-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2014; 4(2): 78-85
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20140402.06
Maternal Transfer of Bacteria to Eggs of Common House Gecko (Hemidactylus frenatus)
Bhoj Raj Singh1, 2, Vidya Singh3, Ngullie Ebibeni1, Raj Karan Singh3
1ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Nagaland Centre, Jharnapani-797 106, Nagaland, India
2Division of Epidemiology, Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izatnagar-243122, India
3National research Centre on Mithun, Jharnapani-797 106, Nagaland, India
Correspondence to: Bhoj Raj Singh, ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Nagaland Centre, Jharnapani-797 106, Nagaland, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Bacteria are commonly reported in eggs and transovarial transfer is known in birds but little is known about geckos. In the present study 72% of gecko eggs had bacteria. Citrobacter freundii (7) were the most commonly isolated bacteria followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (6), C. amalonaticus (4), Enterococcus casselifalvus (3) and Pragia fontium (3). Bacillus licheniformis, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus hirae and Edwardsiella tarda were isolated from two eggs each while C. diversus, Escherichia fergusonii, Enterococcus dispar, Enterobacter agglomerans, Erwinia ananas, Ewingella americana, Klebsiella oxytoca, Proteus penneri, Salmonella enterica ssp. indica, S. enterica ssp. salamae and Staphylococcus aureus were isolated from one egg each. All types of bacteria detected in eggs except B. licheniformis were also detected with similar antibiogram in ova, ovary, liver and intestinal contents of geckos showing good correlation (r, 0.9) among bacteria detected in eggs and ova. Of the 30 ova collected from uterine tubes of geckos, 70% had one or more than one type of bacteria. All five ovaries of non-gravid geckos had one or more type of bacteria. More than 10% isolates had multiple drug resistance. Transovarial transfer of bacteria in geckos appeared to be the most important source of microbes in gecko eggs.
Keywords: Trans-ovarial, Maternal, Bacteria, Drug Resistance
Cite this paper: Bhoj Raj Singh, Vidya Singh, Ngullie Ebibeni, Raj Karan Singh, Maternal Transfer of Bacteria to Eggs of Common House Gecko (Hemidactylus frenatus), Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 78-85. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20140402.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The lizards are often considered as source of many pathogens [1-6] and despite of being quite harmless, most of the people look with fear on common house geckos. Several species of house geckos are known in India varying in distribution in different regions. In the Jharnapani area of Nagaland, common house gecko (Hemidactylus frenatus) is seen in houses, in animal sheds, in offices, in kitchens and stores. Geckos are often reported as carriers of many zoonotic enteropathogens including non-typhoidal salmonellae [1-7], Citrobacter freundii [2, 5, 7], C. intermedius, Erwinia herbicola, Enterobacter cloacae [2, 5, 7], Shigella sonnei, Edwardsiella tarda, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens, Proteus spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli [5, 7], Listonella damsele, Raoultella terrigena, Edwardsiella hoshiniae and Klebsiella oxytoca [7]. Researchers have suspected that lizards have a role as reservoirs in spread and emergence of drug resistant bacteria [2, 5-7]. Lizards are considered as an important reservoir of Salmonella. Generation to generation transfer of Salmonella is hypothesized to be the main reason for carriage of the pathogen by lizards [6]. Close contact with mothers just after hatching has been attributed to be the major mechanism of acquisition of several bacteria by lizards [8]. However, the dilemma is, where from these bacteria come in lizards? Source of bacteria may either be environment, and lizards might acquire them horizontally from air, water, food and contacts or bacteria may be acquired vertically from mother geckos. If it is environment it is same for all the lives in the ecosystem thus of not much significance unless proved that geckos concentrate the zoonotic pathogens. Further, studies have indicated that mothers may transfer microbes to their progeny vertically through different ways depending on their biology [9]. Thus we explored about the possibilities of maternal source of bacteria in common house gecko eggs.
2. Materials and Methods
- All experiments were conducted after due approval from Institute’s Animal Ethics Committee following the protocol laid for handling and euthanasia of geckos.
2.1. Egg Samples
- Twenty five eggs of common house geckos were randomly (every 5th eggs found) collected during regular cleansing (April to July) of offices at National Research Centre on Mithun and of ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Nagaland Centre, Jharnapani, Medziphema, Nagaland. Eggs were picked up with sterile forceps and transferred to 10 ml test tube. Eggs were surface sterilized with 70% ethanol for 10 min.
2.2. Ova, Liver, Intestinal Contents and Ovaries
- From the same premises in the same period of time the geckos were captured using nets. The adult geckos were retained and apparently young were released at the place of their capture. All the adult females were anaesthetized in jars filled with chloroform vapours and rapidly palpated. A total of 30 gravid and five non-gravid females identified through gentle palpitation in vent area and abdomen [10] were retained and males were allowed to go. From none of the office more than two female geckos were retained. All the female geckos were euthanized in CO2 chamber and their bodies were swabbed with 70% ethanol. Then the geckos were ventrally dissected to locate uterine, tubes, ovaries, liver and intestines [11]. From non-gravid geckos ovaries were aseptically collected using sterile forceps and scissors and transferred to sterile 10 ml glass tube containing 5 ml buffered peptone water (BPW, Difco, USA), then with another set of sterile forceps and scissors, liver was collected similarly and transferred to BPW and finally with another set of sterile forceps and scissors part of distal intestine with its contents were collected and transferred to BPW. From gravid geckos, ova were collected first from uterine tube into BPW, then liver and finally the intestine with its contents as described above.
2.3. Processing of Gecko Eggs for Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
- Eggs were surface cleaned with 70% ethanol and were aseptically transferred on to sterile tissue paper to dry. Each dry egg was transferred to a separate sterile 10 ml tube. Using sterile needle eggs were broken, egg shell was taken out, 5 ml of BPW was added in to the tube and the tube was swirled over vortex for 2-3 min. The tubes were incubated for 6-8 h at 37℃. Growth from the tubes was streaked on to MacConkey agar (MA, Hi-Media, India) and 5% sheep blood agar (HEA, Hi-Media, India). Plates were incubated for 24-36 h at 37℃. Each visibly different type of isolated colony was picked up and re-streaked on brain heart infusion agar (BHIA, Hi-Media) for final isolation of pure isolate of bacteria. From BHIA, one isolated colony for each isolate was characterised using morphological, cultural, staining and growth parameters [12] using Hi-AssortedTM Biochemical test kit (Hi-Media, India) and Hi25TM Enterobacteriaceae identification kit (Hi-Media, India) as described by the manufacturer.
2.4. Processing of Samples from Geckos
- All the samples collected from geckos were aseptically homogenized in the respective glass tubes, during homogenisation tubes were kept on ice. The tubes containing ova and ovaries were processed first while remaining samples were stored at 2-4℃ till the results of bacterial isolation and identification were evident (within 3 to 5 days). The tubes containing homogenized ova/ovaries were incubated for 6-8 h at 37℃. Growth from the tubes was streaked on to MacConkey agar (MA, Hi-Media, India) and 5% sheep blood agar (BA, Hi-Media, India) and plates were incubated for 24-36 h at 37℃. Each visibly different type of isolated colony was picked up, purified and identified as described above for bacterial isolates from eggs.Thereafter, liver and intestinal contents were processed specifically to isolate and identify those bacteria isolated from ovaries/ova using the same protocol as used for isolation and identification of bacteria from eggs/ova and ovaries of the corresponding gecko.
2.5. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Assay
- All the bacterial isolates were tested for antimicrobial sensitivity against antimicrobial discs (Hi-Media, India) of ampicillin (10 µg), cefotaxime (30 µg), ceftazidime (30 µg), chloramphenicol (30µg), ciprofloxacin (30µg), cotrimoxazole (25µg), gentamicin (30 µg), nalidixic acid (30µg), netillin (30µg), nitrofurantoin (300µg), streptomycin (10 µg) and tetracycline (30 µg) using disc diffusion method on Muller Hinton agar (MHA, Hi-Media, India) plates and results were interpreted as per CLSI guidelines [13]. Gram positive isolates were also tested against vancomycin (5 µg) discs. Isolates resistant to three or more drugs were classified as multi-drug-resistant (MDR) type.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Bacterial isolation and sensitivity assay data was entered in MS Excel work sheet and analysed using two tailed Chi-square test.
3. Results
- A total of 181 isolates of bacteria (33 Gram positive and 148 Gram negative) belonging to 24 species of 15 genera could be identified from gecko eggs, ova, liver and intestinal contents from gravid geckos and ovaries, liver and intestinal contents of non-gravid geckos (Table. 1). On the basis of resistance pattern of 181 isolates (50 from eggs, 116 from gravid geckos and 15 from non-gravid geckos) could be classified in to 32 resistotypes (Table. 2). A total of 64 isolates were sensitive to all the antimicrobials in the study (35.4%) while 44 (24.3%), 54 (29.8%), 14 (7.7%), 3 (1.7%) and 2 (1.1%) isolates were resistant to one, two, three, four and five antimicrobials, respectively. In total, 19 (10.5%) isolates had multiple drug resistance (MDR) and belonged to 8 species of bacteria including B. licheniformis (2), C. freundii (1), Ec. casseliflavus (3), Ec. dispar (2), Ec. hirae (5), K. pneumoniae (2), S. indica (2) and Staph. aureus (2).Of the 181 isolates, from eggs, gravid and non-gravid gecko samples, none of the strain was resistant to chloramphenicol and gentamicin (Table. 1) while 54.5% strains of Gram positive isolates were resistant to vancomycin. Ampicillin was resisted by the maximum number of isolates (38.1%) followed by nitrofurantoin (24.3%), ceftazidime (18.2%), nalidixic acid (8.8%) and cefotaxime (6.1%). Only few isolates were resistant to other antimicrobials (Table 1). Antimicrobial drug resistance among strains of different species varied significantly for most the drugs including ceftazidime (p, 2.29×10-6), nalidixic acid (p, 2.23×10-4), nitrofurantoin (p, 3.34×10-13), ampicillin (p, 2.84×10-12), tetracycline (p, 3.21×10-13), streptomycin (p, 3.84×10-5), cotrimoxazole (p, 8.97×10-18) and vacomycin (p, 1.37×10-10). However, species of bacteria had little effect on their sensitivity towards ciprofloxacin, cefotaxiome, netillin, chloramphenicol and gentamicin (Table. 1). All Klebsiella and half of the Citrobacter strains were resistant to ampicillin while majority of klebsiellae were resistant to nitrofurantoin. Almost 75% strains of Ec. hirae and Ec. casseliflavus were resistant but all Ec. dispar and Staph. aureus strains were sensitive to vancomycin (Table. 1).Although species of bacteria was an important determinant of antimicrobial drug resistance, their source had no significant (p, >0.1) effect for most of the antimicrobials (Table. 3). However, vancomycin resistance was significantly (p, 0.002) more common among isolates of bacteria from ova and intestinal contents of gravid geckos. Similarly, more number of isolates from intestinal contents of gravid geckos were sensitive to cotrimoxazole (p, 0.05).
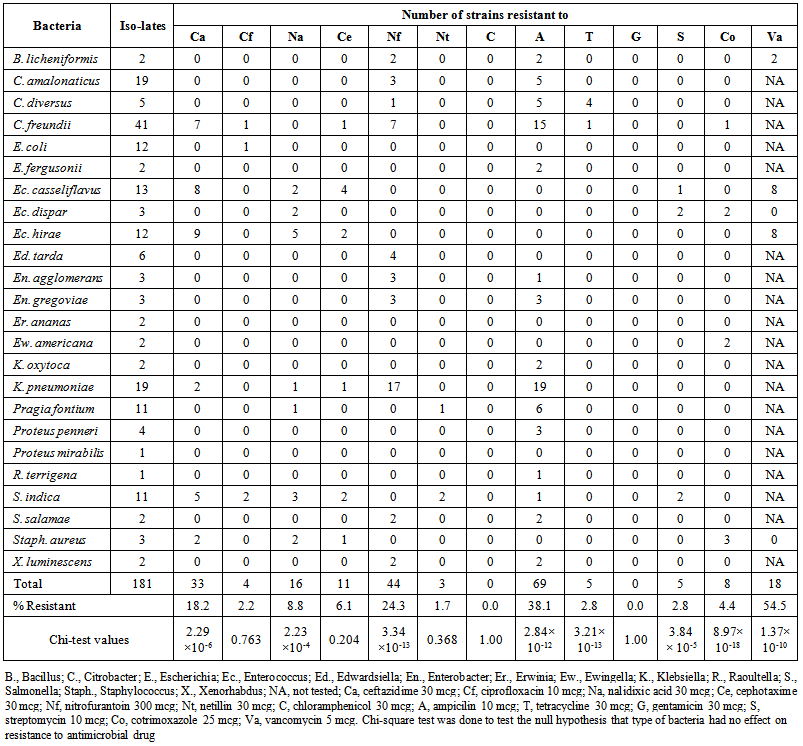 | Table 1. Antimicrobial drug resistance in bacteria isolated from common house gecko eggs, ova (from uterine tubes), ovary, liver and spleen |
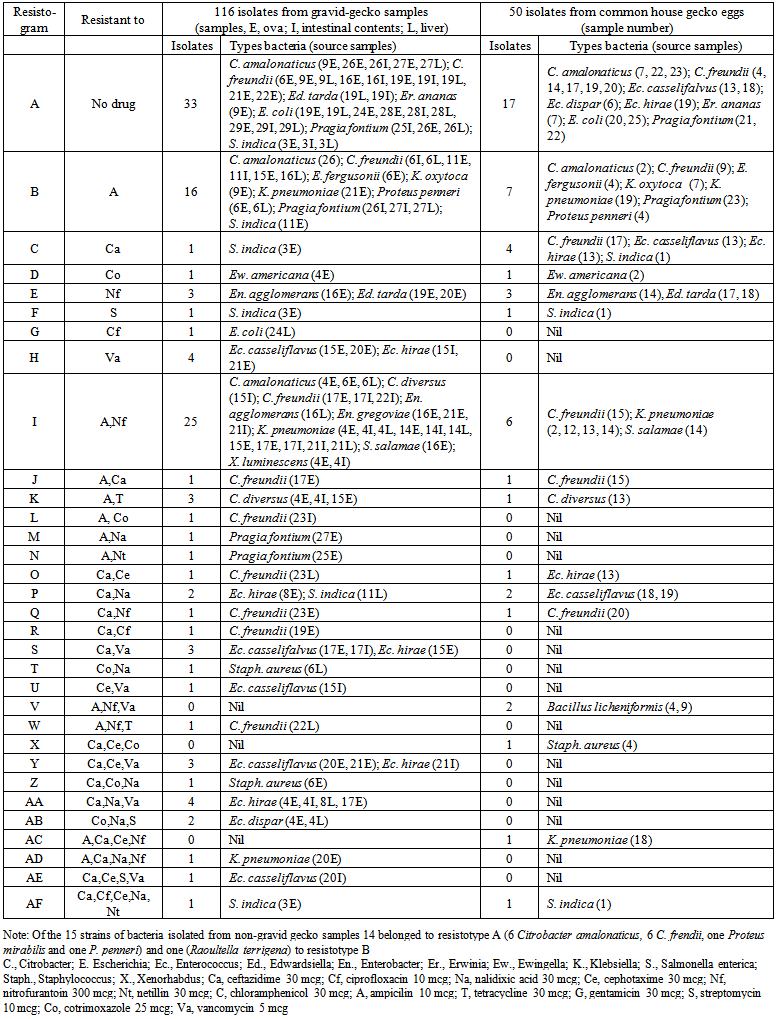 | Table 2. Antibiotic resistance patterns of bacteria isolated from common house gecko eggs, ova, liver and intestinal contents |
3.1. Bacteria in Gecko Eggs
- Of the 25 eggs examined 7 had no bacteria, 6, 5, 3, 3 and one egg contained 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 types of bacteria, respectively (Table 4). From the gecko eggs a total 50 different isolates were identified belonging to 20 different species of bacteria. Citrobacter freundii was the most common bacteria isolated from 7 eggs followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (6), C. amalonaticus (4), Enterococcus casselifalvus (3) and Pragia fontium (3). Bacillus licheniformis, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus hirae, Edwardsiella tarda were isolated from two eggs each while C. diversus, Escherichia fergusonii, , Enterococcus dispar, Enterobacter agglomerans, Erwinia ananas, Ewingella americana, Klebsiella oxytoca, Proteus penneri, Salmonella enterica ssp. indica, S. enterica ssp. salamae and Staphylococcus aureus were isolated from one egg each (Table 4).
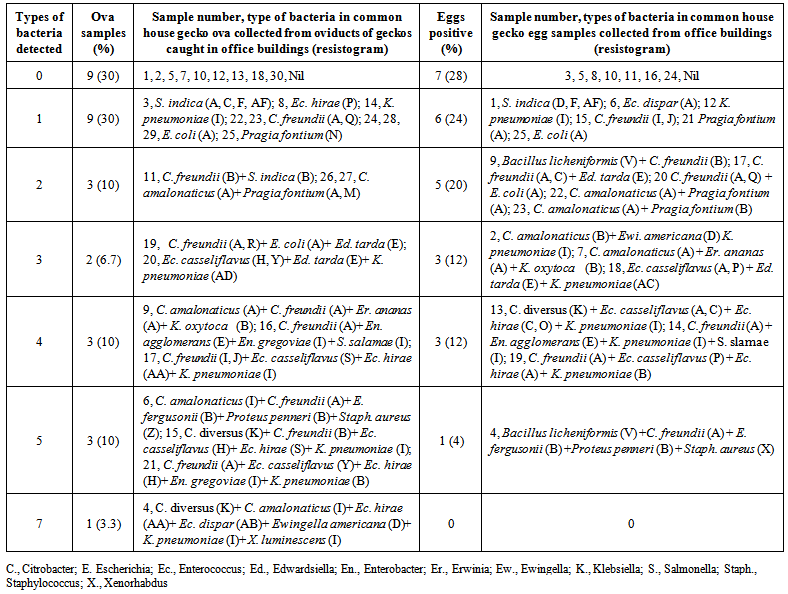 | Table 4. Diversity and multiplicity of bacteria isolated from 25 house gecko eggs and ova collected from 30 gecko oviducts |
3.2. Bacteria in Ovaries, Intestinal Contents and Livers Collected from Non-gravid-geckos
- A total of 15 isolates were identified from the five non-gravid geckos. From non-gravid geckos, Citrobacter amalonaticus and C. frendii both were detected in ovaries, intestinal contents and liver of two geckos while Proteus mirabilis, P. penneri and Raoultella terrigena were detected in one ovary each. Except R. terrigena (resistant to ampicillin) none of the isolate had antimicrobial resistance against any of the 12 antimicrobials tested against Gram negative bacteria. All the fifteen isolates could be classified into two resistotypes (Table. 2), 14 to type A, and one to type B. One strain each of R. terrigena and P. mrirabilis were isolated only from ovaries of non-gravid geckos.
3.3. Bacteria in Ova Collected from Uterine Tubes of Gravid-geckos
- On bacteriological analysis of ova from 30 gravid geckos, 9, 9, 3, 2, 3, 3 and one ova sample contained 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 types of bacteria, respectively (Table 4). Similar to eggs, in ova samples too, C. freundii was the most commonly isolated bacteria (12) followed by K. pneumoniae (6), Ec. hirae (5), C. amalonaticus (5), E. coli (4), Ec. casseliflavus (4) and P. fontium (3). Except B. licheniformis all other bacteria isolated from eggs were also detected in one or more samples of ova (Table 2). Besides, Ec. gregoviae and Xenorhabdus luminescens, not detected in eggs, were also detected in two and one ova samples, respectively. Most of the bacteria detected in ova were simultaneously detected in liver or intestine of the corresponding geckos. Erwinia ananas, Ed. tarda, En. agglomernas, S. enterica ssp. salamae, Ewingella americana, K. oxytoca, E. fergusonii and Staph. aureus detected both in gecko ova and eggs, and B. licheniformis detected in eggs could not detected in intestinal contents and liver of any of the 30 geckos.On the basis of antimicrobial drug resistance pattern, 61, 26 and 29 bacteria isolated from ova, liver and intestinal contents of gravid geckos, respectively could be classified in to 29 resistotypes. Resistotype A and B contents of gravid geckos, respectively could be classified in to 29 resistotypes. Resistotype A and B were the most common ones (Table. 2). Bacterial strains with three of the resistotypes (V, X and AC) detected in gecko eggs were not detected in organs of gravid or non gravid geckos.Most of the bacteria isolated from gecko eggs had good correlation (r, 0.9) with type of bacteria detected in aseptically collected ova from gecko uterine tubes. Interestingly R. terrigena and P. mirabilis detected in ovaries of non-gravid geckos could neither be detected in gecko eggs nor in ova. Of the ova and eggs positive for bacteria, 57.1% ova and 66.6% eggs had more than one type of bacteria (Table. 4) together. Moreover, multiplicity of bacteria was more common in ova than in eggs (though not differed significantly, p, 0.57) indicating that some types of bacteria might get lost in eggs after laying of ova as eggs.
4. Discussion
- It is widely accepted that potentially enteropathogenic and zoonotically important bacteria may be present in intestine of geckos [1-6] and also excreted in their droppings to contaminate environment [7]. Thus the geckos are been seen as potential threat in spread of enteric diseases [1-7]. However, little is known about bacteria present in gecko eggs and their potential origin. This study revealed that eggs, ovaries, ova, liver and intestinal contents of common house geckos of Nagaland also contain similar type of bacteria as reported earlier in intestinal contents [1-5] and faecal droppings of geckos from other parts of the globe [7]. In the study bacteria belonging to 20 different species of 13 genera were detected in gecko eggs and all except Bacillus licheniformis were also detected in ova samples collected from uterine tubes of geckos indicating that majority of bacteria present in gecko eggs might have been acquired by eggs during their formation in uterine tubes/ oviducts.The bacteria which were not detected in ova but detected in eggs only (B. licheniformis) might have been acquired after egg laying from contaminated environment but needs further studies to confirm that gecko eggs may also acquire bacteria from environment. However, non-detection of R. terrigena and P. mirabilis either in eggs or ova but present in ovaries of non-gravid gecko is not possible to explain on the basis of present study. Only more studies can explain either R. terrigena or P. mirabilis are not able to be transferred to ova/ eggs or they get lost when time for reproduction is approached or it was just a chance of non detection of the two bacteria in eggs and ova.In the study bacteria belonging to 24 species of 15 genera were detected in geckos. Most of the bacteria identified from geckos in the study have also been reported earlier from faecal dropping and in intestinal contents of geckos including Citrobacter freundii [2, 5, 7], Edwardsiella tarda, Enterobacter species, Proteus spp., Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli [5, 7], P. mirabilis, R. terrigena, Salmonella indica, S. slamae and Klebsiella oxytoca [7]. Some of the bacteria identified in gecko samples in the present study are reported for the first time from common house geckos include B. licheniformis C. amalonaticus, C. diversus, E. fergusonii, Ec. casseliflavus, Ec. dispar, Ec. hirae, Er. ananas, Ew. americana, Pragia fontium and X. Luminescens, it might be due to diversity of microbiota of geckos of different regions at different stage of maturity or due to the fact that most of the bacteria identified in the present study were from ova or eggs of geckos rather than from intestinal contents examined in most of the previous studies [1-5, 7]. In the study, several bacteria, viz., Erwinia ananas, Ed. tarda, En. agglomernas, S. enterica ssp. salamae, Ewingella americana, K. oxytoca, E. fergusonii and Staph. aureus were detected both in ova and eggs of geckos but not in intestinal contents or liver of geckos. However, a good correlation (r, 0.9) between bacteria isolated from eggs and aseptically collected ova from uterine tubes of geckos revealed that major source of bacteria in gecko eggs might be the maternal source rather than environment. To understand either presence of different bacteria in gecko eggs affect egg hatchability require more studies. Besides, it is also not clear and need to be explored further why types (multiplicity) of bacteria were relatively less in eggs than in ova.Drug resistance has been reported to be of great concern in bacteria isolated from geckos [2- 4, 7, 14], and in the present study 10.5% strains had resistance to three or more drugs. Low rates of drug resistance in bacteria from geckos observed in the present study might be due to lesser loads of antibiotics in Jharnapani environment as Nagaland is a declared organic state of India. Our observations are in concurrence to earlier observation on antimicrobial drug resistance in about 12% of bacteria isolated from faecal droppings of common house gecko in Nagaland [7]. In the study all klebsiellae and R. terrigena isolates were resistant to ampicillin which is an inherent quality of most the Klebsiella and Raoultella strains [15]. Although there appears to be scanty information on bacteria in gecko eggs for true comparison of the findings, several studies on poultry eggs have shown that bacteria are of common occurrence in eggs [16-18]. Isolation of bacteria from 72% of gecko eggs is very high figure than reported earlier for poultry eggs [19]. In one of the study in India 4.7% and 28.3% table eggs harboured Salmonella and E. coli, respectively [19]. Studies on poultry birds [16-18] and several invertebrates [20-21] have evidenced transovarial transmission of bacteria, virus and Chlamydia. Although in reptiles including lizards generation to generation transfer of symbiotic and pathogenic microbes has been reasoned to be the major source for their reservoir status [6, 8], transfer has rarely been shown to be through transovarial route. In a study on lizards [8] the major route of acquisition of bacterial flora by baby herbivore lizards was contact of hatchlings with their parents in early days of their hatching. Although observations of our study indicated that gecko ovaries had bacteria which might had been transferred to ova and retained in eggs, fate of bacteria containing eggs is not clear. Further studies are needed to establish either the bacteria containing eggs hatch normally or nor, and either the baby geckos continue to carry those bacteria or not.
5. Conclusions
- This study concluded that occurrence of bacteria in gecko eggs is common and most of the bacteria present in gecko eggs might have come from maternal source rather than from environment. Bacteria present is gecko eggs, ova, intestinal contents, ovaries and liver were sensitive to most of the commercially available antimicrobials and MDR is relatively less common (10.5%) in bacteria isolated from geckos in Nagaland.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors are thankful to Director and Joint Director of ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Jharnapani for permitting to work, providing laboratory facility and financial support. Authors also acknowledge day to day support in laboratory and also in collecting samplings from different places by Mrs. Moa.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML