-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2013; 3(6): 240-246
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20130306.08
Occurrence of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Tamouda Bay (Morocco)
Boukanjer Abdelkhalek1, 2, 3, Marie-Laure Quilici2, Fassouane Abdelaziz3, Cohen Nozha1
1Division de Microbiologie et d’Hygiène des Produits et de l’Environnement, Institut Pasteur du Maroc, Casablanca Maroc
2Centre National de Référence des Vibrions et du Cholera, Institut Pasteur de Paris, France
3Laboratoire de Biochimie, Département de Biologie, Faculté des Sciences d’El Jadida
Correspondence to: Cohen Nozha, Division de Microbiologie et d’Hygiène des Produits et de l’Environnement, Institut Pasteur du Maroc, Casablanca Maroc.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Samples of seawater, plankton, shellfish and sediments collected from coastal sites located in Mediterranean (Northern Morocco) were examined for the presence of pathogenic Vibrio species and the occurrence of pathogenic strains. The isolation of the microorganisms was performed by using a standard method. A biochemical protocol was applied for the identification of the isolates while polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to confirm the identification of the strains and to detect the virulence genes. Results showed that 14.8%, 8.1%, 31.3% and 28.5% of seawater, plankton, shellfish and sediments samples respectively contained pathogenic Vibrio species. The most frequently isolated pathogenic Vibriospecies was V.parahaemolyticus.Out of 139 strainsof V.parahaemolyticus isolated, 23.7% had trh gene while none was positive for tdh gene. Among V.parahaemolyticus trh positive, 31 (93.9%) strains were urease positive. All 32 strains of V.choleraeisolated during this study were non-O1 non-O139 and negative for the presence of ctxA, ctxB and tcpA genes.
Keywords: Vibrio spp., Pathogenic Vibrio, Mediterranean sea, Morocco
Cite this paper: Boukanjer Abdelkhalek, Marie-Laure Quilici, Fassouane Abdelaziz, Cohen Nozha, Occurrence of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Tamouda Bay (Morocco), Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 3 No. 6, 2013, pp. 240-246. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20130306.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Vibrio is a Gram-negative genus of facultative anaerobes straight or curved rods, motile by one or more polar flagella, that give a positive oxidase test, grow on thiosulfate citrate bile-salt sucrose agar. Most species are sensitive to the Vibriotactic agent O/129. Sodium stimulates growth of all species and required for most species[1]. Vibrios are normal inhabitants of aquatic environments, being very common in marine and estuarine habitats and on the surface and in the intestinal contents of marine animals [2, 3]. Many Vibrio species are pathogenic for humans and/or marine vertebrates and invertebrates, with the virulence mechanisms reflecting the presence of enterotoxin, haemolysin, cytotoxin, protease, lipase, phospholipase, siderophore, adhesive factor and/or haemagglutinins[4, 5]. Among these species, V. cholerae is the most important, as it is associated with epidemic and pandemic diarrhoea outbreaks in many parts of the world[6]. More than 200 serogroups of V. cholerae are known, but only serogroups O1 and O139 cause epidemic and pandemic cholera[5]. The pathogenesis of cholera is a complex process and involves a number of factors which help the pathogen to reach and colonize the epithelium of the small intestine and produce the enterotoxin that disrupts ion transport by intestinal epithelial cells. In V. cholerae, the major virulence genes appear to exist in clusters, and there are at least two regions of the V. cholerae chromosome in which genes encoding virulence factors are clustered[7, 1, 8, 9, 10]. These include the CTX element, which has now been shown to be the genome of a filamentous bacteriophage[11], and the TCP-accessory colonization factor (ACF) gene cluster, referred to as the TCP pathogenicity island[12]. However, other species of Vibrio (including V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus) capable of causing disease in humans have received greater attention in the last decade[2]. Although there are many strains of V. parahaemolyticus, only those that produce the thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and/or the thermostable related hemolysin (TRH) have the ability to cause gastroenteritis[13], and almost all the strains isolated from clinical samples have either or both genes (tdh and trh) which encode the respective hemolysins. V. vulnificus is a human pathogen that is highly invasive, causing fulminant pulmonary septicemia, with mortality rates as high as 75%, one of the highest death rates of any foodborne disease[14, 15]. V. vulnificus infection is most lethal in individuals who have a preexisting chronic illness, are immunocompromised or have preexisting liver disease [14, 15, 16]. V. vulnificus can express various virulence- associated factors, including capsular polysaccharides, lipopolysaccharides, extracellular hemolysin/cytolysin, metalloprotease, pili, Xagella, siderophore, and repeats-in- toxin proteins[15, 17].In an attempt to contribute to the clarification of the ecological relationships between sea environment and Vibrio in the Mediterranean areas, we carried out a two years study to investigate, by both culture and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) the presence of potential pathogenic Vibrio species (V. vulnificus, V. parahaemolyticus and V. cholerae) along Tamouda Bay located in Mediterranean coast of Morocco. In view of the increasing evidence supporting the role of halophylic Vibrios as both human pathogens and a reservoir of Vibrio virulence genes[18, 19]. Another aspect of this work was to investigate the presence of V. vulnificus, V. parahaemolyticus and V. cholerae pathogenicity-associated genes in Vibrio strains isolated.
2. Materiels and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Environmental Sampling
- Samples were collected bimonthly from January 2007 to December 2008 in three sampling sites of Tamouda Bay. The locations of the sites were determined by use of the global positioning system (Fig. 1). For each field visit, four ecological types of samples were collected, namely, seawater, planktons, shellfish and sediments.Seawater samples (2L) were collected from a boat 1m below the surface using sterilized plastic bottles. Planktons were collected by dragging the water horizontally, at a depth of about 1m, with 200-µm-mesh plankton net[20]. Shellfish samples were purchased from local fisherman, while the sediments were collected from the surface of the coast using sterile plastic pots. After collection, the samples were transported immediately to the laboratory in insulated coolers with frozen gel-packs to maintain a temperature at around 4°C.
2.2. Detection of Potential Pathogenic Vibrio Species by a Conventional Method
- In the laboratory, shellfish were immediately removed from the bags, washed and scrubbed under running potable water to remove debris and attached algae; dead mussels or those with broken shells were discarded. Approximately 5 specimens were opened aseptically with a sterilized scalpel. Meat and shell liquid were collected in a sterile jar, cut with scissors and mixed thoroughly. Then, 25 grams liquid and meat were transferred into sterile plastic bags with 250 mL of Alkaline Peptone Water (APW; 1% [wt/vol] peptone, 2% [wt/vol] sodium chloride; pH 8.2) to obtain a 1:10 dilution and subjected to further homogenization for 60 s using a stomacher.All the collected volume (2L) of each water sample was concentrated by filtration through a 0.22 µm-pore-size filter (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA, USA) with a vacuum pump, and filters were subsequently placed in 20 ml of APW to obtain a final concentrated volume corresponding to 100x.
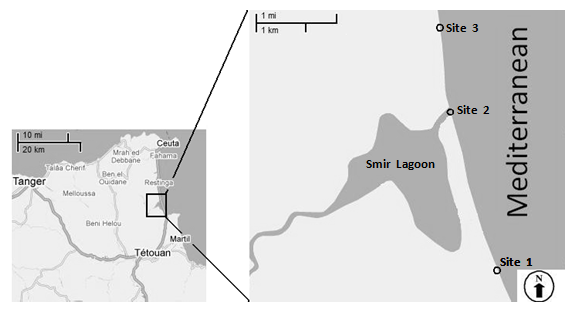 | Figure 1. Map showing the geographical location of three sampling sites (sites 1: 35° 41' 184''N, 005° 19' 258''W; site 2: 35° 41' 402''N, 005° 18' 226''W and site 3: 35° 40' 885"N, 005° 18' 760"W) |
2.3. Molecular Identification of Pathogenic Vibrio Species by PCR
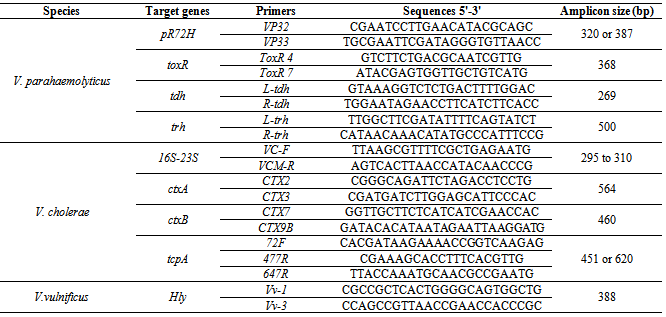
- The biochemical identification of isolated strains identified as pathogenic vibrio species was confirmed by PCR on the purified DNA. DNA extraction: The extraction and purification of DNA was carried out using a previously described method[21] wich was modified as follows. In fact, cells either from 18 h cultures in nutrient agar containing 2% NaCl were harvested or resuspended in 300µL of TENa buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0). Lysis was accomplished by the addition of 50µl of 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and 10µl of pronase. Before use, pronase was self-digested at 37°C for 30 min followed by another incubation at 60°C for the same duration (30min) to remove any contaminating DNases. An equal volume of isoamylic phenol/chloroform was added to the cell lysate and mixture was shaken to equilibrate the phenol and aqueous phases which were then separated by centrifugation for about 10 min at 15000 rpm. Two volumes of cold absolute ethanol were added to the aqueous phase to precipitate nucleic acids.After another centrifugation at 15000 for 10 min, the DNA precipitate was washed with 70% ethanol and air-dried. It was then dissolved in 100µl of TE containing 0.002% of RNase. Purity was calculated following determination of A260/A280 ratios, and DNA concentrations were obtained from the A260 values.Polymerase Chain Reaction: The presence of V. cholerae, V. vulnificus and V. parahaemolyticus was also identified by PCR. Molecular identification of V. cholerae and V. vulnificus was carried out targeting the 16S-23S rDNA[22] and the cytotoxin-hemolysin gene (Hly)[23] respectively, while all strains identified biochemically as V.parahaemolyticus or V. alginolyticus were analyzed targeting pR72H fragment[24] and regulatory gene toxR[25]. The presence of ctxA and ctxB encoding subunits A and B of cholera toxin were determined by using simplex PCR assays followed the methods of Fields et al. and Olsvik et al. respectively[26, 27], while the amplification of the tcpA gene encoding the toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP) was performed using PCR conditions previously described[28]. PCR amplification of the tdh and trh genes encoding respectively the thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and the thermostable related hemolysin (TRH) of V. parahaemolyticus was carried out according to Bej et al.[29]. The various oligonucleotide sequences used in this study are shown in Table 1. PCR products were electrophoresed in a 1.6% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under UV light.
|
3. Results
|
|
4. Discussion
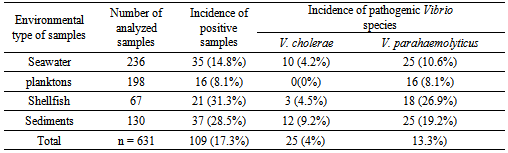
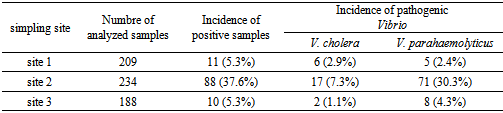
- Despite their clinical and epidemiological relevance and their elevated prevalence in the aquatic environment, most mediterranean countries do not routinely determine the presence of pathogenic Vibrio species in clinical, environmental and food sources. In two years study of pathogenic Vibrio species were detected in marine environment of Tamouda bay. Values encountered were highest than those of the same species found by Ripabelli et al. where of the total of sixty-two samples of Mytilus galloprovincialis (mussels) harvested from approved shellfish waters in the Adriatic Sea in Italy (in the Mediterranean), 1.6% were positive for NCV with the same incidence (1.6%) of positive samples for V.parahaemolyticus[30]. But in the same study 17.7% of samples were positive for V. vulnificus[30] while in our study any sample of shellfish was positive for this species. The incidence of V. parahaemolyticus in shellfish found was also highest than those found by Bouchriti et al.[31] and Cohen et al.[32] where just 5% and 10% where respectively positive for this species. Moreover, out of 109 samples positive for pathogenic Vibrio species (V. cholerae and V. parahaemolyticus), 88 (80.7%) were collected from site 2. This may be explained by the geographic position of this site. In fact, it is located at the point of communication between Smir Lagoon and Mediterranean Sea through an opening of more than 20 meters wide, as well as in addition of Oued Smir's waters; Smir lagoon receives also, through small channels, the domestic waters of M'diq city. Therefore, this site is very rich in nutrients[33]. Is also noted that the incidence of positive samples in shellfish and sediments were highest than those in seawater and plankton. This may be explained by the capability of shellfishes to filtrated seawater and to concentrate the bacteria content in both seawater and planktonin their liquor[34]. Moreover, a lot of studies have showed that the sediments constitute a reservoir of Vibrio spp. which explains the high incidence of pathogenic Vibrio in this type of simples[35, 36, 37].In this study 23.7% of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated showed positive results for the presence of the trh gene while none has been positive for tdh gene. This is in agreement with the literature. In fact, it has been reported that more than 90% of clinical V. parahaemolyticus isolates but less than 1% of food or environmental strains possess tdh[38, 39, 40]. Moreover, the result concerning occurrence of trh gene was similar than that obtained by a previous study reporting that the trh gene was present in 4/20 (20%) of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated from environmental samples collected from the coast of Seto-Inland Sea in Japan[41]. However, it is in contradiction with the results obtained in most previous studies, showing that just 1% to 5% of environmental isolates possess the trh gene[42, 43, 44].Of special interest, among V. parahaemolyticus strains trh positive isolated in our study, 94% were urease positive, this is in total accordance with the results found by DePaola et al[45] and Suthienkul et al.[46] where 97% and 100% respectively of isolated pathogenic V. parahaemolyticus which were urease positive possessed a trh gene. This indicates that urease production by V. parahaemolyticus strains strongly correlates with the possession of the trh gene. Thus, the urease-positive phenotype of V. parahaemolyticus can be considered an indication of virulent (trh-possessing) V. parahaemolyticus strains in clinical diagnosis.It was also noted that out of 204 strains biochemically identified as V. alginolyticus 24 (12%) were confirmed as V. parahaemolyticus by PCR method. It is therefore evident that the PCR technique provides greater specificity than the phenotypic methods to differentiate these two species of Vibrio. In fact, the specificity and sensitivity of PCR compared to the conventional method for the identification of pathogenic Vibrios have been reported by several studies[32, 47, 48, 49, 50].
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, the results obtained showed that pathogenic Vibrio species were detected in shellfish and environmental samples collected from Tamouda bay. Consequently, they could also be present in seafood products in other mediterranean coast. Finally, our results suggest that a long-term monitoring program should be initiated to detect pathogenic vibrio species isolates in the environment, especially during the warm summer months when concentrations of this bacterium are thought to be at their highest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We thank the staff of “centre national de référence des vibrions et du cholerae” (cnrvc) in pasteur institute of paris for technical assistance, as well as all members of royal mounted police brigade of m'diq-fnideq region for their help in carrying out the sampling.This study was carried out with the support of the “vibriosea project. “Vibriosea” is an ongoing international research project funded by the centre national d’etudes spatiales (cnes) and institut pasteur, france. The project is conducted by the Vibriosea Consortium including the following institutions and leading researchers: cnes (Murielle Lafaye), medias (Jean Pierre Lacaux), cls (Jacques Stump) and ifremer (Dominique Hervio-Hearth) from france, university of Verona (Maria del mar Lleò), university of Genova (Carla Pruzzo) and ismar-cnr Venezia (Giorgio Socal) from Italy and the institut Pasteur in Paris (Marie Laure Quilici), Morocco Nozha Cohen), Algeria (Fouzia Mouffok) and Tunisia (Ridha ben Aissa).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML