-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2018; 8(1): 1-8
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20180801.01

Microorganisms Associated with Post Harvest Spoilage of Sweet Potatoes in Ile-Ife, Nigeria
Oduola A. A., Awojobi K. O., Adeyemo S. M.
Food and Industrial Microbiology Unit, Department of Microbiology, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Adeyemo S. M., Food and Industrial Microbiology Unit, Department of Microbiology, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

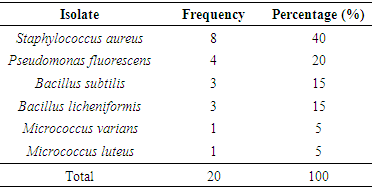
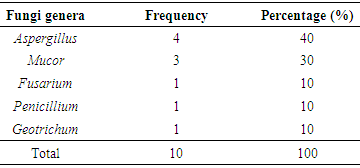
Sweet potatoes are tuber crops consumed in different parts of the world. Its use is however limited by post-harvest spoilage by microorganisms. This study was carried out to isolate, identify, and prevent the microorganisms responsible for the post-harvest spoilage of sweet potato. Five replicate samples of decaying sweet potatoes were obtained randomly at different time intervals from the local markets in Ile-Ife. They were homogenized and serially diluted to ‘thin-out’ the microbial population. Nutrient agar and potato dextrose agar were used for the isolation and identification of bacteria and fungi respectively. The bacterial population were estimated after 24 hours of incubation while the fungi were observed after 5 days of incubation. The organisms were identified using standard morphological and biochemical tests. The total aerobic bacterial count of the samples ranges from 1.81 x 105cfu/g to 1.28 x 107cfu/g while the fungi load ranges from 1.80 x 107sfu/g to 2.90 x 107sfu/g. The genera of the bacteria isolated and their percentage of occurrence include; Staphylococcus (40%), Bacillus (30%), Pseudomonas (20%), Micrococcus (10%), while the genera of the fungi isolated and their percentage of occurrence include; Aspergillus (40%), Mucor (30%), Fusarium (10%), Penicillium (10%), and Geotrichum (10%). The microorganisms gained entry into the sweet potato majorly through openings on the tubers caused by several injuries and are able to proliferate because of the temperature and the humidity of storage condition of the tuber. These microorganisms then breakdown the starch present in the tuber and therefore leads to spoilage of sweet potato.
Keywords: Sweet potato, Post-harvest spoilage, Microorganisms, Physical injuries, Storage
Cite this paper: Oduola A. A., Awojobi K. O., Adeyemo S. M., Microorganisms Associated with Post Harvest Spoilage of Sweet Potatoes in Ile-Ife, Nigeria, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20180801.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- One of the most pressing problems facing the developing nations is food scarcity. Salami and Popoola, (2007); Kana et al., (2012), reported that nearly one billion people are challenged by severe hunger in these nations of which 10% are reported dead from hunger-related complications. In Nigeria, the root crops that are majorly important include cassava, yam, sweet potatoes, and Irish potatoes. After harvest, these tubers suffer losses that result from physical, physiological or pathological factors or the combination of the three factors (Opara and Agugo, 2014). Food security and sustainability is one of the ways of addressing this problem of food scarcity and shortage due to activities of microorganisms after harvesting. In a FAO/WHO report of (2012), food security was defined as a situation in which all people at all times have both physical and economic access to adequate and nutritious food for an active and healthy life; the manner in which the food is produced, preserved and distributed are in consideration of the natural processes of the earth and thus sustainable thus reducing spoilage, scarcity, malnutrition and poverty.Sweet potato has an enormous potential to be an effective and economic source of food energy (Oyeyipo, 2012). It is an important source of antioxidants and anthocyanidins (Oladoye et al., 2013). It can be incorporated with yam to make Amala and pounded yam. The production of sweet potato, especially vegetable potato, is seriously affected by rots. According to the survey carried out in Iran, 10% pre-harvest and 20% post-harvest rots occurred in sweet potato (Bidarigh et al., 2012). These rots constitute major impediments to the drives for food security in Nigeria. Sweet potatoes have been described as having thin, delicate skin that is easily damaged by cuts and abrasion during harvesting, transportation or distribution. Striking the roots with harvesting equipment or dropping them into containers injures their skin. Bruises and abrasions must be kept at a minimum degree to avoid microbial attack. The sweet potato may be cut or bruised if they are placed in containers having sharp edges or roughly hauled or handled and this may give rise to microbial infestation (Rupsa et al., 2017).It has been reported by some workers that the microorganisms that are responsible for the spoilage of sweet potato produce extra-cellular enzymes such as amylases, celluloses, polygalactunases, xylanases, and pectin-methyl esterases and these enzymes degrade the cell wall components of produce that are susceptible leading in some cases to emission of offensive odour and water (Salami and Popoola, 2007; Amadioha, 2012; Oladoye et al., 2013). Several rots that affect sweet potato after harvesting have been substantially reported (Onifade et al., 2004; Oyeyipo, 2012) substantially reported several rots that affect sweet potato after harvesting. These rots are linked to a number of factors that are physiological, physical, and microbiological. During harvesting, storage or transportation, mechanical damage occurs and this damage has been known to be predisposing tuber to spoilage and storage rots (Oyeyipo, 2012). Contamination through natural openings or wounds by the pathogenic microorganism is considered the most critical factor in tuber decay (Udo et al., 2000). According to Arya (2010). Post-harvest pathogens can be divided into those that penetrate the produce on-farm, but develop in their tissues only after harvest, during storage or marketing on one hand; and those that initiate penetration and colonization during or after harvest on the other. Enormous postharvest losses have been attributed to fungal deteriorations (Okigbo, 2002, 2003; Shukla et al., 2012; Khatoon et al., 2012; 2016). Fungal pathogens cause spoilage and post-harvest spoilage of sweet potato by producing various types of mycotoxins. Mycotoxins are low molecular weight toxic secondary metabolites from fungal species. These mycotoxins are dangerous in small quantities and present extreme toxicity due to their heat resistivity (Okigbo, 2004; Shukla et al., 2012). Fumonisins, aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, zearalenone, and deoxynivalenol are mycotoxins of most agricultural importance (Bankole and Adebanjo, 2003). Several fungi have been implicated in the spoilage of sweet potato. In (2002), Onuegbu reported Penicillium sp. Ceratocystis fimbriata, Aspergillus niger, Diaporthe batatalis, and Aspergillus flavus as fungi responsible for the post-harvest decay of sweet potato. Oyewale (2006), reported fungi that were associated with post-harvest fungal rot of sweet potato and they include Motierella ramanniana, Rhizopus stolonifer, Mucor pusiluss, Botrytis cinerea, Erysiphe polygoni and Aspergillus flavus. During the post-harvest storage of sweet potato, Aspergillus flavus is the most dominant fungal species followed by Aspergillus niger, Rhizopus stolonifer, Trichoderma viride, Fusarium oxysporum, Penicillium digitatum, Cladosporium herbarum, and Aspergillus ochraceus. The black rot of sweet potato is caused by Ceratocystis fimbriate (Lewthwaite et al., 2011). The soft rot disease of sweet potato storage roots and post-harvest storage rot is caused by Fusarium solani and Macrophomina phaseolina (Washington, 2013). In some instances, bacteria (Pseudomonas and Erwinia) may play associative roles in rots of vegetables. Only 36% of postharvest rots of vegetables are attributed to bacteria (Agriculture Information Bank, 2013). Staphylococcus acuri and Rabniell sp. were associated with spoilage of vegetable sweet potato based on the DNA sequencing studies in Southwestern Nigeria (Oladoye et al., 2013). The objectives of this study were to isolate, identify and characterize the fungi and bacteria that are possibly responsible for the spoilage of sweet potato. This research work is carried out in response to an increase in post-harvest spoilage of sweet potato and this invariably leads to a shortage of the tuber in Ile-Ife, Market.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
- Replicate samples of decaying sweet potatoes were obtained at different locations at Mayfair and Sabo Markets in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. They were collected in a sterile polythene bags and were brought into the laboratory in Department of Microbiology, Obafemi Awolowo University for microbial analysis.
2.2. Preparation and Sterilization of Media
- The preparation and sterilization of media, water, and glass ware for the experiment all preceded the collection of the sample. All the glass wares were sterilized first by washing and rinsing with 70% ethanol. The pipettes were wrapped with paper and sterilized in a hot air oven. Nutrient agar and potato dextrose agar were used.A weighing balance was used to measure 28 grams of nutrient agar. This was then mixed with 1000ml of distilled water in a conical flask. After mixture, the conical flask was put on a heating mantle to homogenize the medium. After homogenization, it was then put in an autoclave and sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes. Thirty-nine grams (39g) of potato dextrose agar was weighed on a weighing balance and was mixed with 1000ml of distilled water in a conical flask. The conical flask was placed on a heating mantle for homogenization. After homogenization, it was then sterilized in an autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes. After sterilization, 4ml of streptomycin was added aseptically (after the medium has cooled) to the molten PDA to inhibit the growth of bacteria.
2.3. Preparation of Samples
- Cotton wool moistened with 70% ethanol was used to sterilize the workbench, hands and knife. The sterile knife was then used to cut the sample open and the decaying inner part was cut into pieces. A sterile pestle and mortar were used for homogenization. A weighing balance was then used to weigh one gram of the homogenized solid.
2.4. Isolation of Organisms from Sample
- Using the method of Harrigan and McCance (2005), one gram of the sample was poured into 9ml of sterile distilled water and the tube was shaken gently to ensure thorough mixing. After mixing, a serial dilution was then carried out by transferring 1ml from the first test-tube into the second test-tube that contains 9ml of distilled water. The second tube was mixed gently and 1ml was taken from the second tube into the third test-tube, and so on till the fifth test-tube.Isolation of organisms was done using the pour plate method (Harrigan and McCance, 2005). One milliliter (1ml) each from the third test-tube was pipetted using a new sterile pipette into two empty sterile Petri-dishes, one for nutrient agar and the other for potato dextrose agar. Also, 1ml each was pipetted from the fifth test-tube and poured into two empty sterile Petri-dishes (for NA and PDA). After the samples have been poured into the Petri-dishes, the media (NA and PDA) were poured into their respective plates (about 15ml was poured into the plates). Nutrient agar was used for bacteria while potato dextrose agar was used for fungi. After the plates had set, they were then incubated at 37°C for 24 hours (only NA plates). The PDA plates were incubated at 25°C for 3-5 days.
2.5. Gram’s Staining
- A heat fixed smear from 24-hour old bacterial isolates was prepared. The fixed smear was covered with a primary stain (crystal violet) for 2 minutes, this was then poured off and the smear was flooded with Gram’s iodine for 1 minute. It was decolorized rapidly with 70% alcohol within 15 seconds and was immediately rinsed with clean water (running water), the smear was finally flooded with a secondary stain (safranin) for 2 minutes and was washed off by clean water. The slides containing the stained smear were examined under the microscope using the oil immersion objective (x100). Gram-positive bacteria cells appear purple while Gram-negative bacteria cells appear red or pink. The staining technique also showed the shapes and arrangement of the bacterial isolates (Acharya, 2015).
2.6. Lactophenol Cotton Blue Stain
- A drop of lactophenol cotton blue stain was placed on a clean grease-free slide. A small portion of the filamentous part of the fungal isolates was emulsified in the stain. Then, the slide was covered with a coverslip avoiding bubbles. The slide was then viewed under the microscope. This technique shows various microscopic characteristics of the fungal isolates (Onuorah et al., 2015).
2.7. Spore Staining
- A heat fixed smear from a 24-hour old culture was prepared on a grease-free slide and was covered with a square of blotting paper. The blotting paper was saturated with malachite green stain solution and was steamed for 5 minutes, keeping the paper moist and adding more dye as required. The slide was then washed in tap water. Safranin was used to stain the smear for 30 seconds and was washed with tap water and blotted dry. The slide was then examined under oil immersion lens (x100) for the presence of endospores. Endospores are bright green and vegetative cells are brownish red to pink (Onuorah et al., 2015).
2.8. Catalase Test
- A 24-hour old culture was used to make a smear on a clean slide. 3% hydrogen peroxide was then added in drops to the smear. Production of a gas which was indicated by the presence of air bubbles on the slide indicates a positive reaction while a negative reaction shows no gas or bubbles.
 This test was done to determine the presence of enzyme catalase possibly produced by the isolates. The enzyme catalase aids the breakdown of hydrogen peroxides to release water and oxygen gas (Acharya, 2013).
This test was done to determine the presence of enzyme catalase possibly produced by the isolates. The enzyme catalase aids the breakdown of hydrogen peroxides to release water and oxygen gas (Acharya, 2013). 2.9. Oxidase Test
- Whatman filter paper (No 1) was placed in a sterile petri-dish and soaked with some drops of oxidase reagent (1% aqueous tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine hydrogen chloride). A slide was then used to pick a 24-hour old bacterial isolates and then used to touch the oxidase reagent on the filter paper. The development of purple colouration within 5-10 seconds signified an oxidase-positive reaction. A delayed reaction or no colour change indicates a negative reaction (Hemraj et al., 2013). This detects the presence or absence of Cytochrome C as well as the production of oxidase enzyme in microbial isolates. Other tests carried out include; Methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, Indole, Citrate utilization, Starch hydrolysis, Casein hydrolysis, Sugar fermentation.
3. Results
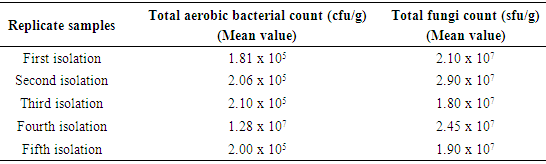
- The microbial load (mean value) of five different samples of sweet potatoes obtained within Ile-Ife is presented in Table 1. The total aerobic bacterial count was measured in colony forming unit per gram (cfu/g) while the total fungi count was measure in spore-forming unit per gram (sfu/g). In general, the fungal load was more than the bacterial load.
|
|
|
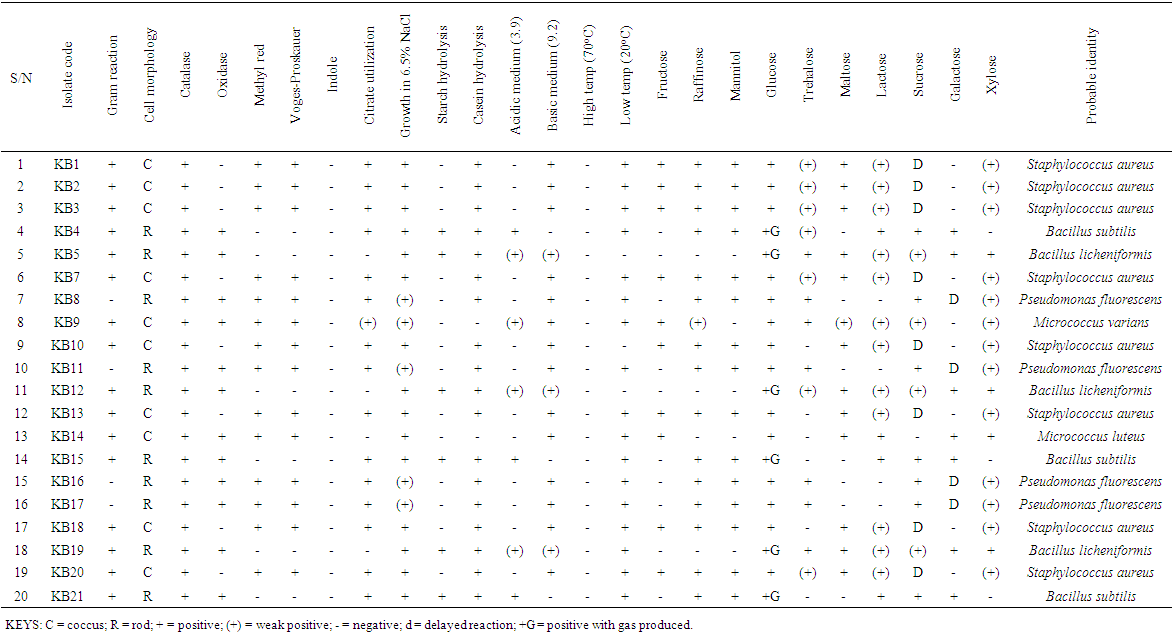 | Table 4. The biochemical Characteristics of bacterial isolates |
|
|
|
4. Discussion
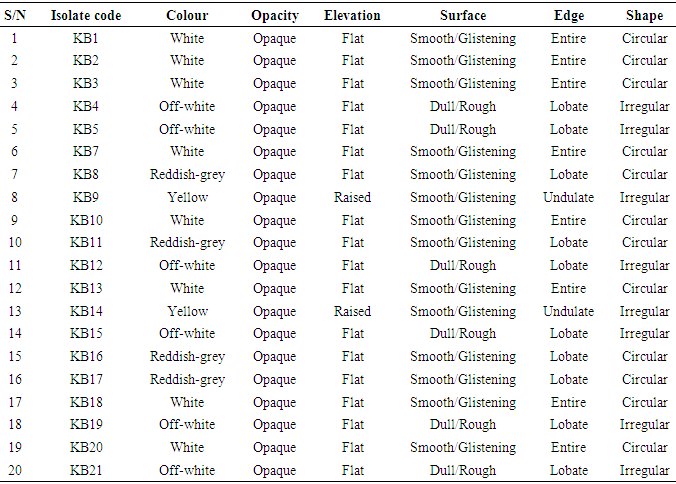
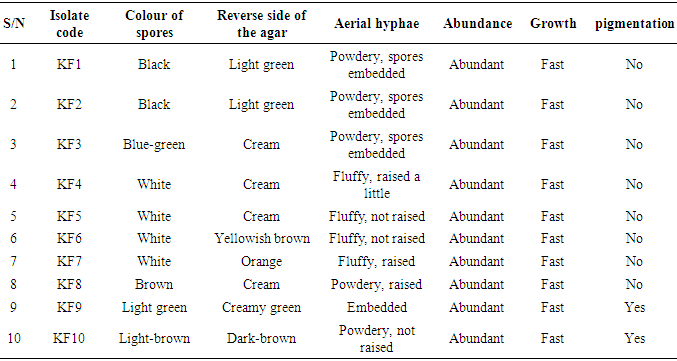
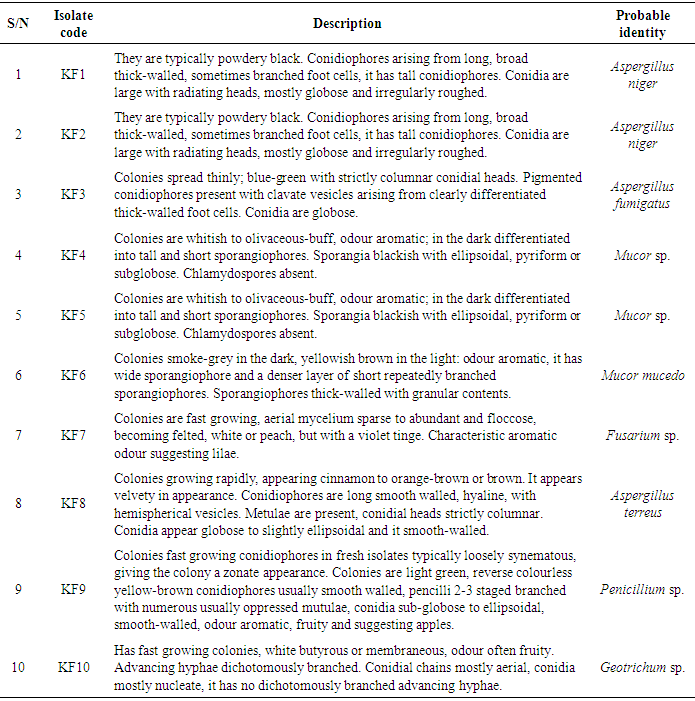
- The total aerobic bacterial count of the samples ranges from 1.81 x 105 cfu/g to 1.28 x 107 cfu/g while the fungi load ranges from 1.80 x 107 sfu/g to 2.90 x 107 sfu/g. The fungi population is much more than the bacteria population and this shows that fungi are the predominant microorganisms responsible for the spoilage of sweet potato during storage. This is in consonance with the report of (Chiejina and Ukeh, 2012).The genera of the bacteria isolated and their percentage of occurrence include; Staphylococcus (40%), Bacillus (30%), Pseudomonas (20%), Micrococcus (10%), while the genera of the fungi isolated and their percentage of occurrence include; Aspergillus (40%), Mucor (30%), Fusarium (10%), Penicillium (10%), and Geotrichum (10%).The microorganisms that have been identified to be responsible for the spoilage of sweet potato during storage have been also documented by many scientists. Oladoye et al. (2013) identified Staphylococcus, Bacillus, Pseudomonas as some of the bacteria that cause spoilage of sweet potato and these bacteria have the abilities to produce enzymes that are capable of degrading sweet potato tissues. Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Geotrichum were isolated and found to be responsible for the spoilage of sweet potato (Khatoon et al., 2012; 2016). Enyiukwu et al. (2014) also states Aspergillus fumigatus as sweet potato pathogen.Washington (2013) reported the soft rot disease of sweet potato storage roots and post-harvest storage rot by the fungi Fusarium solani and Macrophomina phaseolina. He also reported the Geotrichum candidum storage rot of sweet potato. However, few works has been carried out on the post-harvest fungal storage loss of sweet potato root tubers throughout the world (Akhtari et al., 2017, Rupsa et al., 2017).In this work, Staphylococcus was found to be the most predominant bacterial isolates with 40%. This is similar to the work of Oladoye et al. (2013) who also reported Staphylococcus to be predominant out of the bacteria he isolated from a decaying sweet potato. Also, Aspergillus was found to have the highest percentage of occurrence and this is similar to the report of Tortoe et al. (2010) that Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus niger to be abundant fungal species during post-harvest storage of sweet potato. The toxins produced by the fungal isolates are dangerous in small quantities and presents extreme toxicity because of their resistance to heat. Fungal toxins contaminate food products and cause acute or chronic intoxications. This leads to a reduction in life expectancy, worsen disease conditions in humans leading to 40% loss of economic productivity (Okigbo, 2004; Shukla et al., 2012).Since sweet potatoes have been described as having thin, delicate skin that is easily damaged by cuts and abrasion during harvesting, transportation or distribution, concerted efforts should therefore be directed towards minimizing or reducing this so as to avoid physical damage to the tuber and thereby reducing or preventing microbial attack. (Rupsa et al., 2017).Moreover, the growth of the spoilage organisms is influenced by temperature and humidity, a reduction of these parameters can be used as a pointer to reducing the rate at which these microorganisms proliferate and cause damage during storage. Lower temperature for storage of sweet potato will minimize the growth rate of microorganisms since the temperature is a key factor affecting microbial growth. Low humidity storage should be encouraged also since the condition also reduces the growth rate of fungi and bacteria that are associated with spoilage of sweet potato.Food security and sustainability, reduction of post-harvest spoilage or wastage will therefore be minimized if the activities that promote microbial attack during storage are reduced. Efforts should therefore be directed towards increasing food supply and preservation in the Nation.
5. Conclusions
- This work showed that both bacteria and fungi are responsible for the spoilage of sweet potato during storage. This causes a reduction in the availability of sweet potato in the market. In order to mitigate the rate at which microorganisms cause deterioration of sweet potato, several control techniques such proper washing of the harvested tuber, cleaning of transit containers, proper handling of the tuber in order to avoid injuries, good hygienic practices by the handlers, provision of good and healthy storage facilities must be put in place.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML