and unanimously adopted a resolution on the establishment of an UN-wide initiative which focuses on assets of all relevant UN agencies to tackle the crisis was announced on the 18th of September 2014 [110]. International donors and the scientific community successfully analysed the phylogenetic analysis of the full-length sequences using the conventional Sanger method and established a separate clade for the Guinean EBOV strain in sister relationship with other known EBOV strains. This suggests that the EBOV strain from Guinea has evolved in parallel with the strains from the Democratic Republic of Congo and Gabon from a recent ancestor and has not been introduced from the latter countries into Guinea this was a major mile stone in the fight against the epidemic. The Guinean EBOV strain showed 97% identity to EBOV strains from the Democratic Republic of Congo and Gabon. Phylogenetic analysis of the full-length sequences by means of Bayesian and maximum-likelihood methods revealed a separate, basal position of the Guinean EBOV within the EBOV clade [5].Nigeria Health care system and the Scientific community recorded a huge success at the end of July 2014, when a symptomatic case travelled by air from Liberia to Lagos, where he infected a number of HCWs and airport contacts before his condition was recognised to be EVD and was isolated and the spread contained. This was a mile stone achievement for Nigeria and was applauded by the WHO as other countries were urged to borrow from the Nigeria approach which basically was based on effective contact tracing, correct information on EVD transmission and personal hygiene through the various medium of communication. On the 20 October 2014, WHO officially declared Nigeria free of Ebola virus transmission [37]. Liberia recorded success in the fight against Ebola against all odds on the 3rd of September 2015, when Liberia was finally declared Ebola-free after recording 42 days without any new case since the second negative test of the last case on 22 July 2015. On the 18th of January 2015, the government of Mali and WHO officially declared Mali free of Ebola virus transmission while in the month of December the same year WHO declared Spain Ebola-free as 42 days have passed since the confirmed case tested negative [109]. No cases of EVD were reported from West Africa during weeks 40 and 41(28 September to 11 October 2015b) of the Ebola outbreak. This is the first time since March 2014 that no cases were reported during two consecutive weeks this success was recorded due to effective communication through the various media available including the mobile phone technology of bulk SMS on how to prevent Ebola spread [110,111].Since the understanding on the routes of transmission and spread of EVD is of major importance in curbing the spread of the disease further research by the Scientific community has established that sexual mode of transmission of Ebola is possible and was confirmed by WHO and as well published in the ‘Interim advice on the sexual transmission of the Ebola virus disease [112]. Successes have also been recorded in the area of Research by the scientific community on Ebola vaccine and its trial in humans. On the 28th of October 2014, WHO published a press release regarding the approval of an Ebola vaccine trial at Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland. The trial, which is being supported by WHO, is the latest in a series of trials that are ongoing in Mali, UK and the USA [37]. For the vaccine candidate cAd3-EBO Z phase 1 trials was successfully initiated in Switzerland, UK, US, and Mali. First results assessing the cAd3-EBO Z vaccine candidate in the US show that this vaccine candidate was well-tolerated and produced antibody and cell-mediated immune responses in a dose-response manner in all 20 participating healthy adults (18-59 years of age) [113]. The first 300 doses were shipped on the 23rd January to Liberia for use in a phase 3 trial planned to enrol 30,000 and was started in February 2015 [113].In parallel, Phase 2 safety trials was also planned to be conducted in West African countries not affected by Ebola-Cameroon, Ghana, Mali, Nigeria and Senegal. A prime-boost strategy is also being evaluated in the UK using the cAd3-EBO Z candidate as a primer and the MVA-BN Filo as a booster to assess extent of the immune response [114]. For the third vaccine candidate strategy of prime-boost with Ad26-ZEBOV + MVA-BN Filo a Phase 1 trial was initiated on 6 January 2015 in the UK. A phase-3 efficacy ring vaccination trial (‘Ebola ça suffit!’), initiated in April 2015, using rVSV-ZEBOV Ebola vaccine, is continuing in Guinea [115]. In the trial, contacts and contacts of contacts associated with confirmed cases received immediate vaccination. On 1st September, the eligibility criteria for the trial were amended to allow the vaccination of children aged 6 years and above [116]. The ring vaccination trial of the rVSVZEBOV vaccine has been extended from Guinea to Sierra Leone. A phase-3 efficacy ring vaccination trial (‘Ebola ça suffit!’), initiated in April 2015, using rVSVZEBOV Ebola vaccine, is continuing in Guinea [111]. In the trial, contacts and contacts of contacts associated with confirmed cases received immediate vaccination. On 1 September, the eligibility criteria for the trial were amended to allow the vaccination of children aged 6 years and above [110]. The ring vaccination trial of the rVSVZEBOV vaccine has been extended from Guinea to Sierra Leone. Upon strengthening the level community and Religious leaders’ involvement in dialogue and decision making on Ebola, it was resolved that burials be supervised by trained personnel to ensure safe burial procedures in line with international best practices and this has curtailed the emergence of new cases associated Religious burial rights.Contact tracing became more efficient through the use of social media platforms to report suspected Ebola cases, pass effective information and updates on the epidemic. Telecommunication was also explored for Bulk SMS, toll-free calls to the Health agencies and international bodies responsible on contact tracing. The same medium and platforms were also successfully used to further reinforce the message on the importance of hand washing strongly to create awareness to community members. The international hand washing day has further reinforced this awareness ever since the recent outbreak of Ebola in West Africa.Finally, ECDC has successfully set up an extranet to support the Ebola Clinical Network. This network tool aimed to allow EVD Reference Treatment Centres in EU/EEA Member States, with or without experience of EVD cases to support each other by exchanging experiences and updated technical information as well as sharing, in a confidential manner available protocols, methods and similar materials and approaches regarding the treatment of EVD patients, infection prevention and control procedures [117].
4. Conclusions
- In conclusion, the urgent need for a clearer understanding of the immuno-pathogenesis of EBOV is crucial for the development of highly efficacious vaccines and drugs for effective management and treatment of the disease. Targeted therapy and vaccination are an immediate and highest priority. The dangers associated with EBOV, include its highly virulent and infectious nature, the emergence of new strains coupled with the breakdown of public health facilities in West Africa, Inadequate information, poor preventive measures and poor preparedness attitude of the Government, Health and the Scientific community to fight such epidemic were the major reasons for the challenges faced in the recent EVD outbreak in West Africa. If effective steps are not taken to find lasting solution to these challenges, then West Africa is still seated on a time bomb waiting to explode. It is also important to also say that resolving all the issues connected with EBOV will require long term planning and collaboration of the Health and Scientific community with the support of the World Health Organisation, all stake holders and other multinational organizations using multidimensional approach which addresses all cross-cutting issues and challenges associated with Ebola virus disease in West Africa and the world at large.
4.1. Recommendations
- Based on the literature review and the challenges and gaps identified from the Recent West African outbreak, Recommendations that will help in achieving a long lasting solution to these challenges while sustaining the successes already gained have been elaborated. Government at all levels must develop strong political will to make provision for all that is necessary to prevent future emergence of Ebola epidemic in the developing countries of the world.In terms of Research, it is imperative to expand the scope of the current researches ongoing which mainly focuses on fruit bats as putative ZEBOV reservoirs to include the reservoirs of other Ebola species for proper control effectively to stop further emergence of Ebola in West Africa and the world over. Ongoing epidemiological and genomic surveillance is imperative in identifying viral determinants of transmission dynamics and so must be sustained as this will enable Researchers to continue to monitor viral changes and adaptation so as to be on the alert to device new strategies to mitigate against new strains as they evolve.To aid in relief efforts and facilitate rapid global research, all the data generated on the nucleotide sequence of all Ebola strains associated with the past and recent outbreaks must be made generally available to aid further researches by scientists all over the world that are interested in EVD. Medical laboratory scientist must also adhere strictly to the Algorithm for the accurate differential diagnosis of Ebola and contact tracing.Looking at the gaps in funding, the international funding bodies and the Government of each country affected should cooperate to make funds readily should available in the West African countries previously affected by the epidemic for effective differential diagnosis of suspected cases of EVD and other HFs through the use of RT-PCR since it has proven to be the most effective method in the diagnosis of EVD to prevent delay in case finding.The gaps in the effective treatment of EVD, the W.H.O organisation and other international partners in collaboration with research institutes must guide research on therapeutic targets, and refine public-health strategies to improve on the already existing treatment Regimens to contain this epidemic should it re-emerge in future. Research institutes should explore the use of cDNA microarrays to further deepen the understanding on the genomic view of systemic interactions that occur during HF viral infection in other to provide clues to important host–virus interaction in Ebola infection for effective management of EVD. The World Head Organisation in conjunction with other international organisations should make funds available for further Research on the production of exogenous INF gamma and to promote its application in Ebola therapy since it has shown some level of promising results in the treatment of RVF infection.The Health facilities of the West African countries hit by the Ebola epidemic suffered from the effect of an already fractured Health care system therefore, there is an urgent need to provide the needed minimum package of infrastructural development in the Health care sector all over the world to include at least one Ebola isolation centre as a proactive measure to mitigate against the spread of EVD should it emerge again. It is imperative to increase the supplies of tents, buckets, basins, bottles of chlorine and other hand sanitizers as well as basic medical equipment including thermometers, masks, diarrheal diseases treatment kits to government counterparts in order to increase preparedness on prevention EVD and its case management.The Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) Working Group on Ebola Vaccines and Vaccination initiated by the Director General of WHO should be mandated to give its Ebola vaccine recommendations based on the best scientific evidence and public health policy. The final decision on offering vaccines in West Africa should lie with the Ministries of Health in each of the affected countries so as gain acceptance, success and ownership of the vaccination program as a sustainable exit strategy.To overcome fear by the Health workers training and retraining of Health care workers on laid down Standard Operational Procedure (SOP) on isolation of infected persons, use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), control protocols, proper waste and samples management as an essential tool to protect medical personnel and prevent the spread of the virus. Training of selected Health care workers to serve as effective and proactive surveillance team must be inaugurated for effective contact tracing strategies in line with international best practices in all countries affected by EVD in the recent outbreak in West Africa. The Ministry of Health and that of wild life conservation in the affected countries must put in place the adequate modalities required to engage village hunters on training on safe meet handling in their cause of hunting to prevent emergence and spread of Ebola.The role of effective communication cannot be overemphasized in the fight against Ebola. In other to reinforce measures of prevention of the wide spread of EBOV, community-based communication and social mobilization efforts on prevention strategies, care and emergency response in case of an outbreak must be scaled up so as to get to the hard to reach communities of high-risk areas through mobile teams and volunteers, as well as by circulating messages through sensitization campaigns and community radio. Since cultural barriers have constituted a big challenge to the he Health sector, health policies on EVD preventions should not be made by Government alone but in collaboration with traditional and community leaders who are the custodian of the people culture and traditions in other for such policies to see the light of the day.It is important to scale-up social mobilization activities associated with C4D, WASH, health and emergency coordination to support containment and control efforts. Hygiene promotion in both affected and non-affected communities must be scaled up during and after Ebola outbreaks to consolidate on the successes recorded in the last outbreak as well as prevent against the emergence another outbreak in West Africa and the world in General.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML