-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2012; 2(3): 60-67
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20120203.04
Diversity of Heterotrophic Bacteria Isolated from Water in the Paddy Rice Fields of Southern Brazilian
Jeremias Pakulski Panizzon1, Vilmar Machado1, Vera Regina Mussoi Macedo2, Lidia Mariana Fiuza1, 2
1Laboratório de Microbiologia e Toxicologia, PPG em Biologia, Universidade do Vale do Rio dos Sinos, UNISINOS, C.P. 275, CEP 93001-970, São Leopoldo, RS, Brasil
2EEA/Instituto Riograndense do Arroz, C.P. 29, CEP 94930-030, Cachoeirinha, RS, Brasil
Correspondence to: Vilmar Machado, Laboratório de Microbiologia e Toxicologia, PPG em Biologia, Universidade do Vale do Rio dos Sinos, UNISINOS, C.P. 275, CEP 93001-970, São Leopoldo, RS, Brasil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
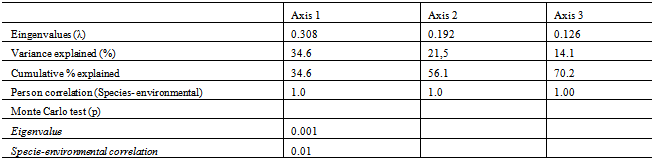
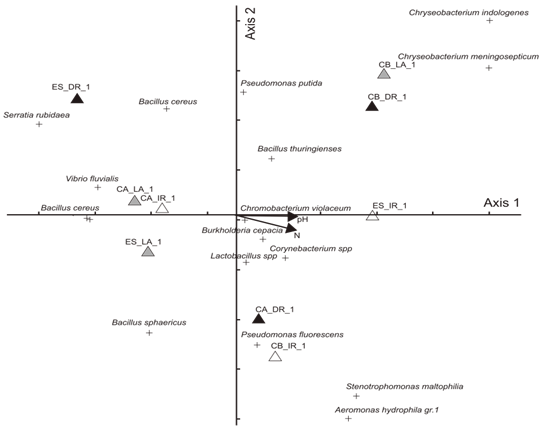
This study evaluated the effects of physic-chemical variables on the diversity of bacterial communities present in the water utilized to irrigate rice field and in the water drained back into the water source. The samples were collected between the months of October and April of the year 2009/2010 in three rice producing areas in the district of Caraá, Campo Bom and Esteio, all located in the Basin of the Rio dos Sinos. The data was analysed utilizing Multivariate Analyses (CCA and DCA), Jaccard Distance and Variance Analyses. The abundance of the bacterial colonies was greater in the irrigation water than in that within the rice field or in the drainage. (F1, 9 = 7.21 p < 0.05); 48.6% were found in the irrigation channel, 25.7% in the water within the field and 25.7% in the water returned to the river (drainage). Colonies of 21 species were registered and of these: 16 were in the irrigation channels; the water in the rice field and the drainage water. The estimated diversity was superior in the irrigation channels (H=2.68) when compared with the values obtained in the drainage water (H=2.25). The results demonstrated that the samples from the irrigation water and the drainage water differ in the composition of the species in all the locations analysed. The two initial axes generated by Detrended Correspondence Analysis explain 56% of the observed variation between the locations. The most important variables for the ordination and correlation with the axis were the pH and Nitrogen. The results show that rice bacteria communities contain several species but few are abundant, such as species of Bacillus, Lactobacillus and Pseudomonas. The reduction in colony abundance on the drainage water shows the ability of the rice field to filter some bacterial species.
Keywords: Bacterial, Rice Field, Irrigation, Diversity, Physical-Chemicals Parameters
Cite this paper: Jeremias Pakulski Panizzon, Vilmar Machado, Vera Regina Mussoi Macedo, Lidia Mariana Fiuza, Diversity of Heterotrophic Bacteria Isolated from Water in the Paddy Rice Fields of Southern Brazilian, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 2 No. 3, 2012, pp. 60-67. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20120203.04.
1. Introduction
- Bacteria present a degree of diversity without parallel in the biological world – they are found in all environments even those that are inhospitable to other live organisms. Studies on the factors that influence the distribution, diversity, and structure are relatively recent, especially those that involve molecular methods. A better understanding of the environmental factors that influence changes in the diversity of the bacterial communities is very important because they realize functions that are indispensable for maintenance of the ecosystems[1-3]. According to Horner-Devine et al.[4], one of the important points of the bacterial ecology is the description of the distribution of the bacterial diversity along the environmental gradients.In freshwater systems these studies can also contribute to activities designed to monitor the water quality and the impact of human activities on that quality[5,6]. Studies on the composition of the bacterial communities (beta diversity) are important for the development of strategies to preserve the biodiversity and for the management of these communities during bioremediation activities and can contribute to the development of theoretical models of the ecology of the microorganisms[7-9].Although in some agricultural areas, studies have been carried out to analyze the effects on bacterial diversity of the chemical substances used for fertilization and pest control [10] arrangements associated to cultivation[11-14], these studies mainly analyze the impact of different factors on the biodiversity of the bacteria in the soil. In areas of rice cultivation the studies are concerned principally with the soil bacteria involved in the processing of the rice plant residues ([15-19], rather than the biodiversity present in the water [20-22]. In this context, any study that helps to evaluate the factors that influence the composition of the bacterial communities in the water utilized for irrigation of rice crops is relevant, especially when one considers the small number of studies available on the subject.The cultivation of irrigated rice is considered worldwide as one of the agricultural activities that consume most water. In Brazil approximately 11,000 kg/ha are produced annually – 60% in the State of Rio Grande do Sul[23]. The importance of water for this culture is associated with the increase in the availability of nutrients, the control of weeds and the regulation of the thermal alterations in the soil. Notwithstanding the importance of water for the productivity of rice field, some problems arise from irrigation especially the possibility of contamination from polluted irrigation water[24,25], the contamination of water resources by chemical substances used for fertilization of the soil and/or pest control[26,27]; and the impact on the biodiversity of the micro-organisms [22].This study was realized with the objective of evaluating the diversity of the bacterial communities found in the water supplied for irrigation of rice fields and in that water returned to the river after passing through the cultivation area. The fundamental aspect of this study was to obtain answers to the following questions; (i) Is the bacterial diversity different in the water entering the rice field for irrigation and that same water when it exits the cultivation area having irrigated the crop? and (ii) What environmental variables influence the composition of the cultivated bacterial communities?
2. Materials and Methods
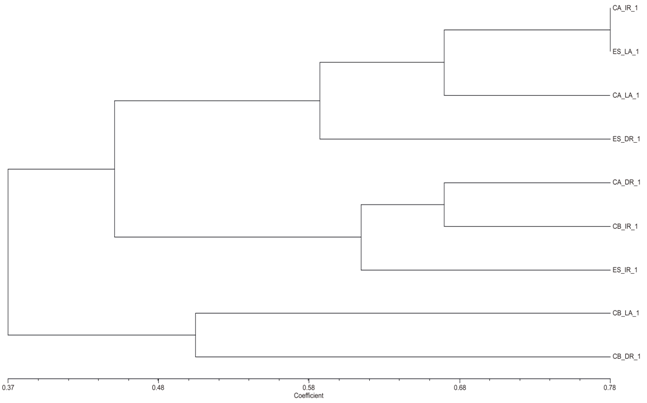
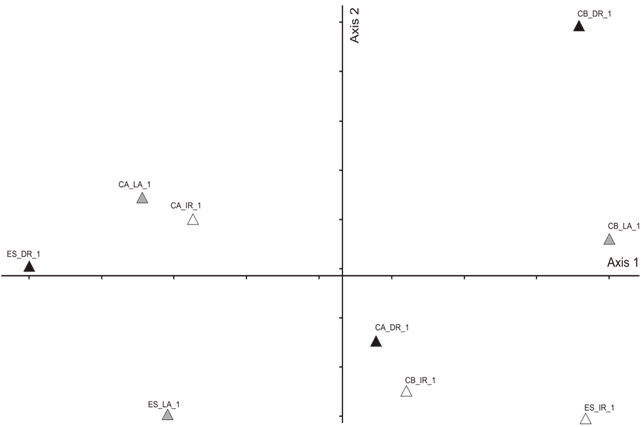
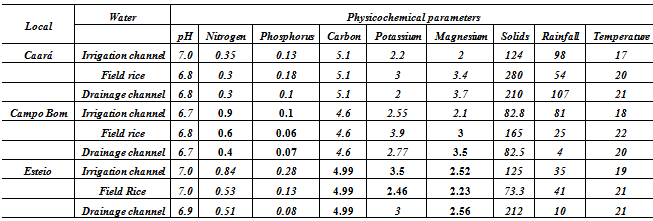
- Area Studied: The hydrographic basin of the Rio-dos- Sinos is located in the Northeast of the State of Rio Grande do Sul (RS), between the 29° and 30° south parallels. It covers an area of 3820 km2 - the principal waterway extends from its origin in the district of Caraá to its discharge in the delta of the Jacuí river. In the Sinos Basin, thirty-two districts with a total of 975.000 inhabitants are located - 13 directly watered by the river from which they obtain water for treatment and consumption and use for sewage disposal. The rice fields draw water from the same river for irrigation and return it to the river afterwards.The locations analyzed in the district of Caraá – RS were: Entrance of the irrigation channel (29°46’53,97’’S and 50°26’52,21’’W); The field rice (29°47’02,50’’S and 50°26’49,15’’W); and the drainage channel °47’04,20’’S and 50°26’53,93’’W). In the district of Campo Bom (RS) the points of analyses were: Entrance of the irrigation channel (29°42’05,98’’S and 51°02’56,39’’W); rice field(29°42’10,04’’S and 51°02’59,78’’W); and the drainage channel (29°42’06,06’’S and 51°03’12,75’’W). In the district of Esteio (RS) the points of analysis were: The entrance of the irrigation channel (29°50’55,23’’S and 51°11’32,08’’W); the rice field (29°50’48,28’’S and 51°11’49,49’’W); and the drainage channel (29°50’45,50’’S and 51°11’52,86’’W).Water Samples: The water samples were collected between October and April of the agricultural years 2009/2010 in three separate irrigated rice fields located in the districts of Caraá, Campo Bom and Esteio (Figure 1). The sample collection was realized once every fortnight in the main irrigation channel, in the sheet of ground-water amongst the plants and in the drainage channel (return of the water to the river).From 100 mL of the sampled water 500 µL was mixed with 4.5 mL of saline solution (NaCl 10%) to produce a dilute solution of 1/102. Then 100 µL was placed in a Petri dish containing Agar Nutrient [digestible gelatin enzyme (5g/L), meat extract (3g/L) and Agar (15g/L)], and incubated in a bacteriological oven at 30℃ for 24 hours. The colonies grown separately were numbered with a colony counter and the bacterial cells analyzed cytologically with an optical microscope (1000 X). The spore-producing bacteria were separated by pasteurization and both groups (spore- producers and non spore-producers) were identified by cellular morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics in accordance with the International Methods of Bacterial Classification described in “Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology”[28]. The gram-negative bacteria were identified by the API Biomerieux 20E method and the level of species determined subsequently using the API Web software.Parameters analyzed: In the EEA-IRGA Soil and Water Analysis Laboratory, the physic-chemical elements that we analyzed were: pH, Nitrogen (mg / L), Phosphorus (mg / L), Magnesium (mg / L), Potassium (mg / L), Carbon (mg / L) and solids (mg / L). The procedures used to estimate the physical/chemical variables were those defined by Tedesco et al. [29].Statistical Analysis: Variance Analysis (ANOVA - P < 0.05) was utilized to evaluate the differences in the abundance of the bacterial colonies present in the water supplied for irrigation, in the plantation itself and in the drainage outlet. The diversity in the rice fields was analyzed using the Shannon and Evenness[30] indices, calculated separately for each water origin and sites. We also analyzed the diversity by the Jaccard[30] coefficient using the total abundance values for each environment (location and water origin) and displaying the results in the form of a dendrogram. The metric UPGMA connection method was used to attribute similarity between the pairs in a less extreme manner. The cluster analysis was made with the NTSYS 2.1 program[31]. The distribution pattern of the taxa between the sample areas and water origin was assessed by Detrended Correspondence Analysis, DCA[32,33], and the values were transformed by the expression log10 (x+1) to compensate for the deviations caused by the low or higher abundance[34]. PC – ORD 4.0[35] was utilized for the DCA analysis.The influence of the physic-chemical parameters on the abundance of the principal species was quantified by the Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) method using the PC-ORD program[35]. The CCA made it possible to produce an analysis of direct ordination of the gradients, explaining the distribution of the species in relation to the environmental variables. The significance of the principal axis of the canonical ordination was evaluated by the Monte Carlo [34] permutation test. For this analysis we used species with more than five colonies per point.
3. Results
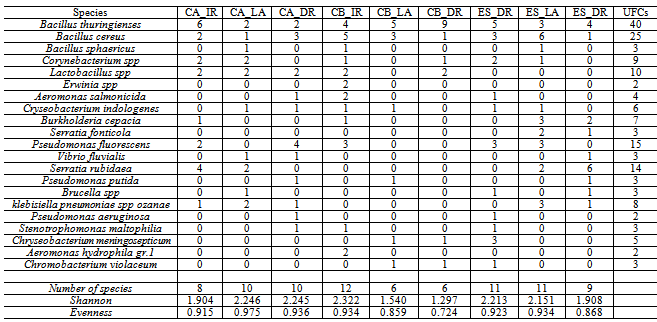
- Colonies of a total of 21 species were registered; of these, 16 were found in the incoming irrigation water, the water within the fields and the drainage water (Table 1). The bacterial abundance, considering all the samples analyzed, was greater in the irrigation water than in the waters within the plantation and in the drainage (F1, 9 = 7.21 p < 0.05). Of this total, 48.6% of the colonies were found in the irrigation channel, 25.7% in the water sheet around the plants and 25.7% in the water returned to the river (drainage).The estimated diversity was greater in the irrigation channels (H=2.68) than the values obtained in the drainage water (H=2.50). The equitability index indicates that the distribution of the species is similar in the two locations (E= 0.86 and 0.82). The observed values of the general diversity of the water around the plants is closer to that observed in the irrigation water and presents a more uniform distribution (H= 2.50; E= 0.92). In a more detailed analysis, comparing each location separately, no well defined patterns were observed. In the district of Campo Bom and Esteio the indices of diversity are greater in the irrigation water than in the drainage channel. In Caará the diversity is greater in the drainage water. The differences found, however, are caused by only a few species, which may be present or absent in any one location to a greater or lesser degree. For example, in Caará the difference between the irrigation and drainage waters is explained by the presence of four colonies of Serratia rubidaea. If we remove this species, the other diversity values of the two waters are similar. In the other locations we observed a greater diversity in the irrigation water channel.
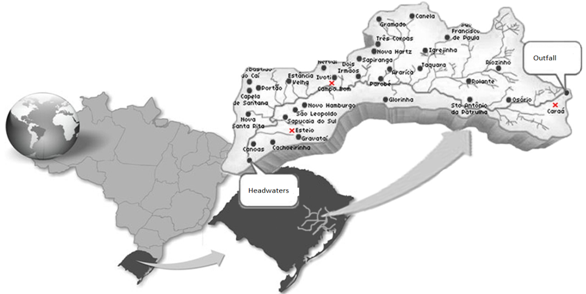 | Figure 1. Map showing studied hydrographic basin and sampling sites |
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The results obtained indicate that the bacterial communities analyzed are made up of many species, but few are abundant – as for example: Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Psedomonas florescens and Lactobacillus spp. The bacteria found most frequently in the water samples analyzed are bacteria from the soil of rice fields, especially the genus Pseudomonas, Bacillus and Lactobacillus [37,38, 19]. The Bacillus thuringiensis species is the genus most often found in rice cultivation soils infecting various pests of the rice culture[39]. Its presence in the water associated to this culture was registered by Reche and Fiuza[20]. The bacteria of the Pseudomonas genus are an important soil group, especially because of their capacity to act as an endophytic, contributing significantly to the development of the plants[18,17]. Various studies have demonstrated the influence that the pH has in the composition and distribution of the species in bacterial communities[3,40,41,9,5]. Alterations in the pH can also cause alterations in other important chemical variations with which they are correlated, such as, for exampla, the heavy metals[42-45].The impact of the increase in the availability of Nitrogen on the diversity of the communities has been studied in plants[46]. In general we observe a reduction of the number of species in the community[47,48]. The impacts of these elements on the bacterial communities in the soil are difficult to analyze and do not permit visualization of the patterns[49], although in some studies they are associated with a reduction of the biomass[50,51]. Studies have demonstrated that the Nitrogen level may influence the soil pH, and this would have an important effect on the composition of the bacterial communities[52,53]. Studies realized in freshwater systems also indicate the influence that the availability of Nitrogen has on the bacterial communities[54,5]. The results presented here demonstrate that cultivated bacteria diversity in the irrigation water entering a rice field is different to that same water when it leaves that field and returns to the supply source. This result can be interpreted in two different ways. On the one hand, this influence (of the plants on the water) may be considered negative as some of the species are not present in the water returned to the river/source. On the other hand, the quality of the water returned is improve as a reduction of some of the physical, chemical and biological parameters is observed[20]. However, in this context it is difficult to evaluate the degree to which management practices make a biological impact on the diversity of irrigated rice plantations because the levels of pollution in the irrigation water are above those observed in unpolluted environments.The analyses realized are a contribution to the study of factors that influence the diversity of heterotrophic bacteria communities in paddy rice fields. Bearing in mind that the water utilized for irrigation contains concentrations of chemical and biological elements well above those in environments where the water is not polluted, it is impossible to determine whether the field management process commonly used in rice crop has a positive or negative effect on the bacterial communities. Even so, and besides the limitation of cultivation-dependent approach, studies such as the present document are relevant for the conservation and sustainable use of freshwater systems. Microorganisms are essential elements in the natural processes responsible for the quality of the water and therefore the acquisition of ever greater knowledge of the diversity of microbial system and of the factors influencing them is of considerable importance.In this study we detected that the diversity of bacteria in rice field floodwater communities was influenced by nitrogen, pH and variables correlated. Relevant information is a reduction of the number of colonies for some species during the water passage by rice field. This reduction shows the ability of rice paddy field to filter some bacterial species improving the quality of returned water.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We acknowledge the Santander Bank (Brazil) S.A. by the financial support to do these research at Biology Graduate Program of UNISINOS. We thank our families, colleagues and friends. I thank my Lord Jesus Christ who died on the cross to save us.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML