-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2013; 3(1): 43-52
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20130301.07
Lipolytic Activity of some Strains of Klebsiella, Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus Spp. from Restaurant Wastewater and Receiving Stream
Odeyemi A. T. 1, Aderiye B. I. 1, Bamidele O. S. 2
1Microbiology Department, Ekiti State University, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
2Biochemistry Department, Federal University of Technology Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Odeyemi A. T. , Microbiology Department, Ekiti State University, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The tendency of some lipolytic bacteria isolated from restaurant wastewater and the receiving stream to biodegrade/utilizes fresh palm oil was investigated. Thirty two (32) lipolytic bacteria isolates were identified and grouped into six genera namely; Enterococcus, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Serratia and Staphylococcus. The weight of these isolates after 24h of inoculation ranged between 0.33 and 0.60mg, whereas the final weight on the 12th day of incubation was between 0.25mg and 0.51mg. Generally, the optimum growth in all the thirty two (32) lipolytic isolates in the fresh oil was observed between the fifth and seventh days. The growth rate per day were 0.02mg in Pseudomonas sp. (n); 0.03mg in Klebsiella sp. (m); 0.04mg in Pseudomonas sp. (j); 0.04mg in Staphylococcus sp. (r); and 0.05mg in Staphylococcus sp. (p).The appreciable enzymatic activity of these microbes ranged; Lipase (0.036 - 0.073 mM/min/ml) with Pseudomonas sp. (n) shown a highest lipase activity (0.073 mM/min/ml) after 12h, protease (50 - 117mM/min/ml) and amylase (7.7 - 117mM/min/ml). It appears that bacteria associated with dietary oil-rich wastewater are the novel source of environmental enzymes for possible commercial applications and may play an important role in enzyme-catalyzed organic matter cycling in domestic environments.
Keywords: Lipolytic Bacteria, Restaurant Wastewater, Palm Oil, Receiving Stream
Cite this paper: Odeyemi A. T. , Aderiye B. I. , Bamidele O. S. , Lipolytic Activity of some Strains of Klebsiella, Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus Spp. from Restaurant Wastewater and Receiving Stream, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 43-52. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20130301.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Lipids are one of the most important components of vegetable oil, many synthetic compounds, and emulsions are found in many pharmaceutical and cosmetic industrial effluents and municipal wastewater[1; 2]. Palm oil, obtained from the fruit of the oil palm tree, is the most widely produced edible vegetable oil in the world and its nutritional and health attributes have been well documented[3]; surpassing soybean oil as the most widely produced vegetable oil in the world[4]. It is consumed worldwide as cooking oil, in making of margarine and shortening, apart from being used as an ingredient in fat blends and avast array of food products[5]. The amount of lipid in municipal wastewater is approximately 30-40% of the total chemical oxygen demand [2].Wastewaters containing fat and oils were traditionally treated physically, which is currently considered insufficient if the fat is in its dispersed form. Biological treatment has been found to be the most efficient method for removing fat, oil and grease by degrading them into miscible molecules[6]. Therefore, manipulation of microorganisms for treatment and bioremediation purposes afford a very efficient tool for purifying contaminated effluents and natural water[7]. The use of lipase enzymes that are produced by all organisms may solve the problem, where they catalyze the synthesis or hydrolysis of fat[8].[9] evaluated a mixed culture composed of P. aeruginosa LP602, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus LP009 (both lipase – producing bacteria) and Bacillus sp. B304 (an amylase and protease producing bacterium) to lower the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) value and lipid content of lipid-rich wastewater. Lipolytic enzymes are currently attracting enormous attention because of their biotechnological potential[10]. Among bacterial lipases, attention has usually been focused on particular classes of enzymes such as the lipases from the genus Pseudomonas, which are especially interesting for biotechnology[11]. Hence, the present work aims at investigating the biodegradability potential of some lipolytic bacteria cells in decomposing/utilizing the dietary oil as a substrate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Wastewater Samples
- Wastewater and water samples were obtained from different sampling points between Falegan restaurant and the receiving stream as follow:D1 - Wastewater sample obtained at the exit of drain pipe from the wash hand basinD2 - Wastewater sample from the drainage at a distance of 5 meters from the exit of the drain pipeD3 - Wastewater sample from the stream at the point of entry of effluent into the stream from the drainage (at a distance of 10 meters to D2)U1 - Water sample from the stream at 5 meters upstream from the point of entry of the effluent into the stream from the drainageU2 - Water sample from the stream at 10 meters upstream from the point of entry of the effluent into the stream from the drainageS1 - Wastewater sample from the stream at 5 meters downstream from the point of entry of the effluent into the stream from the drainageS2 - Wastewater sample from stream at 10 meters downstream from the point of entry of effluent into the stream from the drainageThese samples were collected using 250ml sterile sampling bottles and immediately transported in ice buckets to the Microbiology Laboratory of Ekiti State University, Ado-Ekiti for further work.
2.2. Bacteriological Analysis
- One millilitre of wastewater sample was inoculated and incubated on plate count and MacConkey agar media at 25℃ and 37℃ respectively for 24h. Pure colonies of bacteria isolates were later inoculated on sterile Tributyrin agar and incubated at 37℃ for 24h. Lipolytic activity of bacteria cells were confirmed by zone (s) of clearance around their growth.
2.3. Characterization and Identification of Isolates
- The isolates were classified on the basis of their biochemical, physiological and morphological characteristics and matched against standard microbial cultures[12; 13].
2.4. Bio-degradative Activity of Bacteria Isolates
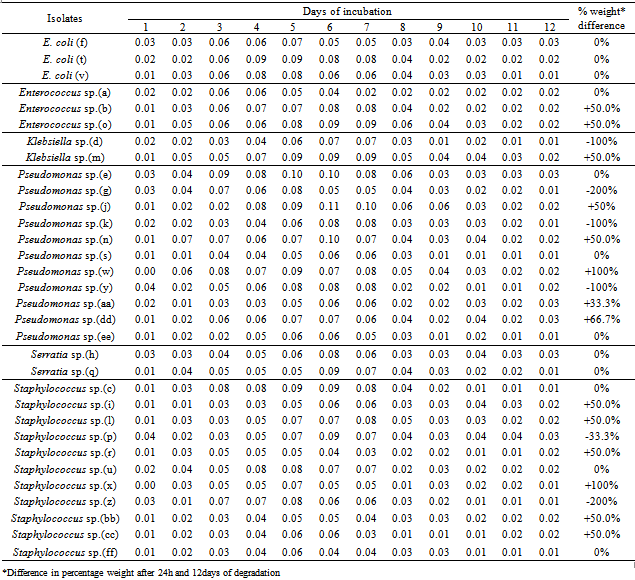
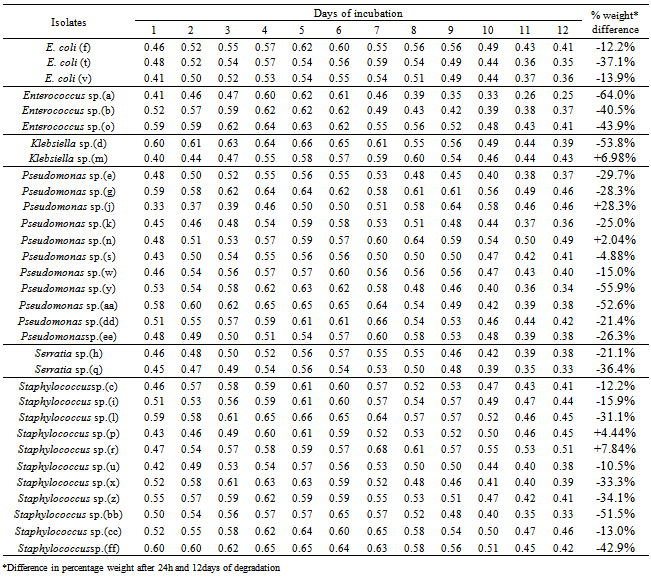
- Fresh palm oil was elucidated with diethyl ether (1:1; v/v) and filtered through non-absorbent cotton wool. A known quantity (1.8ml) of the oil was inoculated with 0.2ml of standardized inoculum of lipolytic bacterial isolates and incubated at ambient temperature over the period of 12 days. The rate of degradation of the dietary oil was monitored by determining the total dry weight of the microbial cell[14].
2.5. Preparation of Wastewater and Fresh Palm Oil for Enzyme Activity
- Wastewater treatment was done by distributing wastewater into five portions of 100 mL each contained in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks followed by inoculating 1 mL of each bacterial culture (OD600∼2:0) into wastewater sample contained in each flask. The flasks were kept in shaking incubator at 30℃ with 150 r.p.m. Samples were drawn from each of the flasks at intervals of 6 h for a period of 48 h and later centrifuged at 5000 x g for 30 minutes at 4℃. Cell free supernatant corresponding to growth phase was used as the crude enzyme for assay and further analysis. Also, Palm oil-containing medium were prepared with 0.2% w/v palm oil, 1.5% K2HSO4, 0.05% MgSO4, 1.0% (NH4)2SO4, 0.2% CaCl2, 0.2% FeSO4 and 0.5% yeast extract, distributed, inoculated and incubated as in the wastewater culture.
2.6. Amylase Assay
- Amylase activity was assayed[15]. Briefly, 0.5 mL of properly diluted enzyme was added into a tube containing 1.5 mL of 2 % (w/v) of potato starch solution and 1 mL of 0.05 M acetate buffer, pH 5.0. The reaction mixture was incubated at 40℃ for 15 min. Then, 1 mL of the mixture was transferred to a new tube containing 1 mL of 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid and kept in boiled water for 10 min. The color density was determined spectrophotometrically at 520 nm. One unit was defined as 1 µmol of glucose released per minute by 1 mL of enzyme.
2.7. Lipase Assay
- The crude enzyme preparation was the culture broth after separation of cells and particles. The enzyme was normally stored at 4℃ until used. Lipolytic activity was determined by colorimetric method based on the activity in cleavage of p-nitrophenylpalmitate (p-NPP) at pH 8.0[16]. The reaction mixture contained 180 µL of solution A (0:062 g of p-NPP in 10 mL of 2-propanol, sonicated for 2 min before use), 1620 µL of solution B (0.4% triton X-100 and 0.1 % gum Arabic in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0) and 200 µL of properly diluted enzyme sample. The product was detected at 410 nm wavelength after incubation for 15 min at 37℃. Under this condition, the molar extinction coefficient (410 nm) of p-nitrophenol (p-NP) released from p-NPP was 15000 M−1. One unit of lipase activity was defined as 1 µmol of p-nitrophenol (p-NP) released per minute by 1 mL of enzyme.
2.8. Protease Assay
- Protease activity was determined[17]. 1 mL of 1.5 % casein solution, pH 7.0 was placed at 37℃ and, then, 1 mL of properly diluted enzyme sample was added. The reaction was incubated for 10 min prior to the addition of 2 mL of 0.4 M trichloroacetic acid. The solution with precipitates was altered and to 0.5 mL of the clear filtrate 2.5 mL of 0.4 M Na2CO3 and 0.5 mL of Folin reagent were added. After further 10 min of incubation, the color density developed was determined at 660 nm. One unit was defined as 1 µmol of tyrosine released per minute by 1 mL of enzyme.
2.9. Protein Determination
- Protein concentration was determined using the Lowry method[18]. Reagent A: 2% NaCO3 in 0.1 N NaOH; Reagent B: 0.5% CuSO4.5H2O in 1% Na or K tartarate; Reagent C: 100ml of Reagent A + 2ml of reagent B and Reagent E: 1:2 dilution of John’s reagent water. Graded concentrations of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) in tubes were prepared. Then 0.3 ml of each concentration was measured into test tubes. 3 ml of reagent C was added, mixed and left for 10 min. Then 0.3ml of reagent E was added, mixed and left for 30 min. The optical density was read at 600nm. The graph of OD versus concentration of BSA was obtained and standard curve of BSA. The same was done for unknown substance and the protein concentrations from the standard curve are read off and obtained by multiplying with dilution factor. All readings were obtained in triplicates.
3. Results and Discussion
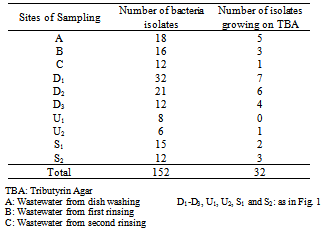
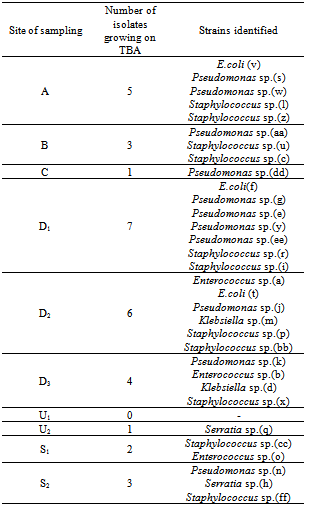
- One hundred and fifty two bacteria isolates were obtained from the wastewater and the receiving stream. Only thirty two of these microbes were lipolytic in nature (Table 1). There was a reduction of about 67% of the initial number of microbial isolates after the second rinsing of the dishes (C), which may be as a result cleansing ability of combined action of water and detergent. This support the findings of[19] who reported that, washing and sanitizing treatment can play an important role in reducing microbial populations on fresh fruits and vegetables. However, this number increased about three folds at the exit of the restaurant. This may be as a result of drained wastewater having contact with the soil already contaminated with decomposed waste foods dumped nearby which may be source of nutrient for the organisms along the drainage. Microorganisms abound in the soil and are critical to decomposing organic residues and recycling soil nutrients. Since most bacteria live under starvation conditions or water stress in the soil, they have adapted to quickly reproduce when water, food, and the environmental conditions are abundant. Bacteria populations can easily double in 30 minutes[20].
|
|
|
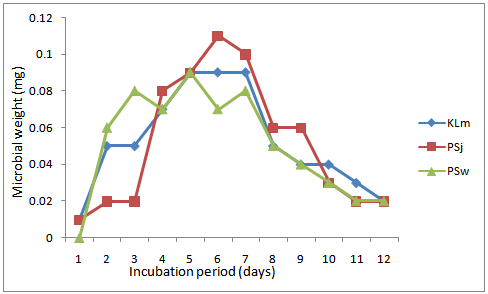 | Figure 1. Growth of selected most effective lipolytic bacteria isolates in oil-rich wastewater |
|
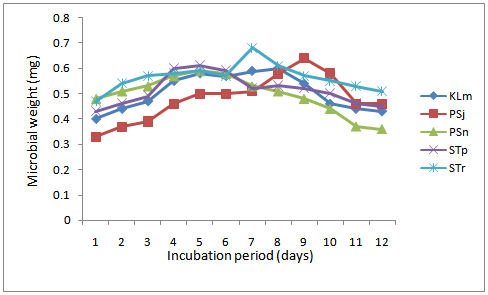 | Figure 2. Growth of selected most effective lipolytic bacteria isolates in fresh palm oil |
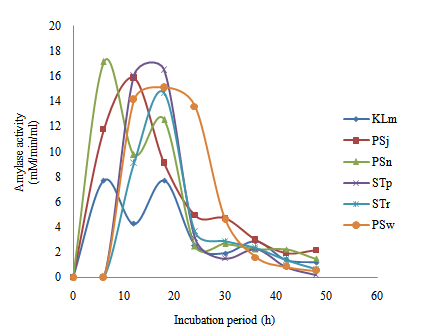 | Figure 3. Time course of extracellular microbial amylase production and activity in wastewater from restaurant |
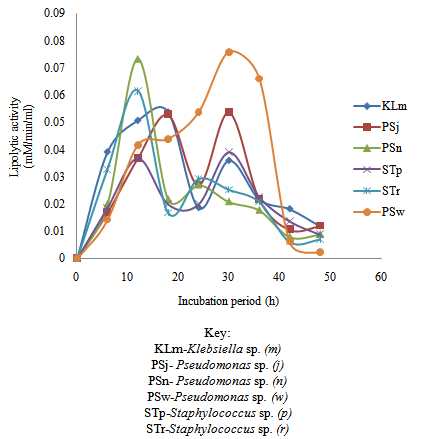 | Figure 4. Time course of extracellular microbial lipase production and activity in wastewater from restaurant |
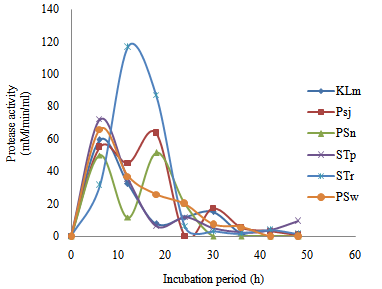 | Figure 5. Time course of extracellular microbial protease production and activity in wastewater from restaurant |
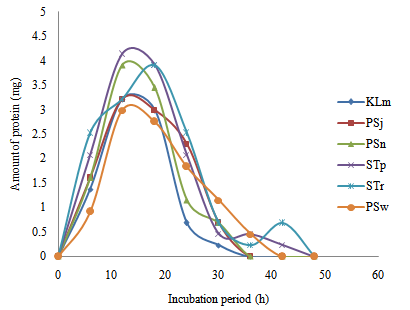 | Figure 6. Time course of extracellular microbial protein production in wastewater from restaurant |
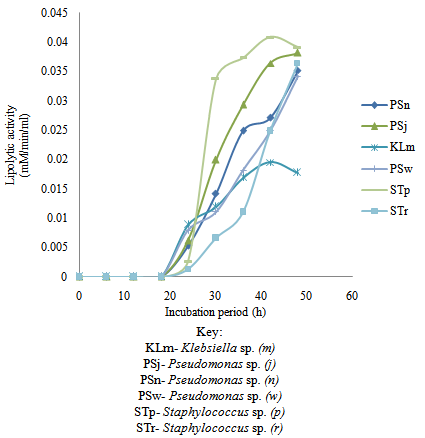 | Figure 7. Time course of extracellular microbial lipase production and activity in palm oil-containing medium |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML