-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2013; 3(1): 11-18
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20130301.02
Characterization of Vibrio Isolates from Carpet Shell Clam (Ruditapes Decussatus) Suffering from Brown Ring Disease (BRD) on Tunisian Coasts
Monia El Bour 1, Fatma Lakhal 1, Radhia Mraouna 1, Annick Jacq 2, Christine Paillard 3, John Klena 4
1Laboratoire de Pathologie, Institut National des Sciences et Technologies de La Mer (INSTM), 2025, Salammbô, Tunisie
2Institut de Génétique et Microbiologie, Université Paris-Sud, CNRS, Orsay, France
3LEMAR UMR, Institut Universitaire Européen de la Mer-CNRS, Plouzané, France
4U.S. Centers for Disease, AU1 Control and Prevention, Unit 7300, Box 0066, DPO AP, US
Correspondence to: Monia El Bour , Laboratoire de Pathologie, Institut National des Sciences et Technologies de La Mer (INSTM), 2025, Salammbô, Tunisie.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
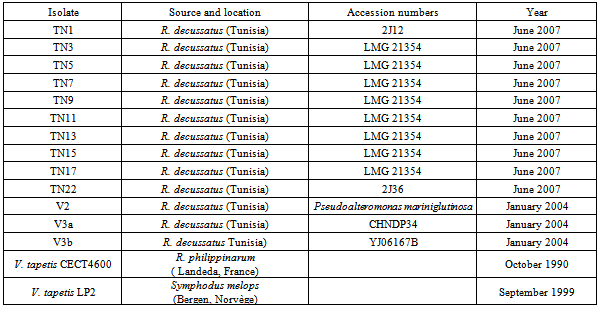
A total of 13 pathogenic Vibrio spp. bacteria were isolated from carpet shell clams (Ruditapes decussatus) with Brown Ring Disease (BRD) in Tunisia. Organisms were identified based on a combination of phenotypic and molecular methods (SSP-PCR and 16SrDNA sequencing). Virulence effects were determined by in vivo testing on R. decussatus and in vitro testing on the Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum). All isolates demonstrated biochemical profiles typical of Vibrio spp; nine different biotypes. Three isolates were identified as V.splendidus biovar II TAE2 but the remaining isolates fell into eight biotypes different from each other and from the V.tapetis biotype. Species delineation based on 16S rDNA sequencing indicated that the isolated Vibrio spp closely resembled V.chagasii (eight isolates), V.splendidus (two isolates), V.alginolyticus(one isolates), Psychrobacter spp. and Pseudoalteromonas mariniglutinosa (one isolates for each). In vitro cytotoxicity effects and mortalities could be induced by the isolates of V.chagasii, V.splendidus and V.alginolyticus at lower dosages than induced by V.tapetis (CECT4600).
Keywords: Vibrio, Brown Ring Disease, Biochemical Profiles, Sequencing, Toxicity, Ruditapes decussatus, Ruditapes Philippinarum
Cite this paper: Monia El Bour , Fatma Lakhal , Radhia Mraouna , Annick Jacq , Christine Paillard , John Klena , Characterization of Vibrio Isolates from Carpet Shell Clam (Ruditapes Decussatus) Suffering from Brown Ring Disease (BRD) on Tunisian Coasts, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 11-18. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20130301.02.
1. Introduction
- Many bacterial diseases in adult bivalves are caused by organisms in the genus Vibrio (Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria) that are widespread in coastal and estuarine environments ([6],[20],[23],[33]). Recent data have shown an expansion in the host range of aquatic organisms affected by pathogenic Vibrio species; these are primarily bivalve invertebrates ([7],[11],[27]). In addition to bivalve bacteriosis, Brown Ring Disease (BRD), a disruption of the periostracal lamina with abnormal conchiolin deposition, which affects mainly the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum and the carpet shell clam Ruditapes decussatus. Infections of BRD have been documented in wild populations and cultured clams isolated from waters around France, England, Ireland, Spain, occasionally in Italy and even in Korea ([2],[33],[35],[37]). In most reports of BRD contaminations, Vibrio tapetis bacteria have been identified ([2],[10],[30]). V.tapetis – like organisms, such as those identified in[35], have also been reported as causing BRD in Manila clams in Korea. BRD could be induced by exposing stocks of Manila clams to V. tapetis[13], resulting in high mortality. However, the number of Vibrio species negatively impacting R. decussatus and R. philippinarum has increased to more than 12 species, including Vibrio alginoyticus and the Vibrio splendidus clade ([7],[8],[9]). Vibrio splendidus and related species Vibrio celticus, Vibrio tasmaniensis, Vibrio neptunius and Vibrio furnissii have been characterized as pathogen inducing mortalities for a number of bivalve species including R. phillipinarum, Venerupis pullastra, Mya arenaria and Meretrix meretrix ([5],[23],[39],[40]). The carpet shell clam represents the most economically important bivalve in Tunisia and is widely distributed along the Tunisian shoreline where it is extensively harvested for local consumption and export to Europe. However, very few studies have been published documenting the health status of this species. In 2003 we reported the occurrence of BRD in several wild populations of carpet shell clam on the Tunisian coast (Southern Mediterranean Sea) with prevalence rates ranging between 1 and 40%, but with no mortalities[14]. More recently[17], we described the results of a 6-year surveillance of BRD in natural populations of carpet shell clams in 14 zones along the Gulf of Gabes (southern coast of Tunisia) with BRD prevalence ranging from 35% to 100% for all sites and mortalities observed at several sites. A positive correlation was demonstrated between BRD prevalence and concentration of Vibrio spp. in clams. Vibrio tapetis was not identified among the bacterial isolates, suggesting that other marine Vibrio species are capable of causing BRD-like illness in local carpet shell clams. Here, we present the first results of identification, characterization, and pathogenicity of Vibrio isolates from BRD affected carpet shell clams sampled in Tunisian natural clam beds.
2. Materials and Methods
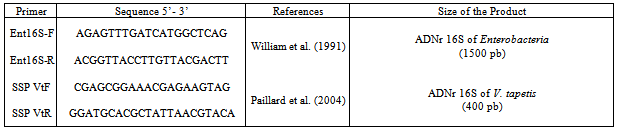
- Bacterial isolation and cultivation 13 isolates were recovered from carpet shell clams with signs of BRD (Table 1). We also included three other strains: a V. tapetis strain CECT4600 previously isolated from a Manilla clam by Paillard and Maes[30] and by[10-32], V. tapetis strain LP2 isolated from the corkwing wrasse Symphodus melops by Jensen[21], and V. splendidus strain ATCC25914 isolated and kindly provided by[20] from a moribund carpet shell clam from SpainBacterial isolation All the isolates were obtained during surveillance for BRD from 2004 to 2007 in natural beds of carpet shell clams in Tunisia and purified from infected shells showing BRD signs of damaged periostracum[17]. All of the bacterial isolates were obtained from extrapallial fluids withdrawn from affected clams and cultured on differential media (TCBS, Zobell – mannitol and marine agar (Difco) at 20℃ as described by Paillard et al[33]. Isolates were maintained on marine agar 2216 (Difco) at 4℃ or stored frozen in marine broth 2216 (Difco) supplemented with 50 % (v/v) glycerol (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) at -80℃.The whole collection of strains is maintained as part of the national collection of the National Institute of Sea Sciences and Technologies (INSTM), Salammbô, in Tunisia. Phenotypic characterization Morphological, physiological and biochemical tests used included: Gram staining, motility and sporulation features, sensitivity to the vibriostatic agent O129, oxidase and catalase tests, temperature growth, and utilization of substrates such as carbon and other energy sources as determined using API 20NE test strips (Bio Merieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France). Agglutination test This assay was performed as described by Paillard et al. (2006). Five milliliters of an overnight liquid culture of each isolate were centrifuged at 13,000xg. Bacteria were re-suspended in 1ml phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and 5µl were placed on a Teflon glass slide with addition of 5µl of anti V. tapetis (CECT 4600) polyclonal antibody solution (IUEM – Brest). Anti V. cholerae (Pasteur Institute, Paris, France) antibody was used as a negative control and all isolates were tested twice. The agglutination test was performed only for Vibrio species as clarified by Paillard et al[33].Extraction of genomic DNA Whole genomic DNA was extracted from overnight cultures of each isolate cultured in LBS medium at 25℃, using a genomic DNA extraction Kit (Sigma); DNA was quantified using a Nanodrop apparatus (Labtech, France).Species-specific primer PCR Identification of V. tapetis species among all isolates was initially made using the species-specific primer-PCR (SSP-PCR) method developed by Paillard et al[33] using V. tapetis specific primers (SSPVtF and SSPVtR; Table 2). A positive identification was inferred if a 416bp fragment of the 16SrDNAwas amplified. As a positive control we used extracted V. tapetis CECT 4600 DNA, while two negative controls were used: T1) deionized water as template (no DNA) and T2) PCR negative DNA tube (CECT4600 DNA without polymerase enzyme).
|
|
3. Results
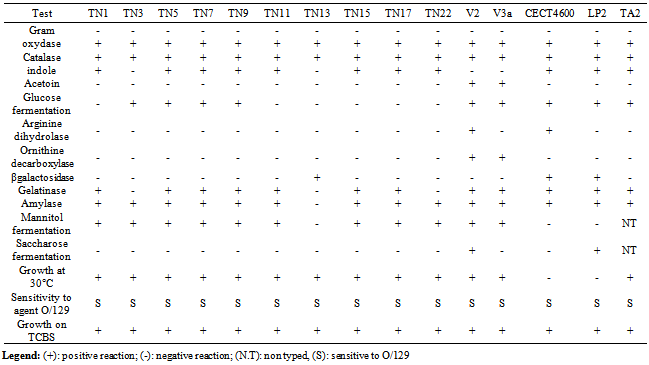
- Although all 13 isolates characterized as a part of this study were recovered from carpet shell clams with apparent BRD, the majority of the isolates could be distinguished from one another based on a series of phenotypic assays (Table 3). Growth on TCBS agar, mannitol and sucrose oxidation/fermentation, production of acetoin, arginine dihydrolase, ornithine decarboxylase and growth at temperature of 30℃ primarily separated the isolates from one another.All isolates were sensitive to the vibriostatic agent O129 and none of the isolates displayed the hallmark characteristics of V. tapetis (failure to ferment mannitol and sucrose, inability to replicate at 30℃). In addition, none of the isolates agglutinated when tested against V. tapetis antisera. On the basis of the phenotypic features, we distinguished the following groups: Group N°1 phenotypically resembling V. splendidus biovar II TA2, isolated from R. decussatus larvae, which included isolates TN5, TN7 and TN9,. Group N°2 including isolates TN1, TN11, TN15 and TN17, displaying a phenotype unique from both V. tapetis CECT 4600 and V. splendidus biovar II TAE2. The remaining isolates TN3, TN13, TN22, V2, V3a and V3b each presented a phenotypic profile that is unique.Molecular identification using the SSP-PCR method showed that only one isolate (V2) amplified a band indistinguishable in size from V. Tapetis (previous data[17]). Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rDNA. 16SrDNA genes were amplified for all isolates using universal Enterobacteriaceae bacterial primers, the 1540 bp products were sequenced and most similar matches were sought using the program Blast from GenBank. A dendrogram derived from the sequence homology comparisons of 16SrRNA gene sequences of isolates with respect to reference sequences of V. tapetis (CECT strains 4600and LP2) and V. splendidus is shown in Fig.1. BlastN identified TN1 and TN22 as V. splendidus with high sequence homology (respectively 99% and 98%) and eight strains: TN3, TN5, TN7, TN9, TN11, TN13, TN15, and TN17 as V. chagasii with sequence homology of 99%, very close to V. splendidus cluster, and V2 as V. alginolyticus with sequence homology of 97%. All sequences were different from those of V. tapetis (CECT4600 and LP2) as shown by the phylogenetic tree.The two isolates V3a and V3b were identified respectively as Psychrobacter and Pseudoalteromonas mariniglutinosa with sequence homology of 99%.
|
 | Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of isolates based on partial 16Sr DNA sequences. The scale bar represents 0.03 substitutions per nucleotide |
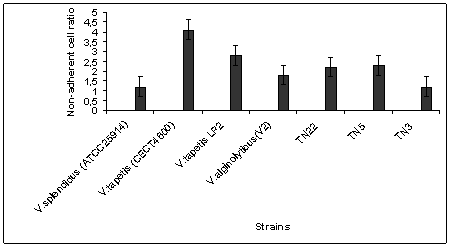 | Figure 2. Effect of different strains of Vibrio on non-adherent cell ratio of clam hemocytes. Incubation time = 3h, 25 bacteria per hemocyte; T℃=18℃ |
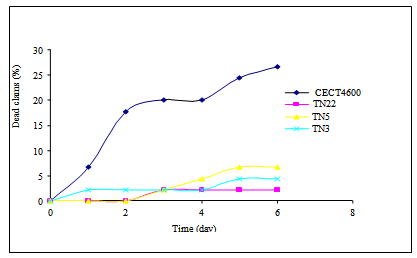 | Figure 3. Mortality kinetics of R.decussatus induced by Vibrio isolates tested |
4. Discussion
- Brown Ring Disease is designated as the main bacterial disease afflicting adult R. philippinarum and R. decussatus clams. BRD has been detected in natural carpet clam populations in coastal parts of Tunisia[14, 15, 16]. Globally clam production is often affected by vibriosis, which leads to high mortality rates as reported by[20] and[33] and. Recent studies have indicated that a wide variety of Vibrio species can cause disease in clams; these organisms can persist with lethal effects in the bivalve tissues despite the depuration process[26].For several northern Mediterranean studies, V. tapetis was the principal agent involved in BRD ([2],[29],[33]). Data previously collected in Tunisia has indicated a strong correlation between BRD prevalence and the concentration of Vibrio spp. found in tissue or extrapallial fluids of infested clams but these studies failed to identify V. tapetis as a causative agent[17]. In this manuscript, we have identified and characterized 13 Vibrio-like isolates from affected carpet shell clams using a combination of phenotypic and molecular tools. We also evaluated their toxicity and lethality using R. philippinarum and R. decussatus. Among the biochemical profiles identified (8 biotypes) one group, including isolates TN5, TN7 and TN19, closely resembled V. splendidus biovar IITA2; the remaining biotypes were different from V. tapetis and V. splendidus as well as each other. These findings highlight the great phenotypic variability associated with environmental isolates, as has been previously reported for of Vibrio species in bivalves from different marine areas ([4],[18],[19]). The diversity of Vibrio spp. associated with cultured clams was also demonstrated by Beaz-Hidalgo et al.[7]; 759 Vibrio isolates were recovered and from these clams more than 13 different species were observed with 3 potentially newly described species. The use of species-specific primer-PCR (SSP-PCR) analysis of a variable region in the present study also did not identify any of the isolates as V. tapetis, even though close band similarity was obtained for the strain V2 (identified as V. alginolyticus by 16Sr DNA sequencing); The application of 16S rDNA sequencing was able to discriminate the Vibrio-like isolates in to 5 clusters: V. chagasaii, V. splendidus, V. alginolyticus, Pseudo-alteromonas mariniglutinosa and Psychrobacter spp.); the majority of isolates appearing to be either V. chagasaii or V. splendidus. These findings demonstrate for the first time that BRD associated with adult carpet shell clams in Tunisia should be caused similarly by V. splendidus. This result is similar to previous findings in the Mediterranean region of Spain where carpet shell and manila clams, oyster Crassostrea gigas, Mya arenaria and fish (Scophtalmus maximus; Symphodus melops) also adversely affected by V. splendidus group, including V. pomeroyi, V. kanalloae and V. aestuarianus ([1],[20],[21]). Besides 16S rDNA sequencing, additional molecular methods such as DNA/DNA hybridization, polymerization of toxin genes and rpoA, pyrH and recA sequencing can be used to increase the differentiation between closely related Vibrio species ([7],[24],[38]). In light of our results, a fast detection PCR test for Vibrio species[23]; mainly for V. splendidus – related group) could potentially greatly benefit surveillance for pathogenic organisms.Most of the isolates tested demonstrated some degree of cytotoxicity to carpet shell clams (i.e. the non-adherent cell ratio >1,2 ) although the observed cytotoxicity was lower than that of V. tapetis strain CECT 4600. According to Allam et al[2], the Vibrio cell wall contains smooth lipopolysaccharides that play an important role in virulence. They help in the penetration of the pathogen into host tissues and allow bacteria to better resist the defense systems of clams, particularly phagocytosis by hemocytes. The viability of clam hemocytes was significantly affected by incubation with both V. splendidus, V. alginolyticus, or the extra cellular products of both species as described by Gomez-Leon et al. (2005). The ability of pathogenic Vibrios to proliferate rapidly in the tissues of R. philippinarum is considerable when compared with R. decussatus which is more resistant to pathogens ([3],[25]). Nevertheless, Prado-Alvarez[36], demonstrated a negative effect on cell viability after treating R. decussatus clams with either living or dead V. splendidus; this result suggests that for bacterial extracellular products might play a role in modulating the bivalve immune response.According to present data, direct injection of Vibrio isolates (V. splendidus or V. chagasii) in to the adductor muscle of R. decussatus clams induced lower rates of mortalities in as compared to V.tapetis. Similar results were obtained by[3] who showed that development of BRD in R. decussatus injected in the pallial cavity is much less pronounced than in R. philippinarum. The resistance of R. decussatus to BRD and therefore lack of animal death is primarily explained as the result of a strong barrier to infection at the perisotracal membrane level and efficient neutralization of any V. tapetis that enter the extrapallial cavity by[31]. According to Labreuche[22], for V.aestruarianus, a pathogen of C. gigas, lethality was modulated by incubation temperature. Present results were obtained for Vibrio isolates cultured at 18°C (the optimal incubation temperature of V. tapetis). Further experiments will be conducted for these local cultures incubated at 30℃ in order to determine eventual temperature effect on lethality of Vibrio isolates.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We are grateful for Dr Bechir Béjaoui for his technical assistance in preparing the manuscript.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML