-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2015; 5(3): 109-117
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20150503.05
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of a Marine Bacterium Isolated from Sundarbans, Bangladesh
Ashish Kumar Sarker1, Md. Anwarul Haque1, Mohammad Sayful Islam2, Md. Uzzal Haque2, Netish Kumar Kundo2, Abu Syed Md Anisuzzaman2, 3, Urmi Saha4, Md. Anwar Ul Islam2
1Department of Pharmacy, Pabna University of Science and Technology, Pabna, Bangladesh
2Department of Pharmacy, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi, Bangladesh
3Department of Hematology & Medical Oncology, Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA
4Eastern Medical College and Hospital, Comilla, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Md. Anwar Ul Islam, Department of Pharmacy, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
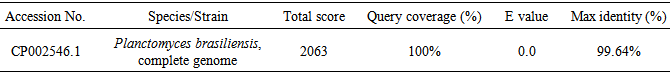
The mangrove ecosystem is a largely unexplored source for bacteria with the potentiality to produce biologically active secondary metabolites. Consequently, we set our research study to isolate, characterize and screen a bacterium producing bioactive compounds from marine soil of Sundarbans, Bangladesh. A total number of 39 marine bacterial colonies were isolated and purified. Representative bioactive isolate, ANAM-5 was characterized using phenotypic and genotypic procedures since it exhibited highest antibacterial activity against a series of test organisms. The 16S rDNA sequence of the strain ANAM-5 showed close similarity with only one bacterium Planctomyces brasiliensis, complete genome (99.64%). But the cultural, morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain and P. brasiliensis were completely different. So, it may not be logical to assign the strain ANAM-5 to the genus Planctomyces. Thus, to confirm the taxonomic position of the strain and to have a correct solution for this taxonomic problem, further studies are needed in respect to the DNA relatedness studies, fatty acid profiling, DNA-DNA hybridization, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF), metabolic finger profiling using BIOLOG, ribotyping, small subunit (SSU) sequences, cell wall composition and other characterizations.
Keywords: Phenotypic, Genotypic, Marine Bacteria, Sundarbans
Cite this paper: Ashish Kumar Sarker, Md. Anwarul Haque, Mohammad Sayful Islam, Md. Uzzal Haque, Netish Kumar Kundo, Abu Syed Md Anisuzzaman, Urmi Saha, Md. Anwar Ul Islam, Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of a Marine Bacterium Isolated from Sundarbans, Bangladesh, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 109-117. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20150503.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Antibiotic resistance is now recognized as a global health problem. Although many pre-existing antibiotics have been modified to yield new derivatives, bacteria have the potential to mutate known resistance mechanisms to combat these molecules [1, 2]. The situation is exacerbated by the fact that no novel antibiotics have been discovered for last 20 years. For this, constant increasing of bacterial resistance, it is now desperately need to search for new sources of antibiotics.Nature is always a boundless source for novel microorganisms producing bioactive compounds having antagonistic activity against pathogenic organisms. Among the bioactive metabolites producers of commercially important drugs, bacteria have proven to be a prolific source with a surprisingly small group of taxa accounting for the vast majority of compounds discovered till date [3]. Among bacteria, actinomycetes particularly the genus Streptomyces is of special interest because it able to produce a wide range of bioactive secondary metabolites, such as antibiotics, antitumor agents, immunosuppressive agents, antifungal, neuritogenic, anticancer, antialgal, antimalarial, anti-inflammatory and enzymes [4]. But, presently, the chance of isolating a novel actinomycete strain from a terrestrial habitat, which would produce new biologically active metabolites, has reduced [5]. So, now much attention has been focused on screening of microorganism from diverse environments such as desert biomes and marine ecosystems. Marine environment harboring a vast variety of organisms differing in their physiology and adaptation capacity. The immense diversity of this habitat along with its underexploitation is the fundamental reason for attracting researchers towards it for discovering novel metabolite producers [5]. It is estimated that less than 1% of potentially useful chemicals from marine environment has been screened so far, with microbial products representing approximately 1% of the total number [6]. As marine environmental conditions are extremely different from terrestrial ones, it is summarized that marine bacteria have different characteristics from those of terrestrial counterparts and therefore might produce different types of bioactive compounds [7].Marine bacteria are efficient producers of new secondary metabolites that show a range of biological activities including antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, insecticidal and enzyme inhibition. Bioactive compounds from marine bacteria possess distinct chemical structures that may form the basis for synthesis of new drugs that could be used to combat resistant pathogens [5]. So, the exploration of microbial secondary metabolites from marine environment has led to the discovery of hundreds of biologically active compounds. Marine bacteria occur on the marine soil, sediments, water and also other biomass (mangrove) and substrates.In order to explore the diversity, antimicrobial activity of marine bacteria from mangrove environments, in the present investigation, an effort was made to screen marine soils from Sundarbans, Bangladesh which is a large unscreened and diverse ecosystem for the isolation of potent antibiotic producing marine bacteria. This research study revealed that the diversity of the Sundarbans as a rich source of new and potential marine bacteria species producing bioactive secondary molecules.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Selection of Marine Bacteria
- From different locations of Sundarbans, Bangladesh (08-16 August, 2010), totally nine marine soil samples were collected carefully from the various depths of the earth, ranging from layers just beneath the upper surface to 1.5 meters depth. By using a spread plate technique [8], isolation of the marine bacteria from these soil samples were done. A total of 39 strains [ANAM-1 to ANAM-48] were isolated and purified as pure culture from these soil samples. All of these purified isolates were preserved on yeast-extract-glucose-agar slants at 4°C. Then by using streak plating technique [9] on yeast-extract-glucose-agar medium, all of these pure isolates were preliminary screened for antibacterial activity. The isolates ANAM-5, a brownish gray colored microorganism was chosen for further characterization since it showed highest antibacterial activity in preliminary antibacterial screening, visibility of the metabolite as well as excellent growth properties.
2.2. Morphological Characterization of the Selected Marine Bacterium
- Morphology is one of the major phenotypic characteristics to identify and distinguish bacteria species. By using the method described by Shirling and Gottlieb [10], morphological characteristics of the strain ANAM-5 was determined. Microscopic characterization was done by cover slip culture method. In this method, three to four sterile covers slip were inserted aseptically into the sterile solidified agar medium in a petri dish at an angle of 45° to 60° by using a sterile forceps and the strain was inoculated by streak plating method, at the free space on the plate. The hyphae of the strain grew and spread on the cover slip and produced spores during the incubation period (at 30.5°C for 8 days). After this incubation period, the cover slips were then taken out smoothly by using sterile forceps, mounted on slides and observed under microscope, using lactophenol cotton blue [11]. Colonies were identified on the basis of their colony morphology and color [10]. The characteristics of the spore-bearing hyphae and spore chains were determined by direct microscopic examination of the culture surface on opining dishes. To establish the presence or absence of chains of spores 200x – 700 x magnifications were used.
2.3. Cultural Characterization of the Selected Marine Bacterium
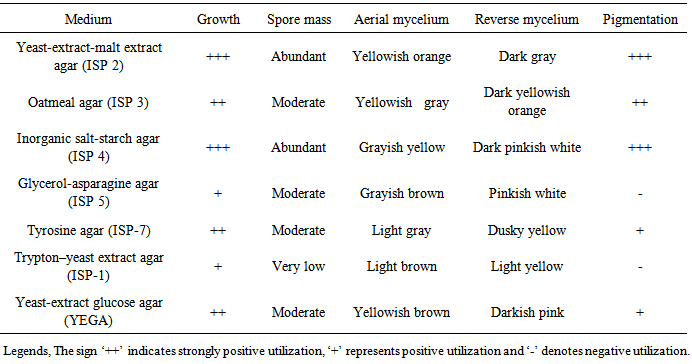
- The cultural characteristic of the strain was also determined according to the method described by Shirling and Gottlieb [10]. Cultural characteristics are best made on a variety of standard cultivation media such as International Streptomyces Project (ISP) 2 (yeast-extract-malt extract agar); ISP 3 (oatmeal agar); ISP 4 (inorganic salts-starch agar); and ISP 5 (glycerol-asparagine agar), ISP 1 (Trypton-yeast extract agar), ISP 7 (Tyrosine agar) and yeast-extract -glucose agar (YEGA). A National Bureau of Standards Color Chart was used to determine the color of the substrate mycelia, aerial mycelia, and spore mass and pigment production [12].
2.4. Biochemical and Physiological Characterization of the Selected Marine Bacterium
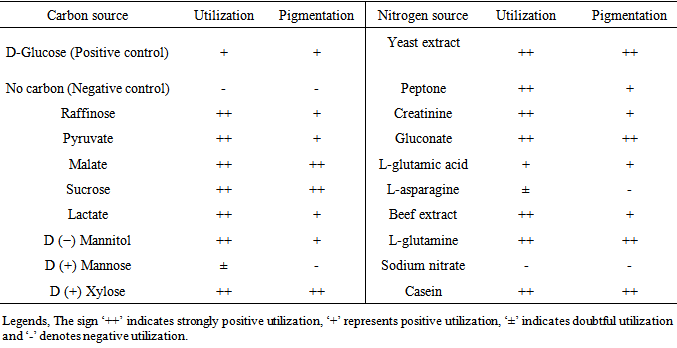
- The biochemical and physiological characteristics of the strain were determined as described by Shirling and Gottlieb [10]. The growth of the strain ANAM-5 was determined on different carbon sources like D-glucose, sucrose, raffinose, D(+)-Xylose, D(−)- Mannitol, fumarate, lactate, malate and pyruate. Here, basal mineral salts agar (ISP medium 9) and different carbon sources were used for the medium of the test. The optimization of nitrogen sources such as yeast extract, peptone, L-glutamic acid, L-glutamine, gluconate, casein, beef extract, creatinine, sodium nitrate and L-asparagine was carried out by adding nitrogen source (0.2%) to the basal medium containing glucose (3%). The pH of the medium was adjusted using hydrochloric acid (1M) and sodium hydroxide (1M). For the optimization of temperature, after sterilizing and inoculating with spores the flasks were incubated at different temperatures (25-45°C).
2.5. Phylogenetic Characterization of the Selected Marine Bacterium
- Phylogenetic studies were also performed. Thus, for the preparation of genomic DNA, the isolated colony from the agar plate was dispersed in 500μl of saline-EDTA buffer (NaCl 150 Mm; EDTA 10 Mm; ph 8.2) and incubated for 1h at 37°C. Then, 10 μl of lysozyme solution (5mg/ml), 5 μl of proteinase K solution (15mg/ml) and 10 μl SDS solution (25%) were added and incubated for 30 minutes at 55°C. Lysate was extracted, purified and dissolved in nano pure, sterile water (60 μl). The 16S rDNA was amplified by the PCR in a reaction mixture containing KOD FX buffer with 200 Μm Dntp, 100 ng genomic DNA and 0.5 μg forward (5’-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’) and 0.5 μg reverse (5’-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3’) primers. Thermal cycle was performed with a model 22331 eppendrof (Germany). The samples were subjected to an initial denaturing step consisting of 2 minutes 98°C, after which 2U of Taq polymerase was added to each sample at 90°C. The thermal profile used was 30 cycles consisting of 1 min annealing at 52°C, 2 min extension at 72°C and 1 min denaturation at 94°C. A final extension step consisting of 4 min at 65°C. PCR amplificants were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized in Dolphin WaveTech. The band was excised and isolated using TAE buffer. Purified by phenol chloroform extraction followed by ethanol precipitation and dissolved in water. The resultant PCR solution was used in sequencing reaction with Pre-Mix and primer. The reaction mixture was applied to thermal cycles in 30 cycles consisting of 10Sec at 98°C, 30Sec at 47°C and 2 min at 68°C. DNA was purified and by using Prep-A-Gene Kit (Bio-Rad). The liquid was evaporated at reduced temperature and using vacuum pressure. The dried DNA was dissolved in 20μl of polyacrylamide sequencing gel and sequenced by Applied Biosystems automated DNA sequencer. The resulting sequences were analyzed with DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank database using analysis softwares- BLAST and BIBI (Bioinformatics Bacterial Identification Tool) [13].
3. Results and Discussion
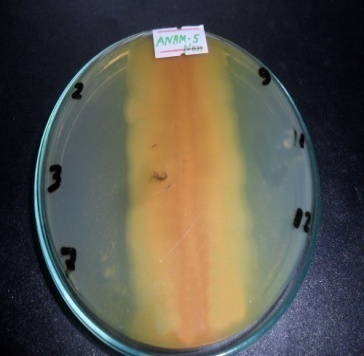
- Marine environment has been proven as an outstanding and attractive resource for innovating new and potent bioactives compounds producing microorganisms. Marine microbes are particularly attractive because they have higher potency required for bioactive compounds to be effective in the marine environment, due to the diluting effect of sea water [14]. This present study was designed with an aim to discover a new marine bacterium strain from marine environment which is capable of producing antibacterial secondary metabolites. Considering this, the isolate ANAM-5, a brownish gray colored microorganism was chosen for further characterization due to the highest preliminary antibacterial activity (Figure 1), visibility of the metabolite as well as excellent growth properties of the strain.
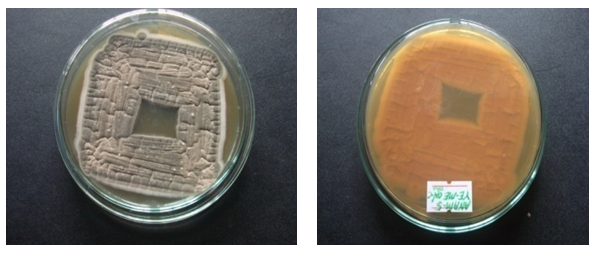 | Figure 2. Gray and brown colonies of ANAM-5 |
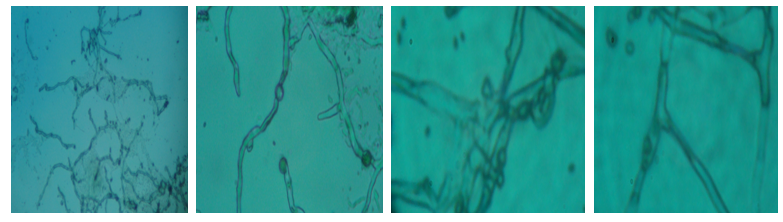 | Figure 3. Microscopic view of the ANAM-5 isolates at different magnification |
|
|
|
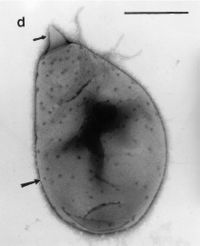 | Figure 4. P. brasiliensis having crateriform structures and the polar unicorn prostheca-like projection [26] |
4. Conclusions
- The marine environment represents a relatively untapped source of biologically active compounds that can be applied in pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries. Our findings explore the resource of a mangrove forest, the Sundarbans for finding antibacterial metabolites producing marine bacterium. The strain ANAM-5 differs morphologically, culturally, physiologically and biochemically from P. brasiliensis. Strain ANAM-5 is phylogenetically most similar to the genus Planctomyces, but the phylogenetic relationship is not sufficient to permit classification of strain ANAM-5 in this genus and for the description of a new bacterial species. So, the strain ANAM-5 may not be assigned to the genus Planctomyces. Thus to confirm the taxonomic position and to provide absolute resolution to these taxonomic problem of the strain ANAM-5, more studies should be carried out in respect of the of the DNA relatedness studies, fatty acid profiling, DNA-DNA hybridization, small subunit (SSU) sequences, cell wall composition, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF), metabolic finger profiling using BIOLOG, ribotyping and other characterizations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was supported by Pharmaceutical Microbiology Laboratory, Department of Pharmacy, University of Rajshahi, Bangladesh. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Abu Sayed Md. Anisuzzaman, Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacy, University of Rajshahi for providing 16S rDNA gene sequencing data to carry out of this research work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML