-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
2012; 2(2): 1-4
doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20120202.01
The Antibacterial Evaluation of Moringa Oleifera Leaf Extracts on Selected Bacterial Pathogens
M. E. Abalaka 1, S. Y. Daniyan 1, S. B. Oyeleke 1, S. O. Adeyemo 2
1Department of Microbiology, Federal university of Technology, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria
2Department of Biochemistry, Bingham University, Karu, Nassarawa State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: M. E. Abalaka , Department of Microbiology, Federal university of Technology, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
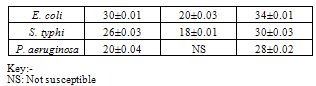
The Antibacterial Activity Of Leaf Extracts Of Moringa oleifera Lam Belonging To The Family Moringaceae Was Determined Using Agar Diffusion Methods. Two Solvents, Water And Chloroform, Were Used For Extraction Of The Active Ingredients In The Plant. The Crude Chloroform Extract Showed Remarkable Activity Against The Growth Of Escherichia Coli, Salmonella Typhi And Pseudomonas aeruginosa With The Diameter Zones Of Inhibition (DZI) Of 30±0.01, 26±0.03 And 20±0.04 Respectively. The Aqueous Extract Of The Leaf Of This Plant Showed Activity Against E. Coli And S. Typhi Showing Diameter Zones Of Inhibition Of 20±0.03 And 18±0.01 But P. aeruginosa Was Resistant At All Test Concentrations. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Ranges From 10-20mg/Ml While The Minimum Bactericidal Concentration Ranges From 20-40mg/Ml. The Phytochemical Screening Of Samples Revealed The Presence Of Secondary Metabolites Such As Alkaloids, Flavonoids, Saponins And Tannins. If Well Researched Into And Refined With The Determination Of Its Toxicity, M. oleifera Could Be A Valuable Drug In The Treatment Of Infections Caused By The Test Organisms.
Keywords: Crude Extracts, Moringa oleifera, Phytochemical Screening, Susceptibility Testing
1. Introduction
- Moringa oleifera is native to the western and sub- Himalayan region, India, Pakistan, Asia minor, Africa and Arabia[1]. The Moringa tree is cultivated and used as a vegetable (leaves, pods flowers, roasted seeds), for spice (mainly roots), cooking and cosmetics oil (seeds) and as a medicinal plant (all plant organs)[2]. Important medicinal properties of the plant include antipyretic, antiepileptic, antiinflamatory, antiulcerative[3] antihypertensive[4], cholesterol lowering[5], antioxidant[6], anti diabetic, hepatoprotective[7], antibacterial and antifungal activities[6]. In addition, M. oleifera seed possesses water purifying powers[8,9]. They are known to be anti-helminthic, antibiotic, detoxifiers, immune builders and have been used to treat malaria[10] and it can also be used as a less expensive bio-absorbent for the removal of heavy metals[11].Moringa oleifera is a highly valued plant, distributed in many countries of the tropics and subtropics. It has impressive range of medicinal uses with high nutritional value. Different parts of this plan contain a profile of important minerals, and a good source of protein, vitamin, â carotene, amino acids and various phenolics[12]. The Moringa plant provides a rich and rare combination of zeatin, quercetin, kaempferom and many other phytochemicals.However, a very important step in the screening of the sanitizing and preservative activity of a plant material is to evaluate its antimicrobial properties. It is important to evaluate the antimicrobial properties of M. oleifera leaves on some selected microorganisms and also to verify its phytochemical constituent.Therefore, the aims and objectives of this research is to determine the phytochemical constituents of the leaf extracts of Moringa oleifera as well as its antimicrobial properties on selected microorganisms.
2. Materials and Methods
- Collection and Processing of Plant MaterialsThe fresh leaves of M. oleifera were collected from Maitumbi area of Minna Niger State, Nigeria. The plant materials were air-dried in the laboratory for two weeks and then grounded into powdered form using a mortar and pestle and stored for future use.ExtractionThe powdered plant material (50g) (leaves) was percolated in 500ml chloroform in one liter capacity conical flasks, stopper and kept for two weeks with intermittent shaking. The percolates were filtered with Whatman’s No. 1 filter paper. The extracts were concentrated at 40℃ under reduced using rotary evaporator (R110). The same quantity of plant material was again percolated with distilled water for one week and after filtration, the aqueous extract was concentrated in hot oven at 40℃[13]. The concentrated extracted were labelled MLC (Molinga leaf chloroform extract) and MLA (Moringa leaf aqueous extract).Phytochemical AnalysisPhytochemical analysis for qualitative detection of alkaloids, flavonoid, tannins, and saponins, was performed on the extract as described by [14] and [15].Screening and standardization of the test organismsThe pure culture of the test organisms used (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhi) were collected from microbiology laboratory of Federal University of Technology, Minna. The isolates were subcultured on agar slant and stored at 4℃ until further use. A loopful of the test organisms was inoculated into 5.0ml of nutrient broth and incubated at 37℃ for 24 hours. 0.2ml from the 24hours culture of the organism was dispensed into 20ml sterile nutrient broth and incubated for 3-5hours to standardize the culture to 106cfu/ml[16].Screening of extracts for antimicrobial activityZero point two (0.2g) of each of extract was dissolved in 2ml of the solvent used for extraction after which 8ml of sterile distilled water was added.The agar diffusion method was used. Sterile nutrient agar plates were prepared. 1ml of the test organisms was added to 19ml of nutrient agar and each plate was properly labelled. A sterile cork borer (7mm) was used to make ditches in each plate for the extract. The base of each ditch was filled with molten nutrient agar to seal the bottom and allowed to gel. 0.5ml of the reconstituted extract with the concentration of 20ug/ml was dispensed into each ditch. The plates were left to allow for diffusion of extract before incubation at 37℃ for 24 hours. The zones of clearance produced around the ditches after incubation were observed, measured and recorded.Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)The broth dilution method was used. 8 test tubes were collected of which the first test tubes contain1.5ml of peptone water, while the rest 7 contains 1ml of peptone water each. 0.5ml of reconstituted extract at 20mg/ml was dispensed into the first test tube. After one fold serial dilution, the test tubes were inoculated with a loopful of the test organisms using sterile loop.Three (3) extra test tubes, the first containing peptone water only, the second containing peptone water plus extract and the third containing peptone water plus the test organisms were incubated along with the batch of the test tubes at 37℃ for 24 hours to serve as a control. The lowest dilution that shows no visible turbidity was regarded as minimum inhibitory concentration[17]. Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)The test tubes that showed no visible turbidity after incubation of the batch of the test tubes were subcultured on nutrient agar plates and incubated at 37℃ for 24 hours. The concentration that shows no visible growth after incubation was considered the minimum bactericidal concentration.
3. Results
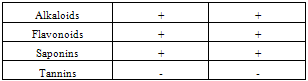
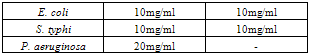
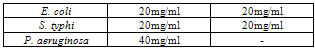
- Table 1 shows the results of the phytochemical screening of the crude extract of Moringa oleifera. The result reveals the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids and saponins in the chloroform and aqueous extracts of M. oleifera while tannins were absent in both the chloroform and aqueous leaf extracts.Table 2 shows the antimicrobial activity of M. oleifera extracts on the test organisms. The result reveals that chloroform and aqueous crude extracts of the leaf of M. oleifera were active against the test organisms. The control (ampiclox) had the highest zone of inhibition (23mm) on E. coli and S. typhi followed by aqueous leaf extract on E.coli (20mm) and chloroform extract on Pseudomonas aeruginosa with zone of inhibition of 18mm. P. aeruginosa was resistant to the activity of the aqueous extract. Table 3 shows the result of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) screening of chloroform and aqueous extract of the leaf of M. oleifera. The result revealed that the MIC of the chloroform and aqueous leaf extract on E. coli and S. typhi were 1.667mg/ml and 0.417mg/ml respectively. The MIC of the chloroform leaf extracts on P. aeruginosa was 0.417mg/ml but there was no MIC of the aqueous leaf extract on P. aeruginosa.The result of the minimum bactericidal (MBC) screening of chloroform and aqueous extract of the leaf of M. oleifera (Table 4) reveal that the MBC of the chloroform and aqueous leaf extract on E. coli and S. typhi were 6.667mg/ml and 1.667mg/ml respectively. The MBC of the chloroform leaf extracts on P. aeruginosa was 6.667mg/ml but there was no MBC of the aqueous leaf extract on P. aeruginosa.
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The preliminary screening of the leaf extracts of M. oleifera (Table 1) revealed the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids and saponins but tannin was absent. Report by[18] revealed the presence of alkaloids, tannins and saponins in chloroform extracts of Moringa leaf. The presence of alkaloids and flavonoids reveal the efficacy of the plant against the pathogenic bacteria. The presence of flavonoid also correlates with the reports of[12] who stated that the M. oleifera plant is one of the highly potential antidiabetic plants, probably because of the presence of the ability of its compounds and some flavonoids to inhibit a-amlylase activity to regulate the amount of glucose in the blood. The extracts have varying degree of antibacterial activities against the test organisms. The chloroform leaf extract had a higher zone of inhibition (30±0.01) when compared with the aqueous extract (20±0.01). Ampicillin (the control) had the highest zone of inhibition (34±0.01) on the test organisms. However, there was no significant difference (P>0.05) between the zones of inhibition of extracts and the control. The strong activities of the leaf suggest that the plant they may be used for treatment of infections caused by these organism except P. aeruginosa which was found to be resistant to the activity of the aqueous leaf extract (Table 2). The antimicrobial activity of M. oleifera leaf may be due to the presence of an array of phytochemicals. [19] and [18] both identified, most importantly, the presence of a short polypeptide named 4 (ά– L – rhamnosyloxy) benzyl- isothiocyanate in M. oleifera. They argued that the peptide may act directly on microorganisms and result in growth inhibition by disrupting cell membrane synthesis or synthesis of essential enzymes. The MIC obtained shows that different concentrations were effective against some of the organisms (Table 3). The most susceptible organisms to the antibacterial activity of M. oleifera was E. coli. The same value obtained from the chloroform leaf extract and aqueous leaf extract on E. coli and S. typhi confirmed that both extracts have the same phytochemical properties (Table 1) and hence exhibit similar inhibitory effects (Table 3) and bactericidal effects (Table 4) on the test organisms. The aqueous leaf extract had no inhibitory or antibacterial effects on P. aeruginosa. [20] reported that P. aeruginosa is well known as a hardy and difficult organism that constitutes problems to researchers.
5. Conclusions
- The results of the present study have shown the potentials of M. oleifera leaves on chloroform and aqueous extracts used contain bio-components whose antibacterial potentials are highly comparable with that of the antibiotic ampliclox against the gram negative and gram positive bacteria tested. The activity of the leaf against both gram positive and gram negative bacteria may be indicative of the presence of broad spectrum bioactive compounds in the leaf. Therefore, M. oleifera could be a promising natural antimicrobial agent with potential applications in pharmaceutical industry for controlling the pathogenic bacteria used in this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML