-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2016; 6(1): 23-27
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20160601.04

Assessment of Listeria Monocytogenes in Unpasteurized Milk Obtained from Cattle in Northern Nigeria
Faeji C. O.1, Fasoro A. A.2, Oni I. O.1, Akingbade A. M.3
1Department of Medical Microbiology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Afe Babalola University, Ado Ekiti, Nigeria
2Department of Community Medicine, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Afe Babalola University, Ado Ekiti, Nigeria
3Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Afe Babalola University, Ado Ekiti, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Faeji C. O., Department of Medical Microbiology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Afe Babalola University, Ado Ekiti, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Listeria monocytogenes is a gram-positive, rod shaped bacterium which grows at 24°C. However, it grows optimally at 37°C. It is an agent of listeriosis, a serious disease caused by the consumption of food contaminated with the bacterium. This study was aimed at assessing the presence of L. monocytogenes in unpasteurized milk and determining the antibiotic susceptibility of the isolates. This was achieved through extensive use of cultural and biochemical characteristics attributed to this organism.A total of 130 raw milk samples were collected and analysed for the presence L. monocytogenes. Nine (6.9%) of the fresh raw milk sample were positive for L. monocytogenes according to the cultural characteristics and biochemical reactions carried out. All the positive isolates were found to be sensitive to Tetracycline, Gentamicin and Ampicillin. This study confirms Listeria sp. as a contaminant of unpasteurized milk, therefore, proper hygienic measures should be put in place and milk lovers should be wary of the consumption of this unregulated and under cooked products as to avoid such contaminations in order to avert potential health dangers associated with it.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes, Unpasteurized milk, Contamination, Antibiotics
Cite this paper: Faeji C. O., Fasoro A. A., Oni I. O., Akingbade A. M., Assessment of Listeria Monocytogenes in Unpasteurized Milk Obtained from Cattle in Northern Nigeria, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 23-27. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20160601.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Listeria monocytogenes is a gram-positive, rod shaped bacterium which grows at 24°C. However, it grows optimally at 37°C. It is an agent of listeriosis, a serious disease caused by the consumption of food contaminated with the bacterium [1]. Listeriosis has been recognized as an emerging global public health problem. L. monocytogenes is considered one of the most important pathogens responsible for food-borne infection. It has been reported to be responsible in outbreaks of human listeriosis [2]. L. monocytogenes is also associated with meningoencephalitis, septicemia and abortion in humans and animals [3, 4]. Pregnant women, infants, immunocompromised and the elderly are the most vulnerable [5]. In a pregnant woman with subclinical infection, intro-uterine infection may result in the death of the foetus or premature delivery of newborn with pneumonic septicaemia and meningitis. An influenza like illness accompanied by diarrhoea may occur in adults [6]. The overt form of the disease has a mortality greater than 25% and its meningitis is often complicated by encephalitis [1]. Listeriosis, in many countries is a notifiable disease placed under closed surveillance even though its cases are fewer than other infections [7]. In the United States, approximately 1,600 persons are estimated to become seriously ill with listeriosis each year, of whom 16% die [8].L. monocytogenes is a food borne pathogen which has been isolated from several food products such as cheese, meat, and milk [1] and it is known that strains of L. monocytogenes are capable of becoming resistant to one or more antimicrobial drugs [9]. In northern Nigeria, it is observed that unpasteurized milk are consumed by the cattle rearers and locals as well as it is being sold to the public by them. This consumption poses potential health hazards to the consumers if contaminated by L. monocytogenes. The objectives of this study were to determine the prevalence of L. monocytogenes in unpasteurised milk and its possible susceptibility to common antimicrobial agents.
2. Methodology
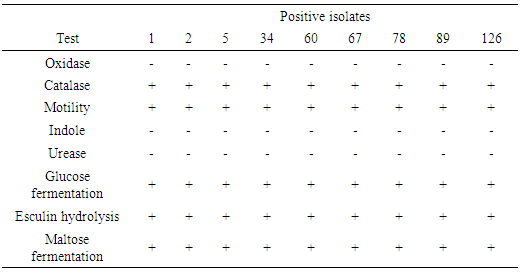
- Sample collection Fresh raw milk samples were collected from Toro LGA, Bauchi State in sterile leak proof universal bottle and labelled appropriately. These were taken to the laboratory for bacteriological examination in cold flask within one to three hours after the samples were collected. The samples were collected from different Fulani herds, 5mls of the composite milk was collected with a sterile syringe, dispensed into a sterile universal bottle and put in a transport flask with ice packs.Enrichment Enrichment for L. monocytogenes was carried out by preparing 9mls of the sample and incubated at 30°C for up to 168hrs [10]. At intervals of 24hrs, 48hrs and 168hrs, 0.1ml of culture of the selective enrichment broth was inoculated unto Listeria selective agar and sheep blood agar [10]. The agar plates were incubated at 37°C for 48hrs. Typical colonies of Listeria sp. were examined after 24hrs and 48hrs of incubation. Gram stain reaction A smear was made on a slide from the isolate and heat-fixed. Crystal violate stain was then poured on the smear of each labelled slide and a mordant was poured. The smear was allowed to stand for one minute before it was decolourized with alcohol for 15 seconds and then counter stained with safranin for one minute. The slide was rinsed off with water and allowed to air-dry and viewed under the microscope using the oil immersion objective lens.Biochemical tests Beta-haemolytic colonies that were also gram-positive and short rod were picked for biochemical test such as oxidase, catalase, motility and Aesculin hydrolysis, indole, urease and sugar fermentation tests.Oxidase test A piece of filter paper was placed on a clean Petri dish and moistened with two to three drops of freshly prepared 1% oxidase reagent. One to two colonies of the organism were picked and smeared on the moistened paper. A positive result was indicated by a purple or blue-black colour within 60 seconds while no colour change indicated a negative result.Catalase test Organism producing the oxido-reductase enzyme catalase, breaks down hydrogen peroxide to water (H2O) and Oxygen (O2) resulting in bubbles. Bacterial isolate was tested by placing drops of hydrogen peroxide on a bacterial colony previously smeared on a slide. The presence of catalase was indicated by the presence of gas bubbles (oxygen) either immediately or within a few seconds later.
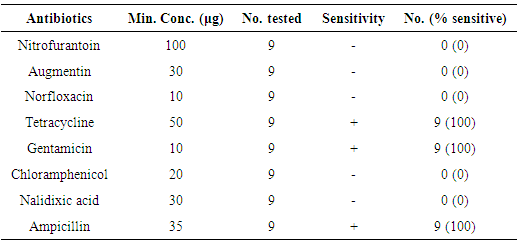
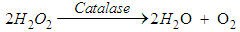 The presence of gas bubbles indicated a positive catalase test.Urease test Organism producing the enzyme urease will break down urea to ammonia and Carbon (IV) oxide (CO2) thus turning the medium alkaline by a change in colour to pink red. The test organism was inoculated heavily in a bijou containing 3ml sterile Christensen’s modified urea broth and incubated at 35 – 37°C for 3–12hrs. A pink colour indicated a positive urease test.Indole test To detect the ability of an organism to break down tryptophan to indole, peptone water in bijou bottle were inoculated with isolates and incubated at 28°C for 24hrs, three to four drops of Kovac’s reagent was then added. A bright pink colour in the layer indicated the presence of indole. Motility test Peptone water in bijou bottles were inoculated with isolates and incubated aerobically at 20°C for 6hrs and a wet preparation was examined for motility. Aesculin hydrolysisSlant of aesculin agar was prepared and streaked with colonies up the slant. The by-product of this hydrolysis with the iron salts in the medium causes the medium to blacken. If the slant turns dark coffee brown/black, it indicates a positive result. If the slant remains yellow, it indicates a negative result.Glucose fermentation testBacteria have enzymes necessary for the aerobic breakdown of glucose (oxidation) and/or for the fermentation of glucose. Bijou bottle containing glucose fermentation broth were inoculated with isolate and incubated at 28°C for 48hrs. The bijou bottles contain inverted Durham tubes to trap the gas. Gas trapped in Durham tubes indicated positive result.Antimicrobial susceptibility test Using the disc diffusion test, sterile forceps were used to place the disc on the inoculated Mueller Hinton agar plate and incubated aerobically at 27°C for 24hrs [11]. The following antibiotic discs were used: Tetracycline (50μg), Ciprofloxacin (5μg), Norfloxacin (10μg), Augmentin (30μg), Nitrofurantoin (100μg), Chloramphenicol (20μg), Gentamicin (10μg), Nalidixic acid (30μg), and Ampicillin (30μg). Zones of inhibition around 18mm were considered sensitive to the antibiotics, 13-17mm were considered intermediate while zones of 12mm or less were considered resistant to the antibiotics [11]. A control test was set up using strains of Escherichia Coli.Statistical analysisData were analysed using Epi Info version 6 statistical software package. The descriptive statistics were presented in frequencies and percentages.
The presence of gas bubbles indicated a positive catalase test.Urease test Organism producing the enzyme urease will break down urea to ammonia and Carbon (IV) oxide (CO2) thus turning the medium alkaline by a change in colour to pink red. The test organism was inoculated heavily in a bijou containing 3ml sterile Christensen’s modified urea broth and incubated at 35 – 37°C for 3–12hrs. A pink colour indicated a positive urease test.Indole test To detect the ability of an organism to break down tryptophan to indole, peptone water in bijou bottle were inoculated with isolates and incubated at 28°C for 24hrs, three to four drops of Kovac’s reagent was then added. A bright pink colour in the layer indicated the presence of indole. Motility test Peptone water in bijou bottles were inoculated with isolates and incubated aerobically at 20°C for 6hrs and a wet preparation was examined for motility. Aesculin hydrolysisSlant of aesculin agar was prepared and streaked with colonies up the slant. The by-product of this hydrolysis with the iron salts in the medium causes the medium to blacken. If the slant turns dark coffee brown/black, it indicates a positive result. If the slant remains yellow, it indicates a negative result.Glucose fermentation testBacteria have enzymes necessary for the aerobic breakdown of glucose (oxidation) and/or for the fermentation of glucose. Bijou bottle containing glucose fermentation broth were inoculated with isolate and incubated at 28°C for 48hrs. The bijou bottles contain inverted Durham tubes to trap the gas. Gas trapped in Durham tubes indicated positive result.Antimicrobial susceptibility test Using the disc diffusion test, sterile forceps were used to place the disc on the inoculated Mueller Hinton agar plate and incubated aerobically at 27°C for 24hrs [11]. The following antibiotic discs were used: Tetracycline (50μg), Ciprofloxacin (5μg), Norfloxacin (10μg), Augmentin (30μg), Nitrofurantoin (100μg), Chloramphenicol (20μg), Gentamicin (10μg), Nalidixic acid (30μg), and Ampicillin (30μg). Zones of inhibition around 18mm were considered sensitive to the antibiotics, 13-17mm were considered intermediate while zones of 12mm or less were considered resistant to the antibiotics [11]. A control test was set up using strains of Escherichia Coli.Statistical analysisData were analysed using Epi Info version 6 statistical software package. The descriptive statistics were presented in frequencies and percentages. 3. Results
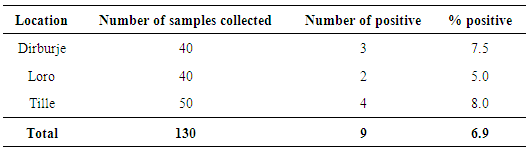
- A total of 130 raw milk samples were collected and analysed for the presence of L. monocytogenes. Nine (6.9%) of the fresh raw milk samples were positive for L. monocytogenes according to the cultural characteristics and biochemical reactions carried out. All the positive isolates were found to be sensitive to Tetracycline, Gentamicin and Ampicillin.
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- This study shows that L. monocytogenes is a contaminant of unpasteurized milk. Nine (6.9%) out of 130 raw milk samples screened for L. monocytogenes were positive. This finding is in agreement with reports from researchers who isolated the organism from unpasteurized milk and other products [12].A report by Chukwu, et al. [13] shows a prevalence of 11% from 450 milk samples collected in Jos, Nigeria. The difference in isolation rates may be due to the different locations, the health care given to the cattle as well as precautions taken by milk handlers. Also, the cattle rearing practice by the herdsmen in the study areas might be a contributing factor to the increase or decrease in the prevalence of the organism as herdsmen could have been health- and hygiene-conscious and have been consulting a veterinary doctor for adequate health service. Prevalence of L. monocytogenes in raw milk in some developed countries such as China is very low (0.23% to 1.2%) [14] and this may be attributed to proper and good hygiene practices in farming and also use of technologies.In the study of Schlegelova et al., [15], they were able to detect the presence of L. monocytogenes in only two (1.8%) out of 111 bulk milk samples tested. Navratilova et al. [7] found six samples (2.1%) contaminated with L. monocytogenes from 278 samples of raw bulk milk in Czech Republic. A study conducted by Pantoja et al. [16] in the United States reported the prevalence of L. monocytogenes to be 7.9%. In their study, they isolated the bacterium from bulk tank milk, milk filter, milking machine, silage, water, faeces, bedding, in-line milk and mammary gland of the animals. This could have been the reason for having such a high prevalence in the United States. However, our finding was close to the prevalence of 8.3% of L. monocytogenes found in eight out of 96 raw milk samples in the city of Fez in centre northern part of Morocco [17]. They also discovered that contamination of milk was highest during winter and autumn periods which they found to be statistically significant (p<0.05). Presence of L. monocytogenes in raw milk have been reported to be either fecal [18] or environmental contamination during milking, storage and transport, infected cows in dairy farms and poor silage quality [19].Food borne L. Monocytogenes leading to listeriosis is a disease of economic and public health importance. It has a high fatality rate of 20 – 30% in those with severe underlying conditions such as cirrhosis that impair the immune system and pregnancy [20]. Infants and the elderly are also vulnerable [5]. Therefore, necessary precautions should be implemented to avoid contracting the disease.The implication of the result of this study clearly confirms L. monocytogenes as probable contaminants of unpasteurized milk and thus questioning the quality of such farming practices leading to the production of such food (milk). Some observational studies reported that environmental and milking hygiene-related risk factors such as milking of cows directly into buckets, lack of pre-milking teat disinfection, poor cow cleanliness, and use of dirty towels in teat pre-milking disinfection were associated with the contamination of milk by L. monocytogenes [21, 22]. If these hygiene-related factors are avoided by these cattle rearers, the presence of L. monocytogenes in milk can be reduced. The animal (cow) from which the milk was produced might also be a probable source of contamination since L. monocytogenes has been isolated from a variety of animals as well as animal products [23]. Milk is normally sterile when it is secreted but when it leaves a cow’s udder, it could rapidly be contaminated with a variety of organisms, usually from the environment [24]. Contamination of feeds is influenced by the conditions of preparation and storage practices. Farmers in rural areas lack training in good agricultural practices and silage making, this may result in the production of quality-compromised produce which may in turn contribute to the contamination of milk with L. monocytogenes in that particular period and region [25].The antimicrobial sensitivity pattern showed that the isolates were resistant to most antibiotics tested with the exception of Tetracycline, Gentamicin, and Ampicillin. This pattern is in agreement with the works of McClain and Lee [26] and Navratilova et al. [7]. The resistance of the isolates to Nalidixic acid, Norfloxacin buttresses the reason why nalidixic acid is in part of the medium used in isolation of Listeria sp. L. monocytogenes isolated from other product such as meat and milk products also showed similar antibiogram with isolates being resistant to Augmentin, Norfloxacin and Chloramphenicol [26] which is in agreement with this current study. Multiple resistance of isolates to some of these drugs could be attributed to the fact that the antibiotics have been abused due to constant and indiscriminate usage on animals [20]. The fact that isolates exhibited multiple drug resistance might also indicate that the sources of contamination of the raw milk sample may have probably been from human because of abuse of antibiotics in humans [27, 28]. This study has shown that Tetracycline, Gentamicin and Ampicillin could be used as a first line drug for the treatment of listeria infection, while awaiting laboratory report. L. monocytogenes causes listeriosis in humans, hence, isolating it from unpasteurized milk which many consume in rural areas of northern Nigeria is a cause of concern.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
- This study confirms the presence of L. monocytogenes in unpasteurized milk which is consumed by individuals from the study location and this has potential adverse implications on the health status of these communities. Therefore, necessary preventive, control and enlightenment measures should be structured so as to avoid disease epidemics in these communities. More hygienic and sanitary measures should be taken during milking process and handling of milk product. This can be achieved through enlightenment of ‘Fulani herdsmen’ on the need to maintain adequate sanitary conditions. Raw milk should be pasteurized or boiled properly before consumption as this will go a long way to reduce the microbial load if not eliminate the flora in milk. Since this infection is contracted through food, high risk communities such as the rural areas of northern Nigeria should be educated on how to maintain good food (milk) hygiene, preparation and storage practices. It is also recommended that children who are more susceptible to this organism be well breastfed for them to develop proper immunity.Government should support and invest in farming practises through provision of appropriate technologies, equipment and also proper public health sensitization of these farmers. Further work needs to be done to detect and characterise strains found in different locality, as well as surveillance of the bacterium and its disease.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML