-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2012; 2(4): 103-107
doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20120204.07
Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli from Beef Carcass
Everlon Cid Rigobelo 1, Fernando Antonio de Ávila 2
1Departament of Animal Science UNESP Dracena, Postcode, 17900-000, Brazil
2Departament of Veterinary Pathology UNESP Jaboticabal, Postcode 14884-900, Brazil
Correspondence to: Everlon Cid Rigobelo , Departament of Animal Science UNESP Dracena, Postcode, 17900-000, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
A survey was performed to estimate the frequency of Escherichia coli and Shiga toxin–producing E. coli (STEC) in carcasses obtained from at an abattoir in Brazil. The aim of present study was to verify the presence of virulence gene in E. coli strains isolated from cattle carcasses and also verify the antimicrobial resistance level these isolates. Thus, three carcass among the 80 tested showed a STEC, stx2-encoding gene. The frequency of carcass contamination by E. coli during processing was tested at three situations, respectively: preevisceration, postevisceration and postprocessing, during the rain and dry seasons. The prevalence of E. coli at the three points was of 14.67%, 37.61%, 14.67% in the rain season and of 7.33%, 11.0%, 14.67% during the dry season, respectively. The highest antimicrobials resistances were to cephalotin, followed by ampicilin and amikacin. The lowest were to trimethoprim, tetracycline and streptomycin. These findings suggest that the cattle carcasses can be vehicles from STEC and also from strains with high antimicrobials resistance for consumers.
Keywords: Escherichia Coli, Cattle, Carcasses
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) can cause a range of serious disease syndromes in humans, including diarrhoea, haemorrhagic colitis and life threatening,haemolytic–uraemic syndrome (HUS) (1). Transmission of STEC can be foodborne, waterborne or from person to person (2). Escherichia coli form part of the bacterial population of the cattle's gastrointestinal tract. In beef carcass processing, E. coli is regarded as an indicator of fecal contamination. Levels of E. coli associated with cattle carcasses can increase or decrease during processing according to factors such as the levels of fecal contamination of live cattle, efficiency of evisceration and hygienic practices in the abattoir. E. coli is regarded as a pathogen of major worldwide importance in commercially produced beef, its presence can lead to significant economic loss (3).Bovine E. coli strains can produce heat labile (LT) or heat stable (st) enterotoxins, Shiga-like toxins (stx), cytotoxic necrotizing factors (CNF1 and CNF2) and hemolysins (a-Hly and E- Hly). Enterotoxin-producing E. coli (ETEC) has been identified as the causative agent of several important diarrheal diseases in animals and humans and are capable of producing thermolabile (LT-I and LT-II) and thermostable (sta and stb) enterotoxins (4). LT I toxin does not occur in bovine samples (4), but sta enterotoxin is quitecommon in bovine cattle (5). CNF-producing E. coli has been isolated from animals with enteritis (6) and from humans with extraintestinal infection (7). Cattle, considered primary reservoirs of both O-157 and non-O157 STEC bacteria (8), frequently carry STEC without showing any pathological symptoms (9). The full list of bacterial virulence determinants necessary for STEC's pathological effects is unknown. However, stx is a key factor in pathogenesis (10). Two types of Shiga toxin, stx1 and stx2 (encoded by stx1 and stx2 genes), are associated with human disease. These toxins vary in their amino-acid sequence (11) antigenicity, and in their activation and receptor specificity (12). The ability of E. coli to adhere to intestinal epithelium is crucial in the colonization of the intestine, and therefore the progression of disease in humans. The protein intimin, encoded by the eae gene, enables intimate attachment of E. coli to intestinal cells (13), causing characteristic attaching/effacing lesions (14)During the processing of the carcass, fecal contamination or transfer of bacteria from the animal's hide to the carcass can facilitate transmission of pathogenic E. coli to food supplies (3). The objective of this study therefore was to determine the virulence profiles and the antimicrobial drug resistance of E. coli isolates from beef carcasses at an abattoir in Brazil.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Carcass samples
- Three hundred and forty bovine carcass samples were collected between March 2008 and August 2009, at an abattoir in São Paulo State, in southwestern Brazil. Samples studied were from carcasses of 90 feedlot cattle raised at pastures. Sampling of 20 feedlot cattle was done in four different occasions, two in the rain season and two in the dry season. Each sample was obtained using a Specie- Sponge (3M- Brazil) moistened with 25 ml of Brilliant Green (BBL/Becton Dickins on) in a stomacher bag. Sponges were wrung out as much as possible within the bag, with drawn and used to swab each area. Each carcass was followed along the processing and sampled at three different stages always at the same site of the rump, near the anus over an area of 10 × 30 cm, delineated by a sterile metal template, from the same half of each carcass. Preevisceration samples were taken immediately after complete hide removal; postvisceration samples were collected after splitting and trimming; postprocessing samples were taken after washing of the carcasses hanging in the cooler. All samples were taken to the laboratory in an ice-cooled bag and kept for 12 h at room temperature.
2.2. Bacterial isolates
- One hundred microliters of each sample was streaked on MacConkey agar plates (Oxoid Ltd) and incubated at 37℃ for 24 h. Colonies showing E. coli characteristics were submitted to Gram staining and identified by standard biochemical tests as oxidase negative, indole positive, Simon's citrate negative, urease negative and hydrogen sulfide negative (15). The isolates were serotyped for the O serotype O157 using the O157 Latex Agglutination test kit (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK). Negative strains were considered non-O157 strains.
2.3. PCR Screening of Samples
- Bacterial strains were grown overnight in nutrient broth (Sigma Chemical Co.) at 37 ℃, were pelleted by centrifugation at 12, 000 g for 1 min, resuspended in 200 µl of sterile distilled water and lyzed by boiling for 10 min. Lysates were centrifuged as described above and 150 µl of the supernatants were used as DNA template for the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (16). A total of 89 E. coli isolates were subjected to PCR; stx1, stx2 and eae genes were detected using the primers and PCR conditions described by (17). The presence of LT-II gene was assessed by PCR amplification using primer pairs and conditions described by (18). The sta gene was detected using the primer and conditions described by (19).
2.4. Expression of E-Hly
- Expression of enterohemolysin was determined based on the method described by (20). Plates were incubated at 37 ℃ for 24 h and observed for hemolysis after 3 h (for expression of a-hemolysin) and 24 h (for E- Hly), respectively. The reference strains used in this assay were E. coli U4– 41 (positive control for a -hemolysin), E. coli 32511 (STEC O157: H7) (positive control for E-Hly), and E. coli K12 (negative control).
2.5. Susceptibility Testing
- Antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests were performed using the disk diffusion method, as recommended by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (21). Eleven antimicrobial agents were selected for the tests: ampicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cephalotin, ceftriaxone, tetracycline, gentamicin, streptomycin, amikacin,trimethoprim, nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin.
3. Results and Discussion
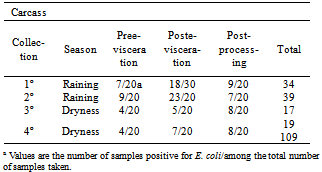
- The distribution of positive carcass responses for E. coli corresponding to each sampling season is shown in Table1. E. coli distribution in the three stages of the sampling, show the same characteristics during the rainy season and the dry season; however, the number of positive carcasses obtained in the rain season was higher than in the dry season. All isolates were confirmed as being E. coli by their biochemical analysis and were submitted to PCR for the detection of sequences of virulence genes. From each MacConkey agar plate a loopful from a confluent bacterial growth was collected and analyzed. All isolates except four were negative for stx, eae, LT-II and sta genes by PCR analysis, as well as for enterohemolysin expression. The four positive isolate was a three stx2- and one stx1 encoding strain. Toxin- profiling studies of O-157: H7 clinical isolates by (22) had shown that patients infected with isolates carrying only stx2 were 6.8 times more likely to develop severe disease than those infected with strains carrying stx1 or both stx1 and stx2. The before, isolates carrying stx2 could represent a potential increased threat to human health. The number of isolates was high 109 strains during rainy season and dry. (Table1).
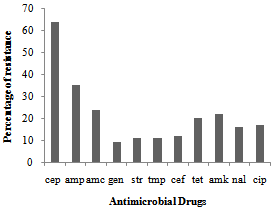 | Figure 1. Antimicrobial resistance patternsin 109 Escherichia coli strains taken from a cattle abattoir in Brazil. Amc — amoxicillin/clavulanic acid; amk — amikacin; amp — ampicilin; cef — ceftriaxone; cep — cephalothin; cip — ciprofloxacin; gen — gentamicin; nal — nalidixic acid; str — streptomycin; tet — tetracycline; tmp — trimethoprim |
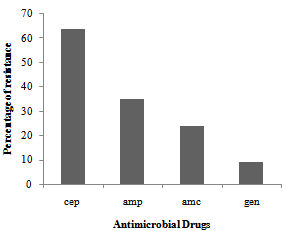 | Figure 2. Distribution of multidrug resistance to 11 antimicrobial drugs among 109 strains of Escherichia coli isolated from a cattle abattoir in Brazil |
4. Conclusions
- We report here a small level (1. 2%) of occurrence of STEC strains on beef carcasses during processing at an abattoir in Brazil. However the E. coli isolates analyzed showed a high level of multidrug resistance capable of causing concern.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- FAPESP Fundação de Amparo Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo financial support
References
| [1] | Madigan M.T, Martinko J.M. “Brock Biology of Microorganisms”. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2003. |
| [2] | Nataro J. P. Kaper Jb. “Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli” . Clinical Microbiology Reviews vol.11, pp. 142–201, 1998. |
| [3] | Bell, R.G. “Distribution and sources of microbial contamination of beef carcasses”. Journal. Applied. Microbiology. v.82, 292–300, 1997. |
| [4] | Butler, D.G., Clarke, R.C. Diarrhoea and dysentery in calves. In: Gyles, C.L. (Ed.), Escherichia coli in Domestic Animals and Humans. Cab International, Wallingford, pp. 91 –116, 1994. |
| [5] | Blanco, J., Blanco, M., Blanco, J.E. Enterotoxigenic, verotoxigenic and necrotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in Spain. American. Journal.Veterinary. Research. v.54, 1446– 1451, 1993. |
| [6] | De Rycke, J., Guillot, J.F., Boivin, R. “Cytotoxins in non-enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from faeces of diarrheic calves”. Veterinary. Microbiology v.15, 137 –150, 1987. |
| [7] | Caprioli, A., Falbo, V., Ruggeri, F.M., Baldassarri, L., Bicicchia, R., Ippolito, G., Romoli, E., Donelli, G. “Cytotoxic necrotizing factor production by hemolytic strains of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections”. Journal. Clinical. Microbiology v.25, 146– 149, 1987. |
| [8] | Bettelheim , K.A. “Role of non - O15 7 VTEC”. Journal. Applied. Microbiology. v.88, 385–505, 2000. |
| [9] | Blanco, M., Blanco, J.E., Blanco, J., Mora, A., Prado, C., Alonso, M.P., Mourino, M., Madrid, C., Balsalobre, C., Juarez, A. “Distribution and characterization of faecal verotoxin producing Escherichia coli (VTEC) isolated from healthy cattle”. Veterinary. Microbiology. v.54, 309–319, 1997. |
| [10] | Acheson, D.W. “How does Escherichia coli O157:H7 testing in meat compare with what we are seeing clinically?” Journal. Food Protection n.63, pp.819–821, 2000. |
| [11] | Kaper JB, O’Brian AD. “Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other Shiga Toxin-producing E. coli Strains . Washington DC : ASM Press, 1998. |
| [12] | Schmitt CK, Meysick KC, O’ Brien AD. “Bacterial toxins : friends or foes ?” Emerging Infecty. Diseases. v.5 : 224–234, 1999. |
| [13] | Donnenberg MS, Kaper JB. “Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli.” Infection. Immunity ; v.60 : 3953– 3961, 1992. |
| [14] | Paton JC, Paton AW. “Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga- to xi n producing Escherichia coli infections . Clinical. Microbiology. Review n.11, pp. 450–479, 1998. |
| [15] | koneman, E.W., Allen, S.D., Schrekenberger, P.C., Janda, W.M., Winn, W.C. Color Atlas and Textbook Microbiology, 5 ed. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1997. |
| [16] | Wani S.,A, Bhat M., A, Samanta I, Nishikawa Y, and Buchh A., S. ” Isolation and characterization of Shiga toxinproducing Escherichia coli (STEC) and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) from calves and lambs with diarrhea in India”. Letters Applied Microbiology. N. 37pp. 121–126. |
| [17] | China, B., Pirson, V., Mainil, J. “Prevalence and molecular typing of attaching and effacing Escherichia coli among calf population in Belgium. Veterinary. Microbiology, v.63, 249 –259, 1998. |
| [18] | Penteado, A.S, Ugrinovich, L.A, Blanco, J., Blanco, M., Blanco, J.E., Andrade, J.R.C, Corrêa, S.S., Pestana de Castro, A.F. “Serobiotypes and virulence genes of Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrheic and healthy rabbits in Brazil”, Veterinary Microbiology vol. 89, pp.41–51, 2002. |
| [19] | Jung, H.K. “Identification of serotype by use of serologic assay and detection of the enterotoxin gene of Escherichia coli by means of a polymerase chain reaction assay for isolates from pigs, chickens, and cows”. American. Journal. Veterinay. Research. v.60, 468– 472, 1997. |
| [20] | Beutin, L., Geier, D., Zimmermann, S., Aleksic, S., Gillespie, H.A., Whittam, T. S. “Epidemiological relatedness and clonal types of natural populations of Escherichia coli strains producing Shiga toxins in separate populations of cattle and sheep”. Applied. Environmental. Microbiology. v.63, 2175–2180, 1989. |
| [21] | (NCCLS), Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Dilution Susceptibility Test for Bacteria Isolated from Animals Approved Standard M31A, v.19,11. NCCLS, Wayne, P.A, 1999. |
| [22] | Ostroff, S.M., Tarr, P.L., Neil, M.A., Lewis, J.H., Hargrett-Bean, N., Kobayashi, J.M. “Toxin genotypes and plasmid profiles as determinants of systemic sequelae in Escherichia coli O157: H7 infections”. Journal. Infection. Diseases. v.160, 994–998, 1989. |
| [23] | Rogerie, F. Marecat, A., Gambade, S., Dupond, F., Beaubois, P., Lange, M. “Characterization of Shiga toxin producing E. coli O157 serotype E. coli isolated in France from healthy domestic cattle. International Journal of food Microbiology, vol.63, pp.217-223, 2001. |
| [24] | Leung, P.H.M., Yam, W.C., NG, W. W. Peiris, J.S. “The prevalence and characterization of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from cattle and pigs in an abattoir in Hong Kong.” Epidemiological. Infection. v.126, 173–179, 2001. |
| [25] | Artthur, T.M., Barkocy-Gallagher, G.A., Rivera-Betancourt, M., Koohmaraie, M. “Prevalence and characterization of non O157 Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli on carcasses in commercial beef cattle processing plants.” Applied. Environmental. Microbiology. n.68, 4847–4852, 2002. |
| [26] | Barkocy-Gallagher, G.A., Arthur, G.A., Siragusa, G.R., Keen, J.E., Elder, R.O., Laegreid, W. W. Koohmaraie, M. “Genotype analyses of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and O157 nonmotile isolates recovered from beef cattle and carcasses at processing plants in the Midwestern states of the United States”. Applied. Environmental. Microbiology. n.67, pp.3810– 3818, 2001. |
| [27] | Gyles, C., Johnson, R., GAO, A., Ziebell, K., Pierard, D., Aleksic, S., Boerlis, P. “Association of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli hemolysin with serotypes of Shiga toxin producing E. coli of humans and bovine origins”. Applied. Environmental. Microbiology v.64, pp.4134 –4141, 1998. |
| [28] | Irino, K., Kato, M.A.M.F., Vaz, T.M.I., Ramos, I.I., Souza, M.A.C., Cruz, A.S., Gomes , T.A.T., Vieira , M.A. M., Guth, B.E.C. “Serotypes and virulence markers of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from dairy cattle in São Paulo State, Brazil” . Veterinary. Microbiology v.105, pp.29 –36, 2005. |
| [29] | Leomil, L., Aidar-Ugrinovich, L., Guth, B.E.C., Irino, K., Vettorato, M.P., Onuma, D.L., DE Castro, A.F.P. “Frequency of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolates among diarrheic and non-diarrheic calves in Brazil”. Veterinary. Microbiology. v.97, pp.103– 109, 2003. |
| [30] | Lira, W.M., Macedo, C., Marin, J.M. “The incidence of Shiga toxinproducing Escherichia coli in cattle with mastitis in Brazil”. Journal Applied Microbiology v.97, pp.861–866, 2004. |
| [31] | Vaz, T.M.I, Irino, K., Kato, M. A. M. F. Dias, A. M. G. Gomes, T. A. T Medeiros, M. I. C. Rocha, M. M. M, Guth, B. E. C. “Virulence Properties and Characteristics of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in São Paulo, Brazil, from 1976 through 1999” Journal of Clinical Microbiology, vol. 42, No. 2, pp. 903–905, 2004. |
| [32] | Zhao, D.G. White, B. Ge, S. Ayers, S. Friedman, L. English, D. Wagner, S. Gaines, J. Meng. “Identification and characterization of integron-mediated antibiotic resistance among Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates” Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67 pp. 1558–1564, 2001. |
| [33] | Khan, A., Das, S.C., Ramamurthy, T., Sikdar, A., Khanam, J., Yamasaki, S., Takeda, Y. , Nair, G.B. “Antibiotic resistance, virulence gene, and molecular profiles of Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli isolates from diverse source in Calcutta India. Journal Clinical, Microbiology. v.40, pp.2009–2015, 2002. |
| [34] | Van den Bogaard, E.E. Stobberingh “Epidemiology of resistance to antibiotics. Links between animals and humans” International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 14, pp. 327–335, 2000. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML