-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2013; 3(5): 163-170
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20130305.01
Evaluation of Microbiological Quality of the Date Fruit Product “Btana” Produced in Adrar South Algeria
Abekhti A.1, 2, Zarour K.2, Boulal A.2, Benmechernene Z.2, Kihal M.1
1Department of Nature and life science, Univesity of Biskra, B.P. 145, R.P., 07000, Biskra, Algeria
2Laboratory of Applied Microbiology, Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Oran University, BP 16, Es-senia, 31100, Oran, Algeria
Correspondence to: Abekhti A., Department of Nature and life science, Univesity of Biskra, B.P. 145, R.P., 07000, Biskra, Algeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Dates, the fruits of date palm (PhoenixdactyliferaL.) are a vital element of the daily diet in the Arabian world. Dates over production needs to be transformed into local traditional products like “Btana”. Our study aimed to describe the dynamic changes of microbial and chemical parameters (pH, water content) of dates during transformation and storage period. Samples were collected from different processing and storage periods from 4 villages in Adrar province located at the south of Algeria. Microbial analysis showed that Lamaize raw dates recorded a high number of APc count (3.5 x 102 ufc/g). In addition Abani samples included a level of faecal coliforms (40 ufc/g) which were absent in other samples. API 20 E assay confirm the presence of Klebsiella (K.terrigena, K.pneumoniaandK.oxytoca) and Yersiniaenterocolica. At the end of the storage period, an important decrease in microbial population was recorded. The highest reduction of APc was observed in Mraguen sample (from 3,5x106 to 5x102 ufc/g ) during four weeks of storage. Fungal population significantly diminished at the fourth week of storage. Both pathogens and bacterial indicators detected on raw dates (S.aureus, faecal coliforms) were completely absent in the stored Btana.
Keywords: Date Fruit, Storage, Microflora, Quality, Indicator, Date Palm, Btana
Cite this paper: Abekhti A., Zarour K., Boulal A., Benmechernene Z., Kihal M., Evaluation of Microbiological Quality of the Date Fruit Product “Btana” Produced in Adrar South Algeria, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 3 No. 5, 2013, pp. 163-170. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20130305.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Dates, the fruits of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) are an important stable food in the diet of population living in the arid and semi-arid regions of North Africa, Middle East and South-Asian countries[1, 2]. Dates have a nutritional value contributing significantly to improve the diet of consumers, for that it is consumed widely and practically during the holy month of Ramadan, popular festivities, funerals and to welcome guests. This fruit is found to contain carbohydrates (44-88%), fats (0.2-0.4%), fiber (6.4-11.5%), minerals, vitamins and an interestingly higher concentration of protein (2.3-5.6%) compared with other major cultivated fruits such as apples, oranges, bananas and grapes that contain only 0.3%, 0.7%, 1.0% and 1.0% of protein respectively[3].So far, other investigations showed that date fruit contain many bioactive compounds like anthocyanins, carotenoids, phenolics, sterols, procyanidins and flavonoids, which are thought to have a beneficial effects on human health[4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14,11, 15].In Algeria, south regions count 18.7 million palm trees scattered over 169361 ha which produce almost 690,000 metric tons[16, 17]. However, 30% of the production of Algerian dates is characterized by a low commercial quality known as common cultivars[18, 19]. The local population has developed many kinds of date by-products like vinegar, flour, syrup, and juice to overcome post-production lost of the common cultivars not commercialized. Btana is a very popular traditional date's preservation methods which include the transformation of raw dates to paste, according to the local knowledge. After transformation, dates could be preserved up to two years in some regions. Recently, a prevailing trend is being stated to more natural and traditional products in consumer’s hobbies and local foods have gained more importance. Several studies were carried out to describe the mode of preparation of these foods[20, 21, 22]. Some authors shift the emphasis on the safety of these foods, the microbial dynamic lengthwise their preparation, storage period as well as the impact on the food quality[23, 24, 25, 26, 27]. However, there are a few previous studies concerning microbial quality of dates and their by-products[1, 28]. So far, hitherto no previous microbial study was consecrated to Btana and its indigenous microflora. The objective of the present study is to screen the microbial quality of Btana, and identify the dominant microflora during its preparation and storage. pH and water content survey were also performed during Btana preparation as they imply Btana quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Date Fruit
- A total of 30 samples of Hmira cultivar were collected from five villages in Adrar (South of Algeria): Abani, Mtarfa, Mraguen, Sali, and Lmaise. Sampling was performed during processing satges: before transformation of crude dates, immediately after preparation of the fresh paste and at different intervals each week in a span of one month of preservation (7, 14, 21, and at 30 days). Samples were collected in sterile bottles, labelled and transported to the laboratory for analysis.
2.2. Chemical Analysis
- Water content and pH were determined according to[29, 7]. pH was determined at 25°C by using a pin electrode of a digital pH-meter (Hanna 210, Limena, Italy). For water content determination, two batches composed of 10 g of dates were weighed and dried at 105°C in furnace till reaching a fixed dry weight, then water content was determined on a fresh weight basis[30].
2.3. Microbial Analysis
- After sampling, 25 g of dates were aseptically mixed with 225 ml of diluents (0,1% tryptone, 0,85% NaCl) in a sterile stomacher bag and homogenized by a StomacherLaboratory-blender. Then serial 10 fold dilutions were prepared according to ISO, NF ISO 6887-1:1999 recommendations [31]. The number of viable microflora in dates and Btana samples were obtained by serial pour or spread plating dilutions according to standard methods on appropriate selective media. Results were expressed as colony forming units per gram (cfu/g) and reported as log ufc/g to facilitate reading.Total aerobic counts (APc) were enumerated on plate count agar (PCA) by pour-plating of 1ml of dilutions in duplicate; plates are incubated aerobically at 30°C for 72 h[32]. Coliforms, were enumerated by pour plating of 1 ml of dilution in duplicate on Petri dishes of violet red bile lactose agar (VRBL). The plates were overlaid with 3-4 ml of VRBL, and incubated at 37ºC for total coliforms and at 44°C for faecal coliforms for 24h. Staphylococcus aureus were counted on Baird Parker medium supplemented with a sterile emulsion of Egg Yolk and potassium tellurite solution[33]. Enterococci were determined by spread plating of 0.1 ml of correspond dilutions on Slanetz and Bartley (SB) agar Petri dishes, incubation is carried out at 42°C for 48 h[34]. Sulphite-reducer Anaerobic microorganisms were determined by cultivation of 1ml of dilutions (previously heated at 80°C for 10 min and rapidly cooled to room temperature) in tube (18 ml); then 17 ml of meat-liver agar supplemented with iron citrate and sodium sulphate were added[32]. Moulds and yeasts were counted by surface cultivation on OGA (Oxytetracycline-glucose agar) containing 10 µg/ml of oxytetracycline. Plates were incubated aerobically at 25°C for 5 days[35].
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analysis
- Changes in pH values are described for each sample in Fig 1. Raw dates destined for transformation to Btana are weakly acid, with a pH ranged between 5.46 and 5.84. As shown in table.1, pH had been increased by 0.14, 0.22, 0.10 unit in Lmaiz, Abani, and Mtarfa samples respectively at the beginning of transformation. However, in Sali and Mraguen pastes the pH was decreased by 0.04 and 0.08 units respectively. Survey of pH evolution through preservation period limited at four weeks showed a pH regression which was accelerated with age of Btana. After the first week, pH had been significantly regressed; Mraguen sample exhibited the faster reduction of pH value by 0.91 U (5.83 to 4.92). After the second week of storage, pH continued to decrease gradually. At the last week of storage, Abani sample reached the lowest values of pH (4.90) comparing with other samples. However Mraguen sample record the most reduction rate (0.91 U) in comparison with initial pH.
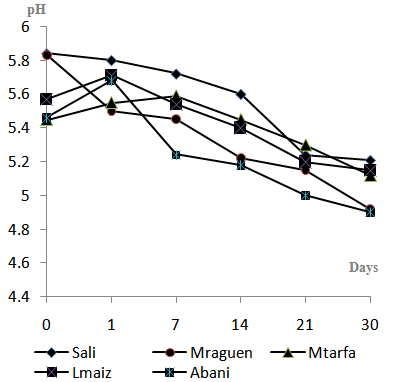 | Figure 1. pH evolution during Btana preparation and 30 days of storage |
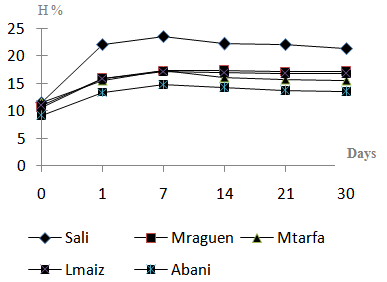 | Figure 2. Water content (H%) evolution in dates and Btana samples during four weeks of storage |
|
3.2. Microbial Analysis
- Microbial analysis, of raw dates and the Btana made of after transformation and during four weeks of storage are are presented in Table 1.Total coliforms were present in all raw dates. In addition Abani samples included faecal coliforms (1.60 log ufc/g) which is mostly the same number recorded for total coliforms. Identification of five total coliforms from Abani sample using API 20E assay showed the presence of three species of Klebsiella (K. Terrigena (2), K. pneumonia, K. oxytoca) and Yersinia enterocolitica. Enterocci were detected in Abani, Lamaize and Sali samples. Fungi microflora is found in a substantial number in all samples, it ranges from 2.36 log ufc/g to 5.18 log ufc/g.Transformation to Btana had influenced markedly the initial microbial load present in raw dates which was drastically decreased. A high decrease (-98.86%) was shown in fungi microflora practically in Abani Btana that had recorded the highest rate of regression. The other samples have recorded the same decline; Sali (-90.25%), Mraguen (-72.30%), Mtarfa (-47.82%). A similar decrease was observed in APc by more than 50% in Abani, Sali, Lmaize and Mtarfa Btana, and about 31.72 % in Mraguen samples. In the same way, the other microbial populations were remarkably reduced. However, Entercocci and total coliform were increased by +72.78% and +56.66% in Abani and Mtarfa samples respectively. By far, S. aureus found in Sali and Abani dates were despaired in Btana samples. During the next weeks of storage, more regression was stated on APc and fungi microflora while Enterococci, total coliform, and fecal coliform, were totally eliminated by the second week of storage in four samples. Nevertheless, Sali Btana showed a slight recrudescence in fungi flora which might be resulted from reactivation of some spores after culture on PDA medium.At the end of the limited storage period, microbial analyses showed an important decrease in number of microbial population in comparison of their initial load, for these reasons this method was useful and effective in the decrease of initial Abani’s dates APc from 7.27 log ufc/g (5.23x107 ufc/g) to 4.72 log ufc/g (5.3x 104ufc/g), with a rate of 99.98%. Other samples had recorded a higher reduction rates with 99.99, 99.98, 99.98% for Mtarfa, Lamaize, and Mraguen Btana respectively. The lowest reduction rate was recorded in Sali samples with 40.36% only. In the other hand, Fungi had been significantly diminished at the fourth week, the high rate of reduction was observed in Abani and Mraguen samples (99.99%). Pathogens and indicators of poor hygiene detected on raw dates (S. aureus, faecal coliform, Entercocci) were totally eliminated in the stored Btana.
4. Discussion
- Because of the paucity of studies on this kind of preservation methods, we have followed approach already used by many authors that investigate effectiveness of traditional preservation methods[36, 21, 37, l, 20 27, 38, 39]. It should be noted that, since preparation of Btana is related to people knowledge, it could be found some differences in conditions under which Btana was carried out, even so results of analysis should be affected by the manner of handling and preparing process. The previous results indicates that date’s pH vary widely among the raw dates analysed that belong to the same cultivar. This variation could be attributed to their origins which could be influenced by type of soil, mineral availability, fertilisers’ application and quality of irrigation water[40]. In addition, according to[41] pH of dates vary also with the amount of organic acids (citric, malic and oxalic acids) and residues of polyphenol in fruits. In quality order; Mtarfa, Abani and Lmaize dates are considered acceptable. Sali and Mraguen dates are of best quality (5.84, 5.83) respectively according to[30].The pH decrease in Btana during storage can be explained by the microbial activity of epiphytical microflora which hydrolyse and convert carbohydrates under anaerobic conditions into organic acids that reduce pH. In other hand, differences in pH measured could be due to the number and diversity of the initial microflora that affect the final pH of product[42]. However, there is no correlation between the number of initial microflora and the final pH, due probably to heterogenic distribution of microorganisms responsible of acidification. The final measure of pH at the fourth week showed that it had a low value which contributed to low water activity of dates in order to prevent and decrease the activity of spoilage’s microorganisms Depending on moisture content, raw dates studied, are classified in semi-dry varieties according to[43, 1, 44]. The low level of water content recorded in raw dates is due to dryness effect resulting of the long period of storage after harvest which can reach several months after harvest in some regions. Dates are generally stocked in perforated alpha bags that facilitate continued dehydration of dates. Variations observed in moisture content among samples of the same variety which were grown in the same region have already been reported by different authors and could be attributed, to harvest and post-harvest treatments[41, 45, 46]. Determination of water content has two principal objectives; one is technologic that informs us about dates’s behaviour during transformation process and storage period. The second objective deals with the safety of Btana as it is known that water content has an effect on microbial community growth[47]. It was reported that dates have a very high sugar concentration which gives them a hygroscopic character leading to retain water away from microbial activity. This character is already used in preservation of many food products[49, 48, 50]. Water activity (aw), derived from water content is the best parameter used to determine the availability of microbial growth in foods, therefore many authors had established a strength relation between aw and moisture content[49, 51]. We have focused on this parameter in our study. During Btana preparation dates are soaking in water to eliminate contaminants and to improve their organoleptic quality by softening hardness. Therefore, water content has risen remarkably after transformation. Nevertheless, storage under dry condition allows water content to decrease gradually. The slight increase seen in Mraguen and Abani samples could be attributed to the continued solubilisation of date components.As storage progress, Btana become more compact and thus ready for consumption. Differences encountered in water content variation are due to absence of standardisation on the amount of water to be used for date transformation, also no precise water/date ration (v/w) is recommended in Btana preparation. To appreciate microbiological quality of food, microbiologists consider that count of APc is a reliable measure that indicates the degree of pollution[52, 53, 54]. Diawara et al pointed out that fruits are always bearer of a high number of microorganisms in all geographic area and climatic conditions before and after harvesting[55]. Contamination of date’s fruit takes place mainly through the outlet cortex of fresh date that is contaminated by fungi and bacteria during the stage of maturation as so as during post-harvesting operations. Material and recipients used during this operation such as bags of storage and transport are also an origin of this fruit's contamination[28, 1,56, 57, 58, 59].In our study, the high number of APc (7.22 log ufc/g) occurred in Abani raw dates was due to a particulate dryness mode practiced in this village; commonly dates are buried under sunned sand for few days to accelerate dehydration process. Under such conditions, telluric microflora associate dates by a direct contact with sand. It is clear that all raw dates' samples are polluted and not suitable for direct consumption since they present more than 3 105ufc/g of APc, which is the limit concentration acceptable in foods[28]. In view of this funding citizens are induced and advised to improve raw date’s quality by using a clean material in harvest and post-harvested operations.Furthermore, microbiological analysis revealed that raw dates destined for Btana preparation and transported under low hygienic measures, had a high level of coliforms. The presence of coliforms in dates was already reported by[60] who investigated a number of Saudi dates. However sulphite-reducing clostridia are absent in all samples, and the only pathogen detected is Staphylococcus aureus, relatively in a low counts in Sali and Abani samples. The presence of such pathogen in dates indicates a human contamination across corporal hygiene contamination.A high number of fungi have been detected in the studied samples. Many authors revealed that yeast and moulds are the common contaminants of dates. These fungi included Aspergillus sp., Stemphylium botryosum, Phomopsis diopspyri, Cladosporium sp., Citromyces ramosus, Macrosporium sp., Alternaria sp. and Penicillium[61, 62]. These fungus attack fruits at the early stages of maturation, but at Tamar stage their number decreased and only xerophilic fungi as Catenularia fuliginia are able to grow on dried dates. So far, in south of Algeria, precisely in Adrar city; the harvest of dried date named locally (Algataa) is practiced during autumn season which is characterised by powerful winds that participate in spore dissemination. Raw dates destined for Btana preparation are in most cases soaked in hot water (approximately 70°C) for the softening's date hardness that result consequently in reducing the initial microbial load by a thermal choc. This has been observed by the recorded regression in microflora on Sali, Lmaize, Mraguen fresh paste samples (Table.3). However, an increase was observed in enterococci and coliform in Abani and Mtarfa fresh paste samples respectively. This can be explained by the poor quality of water used in cleaning and soaking dates. Or to its insufficient sterilizing temperature. Quality of material used during this operation is also a doubt factor in microbial paste quality. During preservation period the observed regression of microbial microflora could be resulting from gradual decrease of pH (Table.1). In these conditions microorganisms spend energy for expulsing the extra protons from their cytoplasm in order to uphold the internal pH, but it should maintain by the same way its haemostasis damaged by osmotic pressure induced by high sugar content in dates[63]. These two microbial processes were assisted by spending much energy that slow down microbial growth in the first time and when taking a long stage lead to death as microorganisms could not supply the necessary energy requited to enhance pH and haemostasis stability[17]. Furthermore each decrease in pH of the medium result an increase of the inferior limit of aw that permits an optimal microbial growth, equally a slight decrease in aw increase the value of pH optimal to growth. Some authors explain this by increasing of water stress at the lower aw[64]. It seems that in Btana the value of these two factors are sufficient to prevent development of most bacteria during preservation. Furthermore weak acids were studied for their possibility of use as antifungal preservatives in low-acid intermediate moisture food since it is known that weak acids have a high antimicrobial activity in their undissociated form[64]. So far[65] demonstrated that dissociated forms of weak acids such as sorbic acid can exhibit an antimicrobial activity particularly towards fungi populations. Their antimicrobial activity is observed in low-acid food (pH > 4.6) when the dissociation is incomplete with a substantial amount existing in a dissociated form[64]. Moreover it has been demonstrated that most microorganisms are neutrophilic and are unable to grow when the pH is below 6.6 to 6.8 or to proliferate when aw is reduced below 0.8[63, 66]. But when these two factors are combined in the same food, microbial effect would be added while many authors confirmed that the combination of two factors of inhibition assures microbial food safety, improve quality stability and increase preservation period[67]. The persisted microflora detected in Btana samples would be composed of osmophilic yeasts and bacteria that could resist to theses harmful conditions and are able to growth at low aw[66, 67].A sample examination of this traditional storage method, demonstrate that the main principles of preservation is due to the date paste high sugar content, low moisture content (related to aw), low pH, anaerobiosis and the high osmotic pressure, which are eventually responsible for elimination of the most microflora existed previously on raw dates. Beyond these mentioned abiotic factors, some biotic agents could be efficient to control microbial growth in dates. Antimicrobial molecules present naturally in dates or those derived from medicinal plants suspended over date pastes during preparation are thought to be a part of the preserving parameters. Frequently, citizens used a mixture of additives composed of medicinal plants as basil (Ocinum basilicum), Juniperus (Juniperus phonicea), Rosemary(Rosmarinusofficinalis), Artemisia (Artemisia vulgaris) which exerted an antimicrobial effect. The activity of these medicinal plants wasn’t assayed in this work, however many previous studies reported their effectiveness on improving food safety and overall microbial quality[68]. Mrabet et al determined the antimicrobial effect of Juniperus phonicea on traditional date past named (Reffis). They observed a significant decrease (66 %) of moulds and yeasts after 45 days of incubation[28].
5. Conclusions
- The results presented in this study reveal effectiveness of this traditional method in preserving dates and valorise indigene knowledge for maintaining a stable and safe food source over the year, however many factors might play probably a key roles in preservation. According to our quest, Btana is prepared in many regions of Adrar by a variety of ways and means thus there is diversity in effectiveness with respect to the area of production. In other hand the handling of making Btana could represent an important and efficient tool to control quality of commercialized dates and to preserving their typical character. Therefore further investigations should be envisaged for highlight interactions existed between factors including climatic conditions, chemical composition of date paste, and active compounds found in medicinal plants for improving the quality and safety of these traditionally made food. Future works should also focus on characterization and identification of dominant microflora and substances that could contribute to control of initial microbial population.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML