-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2014; 4(4): 153-160
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20140404.01
The Use of Corn Starch for Growth and Production of α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis
Alfred O. Ubalua
Tissue Culture Unit, Biotechnology Research and Development Center, National Root Crops Research Institute (NRCRI) Umudike, PMB 7006 Umuahia, Abia State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Alfred O. Ubalua, Tissue Culture Unit, Biotechnology Research and Development Center, National Root Crops Research Institute (NRCRI) Umudike, PMB 7006 Umuahia, Abia State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Thirteen thermophilic bacterial strains were isolated from garden soil at NRCRI Umudike Nigeria. One strain was selected based on its ability to produce significant amylolytic activity on nutrient agar medium containing 1% soluble starch. The organism was identified as Bacillus subtilis based on its morphological, biochemical and physiological properties. Maximum amylase activity of 10.4±1.3 U mg-1 was obtained on corn starch mineral salts medium on the 3rd day of the 6–day fermentation period which corresponded with the late exponential phase of the organism. Soluble starch mineral salts medium produced 9.40±0.71 U mg-1. A pH and temperature optimum of 6.5 and 65℃ respectively were observed when the organism expressed its highest amylase activity. The new strain may offer an attractive source of enzymes for application in food and brewing industries.
Keywords: Soil, Bacillus subtilis, Submerged fermentation, α-amylase production, Amylase activity
Cite this paper: Alfred O. Ubalua, The Use of Corn Starch for Growth and Production of α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 4 No. 4, 2014, pp. 153-160. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20140404.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Soil as a habitat for microorganisms, is probably the most complex and diverse on the planet. It is a biomembrane and can be a source or sink for most gases. A further source of complexity in soil biological activity is the existence of exocellular enzymes, presumably derived from past populations of organisms but stabilized by sorption on mineral surfaces and retaining at least part of their activity [1]. Many of these microorganisms are highly active in nutrient recycling, mainly in the degradation of vegetable polysaccharides such as lignocellulose and its phenolic-derived compounds. The microbial diversity of each soil depends on nutrient availability and several physicochemical properties related to the climate and type of the soil [2]. Arguably, all microorganisms follow a normal distribution pattern based on the pH dependence for their optimal growth, and the majority of these microorganisms are known to proliferate well at near-neutral pH values [3]. As such, as the pH moves away from this neutral range, the number of microorganisms decreases [4]. Thus, Grant et al., [5] reported normal garden soil to be a preferred source for isolation, presumably because of the various biological activities that generate transient alkaline conditions in such environments.Amylolytic enzymes degrade starch. Industrial processes for starch hydrolysis to glucose rely on inorganic acids or enzyme catalysis. The use of enzymes is preferred as it offers a number of advantages including improved yields of pure glucose, low environmental impact and mild reaction conditions, greater control over amylolysis, specificity of the reaction, and the stability of the generated products [6]. The aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria of the genus Bacillus have for long dominated the market for α-amylase along with the “liquefying” enzymes from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus subtilis and more recently Bacillus licheniformis. The enzymes from these microbial sources are thermostable; particularly the latter has a temperature optimum for activity around 90℃ and can be used to hydrolyze starch at even higher temperatures [7]. They are ideally suited for the initial size reduction of amylose and amylopectin molecules in starch during the process termed liquefaction. Medium composition is a prerequisite for a successful enzyme production. The regular use of soluble starch-based fermentation medium is not commercially viable for industries in the tropics. For efficient commercial production in the tropics, a continuous effort is being made to find cheaper substrate sources. Available carbon and nitrogenous sources are the decisive factors in the optimum production of enzymes, and these differ very much from substrate to substrate. In Nigeria, agricultural produce like corn is abundant; and a valuable percentage are perennially lost due to inadequate storage and processing. Corn is a major source of starch and enzymes responsible for its breakdown are widely distributed in nature. Grown extensively in the Southern and Northern parts of Nigeria during rainy season, corn grains are prone to postharvest rot due to inadequate storage and processing. In this study, the potential of obtaining good yield of α-amylase from a thermophilic strain of Bacillus subtilis isolated from garden soil using locally available and cheap corn starch in comparison with the conventional soluble starch is described.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Starch Milk
- Seven (7.0) kg of corn grains were homogenized in a mortar. The homogenized corn grains were placed on a muslin cloth, sieved and flushed with clean water until the starch stream ceases. The crude starch milks were kept in a refrigerator overnight to discourage microbial growth and degradation. The supernatants were decanted leaving the precipitated starch.
2.2. Purification of the Starch
- Twelve (12) liters of clean water equivalent to three times of 4 liters of the crude starch was added and stirred until all the starches were suspended in the water. The suspension was undisturbed until sedimentation ceases. The supernatant was decanted leaving the sediments in a plastic bucket. An equivalent volume of fresh clean water was added again to the volume of the starch sediments and stirred until all starch was suspended in the water. The starch slurry was filtered through a muslin cloth sieve of about 125 micron pore size and flushed with water. The filtrate was allowed to sediment for 20 minutes and the supernatant decanted. This procedure was repeated two times yielding a clean starch cake.
2.3. Quality Control of the Starches
- A teaspoonful sample was taken from the top of the clean starch cake sediment and dissolved in a 15 ml of water in a test tube. The tube and its content were centrifuged for 20 minutes at 2000 rpm and a small sample was drawn from the boundary between the liquid and the sediment using a pipette. Observation was done under a microscope (magnification x100). Absence of particles in the sample under observation confirmed its purity.
2.4. Drying and Storage
- The starch cakes were spread on a table and allowed to dry at room temperature. They were pulverized with a milling machine (Thomas Wiley Mill-model Ed-5, Philadelphia, USA, 1982), stored in bottles and kept in a refrigerator (Haier Thermocool, model HRF-350, 2001).
2.5. Sampling Procedure
- Twenty (20) garden soil samples from 5 different locations at NRCRI Umudike, Umuahia, Nigeria were used for the analysis. Three samples from each location were collected at a distance of 300 meters interval in a randomized block design from a depth of 5 and 10 cm into sterile bottles with sterile hand shovel and clearly labeled. The soil samples were thereafter taken to NRCRI Microbiology laboratory. They were immediately homogenized, mixed and sieved through a 2 mm pore size sieve (Retsch, Germany) to sieve out large debris and used for isolation and enumeration purposes [8], [9].
2.6. Isolation of Bacillus Colonies from the Soil
- Isolation and enumeration of the Bacillus were performed using dilution method with nutrient agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) medium. Ten (10) g of each soil sample were suspended in 90 ml of 0.85% normal saline (pH 7.0) and shaken vigorously at 150 rpm at 18℃ for 1h according to Agrawal and Agrawal, [10]. The resulting slurries were serially diluted with 0.85% normal saline. A 0.1 ml of the 10-4 dilution was spread plated in triplicate on nutrient agar medium. Cultures were incubated at 37℃ ±2 for 24 h. Each colony was assayed for morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics and were further compared with standard descriptions given in Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology [11]. Identified isolates were screened for starch hydrolysis as described by Chu [12]. This was done with NA containing 1% soluble starch (potato, BDH, Poole, UK). Amylolytic activity was demonstrated by streaking the isolates on the NA. Incubation was at 37℃ for 24 h before flooding with iodine solution. In situ enzyme production was observed with the clearing of zone of whitish appearance in the area surrounding the isolate.
2.7. Amylase Production
- 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks were used for the amylase production. Each contained 50 ml of the culture medium with the following composition (g/l): Soluble starch or corn starch (20), K2HPO4 (2), (NH4)2SO4 (2), NH4NO3 (2), MgSO4.7H2O (0.005), CaCl2.2H2O (0.005), and Peptone (0.5). The medium pH was adjusted to 7.0 with 1N H2SO4 and/or 1N NaOH before sterilization at 121℃ for 15 min and allowed to cool down to room temperature. Two (2) ml of sterile distilled water was aseptically introduced into an overnight culture of Bacillus subtilis and an aliquot (0.5 ml) of the suspension were inoculated into three 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50 ml each of the medium according to Uguru et al., [13]. Fermentation was done with mild agitation on a rotary shaker at 200 rpm for 48 h and at room temperature. The following variables (protein content, enzyme activity and specific activity) were monitored daily and determined.
2.8. Assay of α-amylase Production
- Amylase activity was determined in 1 ml containing 0.5 ml of 1% (w/v) soluble starch, 0.1 ml of the enzyme solution and 0.4 ml of 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH 6.0). After 5 min at 25℃, reducing sugar was determined by the method of Nelson, [14]. One unit of α-amylase is defined as the amount of enzyme that releases one µmole of reducing sugar (with glucose as standard) per minute under the assay conditions. Specific activity was expressed as U mg-1 protein.
2.9. Physicochemical Properties
2.9.1. Effect of Carbon Sources on the Production of α-amylase
- Maltose, glucose and starches (corn, cassava, potato and sweet potato) for amylase production were monitored in the basal medium by substituting the soluble starch in the amylase producing medium with each of the above mentioned sugars and starches. They were previously sterilized in a hot air oven at 175℃ for 40 min with the powder depth not exceeding 1 cm according to El-Tayeb et al., [15] before substituting in the amylase medium. The concentration used was 2.0% (w/v). Fifty (50) ml of each starch mineral salts medium of concentration 2.0% (w/v) was introduced into separate flasks with 0.5 ml of the crude amylase. A control experiment without the carbon source was also set up. Fermentation was done on a rotary shaker at 200 rpm for 24 h at room temperature and at pH 6.5. The reaction media were terminated by increasing the temperature to 100℃ for 5 minutes and 5 ml of iodine solution was added to 0.5 ml of the medium in order to assess the extent of hydrolysis. Enzyme activity was determined using the method of Nelson Somogy. One unit of amylase is defined as the amount of enzyme that releases one µmole glucose equivalent per minute under the assay conditions.
2.9.2. Effect of Temperature on Growth and Amylase Production
- Bacillus subtilis culture was incubated at various temperatures (40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70 and 75℃) for 48 h according to Uguru et al., (13). Optimum temperature of growth and amylase activity were determined.
2.9.3. Effect of pH on Growth and Amylase Production
- Buffered amylase medium was used for the determination of the growth measurements as described by Uguru et al., [13]. The pHs considered were 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10. The flasks were incubated at a temperature of 65℃ for 24 h and the reaction was terminated before assaying for optimum pH of activity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Bacillus Subtilis
- In this study native microorganisms growing in an organic matter-rich environment were isolated from twenty soil samples. Out of the 13 isolates observed, isolate CNS3 (Bacillus subtilis) demonstrated highest starch hydrolyzing ability by showing area of clear zone along the line of streaking after 24 h incubation and flooding with iodine solution (Plate 1). Some of the soil samples on subjection to boiling for 10 minutes at 80℃ and subsequent incubation on nutrient agar plates at 37℃ for 24 h produced a bacterial growth that exhibited the characteristics of an organism that belongs to the genus Bacillus based on its morphological, biochemical and physiological properties. Similar isolation and identification was made by Priest [16] in which he classified the organism to be a member of the phenotypic group 11 (Bacillus subtilis group) and of the genus Bacillus.
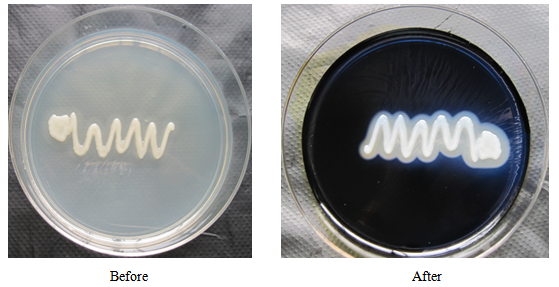 | Plate 1. Isolate CNS3 (Bacillus subtilis), with zone of clearing |
|
3.2. Growth and α-amylase Synthesis from Bacillus subtilis
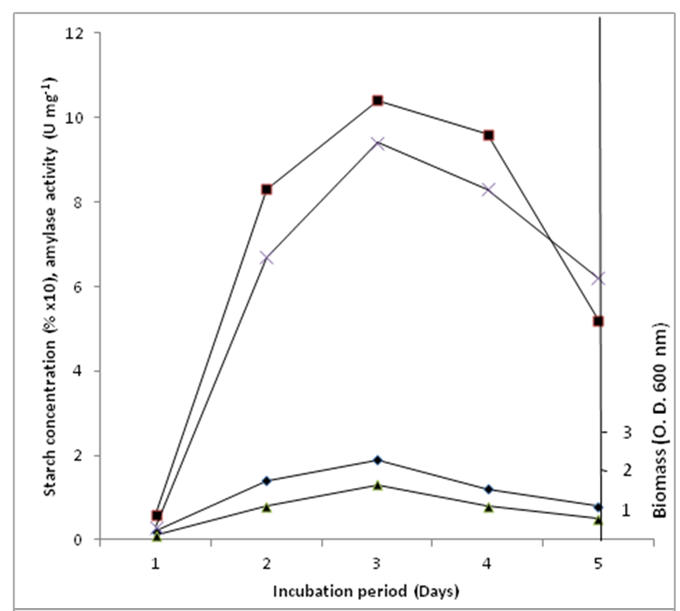
- The patterns of α-amylase production, as well as biomass, and starch depletion were followed with time (Fig. 1). At the onset of the experiment, adaptation, growth and multiplication of the organism was slow. This might not be unconnected with the adaptation of the organism to its new environment and the time required for the organism to hydrolyse starch in the medium to utilizable units. The implication is that this may be accomplished by the consistent secretion of a low basal level of hydrolyzing enzymes [17], [18]. Moreover, it appears that the biosynthesis of α-amylase by B. subtilis is growth-related since the enzyme in this organism is primarily produced during the exponential phase. This trend is similar to the pattern of amylase synthesis by Clostridium acetobutylicum as reported by Annous and Blaschek, [18] and that of thermoactive α-amylase from B. subtilis observed by Uguru et al., [13]. Both corn and soluble starch media produced variable amylase activities at 2% (w/v) concentration as sole carbon source. Maximum activity of 10.4±1.3 U mg-1 was recorded in corn starch mineral salts (MS) medium against 9.4±0.71 U mg-1 in soluble starch medium (Fig. 1) during its late exponential phase of growth. In contrast, Sani et al., [19] and Uguru et al., [20] observed highest amylase activity during late stationary phase and early stationary phase for Aspergillus sp. and Aspergillus niger respectively. At the maximum amylase activity, about 80% of the corn starch and 68% of the soluble starch has been utilized. This is a demonstration of easy utilization of the corn starch in the medium in preference to the soluble starch, a phenomenon that recommends corn starch for industrial application especially in the sub-Saharan Africa.
3.3. Substrate Specificity of α-amylase Produced from Bacillus subtilis
- Typical growth and enzyme production profiles in the medium showed that amylase production was highest in the corn starch medium compared to soluble starch medium (Fig. 1). Growth of the organism in the mineral salts medium without carbon source was slow and low. Under this condition amylase induction did not occur but when corn starch was introduced as carbon source it produced the highest α-amylase activity of 10.4±1.3 Umg-1 compared to 9.40±0.71 Umg-1 produced in soluble starch medium. The overall picture implies that carbon source is of importance for the synthesis of the enzyme although mineral salts are still critical for their basic biomolecular functions. All the tested native starches and sugars yielded titres of amylase as shown in the following decreasing order (in U mg-1): corn (10.4) > soluble starch (9.40) > sweet potato (8.24) potato (7.59) > cassava (5.093) > maltose (4.67) > glucose (2.84). The enhanced amylase induction in the corn starch mineral salts medium could be as a consequence of the presence of proteins, amino acids, soluble carbohydrates and other compounds in contrast to highly purified soluble starch. Similar observations have been made by Sani et al., [19] and Uguru et al., [13]. Furthermore, the observed high levels of amylase produced during growth on complex sugars compared to simple sugars could be in response to a need to convert the complex sugars into simple sugars that could be utilizable by the organism. Such patterns of behavior have been reported by several authors [21], [22]. Biomass production was also monitored throughout the 5-day experimental period. Maximum growth was observed at the end of 36 h of experimental period (Fig. 1). Although growth was not significant in mineral salts medium without carbon source, it appreciated when corn or soluble starch was added in the MS growth medium to a level of 1.9 and 1.3 mg biomass respectively. Result therefore indicates that α-amylase production from B. subtilis could be realizable using a readily cheap carbon source like corn. Such a development could serve as an alternative to the more expensive soluble starch in most developing countries of the world especially in the sub-Saharan Africa.
3.4. Physicochemical Properties
3.4.1. Effect of pH of Growth Medium on Amylase Production by Bacillus Subtilis
- An important characteristic of most microorganisms is their strong dependence on the extracellular pH for cell growth and enzyme production. Among the physical parameters, the pH of the growth medium plays an important role by inducing morphological changes in the organism and in enzyme secretion as they are sensitive to the concentration of hydrogen ions present in the medium. For increased α-amylase yield, the pH of the medium is expected to be around pH 5.5 – 8.5 for α-amylase. The culture pH also strongly affects many enzymatic processes and transport of various components across the cell membrane [23]. In view of a close relationship between amylase synthesis and the utilization of the carbon source, pH variations during fermentation may give information about the amylase production, such as the start and the end of the enzyme production period. In this study, amylase activity increased progressively as pH increases from 3.0 to 11 but peaked at pH 6.5 with corresponding maximum enzyme activities of 10.4±1.3 and 9.4±0.71 U mg-1 (Fig. 2). Gupta et al. [24] reported that most Bacillus strains used commercially for the production of bacterial α-amylase by submerged fermentation (SmF) have an optimum pH between 6.0 and 7.0 for growth and enzyme production and that such is also applicable to strains used in the production of the enzyme by solid state fermentation (SSF). Cordeira et al. [25] in their own account reported an optimum pH of 7.5, with a very broad active range of pH 5.5 – 10.0 for Bacillus species. The reported pH range by these authors agrees with the observed maximum pH value obtained in this study for Bacillus subtilis. In addition, Haq et al. [26] and other workers [23-24] also reported that bacterial cultures such as B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, and B. amyloliquefaciens required an initial pH of 7.0 for optimum yields of α-amylase, suggesting that the obtained optimum pH of 6.5 for α-amylase (Fig. 2) falls within the reported pH values in the literature.
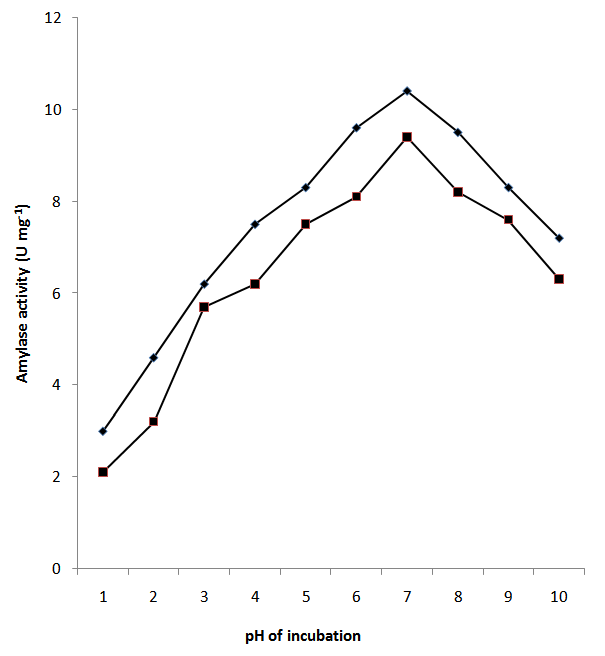 | Figure 2. Effect of pH of the growth medium on amylase prduction by Bacillus subtilis. Amylase activity on corn starch medium (■); Amylase activity on soluble starch medium  (♦) (♦) |
3.4.2. Effect of Temperature of Growth on Amylase Production by B. subtilis
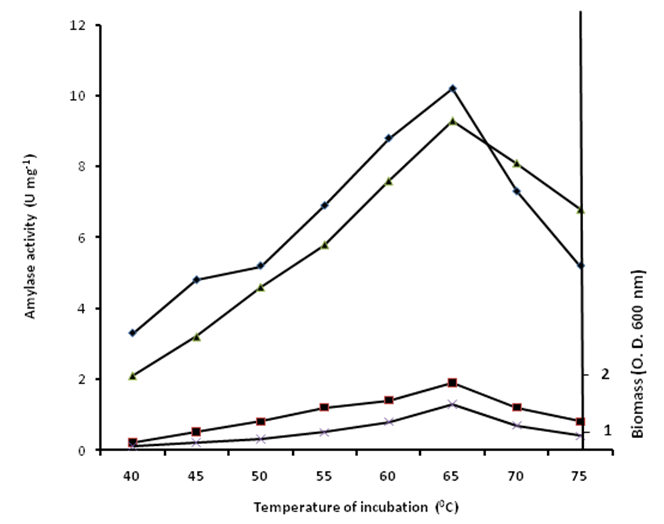
- Temperature is of essence and the influence of temperature on amylase production is related to the growth of the organism. Thus, temperature is another critical parameter that has to be controlled and varied from organism to organism. The enzyme showed a maximum activity of 9.4±1.3 and 10.3±2.1 U mg-1 on soluble and corn starch media respectively at 65℃ (Fig. 3). Conversely, at 25 and 75℃, the enzyme produced the least amylase activity of 0.2±0.01 and 1.6±0.07 U mg-1 respectively (Fig. 3). The observed low levels of activity at 25 and 75℃ could be ascribed to poor growth of B. subtilis which is within the range of findings of many authors in the literature [27-30]. However, temperatures as high as 80℃ have been used for amylase production from the hyperthermophilic Thermococcus profundus [31]. Maximum biomass production of 1.8 and 1.2 mg was also observed at the maximum temperature of 65℃ for corn and soluble starch media. In summary the maximum temperature of 65℃ for α-amylase with its broad pH range of 5 to 8 suggests that the enzyme may have potential for application in the brewing industry.
4. Conclusions
- Bacillus subtilis was isolated from soil. This organism was able to grow and produce α-amylase on a cheap and locally available corn starch medium compared to the conventional soluble starch medium. The successful isolation of Bacillus subtilis and its ability to express considerable quantity of amylase on corn starch medium is an attractive alternative in starch and brewing industries especially in the sub-Saharan Africa where the cost of medium components is relatively expensive.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML