-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2012; 2(2): 41-46
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20120202.07
Diversity and Antibacterial Screening of Actinomycetes from Javadi Hill Forest Soil, Tamilnadu, India
Sakthi Velayudham1, Kasi Murugan2
1Research and Development Center, Bharathiyar University, Coimbatore-46, Tamilnadu, India
2Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, P.O.Box 2455, Riyadh-11451, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Kasi Murugan, Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, P.O.Box 2455, Riyadh-11451, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Actinomycetes from diverse environments are known to produce novel antibacterial and antifungal substances. Herein we report isolation of antibiotic producing actinomycetes from forest soil of ancient human inhabited Javadi hill, Tamilnadu, India, an environment that is under explored. Thirty six isolates were obtained from five soil samples using nalidixic acid and nystatin supplemented starch casein agar and actinomycete isolation agar medium. These colonies NLO were characterized based on their mycelium structure, colour and arrangement of spores on the mycelium. Further they were evaluated for their antimicrobial activity against a range of pathogenic resistant bacteria including Escherichia coli (MTCC 739), Bacillus cereus (MTCC 1272), Staphylococcus aureus (MTCC 1144), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 1688), Proteus mirabilis (MTCC 1425)and Klebsiella pneumonia (MTCC 109) adopting agar plug method and confirmed by cross streak method.
Keywords: Actinomycetes, antibacterial activity, antagonistic activity, pathogens
Cite this paper: Sakthi Velayudham, Kasi Murugan, Diversity and Antibacterial Screening of Actinomycetes from Javadi Hill Forest Soil, Tamilnadu, India, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 2 No. 2, 2012, pp. 41-46. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20120202.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Microorganisms are virtually an unlimited source of novel substances with many therapeutic applications and consequently their secondary metabolite screening for pharmaceutically significant novel antibiotic and non - antibiotic compounds and drug lead molecules has assumed greater attention in recent times. Many soil-inhabiting bacteria are known to produce secondary metabolites that can suppress microorganisms competing for the same resources[1].Actinomycetes are the most commonly distributed microbes in nature which largely inhabits the soil environment[2]. They form the dominant and significant group among the soil microbial community and comprise about 50% of the uncultivable soil microbes. They play a major role in the recycling of organic matter, production of novel pharmaceuticals, nutritional materials, cosmetics, enzymes, antitumor agents, enzyme inhibitors, immune modulators, and vitamins. Numerous naturally occurring antibiotics have been discovered from actinomycetes ever since the discovery of Selman Waksman,s streptomycin from this group and several studies signify their noteworthy antibiotic production[3]. Further, about two thirds of known significant naturally occurring antibiotics are actinomycete derived one and are the prominent candidates receiving number of product and processes related patents.Though ecological studies on soil actinomycetes from various habitats including grasslands, beach sands, underground caves, rice-paddies, orchards and sub-glacial ice of Antarctica were reported, only few reports are available on forest soil actinomycete communities[4]. These ubiquitous organisms are deemed to have a preference over the soil constituents such as humus, litter, dung and even rock surfaces. In fact actinomycetes are the dominant microflora showing viable counts reaching 106 per gram of dry weight soil in relatively dry, humic, and calcareous soils,[5]. The Eastern Ghats is a discontinuous range of mountains along the east coast of India, located between 10º 05' and 22º 30' N latitude and 76º 23' and 86 º 50’ E longitudes in north east to southwest strike, which is broken and comprises many viz. Shevaroys, Kalrayan, Chitteri, Kollimalai, Pachchimalai hills of Tamilnadu. Very little information is available on the actinomycetes population of these hills including those from Kollimalai[6] and Pachamalai[7].Wealth of information/ knowledge is available on the early inhabitants of Javadi hills, a place inhabited by human being even during Stone Age. Claims for supporting this are available in the form of 4000 years old Stone Age tribal caves. There are traces of evidence depicting the presence of Chitra Kullers before the invasion of present day outsiders. The rock houses still exist at Chepli above Pattaraikadu giving an affirmation that they might be kullers or the early tribes who lived as hunters. The glory of Javadi hills was prized even in the Patthu pattu, one of the earliest classical language Tamil literatures.The Javadi Hills, the largest of Eastern Ghats forest consists of dray mixed deciduous to thorny shrubs with occasional patches of dray ever green growth. The maximum temperature go up to 44.4 0 C during the summer month May and minimum temperature falls to 11.70 C during the winter month January. The average rain fall is about 886mm. Amirthi forest is situated under the Javvadu/Javadi Hills of Tellai across Amirthi River contains a wide variety of flora and fauna. The soil is highly rich in organic matter and suitable for the growth of microorganisms[8].Although there are a number of reports on distribution and traditional uses of medicinal plants from these early human inhabitated areas are readily available, data on their microbial resources are scarce, imprecise, and not well documented. Due to uniqueness, large geographic variation, different soil types and their contents of this forest, it is quite likely that there is vast distribution of antibiotic producing actinomycetes in this environment. The present study was carried out to screen the most assured antimicrobial compounds producing actinomycetes from these unexplored soils for possible harnessing of potential antibiotics from the actinomycetes towards combating highly resistant pathogenic bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area and Sample Collection
- The Javadi Hills, the largest of Eastern Ghats are located in Vellore district (Tamilnadu, India) at an altitude of 300–1000m above sea level (longitude 78° 40' E; latitude 12° 40' N ), in North to South direction, covering a distance of 80 km in width and 32 km in length. Its average height is about 214 m, bisected into eastern and western sections by the Cheyyar and Agaram rivers. The centre of the Javadi hills consists of extensive undulating plateau with large valleys ranging from 500–800 metres. Soil samples were collected from this hill at 10-15 cm depth of the soil[9], air-dried for 1 week[10], crushed, and sieved. The sieved soils were then used for isolation of actinomycete.
2.2. Isolation of Actinomycetes Isolates
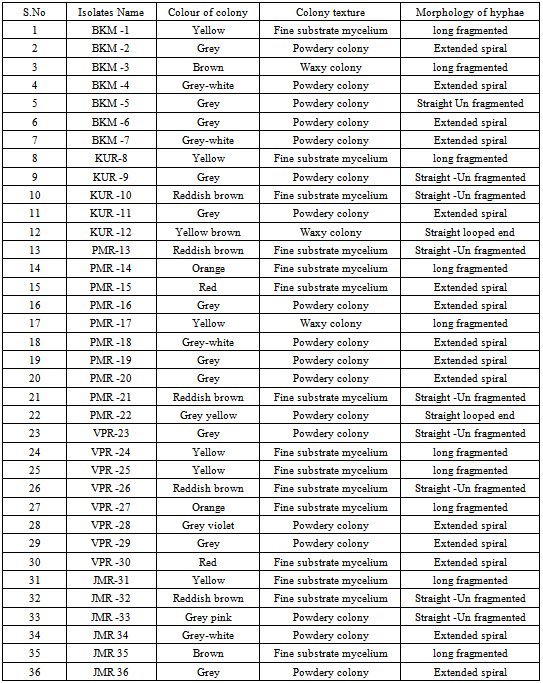
- The actinomycetes from crushed and sieved soil samples were isolated as described previously[11] employing serial dilution and spread plate technique. One gram of soil sample was transferred into 9 ml of sterile double distilled water (101) and serially diluted up to 10-5 dilutions using each 9 ml of sterile double distilled water blanks. Hundred microliter of diluted soil sample from 10-3, 10-4 and 10-5 dilutions was spreaded on starch casein agar[12] plates supplemented with nalidixic acid (20µg/ml) and nystatin (100µg/ml) as well as actinomycete isolation agar (M490, HiMedia, Mumbai, India). Plating was done in triplicate and all the plates were incubated at 28ºC for one week. The individual colonies were selected based on morphology and purified by inoculation onto ISP-2 (International Streptomyces Project) agar plates which were incubated for 7–14 days at 28ºC. Morphologically distinct colonies were selected for further studies.
2.3. Microorganisms Used
- The bacterial strains of Escherichia coli (MTCC 739), Bacillus cereus (MTCC 1272), Staphylococcus aureus (MTCC 1144), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 1688), Proteus mirabilis (MTCC 1425) Klebsiella pneumonia (MTCC 109) as well as Candida albicans obtained from microbial type culture collection (MTTC) Chandigarh, India were used in this study.
2.4. Determination of Bacterial Antagonistic Activity
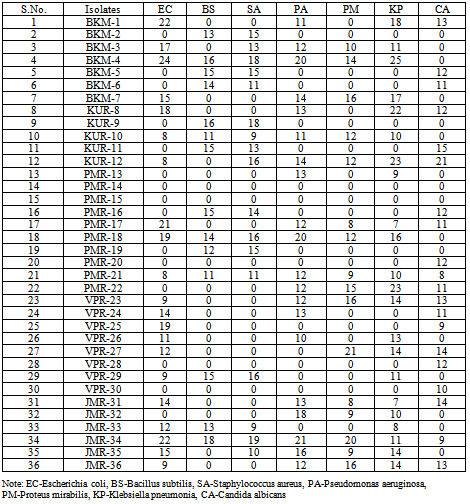
- Antagonistic activities of the selected isolates were tested by adopting agar plug method[13]. The isolates were inoculated onto ISP2 agar plates and were allowed to grow restricted towards one end of the plate for 10 days. Later 5 mm diameter core agar plug were removed from the grown cultures and the surface growth on agar was removed with sterile knife to allow remaining of only the diffused microbial metabolites in the agar plugs. The agar plugs were placed onto the nutrient agar plate which was previously swabbed with the test pathogens. All the plates were then incubated at 37º C for 24 h. After incubation, antimicrobial activity indicated by the formation of an inhibition zone surrounding the agar plug was measured. The absence of an inhibition zone around the plugs indicated a negative result. The observed growth inhibitory activities of the isolates were further confirmed by cross streak test. The isolates showing significant inhibitory activities were inoculated on modified nutrient glucose agar (MNGA) plates by single streak in the center and incubated at 28oC for four days. The previously used test pathogenic organisms were inoculated perpendicular to the actinomycetes growth and incubated at 37oC for 24 h. The antagonistic activities of the isolate were confirmed by their growth inhibition. Isolates showing significant inhibitory activity against at least two pathogenic test organisms were further selected for secondary screening.
2.5. Determination of Bioactive Compound production and Their Inhibitory Activity
- The bioactive substance producing ability of the isolates that showed antagonistic activity was determined by a method described by Mohanraj et al.[14]. Briefly, the selected bacterial antagonistic isolates were grown in submerged fermentation condition by adopting shake flask method. Initially 10% of culture inoculum was transferred into each 100 ml of ISP2 broth and incubated in a rotary shaker with 95 rpm at 280C for 7 days. The cell free supernatant was obtained and 100 μl was poured into 5mm well made in nutrient agar (NA) plates. The NA plates were previously inoculated with test organism cultures as described. After incubation the diameter of the zone of inhibition was measured in millimeter and recorded. The isolates were designated as BKM (Bheemakulam), KUR (Kavalur ), PMR (Palamarathur), VPR (Veerappanur) as well as JMR (Jamunamathur) according to the place of collection and preserved in 15% glycerol (v/v) slants at -20oC.
3. Results and Discussion
- Antibiotics are an indispensable part of modern medicine. The emergence of antibiotic-resistance among pathogenic bacteria is apparently certain, and results, within a few decades, in decreased efficacy and withdrawal of the antibiotic from general practice. Hence for the continuance of modern medicine in its present form, novel families of antibiotics must be available in the market at regular intervals[15]. Many important bioactive compounds of high commercial value were obtained from actinomycetes and the screening is being continued for deriving new bioactive compounds especially novel antibiotics active against resistant organisms. This endeavour was undertaken with an objective of identifying culturable new actinomycetes having novel anti-bacterial activity against the resistant pathogenic bacteria from the virgin soils of Javadi hills.
|
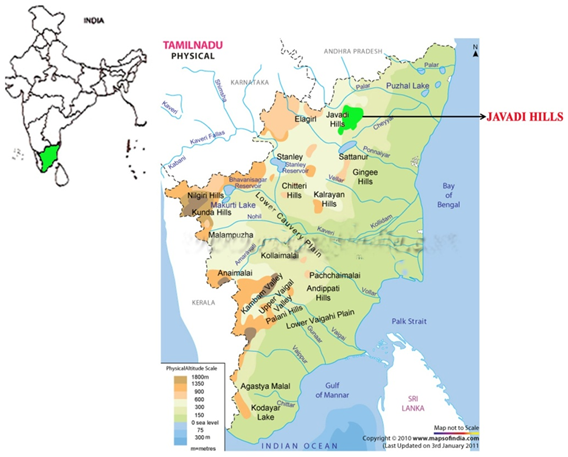 | Figure 1. Schematic map showing the location of Javadi hills, Tamilnadu, India(Courtesy:www.mapsof India) |
|
4. Conclusions
- Considering the outcome of the present investigation, it was concluded that Javadhu hills is a rich source for deriving economically important Actinomyces. The antibiogram results indicated that the hill soils are source for hyperactive actinomycetes antagonistic against the pathogenic bacteria and fungi. The widest activity spectrum and the largest inhibition zones were shown by strains BKM-4, JMR-34 and PMR-18 while the first exhibited the best performance. Thus there is definite scope for bioprospecting of antagonistic actinomycetes from Javadi hill forest soil ecosystem once appropriate further studies are undertaken.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML