-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Basic Sciences of Medicine
p-ISSN: 2167-7344 e-ISSN: 2167-7352
2020; 9(1): 10-14
doi:10.5923/j.medicine.20200901.03

Surgical Anatomy of Thyroid Gland - A Comprehensive Review
Rajani Singh
Department of Anatomy, UP University of Medical Sciences, Saifai, Etawah, UP
Correspondence to: Rajani Singh, Department of Anatomy, UP University of Medical Sciences, Saifai, Etawah, UP.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland and thyroid diseases are common health problems especially in females. Thyroid disorders like goitre, adenoma and carcinoma can be manipulated mainly through surgical interventions. A thorough and in depth knowledge of thyroid anatomy is essential for safe thyroid surgery to minimise postoperative complications. Thus the aim of present study was to elucidate surgical anatomy of the thyroid gland to update and consolidate the information associated with thyroid gland for ready use for future endocrinologists and thyroid surgeons. The literature search was carried out using data bases, Scielo, Scopmed, medline, Web of Science, Meditext, Amed, pubmed and Wiley online library and terms related to thyroid gland were used to search literature. Literature search brought out complete anatomy of thyroid gland and associated clinical significance which will be of utmost use as ready reference to thyroid surgeons and endocrinologists.
Keywords: Thyroid gland, Thyroid anatomy, Thyroid surgeons, Endocrinologist
Cite this paper: Rajani Singh, Surgical Anatomy of Thyroid Gland - A Comprehensive Review, Basic Sciences of Medicine , Vol. 9 No. 1, 2020, pp. 10-14. doi: 10.5923/j.medicine.20200901.03.
1. Introduction
- The thyroid gland is enshrined on the front of the neck below adam's apple along the front of the trachea. Thyroid ailments are common health problems reported to endocrino-pathologists and 5% of the world population are found to be affected by various thyroid diseases [1] namely goitre, thyrotoxicosis, adenoma, carcinoma etc. These thyroid disorders are associated with enlargement of the gland and can be manipulated by medical and surgical therapy [2]. Hence to carry out safe and effective thyroid surgery, thorough knowledge and understanding of thyroid anatomy and pathology is imperative [3]. For performance of surgical interventions like total thyroid lobectomy and total thyroidectomy with minimal risk of invasion to neurovascular structures associated with thyroid and parathyroid glands comprehension of thyroid anatomy is very essential. Considering immense surgical implications pertaining to damage to neurovascular structures of thyroid during thyroidectomy, the study highlighting surgical anatomy of the thyroid gland has been carried out. The study will be updating and consolidating present and past research work and make the information available for ready use to future researchers, thyroid surgeons to carry out thyroid surgery with minimal damage to neurovascular structures of thyroid gland.
2. Material and Methods
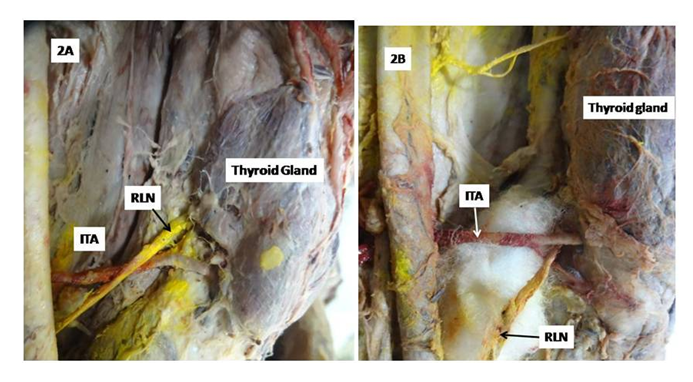
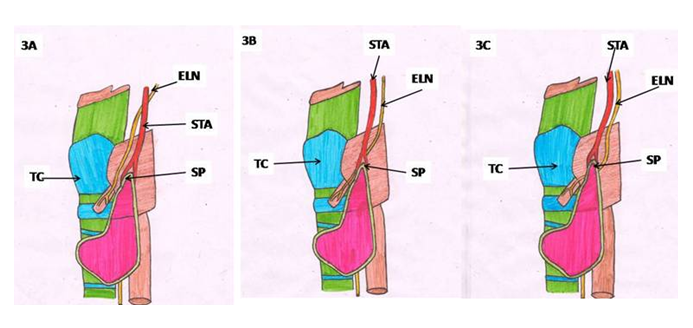
- Literature search was conducted in the department of Anatomy UPUMS Saifai during September 2019- December 2019 using the data bases appended below: Scielo, Scopmed, medline, Web of Science, Meditext, Amed, pubmed and Wiley online library. Papers containing original data were selected and secondary references retrieved from bibliographies. The search was restricted to English language articles and selected reference text books. Various terms used to search literature were as illustrated below: Thyroid gland, surgical anatomy of thyroid gland, recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), variations of recurrent laryngeal nerve, variations of external laryngeal nerve, blood supply of thyroid gland, clinical implications of recurrent laryngeal nerve and clinical implications of external laryngeal nerve. Data after surveying was consolidated and presented here.
3. Results and Discussion
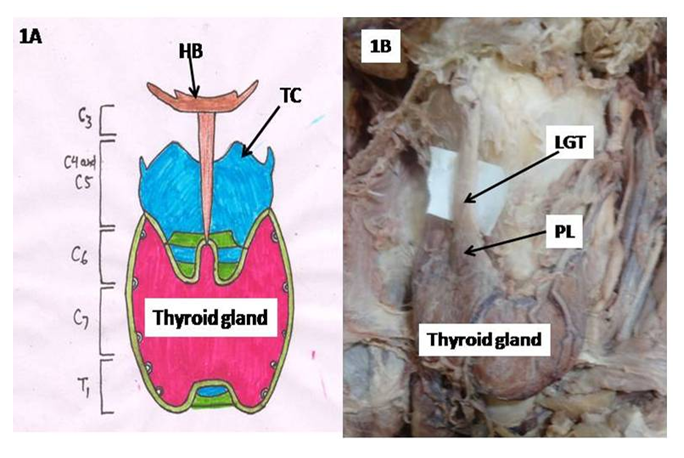
- Location of Thyroid Gland:Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland. It is situated opposite C5- C7 and T1 vertebra (Fig 1A) embracing anterolateral part of trachea [3]. The gland is related medially to trachea and oesophagus and carotid sheath laterally. The gland is covered anterolaterally by sternocleidomastoid and three ribbon muscles, sternohyoid, sternothyroid and superior belly of omohyoid muscles. There are numerous variations in the shape and extent of thyroid gland. The alterations in shape and size of the thyroid gland along with moderation of its anatomical borders occur under the conditions, thyroiditis, malignancy, goiter, substernal goiter, hypothyroidism, prior cervical surgery and prior radioiodine ablation [2]. Thyroid gland comprised of left and right lobes which are connected to each other by isthmus, a horizontal band of thyroid tissue. Each thyroid lobe extends from mid-thyroid cartilage superiorly to the 4th or 5th tracheal ring inferiorly and common carotid arteries laterally. Though thyroid lobes are normally flat or globular yet partially cover the trachea posteriorly by a three-dimensional shape.Variations are observed in the occurrence of lobes, isthmus, arterial supply, venous drainage and innervation pattern of thyroid gland. These are discussed one by one as under:Pyramidal lobe:A variation of thyroid lobes is also seen having a third lobe known as pyramidal lobe (PL) besides two normally found lateral lobes. Pyramidal lobe may project upward from the isthmus or from one of the lobes of thyroid gland (Fig 1B). Occasionally, a fibrous or fibromuscular band known as levator glandulae thyroidae may extend from hyoid bone to either isthmus or PL.
4. Conclusions
- Knowledge of anatomical variations of thyroid gland and neurovascular configuration coupled with their variations help in proper identification of thyroid gland, associated vessels and nerves for routine surgical procedure during and after neck surgeries of thyroid in order to avoid major complications. Detailed thyroid anatomy and its associated anatomical variants are of paramount importance to endocrinologist and neck surgeons, so that these anomalies are taken into account in diagnosis and treatment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML