-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2016; 6(1): 14-22
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20160601.03

Soilborne Fungi of the Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera in a Preserved Region of the Brazilian Cerrado Biome
Mônica Cristina Pereira Monteiro 1, Fabiana Reinis Franca Passamani 2, Michelle Ferreira Terra 2, Daiani Maria da Silva 1, Marcelo Ângelo Cirillo 3, Luís Roberto Batista 2
1Federal University of Lavras – UFLA - Department of Biology, Brasil
2Federal University of Lavras – UFLA - Department of Food Science, Brasil
3Federal University of Lavras – UFLA - Department of Exact Sciences, Brasil
Correspondence to: Luís Roberto Batista , Federal University of Lavras – UFLA - Department of Food Science, Brasil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Conducting studies on the fungi that are present in the soils of preserved biomes of natural ecosystems is important; such research leads to knowledge regarding the biodiversity of species and to the discovery of new products of importance to human health. However there is little information about the biodiversity of the filamentous fungi in the cerrado biome of Brazil. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the fungi of the genera Aspergillus and Penicillium present in the preserved soils of the Brazilian cerrado. Thirty soil samples were collected during periods of high and low rainfall in three different regions. The filamentous fungi present in the soil were isolated using a serial dilution technique and were incubated in two culture media, Dichloran Glycerol (DG-18) and Corn Meal Agar (CMA). A total of 183 isolates belonging to the Aspergillus (82) and Penicillium (101) genera were identified. The following species were the most abundant: Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus ostianus and Penicillium citrinum. Species of Aspergillus and Penicillium that are potentially toxigenic and of biotechnological importance are naturally present in preserved areas of the Brazilian cerrado.
Keywords: Biodiversity, Soil, Cerrado, Aspergillus
Cite this paper: Mônica Cristina Pereira Monteiro , Fabiana Reinis Franca Passamani , Michelle Ferreira Terra , Daiani Maria da Silva , Marcelo Ângelo Cirillo , Luís Roberto Batista , Soilborne Fungi of the Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera in a Preserved Region of the Brazilian Cerrado Biome, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 14-22. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20160601.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Brazil is among the most biologically rich countries, and it maintains substantial areas of high value for the preservation of biodiversity (Sparovek et al. 2012). Among these biologically important areas is the cerrado biome. “Cerrado” is the Portuguese word for the plateau of woodlands, savannas, grasslands, gallery and dry forests in central Brazil (Klink & Machado, 2005). The cerrado is the second largest biome in South America, where it is only surpassed in area by the Amazon forest. This ecosystem occupies approximately 20% of Brazil andincludes parts of the following Brazilian states: Bahia, Goias, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Parana, Piaui, Sao Paulo, and Tocantins (Ratter et al. 1997; Sano et al. 2010).The cerrado biome is considered a biodiversity hotspot and contains a large number of endemic species (Myers et al. 2000). However, the cerrado is one of the most endangered biomes worldwide. The indiscriminate advances caused by the expansion of agriculture and animal farming have endangered this biome (Klink and Machado, 2005). Large areas of monoculture cover savannah regions in the south of Minas Gerais (Myers et al. 2000; Giannetti et al. 2011). Despite its importance, the biodiversity of the cerrado has been poorly studied, particularly the subject of microorganisms. Little is known about the soil microbiota. Soil microorganisms are fundamental for the maintenance of terrestrial ecosystems (Moreira and Siqueira, 2001), and fungi constitute an important part of the soil biomass (Ritz and Young, 2004). In the biosphere, the richest fungal habitat is the soil. Processes such as soil aggregation, the decomposition of organic residues, nutrient mineralization, the establishment of symbiotic relationships and the control of plagues and diseases rely on the effective participation of fungi (Pfenning and Abreu, 2006).Fungi belonging to the Aspergillus and Penicillium genera play important roles in food contamination and deterioration, and some species produce mycotoxins that may have harmful effects on human and animal health (Pitt, 2000). Aspergillus and Penicillium, which include many economically interesting species (Peterson, 2012), are two of the most studied genera (Pitt, 2000; Klich, 2002; Varga et al. 2004). These fungi are of great importance, not only in terms of biotechnological applications but also for economic reasons, due to their metabolic properties (Hoffmeister and Keller, 2007). Thus, the importance of these genera in ecosystems and in the daily life of the human species ranges from basic research to microbial ecology, environmental purification and biotechnology applications, which reinforces the urgent need to conserve natural areas (Tauk-Tornisielo et al. 2005). Considering the importance of the Aspergillus and Penicillium genera and due to the dearth of information about Aspergillus and Penicillium species in the savannah soils in the state of Minas Gerais, the aim of this work was to isolate and identify fungi of these genera in preserved soils of the savannah biome in Minas Gerais using morphologic methods in three different locations during periods of high and low rainfall.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
- The study sites were located in the state of Minas Gerais in the municipalities of Arcos, Luminarias, and Passos, which have preserved cerrado regions. The Arcos region is located in the upper Sao Francisco zone, in the midwestern region of the state of Minas Gerais, at the following geographical coordinates: 20º17’29”Sand 45º32'23"W. The Luminarias region is in the southern Minas region at the following coordinates: 21°31'26"S and 44°54'11"W. The Passos region is also located in the south of the state, at the following coordinates: 20º43'08"S and 46º36'35"W. The climate is seasonal (wet from October to March and dry from April to September) and mild year-round, with temperatures ranging from 22 to 27° C. The average annual rainfall is 1500 mm (Klink & Machado, 2005).
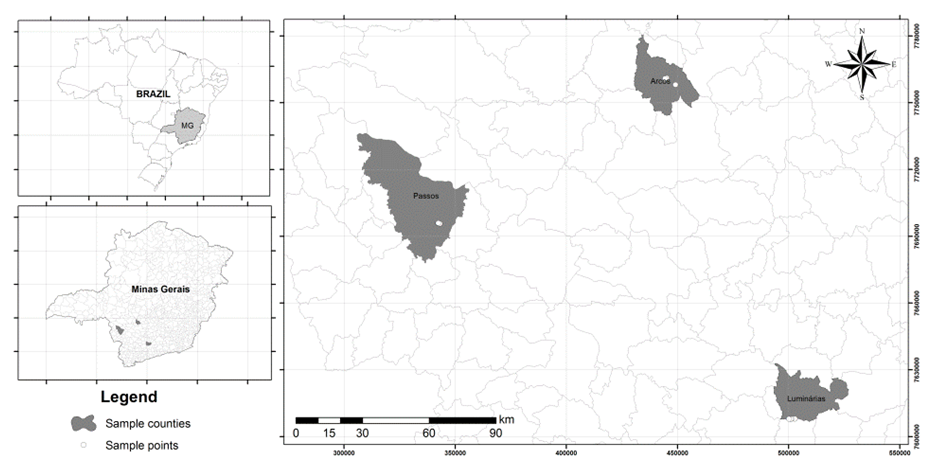 | Figure 1. Location of the study area |
2.2. Sampling
- The soil sampling was conducted during periods of high and low rainfall in the regions of Arcos, Luminarias, and Passos, which are preserved savannah areas in the state of Minas Gerais. A total of 5 compound samples were collected in the 3 areas of study, in the 2 periods, January and August of 2010, totaling 30 soil samples. A total of 300 g of soil collected in these regions was used for the sample processing. For each sampling point, 12 subsamples were collected in two concentric circles with radii of 3 and 6 m from the center at a depth of 20 cm. The soil samples were extracted with the aid of an auger that had been washed in alcohol and flamed. Subsequently, the samples were stored in sterile plastic bags and were transported to the laboratory.
2.3. Isolation of Aspergillus and Penicillium from the Soil
- For the isolation of these fungi from the soil samples, 10.0 g of soil was weighed and added to 90.0 mL of sterilized Peptone water (1.0 %). Each sample was homogenized in a shaker at 120 rpm for 30 minutes. Serial dilutions were performed in two different culture media. After successive dilutions up to 10-3, an aliquot of 0.1 mL was added to DG18 culture medium (dichloran1.0 mL; bacteriological peptone 5.0 g; KH2PO4 1.0 g; MgSO4·7H2O0.5 g; glycerol 220 g; chloramphenicol 1 mg; agar15.0 g; and distilled water 1000 mL) and CMA (filtered cooked cornmeal 30.0g; agar 15.0 g; distilled water 1000 mL; and chloramphenicol 1mg), and the aliquot was spread with a Drigalski spatula. The plates were incubated at 25ºC for seven days. The results were expressed as colony-forming units per gram of soil.
2.4. Morphological Identification of Species Belonging to the Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera
- After pure cultures were obtained, isolates belonging to the Aspergillus genus were inoculated into culture media with the following formulations: CYA (K2HPO4 1.0g; Czapek concentrate 10.0 mL; metal solution 1mL; yeast extract 5.0g; agar 15.0g; sucrose 30.0 g; and distilled water 1000 mL) and MEA (malt extract 20.0g; bacteriological peptone 1.0g; glucose 20.0g; agar 20;and distilled water 1000 mL). The cultures were incubated for seven days, with CYA at 25ºC and 37ºC and MEA at 25ºC.For the morphological identification of Aspergillus species, macroscopic characteristics were analyzed, such as colony color, mycelia color, the presence of exudate, reverse color, colony diameter, the presence of soluble pigmentation, and cleistothecia/sclerotia, according to Klich (2002). The identification Manual were based on those of Pitt and Hocking (2009), Domsch, Gams, and Anderson (2007) Samson et al (2014) and others.Isolates belonging to the Penicillium genus were inoculated into standard culture media as previously described, with CYA at 25ºC and 37 ºC, MEA at 25ºC and Creatine Sucrose AgarCREA (creatine 3.0 g; sucrose 30g; HCl 0.5 g; MgSO4 0.5 g; K2HPO4·3H2O 0.5g; FeSO4·7H2O 0.01g; and distilled water 1000 mL).The Penicillium species were identified based on the methods of Pitt (2000), Pitt and Hocking (2009), Samson et al. (2004), and Domsch, Gams, and Anderson (2007) and others.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
- In this study, analyses of variance and comparison tests of averages were not used because these techniques assume that the samples are independent and normally distributed. However, these assumptions do not apply to incidence data or the identification of isolates; these are count data that are highly dispersed in relation to the evaluated regions. Thus, the data were organized into contingency tables, which enabled the application of a simple correspondence analysis (Greenake and Blasius 2006) and allowed the construction of percentage maps, with the results displayed as a graphic distribution of the analyzed variables.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation of Aspergillus and Penicillium from the Soil
- Thirty soil samples containing 813 isolates were analyzed. Isolates belonging to the genera Aspergillus and Penicillium were found in both culture media (Figure 2), and serial dilutions were performed. Penicillium was the dominant genus in all the samples, demonstrating that species of this genus are the best adapted to the soil in the area studied. The Penicillium colonies exhibited rapid growth and abundant sporulation in the DG18 culture medium (Figure 2A, 2B).
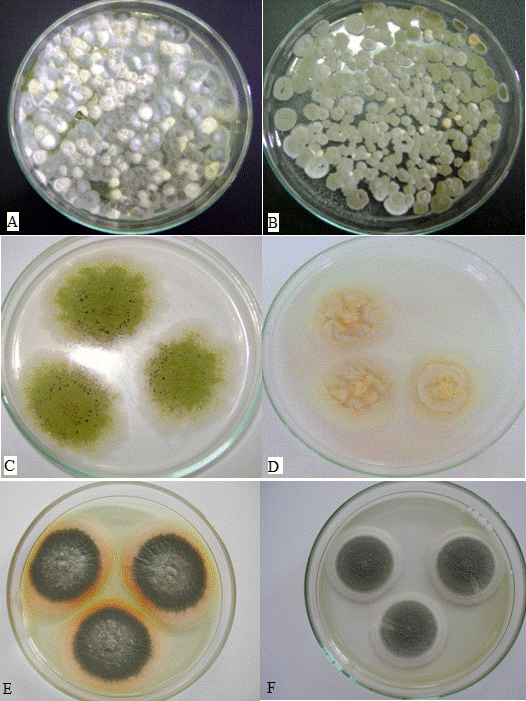 | Figure 2. Fungi isolation from soils sample, (A and B) in the DG18 culture medium, (C and D) Aspergillus colonies in the CYA culture medium, (E and F) Penicillium colonies in the CYA culture medium |
3.2. Morphological Identification of Isolates Belonging to the Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera
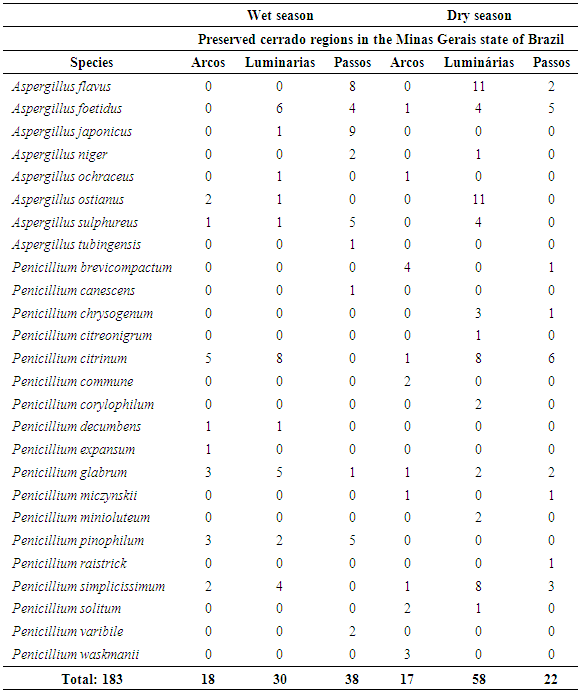
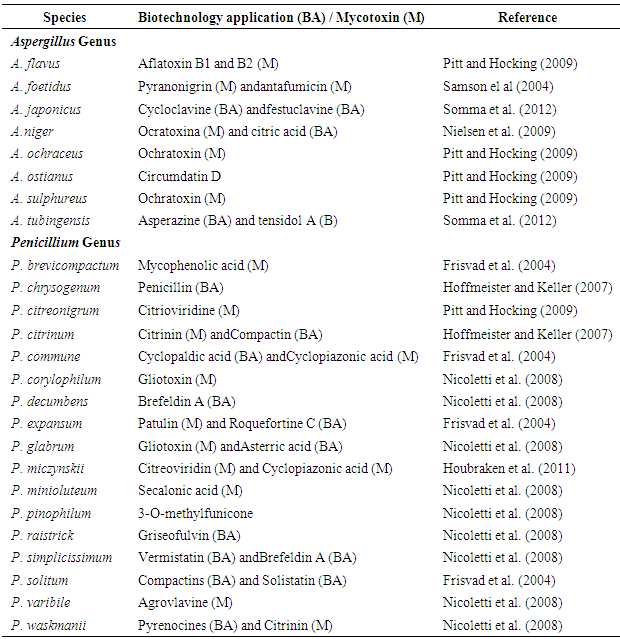
- Through the analysis of the morphological characteristics of the encountered fungi, 183 isolates belonging to the Aspergillus (82) and Penicillium (101) genera were identified. There were eight Aspergillus species (A. flavus; A. japonicus; A. foetidus; A. niger; A. ochraceus; A. tubingensis; A. sulphureus; and A. ostianus) and eighteen Penicilliums pecies (P. citrinum; P. decumbens; P. solitum; P. glabrum; P. expansum; P. simplicissimum; P. canescens; P. waksmanii; P. citrinum; P. chrysogenum; P. raistrick; P. minioluteum; P.miczynskii; P. varibile; P. corylophilum; P. commune; P. brevicompactum; and P. pinophilum), for a total of 26 identified species (Table 1).
|
3.3. Simple Correspondence Analyses (CA)
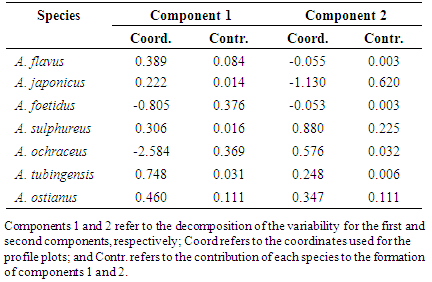
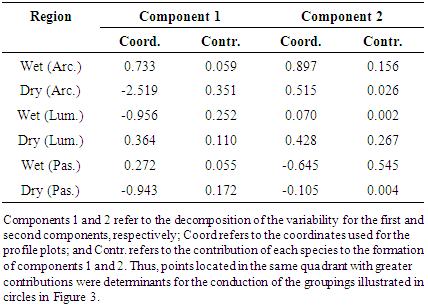
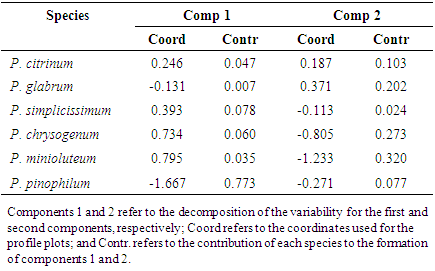
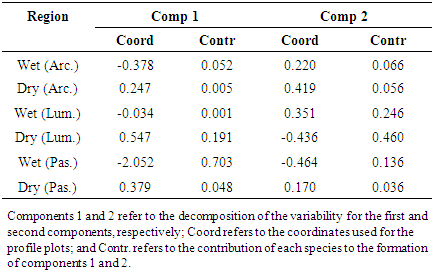
- The results of the simple correspondence analyses (CA) of the fungal species of the Aspergillus and Penicillium genera in the three regions and in the two different collection periods indicated revealed a significant association between the Aspergillus and Penicillium species with the savannah regions in the different seasonal periods. The determination of these groups and the estimation of the components were based on the results of the contributions of the line and column profiles (Tables 2 and 3) in relation to the components used for the construction of the percentage map. In the interpretation of these components, it was noted that the variability of the points decomposed into each component. Thus, the coefficients specified in Contr (contributed) in the Table 2, indicate the amount that each point contributed to the determination of the direction of the axes. Finally, the coordinates specified in Coord (Table 2) represent the scores obtainedfor each component.Thus, analogous to the interpretation of the values described in Table 2, the contributions and the coordinates obtained for the components were interpreted in relation to the variables during different seasonal periods.
|
|
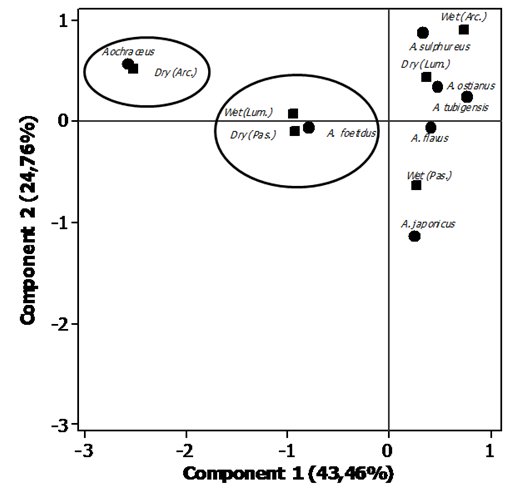 | Figure 3. Percentage map for the fungal species of the Aspergillus genus based on region and seasonal period |
|
|
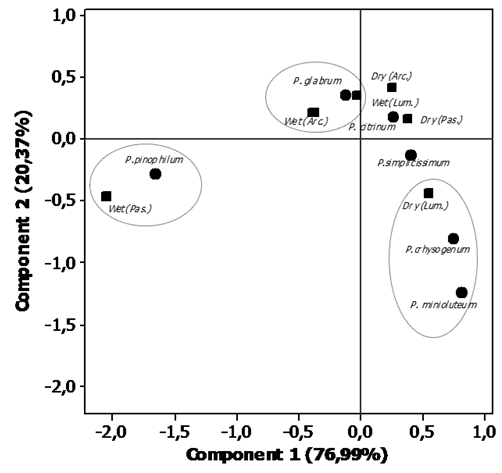 | Figure 4. Percentage map for the fungal species of the Penicillium genus based on region and seasonal period |
|
4. Conclusions
- In conclusion, the results obtained in this study indicate that species of Aspergillus and Penicillium are naturally present in preserved areas of the Brazilian cerrado. The species A. ochraceus, A. japonicus, P. pinophilum and P. glabrun were associated with the rainy season, while P. chrysogenum and P. minioluteum were associated with drought. This results provide valuable information about the microbiota of Aspergillus and Penicillium, including significant evidence that these genera are present at relevant frequencies in Brazilian cerrado regions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors of this study would like to thank the CNPq, CAPES and FAPEMIG for financial support.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML