-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2014; 4(6): 201-209
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20140406.03

Rice Straw as Nematicidal on Root-knot Nematode and Microbial Impact of Population in Rhizosphere of Faba Bean Plant
Abdelazzez Heba M.1, Tewfike T. A.2
1Agriculture Microbiology Institute, Agric. Research Center, Giza, Egypt
2Department of Botany (Microbiology), Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Abdelazzez Heba M., Agriculture Microbiology Institute, Agric. Research Center, Giza, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

A field experiment was carried out at Al-Arish Res. Station, Agric. Res. Center, North Saini, Governorate, Egypt during the winter season (2013) to study the effect of rice straw and plant growth promoting microorganisms (biofertile) on microbial population and controlling nematode infecting faba bean plants. The treatments with rice straw compost and biofertile (PGPM) led to non-significant values of pH and EC of the soil during 45 to 75 days. However, rice straw or/and biofertile significantly increased nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and organic matter contents of the soil, increased soil biological activity and reducing the appearance of infected root-knot nematode population and actualized prodigious depletion in egg production. Whereas rice straw compost application in faba bean rhizosphere resulted reducing root-knot nematode population by 74.9%. The rice straw extract was effect on root-knot nematode as nematicidal where died through 25 hr with 100%. As well as to maximize the benefit of the plant nutrients. The most prominent rice straw compost which surpassed all treatments including the mineral and biofertilizers were those contained vinasse. Generally, mixture of biofertile and rice straw compost was useful for the faba bean crop and enhancement of soil chemical and biological properties.
Keywords: Faba bean, Biofertile ( PGPM), Rice straw, Root-knot nematode, Nematicidal
Cite this paper: Abdelazzez Heba M., Tewfike T. A., Rice Straw as Nematicidal on Root-knot Nematode and Microbial Impact of Population in Rhizosphere of Faba Bean Plant, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 201-209. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20140406.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Cereals straw incorporation into soil is being promoted as an alternative way of managing crop residues. The recycling of crop residues has the potential to convert the surplus farm wastes to a useful product so as to meet up with the nutrient requirement of crops. It also maintains the soil physical, chemical and biological conditions improves the overall ecological balance of the crop production system [1]. Incorporation of crop residues with high C:N ratio into soil could enhance microbial immobilization of N and thus reduce nitrate leaching [2, 3], but could also substantially increase the production of N2O and CO2. This act leads to loss of huge biomass and environmental pollution. Among the proposed solutions to problems associated with the usage of straw as soil amendment is the inoculation with a cellulose degrading microbial compound to hasten decomposition. It has been established that microorganisms are crucial to the functioning of ecosystem and contribute to the biogeochemical cycles [4] such as nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition. Some beneficiary microorganisms have been used in trans-formation and remediation of polluted soil [5] leading to improved soil fertility and crop productivity [6], and enhancement of straw composting [4]. However, the direct inoculation of straw incorporated into soil to increase straw decomposition rate is uncommon [7]. According to [8], obstinacy of the soil ecosystem which acts as a buffer against soil inoculants is the main limiting factor to soil inoculation. To optimize the potential of these products, proper investigation is required since their survival and catabolic activity is the key to successful inoculation Soil organic carbon (SOC) is an important soil property considered as one of soil quality indicators and has direct and indirect relationship with soil physical, chemical and biological properties. Other biological soil quality indicators include microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and soil respiration [9], soil microbial population and soil enzyme [10]. For decades, studies have concentrated on soil microflora, ignoring the influence of extracellular enzymes produced by microorganisms on the decomposition of organic matter. Soil enzymes catalysis several reactions of soil microorganisms, play a role in stabilization of soil structure, decomposition of organic wastes, organic matter formation, and provide early indication of changes in soil and agricultural management [11, 12]. The decrease in pH in soil might be attributed to the effect of microorganisms on decomposing organic matter releasing organic acids and producing several phytohormones such as indole acetic acid and cytokines [13-15]. Although the application of chemical nematicides have been found as an effective measure for controlling nematodes but due to high toxic residual effect of chemicals on the environment particularly on non-target organisms and human health. In addition, use of chemical nematicides are prohibited in organic farming. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop alternative environmental safe strategies for controlling nematodes [16, 17]. The present study was conducted with the aim of examining the effects of rice straw compost compounds and biofertile (PGPM) on root-knot nematodes, microbial population and soil biological and physico-chemical properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
- The field experiments were conducted at the experimental farm of Al-Areesh Res. Station, North Saini, Governorate, Agric. Res. Center during winter season of 2013 to evaluate the response of Faba bean (Vicia faba L. cv. Giza1) in soil infected nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) to application with rice straw compost and, Biofertile, either each applied individually or in alternative combination.
2.2. Faba Bean Seeds
- (Vicia fabaL. cv. Giza1) were obtained from Crops Res. Ins.Mobcap (Nematicide) was obtained from Plant Protection Ins., Agric., Res., Center (ARC) Giza, Egypt.
2.3. Biofertile
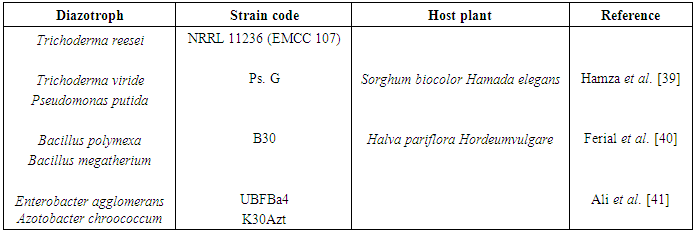
- An innovative bioformulation produced by Water and soil inst., Agric. Res. Center (ARC). This biopreparate is a plant growth promoting microorganisms (PGPM) of associative and endophytic diazotrophs table (1).
|
2.4. Rice Straw Compost
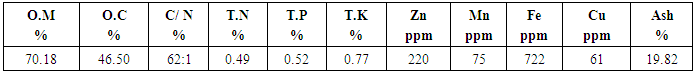
- Rice straw was collected from El-Arish Agric Res farm Station, at El-Arish Governorate. It was dry an aerobically. Air-dried rice straw was chopped into small pieces 3-6 cm using shredding machine. The analyses of the rice straw was determined (Table 2) according to the standard methods described by [18, 19]. Composting piles were constructed by laying several layers of rice straw and rock phosphate one over another and inoculated with buffalo’s manure, each layer was watered to keep about 70% moisture and mixed with proper amounts of other additives. The dimensions of each pile at the beginning were about 1.5m length, 1.0 m width and 0.80m height [20].
|
2.5. Soil
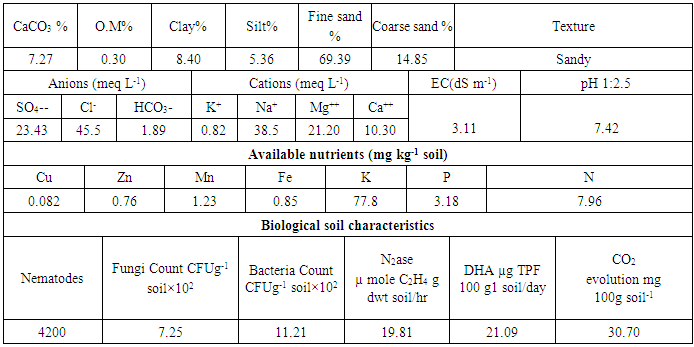
- Air dried sandy soils were crushed to pass a 2 mm sieve and analyzed for major physical, chemical and biological properties according to [18, 19] as shown in table (3). Biological properties of the soil were determined as follow: Ten grams of soil were taken from the rihzosphere of plants at 45 and 75 days after cultivation for determination of total viable counts of bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes. The plate count using the suitable serial dilutions and specific media was applied for estimation of the examined microbial groups. The media include: Nutrient agar [21] for total count of bacteria, Martin’s agar medium [22] for fungi and Jensen’s medium [22] for actinomycetes. As well as, the subsequent physicochemical analysis e.g. pH, EC, organic matter (OM), total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.CO2 evolution was determined according to [23]. Dehydrogenase activity of the rhizosphere soil assay according to [24] while, nitrogenase activity measured by acetylene reduction as described by [25].
|
2.6. In Vitro: Effect of Water Extracted Rice Straw on Second Stage Juveniles of the Root- Knot Nematode
- Finally air dried a rice straw powder was soaked in warm water (65°C) with 1:10 (w/v) at one hour. The aqueous extract was used in this experiment. The fresh galls were collected from faba bean root infected with knot root nematode. A short time of galls parts in electric mixer and run for a brief moment for flooded with water. The mixer contents were poor over a series of laboratory sieves (3-5 sieves) diameters ranging from 0.8 mm at the top to 0.04 mm at the bottom. The contents of upper sieve were washed by spray water. The second stage juveniles (J2) of the root-knot nematode were accumulated in the bottle an hour, scanned and counted by nematode Lab. Plant Protection Ins., Agric., Res., Center. One ml of nematode suspension (1000 juveniles in 9 mL water) was used as control while another one ml was immerged in 9 mL of rice straw extract under room temperature. Number of viable nematode were counted at 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 hr time intervals.
2.7. Field Experimental Treatments and Layout
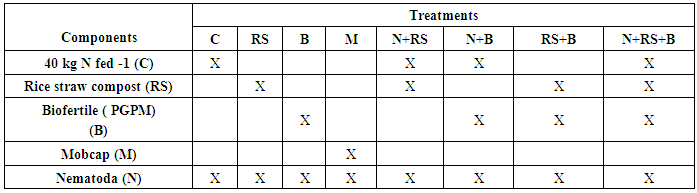
- The field experiments were conducted to evaluate the response of faba bean plant cv Giza 1 cultivated in soil infested with nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) at level was 2000 second stage juveniles (J2)/g soil, to application with rice straw compost and Biofertile (PGPM),either individually or in combination, after applying the traditional agricultural practices including ploughing and compacting. The experimental area was divided into plots of 8.4 m2 with 3 rows, each 4.0 m long and 0.7 m width. Land preparation encompassed the introduction of 30kg P2O5 and 50kg K2O fed.-1 as well. Nitrogen was incorporated into soil in the form of ammonium nitrate (33% N) at levels representing the recommended rate (40 kg N fed.-1) and half of it in the treatments which received biofertile (PGPM). Mobcap (nematicide) was applied (0.2%) on untreated plants as positive control. Each treatment was replicated three times. Composts were added by incorporation with the top soil surface concomitant with nematode in soil. The experimental layout comprised 8 treatments (Table 4) including mineral N fertilization and inoculation with Biofertile and/or compost.
|
2.8. Plant analysis
- At the end of the experiment, plants were harvested and plant growth parameters (number of pods, plant height, dry weight of whole plant and pods, weight of 100 seeds) were recorded. The oven dried plant materials were taken and determined by methods of [19].
2.9. Population of Nematode
- After 45 and 75 days after cultivation plants, nematodes were isolated as described by [26] from soil and the root-knot nematode on faba bean roots were calculated. The isolated nematode was identified at Plant Protection Dept. Fac. Agric. Ain Shams Univ. The following Mathematical equation was used to calculate of root-knot nematode and determine the nematode population.
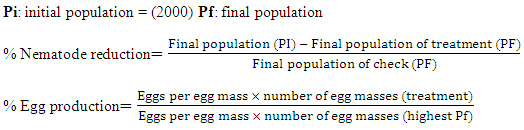
2.10. Statistical Analysis
- Data were subjected to the statistical analysis according to [27] and the means were compared using L.S.D test at 5% significance level.
3. Results and Discussion
- Rice straw compost incorporation into soil was promoted as an alternative way of managing faba bean crop residues, improving the soil biological, physicochemical and reducing of root-knot nematode. As well as improves the overall ecological balance of the crop production system.
3.1. Effect of Rice Straw on the Experimental Soil Characters
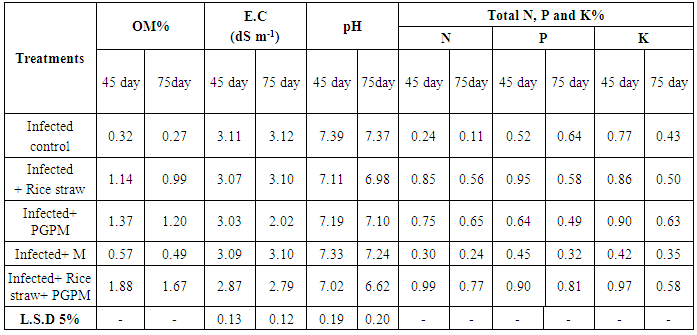
- Soil chemical properties: Results in table (5) showed the changes occurring in some chemical properties of the sandy soil cultivated with faba bean plants and treated with rice straw compost (RS) and biofertile (PGPM). Soil organic matter after faba bean harvesting was increased by the added biofertile and/or rice straw compost treatments. Results revealed that only the incorporation either with or without rice straw increased the soil organic matter throughout first 45 days. Treatments RS and PGPM (B) achieved high result after 45 day which recorded 1.14, 1.37 and 1.88%, respectively compared to infected control 0.32%. This may be due to PGPM and rice straw compost contents bio-organic fertilizers which contribute in stimulate activity of microorganisms. It was worthy to mention RS+B gave high result than B or RS because its contents rice straw as organic matter with bio-organic fertilizers. All treatments with rice straw tended to achieve relatively higher values of total N, P and K, as well as enhanced the organic matter in sandy soil, compared to the treatment without rice straw (control). However, there was a very slight effect in organic matter % and pH value. More flourishing in chemical and biological properties of the sandy soil was attained due to the enriched bio-organic fertilizers with rice straw.The pH value and EC of the sandy soil was very slightly affected of any treatment without rice straw, while diminution of the pH value and EC were much pronounced of the enriched bio-organic fertilizers with rice straw. These results are in agreement with those obtained by [15, 28].Results of organic matter, total-N given in table (5) revealed that addition of rice straw led to relative increase in such chemical parameters as compared with control. Moreover, rice straw, bio-organic fertilizers attained the highest values of organic matter, total-N. In addition application of the compost to the same preceded treatments exhibited more advancement in the obtained values. The highest values of total-N by using bio-organic fertilizers with rice straw compost or/with Biofertile with recorded at 45 and 75 days. Similar results were obtained by [29]. Concerning the Total P and K in soil, data in Table (5) declared that addition of PGPR tended to increase P and K in the soil, particularly with the combined inoculation treatment as compared with other treatments. The obtained results again confirmed the superiority of using the bio-organic fertilizers when accompanied with rice straw. The highest values of total-P and Total-K were recorded when plants received combination of biofertile and compost. This result was mainly related to the ability of Biofertile (Bacillus and Pseudomonas) to dissolve insoluble phosphate via formation of organic acids and chelating substances. Similar trend was obtained by [28]. Moreover, the presence of organic materials can exhibit same trend phosphate solubilization beside their vital role in enhancement of phosphate dissolvers, as well as increasing soil moisture retention and thus more availability of phosphorus and potassium. These results are closed to those reported by [29].
|
3.2. Biological Properties of Rhizospher Soil
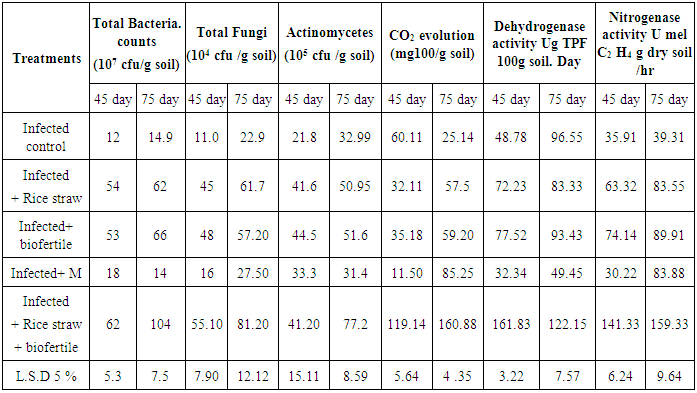
- Data in Table (6) indicated that, total count of bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi as affected by blowing with rice straw compost and inoculation with biofertile (PGPM) compared to uninoculated treatments in the infected soil with root-knot nematode. Results pointed out that in all tested treatments, increasing the time of soil sampling from initial to flowering time increased the count of all tested microorganisms. Due to the effect of the tested treatments of either biofertile inoculation or rice straw compost and their combination, initially, no definite trend was detected, since the count of bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi, slightly increased in response of these treatments all with or without rice straw. However, at flowering stage, the inoculation with either biofertile or rice straw compost or their combination increased the count of all tested microorganisms compared to those recorded by uninoculated treatments. However, the treatment rice straw compost and biofertile gave the highest values of all soil biological activity parameters treatment. i.e., total bacteria count 62 x 107 and 104 x 107, total fungi 55.1 x 104 and 81.2 x 104, total actinomycetes 41.2 x105 and 77.2 x105 cfu g-1 dry at 45 and 75 days, respectively. Application of mobcap as chemical control for nematode decreased, total bacteria count 18 x 107 and 14 x 107, total fungi 16 x 104 and 27.5 x 104 and total actinomycetes 33.3 x 105 and 31.4 x103cfu g-1 dry at 45 and 75 days, respectively(table 6).On the other hand, CO2 evolution was increased with treatment blowing rice straw and inoculated PGPM being 119.14 to 160.88 mg CO2/ 100g dry soil day.-1. Meanwhile, dehydrognase enzyme was the same behaviour which application of compost and biofertile gave the highest values being 161.83 to 122.15 μg TPF g-1 dry soil. Also nitrogenase activity gave higher values being 141.33to 159.33 m mole C2H4 g-1 dry soil h-1 at 45 and 75 day, respectively at the same treatment (table 6).
|
3.3. Yield Components of Faba Bean
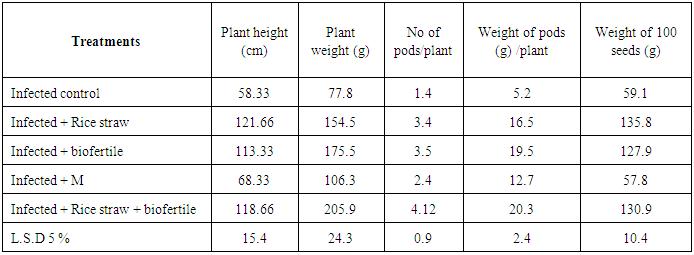
- Soil treatment with rice straw compost had significant result on plant growth and yield components of faba bean cultivated in nematode infected soil comparison with untreated plants. Addition to biofertile combination with rice straw treatments gave the highest significant result in plant growth parameters and yield components. Therefore, a significant increase of plant height and dry weight, number of pods and weight of 100 seeds of rice straw compost or/and biofertile compared to negative and positive control. Data in table (7) showed that, the plant height of faba bean plants significantly increased with 121.66; 113.33; 118.66 for rice straw; biofertile (PGPM) and combination of them comparison with 58.33 and 68.33 cm of control and plants that treated with mobcap, respectively. The tested treatments significantly increased plant dry weight 154.5; 175.5; 205.9 of (C+RS); (C+B); (C+RS+B) comparing to77.8; 106.3 gm of (C) and (M) controls, respectively (Table 7). The obtained results revealed significant increase of number of pods per plant were 3.4; 3.5;4.12 of rice straw compost; biofertile and the combination of them comparing to 1.4; 2.4 of control and infected plants treated with mobcap, respectively follow-up the weight of pods per plant. The same trend was observed with weight of 100 seeds(g) which its values were 135.8, 127.9and 130.9 gm for straw compost, biofertile and mixer of them, respectively. All the tested treatments resulted in significant increase in 100 seeds weight comparison with treatment without rice straw and biofertile. These results are in agreement with those of [30] and similar were reported by [31] who stated that the application of biofertilizer is an acceptable approach for higher yield with good quality for human consumption. Rice straw is agricultural waste produced in large amounts from rice cultivation and consists of different biopolymers such as cellulose (32-37%), hemicellulose (29-37%) and lignin (5-15%) [32]. The polysaccharides in the straw may serve as substrates for complex microbial communities. The microbial metabolic pathways for the anaerobic degradation of ‘dead’ organic matter is in principle well known and involves hydrolysis of organic polymers; fermentation of the resulting monomers to fatty acids, alcohols, CO2 and H2 [32]. Among the fatty acids, acetate is a major product from anaerobic digestion and this is an important carbon source for the growth of some types of bacteria [33].
|
3.4. In vitro: Impact of Extracted Rice Straw on Second Stage of Juveniles the Root-Knot Nematode
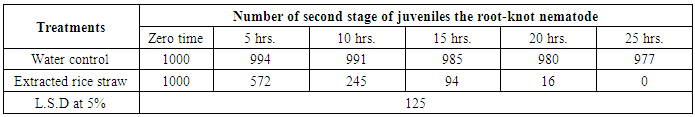
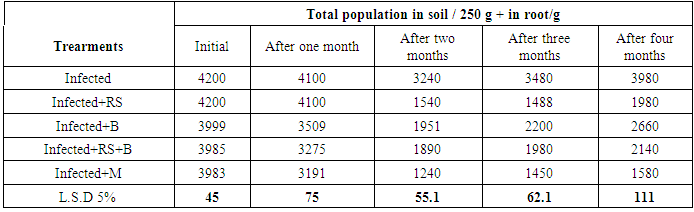
- Irrespective of the extracted rice straw and application time, significant reduction in number of nematode were observed comparing to water control. However, the highest reduction of nematode was obtained after 15, 20 and 25 hrimagining in extracted rice straw (Table 8). The highest reduction rate of root-knot nematodes 75,93 and 100%, respectively. The effect of rice straw on nematode due to the aqueous extracts of decomposing rice residues in soil inhibited nematode. Maximum toxicity occurred in the first month of decomposition and declined thereafter with the toxicity persistent for 4 months also in rice residues decaying. Chou and Lin [34] and Rashad et. al. [35] concluded that the decline in productivity of rice subsequent to the first crop is due chiefly to the allelopathic effects of decaying rice residues in the paddy soil rice straw in decomposing into soil to produce organic acids five phytotoxins-p-hydroxybenzoic, p-cumaric, vanillic, ferulic, O-hydroxyphenylacetic acids-were identified from decomposing rice residues into soil who reported that the decrease in pH.
|
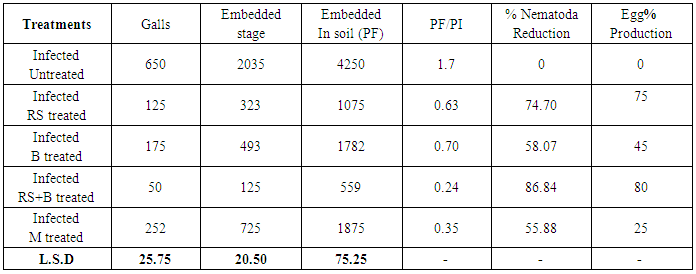
3.5. In vivo: Effect of Rice Straw Compost on the Root-Knot Nematode Populations
- Irrespective of the rice straw compost or/and Biofertile application, significant reduction in numbers of galls formed on faba bean plant root, embedded stages and egg production were observed comparing to infected untreated control. The highest reduction rate, of Meloidogyne incognita reproduction was recorded in tables (9 and 10). Taken as a whole, the rice straw compost and Biofertile (PGPM) application reduced the nematode population and egg production by 74.7; 58.08 and 75; 45%, respectively, versus to 86.84 and 80 % reduction when they added in combination. Moreover, treated with Mobcap led to nematode reduction by 55.88 and 25%, respectively. On the other hand, it was observed the nematode population was reduction in soil rhizosphere of faba bean root gradually at three months from application but the nematode population was increased after four months from rice straw application (table 10).Concerning the effect each of rice straw compost, Biofertile (PGPM) and combination on the plant parasitic root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita), the results showed that rice straw compost only or with Biofertile recorded high significantly reduced galls formation on plant roots, the embedded stages, the final population as well as the rate of nematode reproduction (pf/pi) as shown in table (9). The present study proved that compost significantly supported the growth of faba bean and enabled infected plants to overcome nematode infection (Table 9). The best results were achieved when rice straw compost applied at the high rate in infected soil with nematode which resulted in reducing final nematode population by 58 to 86%.The action of soil microorganisms on an organic material during the decomposition process can produce a wide range of chemicals like, ammonia, nitrites, hydrogen sulfide, organic acids and enzymes [36]. These chemicals are known to possess nematicidal properties that affect egg hatch and/ or motility of juveniles [37]. However, it is possible that nematicidal activity of nitrogenous by–products So, higher effective of toxic by-products occurred the increase of plant growth may be increase the mineralization of N and P releasing nutrients. Biological inoculation of soil led to reduction in soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC). Volatile compounds, fatty acids, hydrogen sulfide, enzymes, hormones, alcohol and phenolic compounds are among the bacterial products implicated in the control of plant parasitic nematodes [38]. Such products may be toxic to nematodes directly or it may be indirectly suppress nematode population by modifying the rhizosphere environment.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- It is forte palpable that rice straw compost is indispensable for the sustainability of agriculture and for organic farming systems. The tested rice straw compost have a positive effect as it improved the soil properties, ameliorated the plant growth, enhanced nutrient’s uptake and, in the same time, reduced the populations of plant parasitic nematodes. Combination of rice straw compost at ½ MF significantly improved all tested criteria, therefore, it is recommended to obtain higher yields for high nutrient-demanding crops. Overcoming nematode infection by compost was depended on adding time and dose, so, it is recommended to control plant parasitic nematodes or at least to keep nematode populations always under the economic threshold especially in organic farms.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML