-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2020; 10(1): 6-10
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20201001.02

Nasal Carriage of Staphylococcus Species among Sudanese Community in Khartoum State, Sudan
Elsanousi R. M. A.1, Elsanousi S. M.2
1Department of Microbiology, University of Bahri, Sudan
2Department of Microbiology, University of Khartoum, Sudan
Correspondence to: Elsanousi R. M. A., Department of Microbiology, University of Bahri, Sudan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study was designed to determin the prevalence of Staphylococcus nasal carriage in the Sudanese community. Healthy individuals were divided into four groups: Hospital staff, Subjects in direct contact with animals, Subjects working in clean environments (with no contact with patients or animals) and Children in different ages (neonates, infants and school children). Atotal of 220 nasal speciemens were collected. Speciemens were divided as fifty speciemens for each group. Twenty speciemens were collected to compare between mothers and their infants. All speciemens were cultured, isolates were identified using conventional cultural procedures and biochemical tests. Hospital staff showed 100% carraige, 92% for those in direct contact with animals, 72% for the children group and 64% for subjects working in clean environments. The total of Staphylococcus species isolated from all groups were eleven species and two subspecies: Staph epidermidis, Staph aureus, Staph capitis, Staph hyicus (coagulase positive), Staph hyicus (coagulase negative), Staph caseolyticus, staph Simians, Staph lugdunensis, Staph delphini, Staph schleiferi, Staph hominis, Staph capitis subspp ureolyticus and Staph cohni subspp ureolyticus. Staph epidermidis was the dominant species in this study. The over all positive results of Staphylococcus species obtained from different groups under study were (82%). Fifty percent of the speciemens used to compare between mothers and their infants represented identical species.
Keywords: Staphylococus species, Nasocarriers, Healthy individuals
Cite this paper: Elsanousi R. M. A., Elsanousi S. M., Nasal Carriage of Staphylococcus Species among Sudanese Community in Khartoum State, Sudan, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 10 No. 1, 2020, pp. 6-10. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20201001.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Transient and sustained carriage of potentially pathogenic bacteria in the nasal vestibule, including both methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S.aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci, are recognized to contribute significantly to the risk of postsurgical infections [21,26]. The anterior nares have been demonstrated to harbour staphylococci than any other part of the body and in a very high percentage of the population [25]. The anterior nares is considered the primary source for replication and spread to other body sites [16,18]. In a study conducted by Liu et al. [12] on the nasal microbiota of 178 adults, 90.4% were Staphylococcus epidermidis carriers. Staph epidermidis nasal carriers increased with the usage of implanted prosthetic devices [5]. It was regarded as a commensal but, now it recognised as a major threat in prosthetic vascular and orthopaedic surgery. It concidered in hospitals as a nosocomially-acquired organism, multiple resistant coagulase negative Staphylococci (MRCNS) [15]. Approximately 20% of individuals are persistently nasal carriers of S. aureus and 30% are intermittently colonized [20]. The isolation of methicillin-resistant S.aureus (MRSA) from nasal colonization was initially among hospitalized patients. This rapidly spread to include healthy individuals in the communities. The worrisome dismenssion is the isolation in vulnerable groups like children, with potential risk of systemic infections [23]. A previous study found identical strains in 80% of infants and their–mothers. In 90% of these newborns, the source of S. aureus was the maternal nasal strains [11]. After birth hands are the main source of S. aureus transmission from surfaces to the nose [27]. Coagulase negative Staphylococci (CNS) and their habitat as well as their pathogenicity of man and animals were clearly described by Mahon and Monsueli [14]. Mirt [17] reported lesions of flank biting and necrotic ear syndrome associated with Staphylococcus hyicus infection. Hont et al. [8] reported a case of highly invasive native valve endocarditis occurring in a young man with a pre-existing cardiac anomaly that was caused by Staphylococcus lugdunensis. This organism is a major cause of destructive endocarditis, which is accompanied by high mortality. Postoperative endophthalmitis is caused by Staphylococcus lugdunensis and Staphylococcus haemolyticus [3]. Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staph hominis, Staph capitis and Staph xilosus were the most common isolates in cases of filarial lymphoedema which is complicated by frequent episodes of dermatolymphangioadenitis (DLA) [19]. Breuer et al. [6] described a case in a 73-year- old male who developed native-valve infective endocarditis due to Staphylococcus capitis as a consequence of repeated oesophageal dilation.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Samples Collection
- A total of 220 nasal swabs were collected from different groups of healthy individuals in Khartoum State. Fifty samples were collected from each group under the study, which were: hospital staff, subjects who were in direct contact with animals, subjects worked in clean environments and children. Children group was divided into: neonates (12 samples), infants: (13 samples) and schoolchildren (25 samples). Twenty samples were collected to compare between mothers and their infants. The samples were taken from the anterior nares. The specimens were labelled, put into thermo flask containing ice and transferred immediately to research laboratory for bacteriological examination.
2.2. Isolation and Purification of the Isolates
- The swabs were inoculated onto blood agar plates for primary isolation, incubated at 37°C for 24 hours under aerobic conditions. Cultures were examined for growth and colonial morphology. Plates with visible growth, were subjected to subsequent bacteriological tests. Others with no growth were re incubated and examined daily for up to seven days before they were regarded as negative. The primary isolates were subcultured on nutrient agar to obtain purified colonies. For pigment production, nutrient agar plates were inoculated with the tested organisms, incubated for 24 hours at 37°C and then transferred to room temperature for observation for up to five days. The isolates were subjected to Hugh and Leifsons (O-F) media to diffrentiate between Staphylococci and micrococci.
2.3. Identification of the Isolates
- Primary identification was done by Gram’s Stain technique according to Barrow and Feltham [4]. Secondary idetification was done using biochemical tests like catalase, oxidase, coagulase, sugars fermentation tests (D-manitol, D -mannose, D-trehalose. maltose, lactose, sucrose, rafinose and fructos), urease test, voges Proskaeür test which were performed according to Sneath et al. [22] and Barrow and Feltham [4]. Novobiocin sensitivity test was performed using Standard disc diffusion method [5 mg of novobiocin sensitivity disc (Oxoid)]. Secondary identification was done following the scheme for the identification of Staphylococcus spp. prescribed by El Sanousi et al. [7].
2.4. Preservation of Cultures
- Pure, full identified cultures were inoculated on Dorset egg medium, cooked meat medium or nutrient agar (slants), incubated at 37°C for 24-48 hours and then preserved at 4°C in the refrigerator. All media were prepared according to the methods described by Oxoid (Oxoid, Laboratories, London). Reagents used in this study were prepared according to Barrow and Feltham [4]. They were obtained from the British Drug House Chemicals (BDH ltd Poole, England).
2.5. Data Analysis
- The results were subjected to statistical analysis in the form of frequencies and percentages using SPSS 21. The significance of these frequencies was tested using chi- square test. Data analysis revealed that P-value was less than (0.05).
3. Results
- The over all positive results of Staphylococcus species obtained from different groups of healthy individuals in Sudanese community under the study were (82%). The total of Staphylococcus species isolates were eleven species and two subspecies: Staphylococcus epidermidis, S.aurus, S.capitis, Staphylococcus capitis subspp ureolyticus, S.hyicus (coagulase—positivte) S.hyicus (coagulase -negative), S.caseolyilcus, S.simians, S.lugdunensis, S.deiphini, Staphylococcus cohni subsppureolyticus, S. schleferi and S. hominis. Staphylococcus epidermidis was the most frequently isolate from all groups.
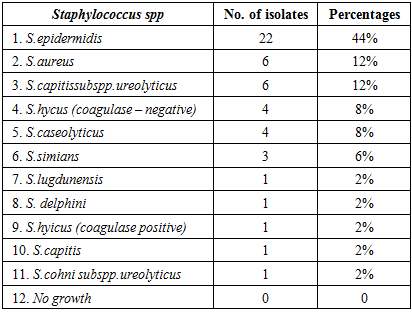
3.1. Hospital Staff (Group 1)
- This group gave (100%) positive results from a total of 50 collected samples, included eleven species and subspecies: S.epidermidis (44%), S.aureus (12%), S.capitis subpp.ureolyticus (12%), S.hyicus coagulase negative (8%), S.caseolyticus (8%), S.simians (6%), S.lugdunensis (2%), S.delphini (2%), S.hyicus coagulase positive (2%), S.capitis (2%) and S.cohni subspp ureolyticus (2%) (Table -1).
|
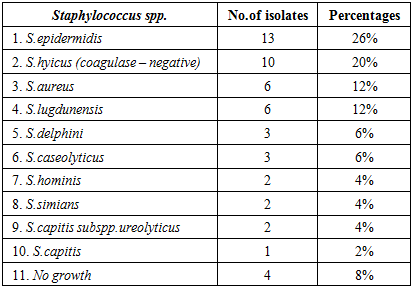
3.2. Subjects in Direct contact with Animals (Group 2)
- The Staphylococcus species positive results were (92%) from the total collected samples. Staphylococcus epidermidis represented (26%). S.hyicus (coagulase-negative) (20%), S.aureus (12%), S.lugdunensis (12%), S.delphini (6%), S.caseolyticus (6%), S.hominis (4%), S.simians (4%), S.capitis sub spp ureolyticus (4%) and S.capitis (2%). Four specimens (8%) gave negative growth to the genus Staphylococci. In this group two speciemens gave more than one species of the genus Staphylococci. One of them gave growth to Staphylococcus simians and Staphylococcus epidermidis, while the other gave growth to Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus caseolyticus (Table - 2).
|
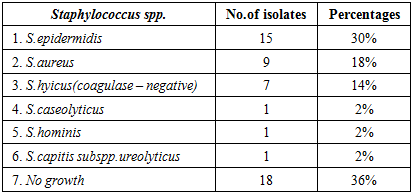
3.3. Subjects Worked in Clean Environments (Group 3)
- Staphylococcus positive results were (64%), S.epidermidis (30%), S. aureus (18%), S.hyicus coagulase negative (14%), S.caseolyticus (2%), S.hominis (2%) and S.capitis subspp ureolyticus (2%). Two specimens gave more than one species of the genus Staphylococcus. One of them showed growth to Staph.horninis and Staph.hyicus (coagulase-negative) and another one gave growth to Staph.coseolyticus and Staph epidermidis (Table - 3).
|
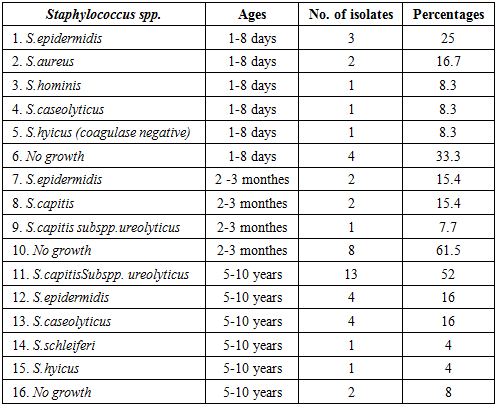
3.4. Children in Different Ages (Group 4)
- This group was divided into three subgroups: neonates (ages between 1 - 8 days), infants (ages between 2 - 3 months) and school children (ages between 5 -10 years). Twelve samples were collected from neonates, thirteen from infants and twenty five from school children. The over all positive results of Staphylococcus species obtained from this group were (72%). Neonates subgroup showed: S.epidermidis (25%), S.aureus (16.7%), S.hominis (8.3%), S.caseolyticus (8.3%) and S.hyicus coagulase negative (8.3%). The total positive results of this sub group were (66.7%). Infant subgroup gave: Staph epidermidis (15.4%), S.capitis (15.4) and S.capitis subspp ureolyticus (7.7), with 38.5% total positive result.School children showed (92%) of Staphylococcus species positive results: S.capitis subsppureolyticus (52%), S.epidermidis (16%), S.caseolyticus (16%), S.chleferi (4%) and S.hyicus (4%) (Table - 4).
|
4. Discusstion
- Staphylococcus epidermidis was the most frequently isolate from all groups. Group one gave 44%, 30% for group three, 26% for group two and group four showed 25% for neonates, 15.4% for infants and 16% for school children. This higher prevalence of Saphylococcus epidermidis may refer to the presence of hair follicles and sebaceous glands in the nose, which were favourable sites for growth and multiplication of the organism. The flora of the nose consists of prominent coryne bacteria, staphylococci (S. epidermidis and S.aureus) and Streptococci [9]. A previous study was done by Lu et al. [13] in Japan to evaluate the staphylococcal nasal carriage. The study exhibited the highest viability of Staphylococcus epidermidis in nasal microbiota, which agrees with our result. Staphylococcus aureus represented the second higher prevalence which gave 18% for group three, 16.7% for groupfour- neonates, 12% for group one and 12% for group two. Kolmos [10] carried out a similar study in Scandinavia. He studied the epidemiological and prophylactic aspects of Staphylococcus aureus carriers. His study revealed that 20% of normal population were nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus. Another study was performed in Tyland by Suvarnsit et al. [24] to investigate the prevalence of nasal carriage of S. aureus in hundred healthy individuals and patients with allergic rhinitis. Nasal swab were positive for S. aureus in 20% of subjects in the healthy individuals group, and in 21% of subjects in patients with allergic rhinitis group. these results were compareable with our finding. The prevalence rate of Staphylococcus species among the hospital staff was 100%, which was identical to the result reported by Alawad [2], who was studied the nasal carriage of Staphylococcus species in Khartoum State. These results assure that hospital staff group became a risk factor to the patients in hospitals and clinics, especially those patients under major surgical procedures or catheterization or patients in intensive care units. They also represent a risk factor for neonates who are having immature immunity system. Group two (subjects in direct contact with animals) carried a high percentage of Staphylococcus hyicus (coagulose-negatjve). It represented 20%, which was the second higher prevalence after Staphylococcus epidermidis. This may be due to direct contact with animals carrying Staphylococccus hyicus. Subjects in this group also carried some other animals’ species of the genus Staphylococcus, like Staphylococcus lugdunensis, Staphylococcus delphini, Staphylococcus caseolyticus and Staphylococus simians. The total carriage of Staphylococcus species among this group were 92%, which was less than the percentage reported in group one, and this might be attributed to colonisation of other bacteria like Gram-positive bacilli and streptococci. Groupthree (subjects working in clean environments): this group did not differ totally from other groups in that the most prevailing species was Staphylococcus epidermidis and the second prevailing species was Staphylococcus aureus. But, it differed from other groups in reporting no growth of Staphylococcus species in 36% of subjects under the study. The prevalence rate of Staphylococcus species in this group were 64%. This low prevalence rate assures that working in clean environments minimises the probability of getting infection with Staphylococcus species. The over all positive results in group four were 72%. Group four was subdivided into three subgroups; neonates and infants were reported to have the highest prevalence rate of Staphylococcus epidermidis, while the school children were reported to have the highest prevalence nasal carriage of Staphylococcus capitis subspp ureolyticus 52%. We think that this might be due to the close intercommunication and the crowding of the children in the school classes, which facilitate cross infection among this age group. A recent study was done by Ahmed etal [1] about nasal colonisation of coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CONS) among neonates at day one and day three of the admission to the neonatal intensive care units in Egyptian hospital, which revealed, 50% positive result to CONS from the total nasal speciemens. The most frequently isolated species were S. haemolyticus and S. epidermidis. This result demonstrated the increase in nasal colonisation. A comparative study between infants and their mothers was done during this investigation. We observed that 50% of the infants and their mothers had identical organisms in their nares.
5. Conclusions
- This study was concluded that Staphylococcus nasal carriage rate in Sudanese commnity has a considerable value in compare with different world studies which may become a threat if not treated.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML