-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2013; 3(5): 176-184
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20130305.03
A Disseminated Microsporidian Pathogen in a New Host
Hanaa A. Gouda
Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Hanaa A. Gouda, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Microsporidiosis was detected in the freshwater leech; Barbronia assiuti from Al-Sont canal, Assiut, Egypt. Infection was easily detected as white irregular batches within the semitransparent body of the leech. Infestation was wide spread; in the epidermis, botriodal tissue, connective tissue and within the gut lining and lumen. Light and electron microscopy showed that the pathogen appeared monomorphic, diplokaryotic and without sporophorous vacuole (apansporoblastic). Spores measuring 3.5-5 x -1.5- 2 um, spore wall ~ 370 nm thick which was composed of electron dense exospore (~ 250 nm thick) and electron lucent endospore (~ 120 nm thick), polar filament having 13-15 coils in one layer all with the same diameter (isofilar type). These characteristics allowed its placement in the genus Nosema. Serial L.S. showed characteristic xenomas enclosed numerous mature spores. Histopathology revealed migration of chromatophores and fibrocytes around the xenomas. Fibrosis, granuloma and vesiculation could be detected within the connective tissue.
Keywords: Leeches, Microsporidia, Morphology, Ultrastructure, Histopathology, Egypt
Cite this paper: Hanaa A. Gouda, A Disseminated Microsporidian Pathogen in a New Host, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 3 No. 5, 2013, pp. 176-184. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20130305.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Leeches (Phylum: Annelida) are distributed allover the world in a diversity of habitats; in freshwaters, seas and desert oases. They are important components in food chains; as predators, vectors of parasites, preys of aquatic animals[1] and hosts or intermediate hosts in the life cycles of disease-causing blood protozoans, trematodes and cestodes of fishes[2-5].The obligate intracellular microsporidian parasites are common in both vertebrates and invertebrates[6,7], but rarely occur in leeches[8]. The life cycle involves a proliferative merogonic stage followed by sporogony, which results in spores containing a tubular extrusion apparatus (polar tubule) for injecting infective spore contents into the host cell[9,10]. Most Nosema species are parasitic in invertebrates[11,12].Till now, only four species of microsporids were reported within leeches. All belong to the genus Nosema. The first was Nosema glossiphoniae[13] from the leech Glossiphonia complanata, the second was Nosema herpobdellae[14] from the leech Erpobdella octoculata, the third was Nosema tractabile Larsson, 1981 from the leech Helobdella stagnalis and the fourth was Nosema sp.[15] from the leech Salifa delicata. The present study represents the fifth infection in leeches. Light and electron microscopy revealed the structure of the present Nosema sp and histopathology on the freshwater leech; Barbronia assiuti.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
- Leeches were collected from Al-Sont canal
 near Assiut city. Leeches were found clinging to the underside of stones, sticks, logs and plastic sheets as well as on floating plants such as Eichhornia crassipes. Leeches were hand-picked, manipulated with the tip of a finger and then rinsed into a collecting plastic jar with some water from the habitat. Water temperature was measured during sampling. In the laboratory, the leeches were examined alive at the same day of collection before transferring to the laboratory containers. Eleven leeches of total 321 catch of Barbronia assiuti were found to be infected (% 3.4) during 2011-2012.
near Assiut city. Leeches were found clinging to the underside of stones, sticks, logs and plastic sheets as well as on floating plants such as Eichhornia crassipes. Leeches were hand-picked, manipulated with the tip of a finger and then rinsed into a collecting plastic jar with some water from the habitat. Water temperature was measured during sampling. In the laboratory, the leeches were examined alive at the same day of collection before transferring to the laboratory containers. Eleven leeches of total 321 catch of Barbronia assiuti were found to be infected (% 3.4) during 2011-2012. 2.2. Identification
- Identification was carried according to[16,17] based on characteristics of the adult spores ultrastructurally; by using the electron microscopy.
2.3. Smearing
- In the laboratory, the infected leeches were separated relied on the morphological signs of infection. Some of these leeches were pined and punctured at the site of white batches for smear preparation[16]. A viscous, milky fluid was observed. The smears were stained by haematoxylin- eosin and toluidine blue[18].
2.4. Relaxation and Fixation
- Eight infected leeches were relaxed in 8% ethanol. Tree specimens were fixed in formol saline (1g calcium + 100 ml neutral formalin) for serial longitudinal paraffin sections. The other five specimens were placed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde and sent to the E.M. unit at Assiut University for electron microscopy (two for SEM and three specimens for TEM).
2.5. Paraffin Sections
- Tissues were dehydrated, cleared, then embedded in paraffin, and processed routinely for light microscopy according to[18]. Serial longitudinal sections at 6 um for five adult infected leeches. Sections were stained in periodic acid Schiff's reagent and haematoxylin (PAS & Hx), haematoxylin and eosin (Hx & E) and Masson's trichrome. After examination, photomicrographs were taken by a digital camera (Canon G6) fixed on a binocular Zeiss light microscope.
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
- The fixed specimens were prepared according to the method of[19]. Specimens were cut at the xenomas level and stuck onto holders covered by double cellotape, then coated with approximately 100 Ao gold and viewed by stereo scanning electron microscope (JEOL TEM – T200) at the Electron Microscopy Unit (EMU) of Assiut University.
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
- The fixed specimens were washed in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 7.2 at room temperature. The specimens were post fixed in 1% buffered osmium tetroxide at pH 7.2 for 3 hours at 4℃. They were then dehydrated and embedded in Epon. Semithin sections of 1 um were cut and stained with toluidine blue for examination under light microscope. The xenomas were determined through the semithin sections. Ultrathin sections from selected areas of the trimmed blocks were made and collected in copper grids. The ultrathin sections were contrasted in uranyl acetate for 10 minutes, lead citrate for 5 minutes and examined under transmission electron microscope JEM, 100 C x 11 TEM, at the EMU, Assiut University.
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Account
- Family: Nosematidae Labbé, 1899Genus: Nosema Naegeli, 1857
3.2. Diagnosis
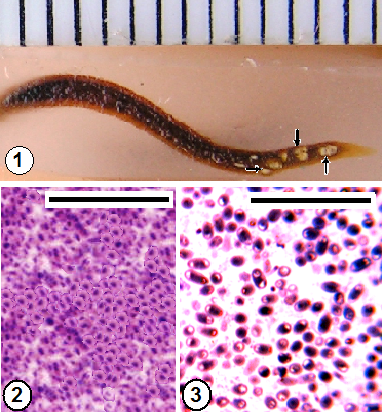
- Morphologically, by the characteristic white batches through the leech body (Fig. 1). Histologically, these batches appeared as capsules (xenomas) within the host's tissues (Figs. 8-11,13,18,19). Light and electron microscopy showed the presence of adult spores of the pathogen (Figs. 12,14,24). Elongated, oval spores appeared in smears (Figs. 2,3), SEM (Figs. 4,5) and TEM (Fig. 6). The unique structure of the polar filament with its coils and spore wall and other characteristics could be revealed through TEM (Figs. 6,7).
3.3. Infection (Fig. 1)
- Microsporidiosis was easily observed, by naked eye, at the characteristic white batches through the semitransparent leech body (Fig. 1). Infection occurred in the field during the cooler months (from December 2011 to February 2012) when water temperature was ranging from 10℃ to 21℃. The level of infection was low (% 3.4).
3.4. Spores (Figs. 2-7)
- Light microscopic examination of the fixed smears from the punctured batches showed numerous elongated oval mature spores of one type (Figs. 2,3). Scanning electron microscopy revealed that the surface of the spores seemed smooth, without sculptures (Fig. 4). All measurements recorded were the mean of 15 mature spores. TEM (Figs. 6,7) revealed enlarged spores measuring 3.5-5 x -1.5- 2 um, spore wall ~ 370 nm thick which was composed of electron dense exospore (~ 250 nm thick) and electron lucent endospore (~ 120 nm thick), polar filament having 13-15 coils in one layer all with the same diameter (isofilar type), anchoring disc; the site from which the unique filament protruded and injected suddenly within the victim's body and lamellate like structure polaroplast (Figs. 5,6). The diplokaryon occupied a position between the polaroplast and the posterior vacuole, surrounded by aggregate polyribosomes (Fig. 7). Absence of the sporophorous vacuole.
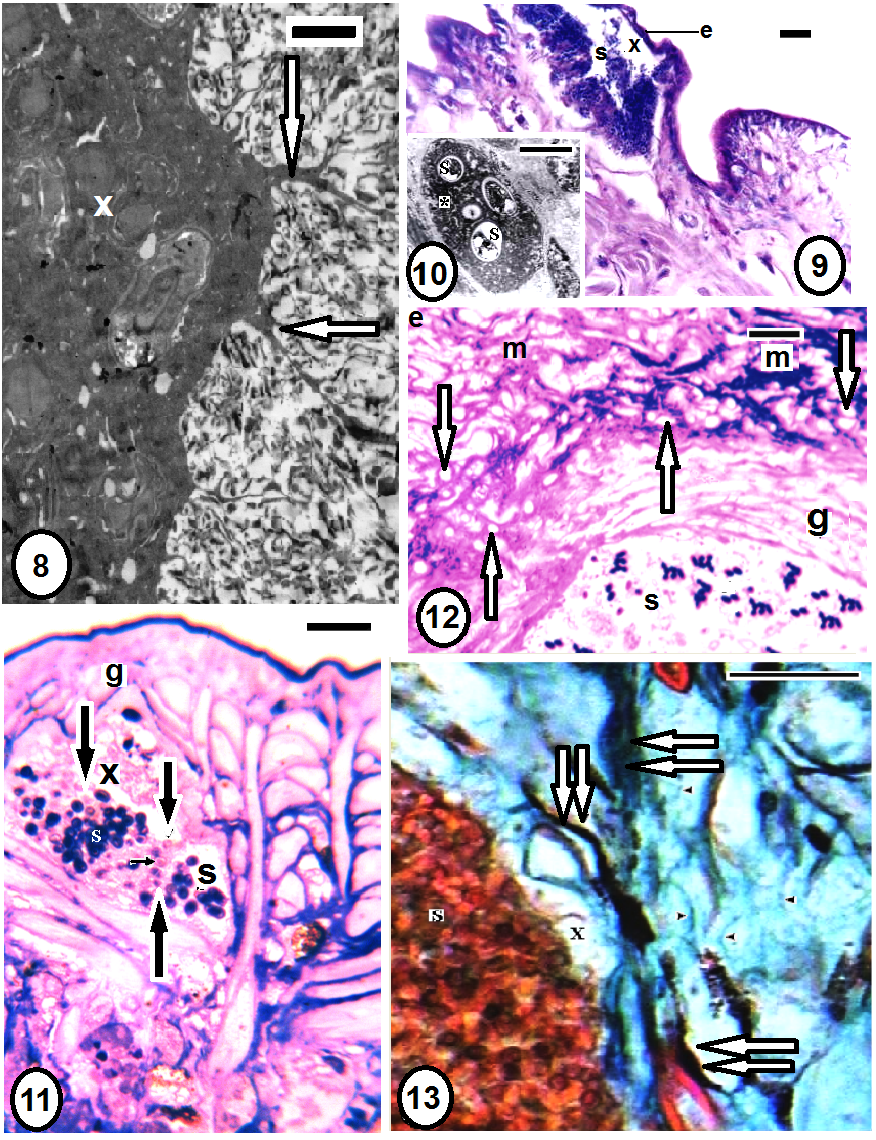
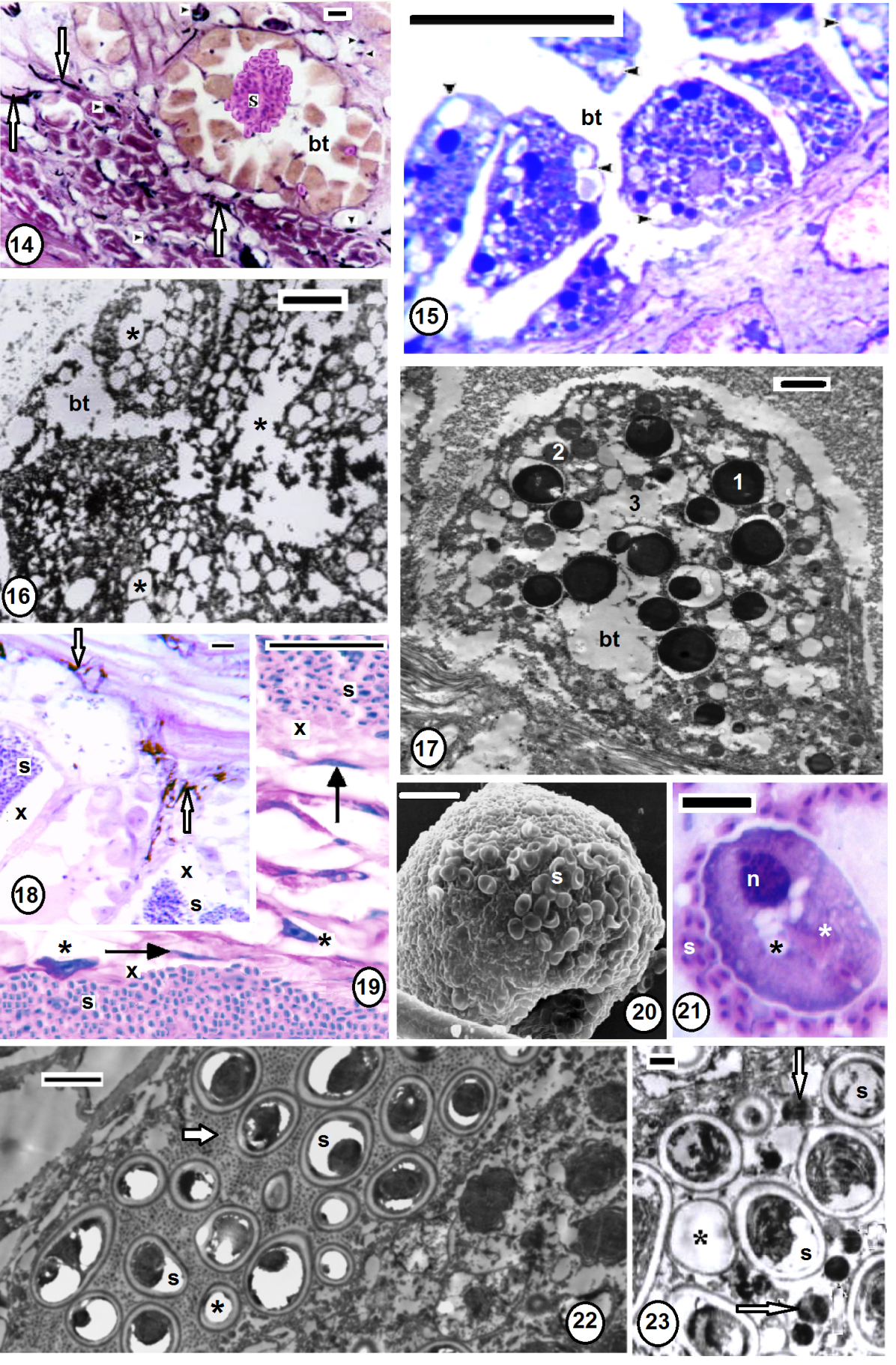
3.5. Histopathology (Figs. 8-30)
- Serial longitudinal paraffins, semi- and ultrathin sections revealed characteristic spore capsules or xenomas (Figs. 8,9,11) extending several branches towards the infected tissue. These xenomas enclosed numerous developmental stages of the pathogen. Spores were detected throughout various tissues of Babronia assiuti; within the epidermis (Fig. 9), the epidermal cells (Fig. 10), the botryoidal tissue (Figs. 14,24), in the muscular wall of the gut (Fig. 11), within the connective tissue (Figs. 18,19) and even within the lumen of the gut (Fig. 12). Both paraffin (Fig. 14) and ultrathin sections (Fig. 23) showed deep black or electron dense granules (granuloma) within the connective tissue. Some chromatophores (Figs. 13,14,18), fibrocytes (Fig. 19) and macrophages (Figs. 19-21) were observed external to the xenomas. Some discharged spores were also detected (Figs. 11,22,23). Semi thin sections showed numerous vesicles within the connective tissue (Fig. 12). Highly vesiculated cytoplasm in the botryoidal cells (Figs. 15,16,24) was detected compared to the normal structure with three types of secretions (Fig. 17). Fibrosis was also clear through fragmentation of the collagenous fibers, especially, near the xenomas (Fig. 13). Furthermore, semithin sections showed disorder in the arrangement of myofilaments of the striated cortex within the longitudinal muscle fibers (Figs. 24,25), besides hypertrophy and hypotrophy of the muscle cells (Fig. 25), compared to the normal muscle fiber (Fig. 26). Ultra thin sections revealed the healthy muscles were closely arranged in groups, in which each muscle was characterized by a striated contractile cortex close to the surrounding sarcolemma (Fig. 27). This contractile cortex was composed of sarcomeric units; each is demarcated by dot-like myofilaments (Fig. 28). Numerous mitochondria present in the muscle core. In the unhealthy muscles, the contractile cortex became reduced in size and the sarcomeric units appeared disintegrated (Figs. 29, 30). The muscle cell was hypertrophied with enlarged, lobed nucleus that occupied most of the muscle core (Fig. 29). Also, there were some empty muscle cells, in each, the sarcolemma was only found and the contractile cortex was totally disintegrated and disappeared (Fig. 25). Finally, necrosis was distributed throughout the whole body regions; the epidermis, dermis, muscle layers and even the gut wall were damaged (Fig. 12).
4. Discussion
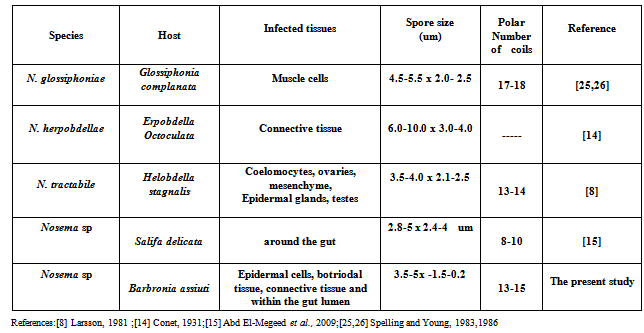
- Successive developmental stages of the current pathogen couldn’t be examined clearly, because of some technical problems, to detect its species. Therefore, identification was relied on the morphological and ultrastructural features of only adult spores according to Larsson[16,17] till genus level. The important morphological characters used for taxonomic purposes include: spore shape, one spore type, shape, number and location of the nuclei; shape and number of coils (isofilar type) in the polar filament, absence of the sporophorous vacuole and the new invertebrate host, besides the direct contact of the pathogen to the host tissue supported its assignment to the genus Nosema. The present spore wall appeared smooth, without sculptures either by light or electron microscopy. Other forms of spore surface have been recorded in various Nosema species, including smooth in N. lymantriae; wrinkled in N. bombycis, N. heliothidis, N. ploidae, N. tortricis[20]; smooth in N. blissi[21]; and rough in N. whitei[22]. The surface of N. tractabile, a pathogen of the freshwater leech Helobdella stagnalis, was slightly rough and without sculpturing[8]. The polar tube is an important diagnostic character among the microsporidia. The number of polar tube coils is shown to be different in the various species that were studied has been shown to vary from 12 in N. eurytremae[23] to 17-18 coils in N. heliothidis[24] and N. glossiphoniae[25,26]. In the present Nosema, polar filament having 13-15 coils in one layer. Table (1) summarized Nosema spp. that parasitized on leeches. The present pathogen was close to N. tractabile than both N. glossiphoniae and N. herpobdellae but different in shape, texture of the spore and host.
|
5. Conclusions
- Microsporidiosis was easily observed, by naked eye, at the characteristic white batches through the semitransparent body of the leech Barbronia assiuti. Current study showed that pathogen spores appeared monomorphic, diplokaryotic, apansporoblastic and 13-15 isofilar coils of polar filament. These characteristics helped in its displacement under the genus Nosema. Histopathology revealed migration of chromatophores, fibrocytes and macrophages around the xenomas. Fibrosis, granuloma and vesiculation could be detected within the infected botryoidal and connective tissues.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Sincere thanks are due to Prof. Dr. Larsson, Lund, Sweden for supplying evaluable references and advice for the current study and also, the reviewers’ suggestions to improve the manuscript.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML