-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Basic Sciences of Medicine
p-ISSN: 2167-7344 e-ISSN: 2167-7352
2016; 5(1): 8-10
doi:10.5923/j.medicine.20160501.03

Aberrant Configuration and Branching Pattern of Circumflex and Profunda Femoris Arteries
Rajani Singh , Munish Wadhwan
Department of Anatomy, AIIMS Rishikesh, India
Correspondence to: Rajani Singh , Department of Anatomy, AIIMS Rishikesh, India.
| Email: | 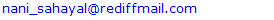 |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

During dissection of femoral triangles of female cadaver aged 70 years fixed in 10% formalin for teaching purpose in the department of Anatomy, AIIMS Rishikesh, variant configuration of profunda femoris and its branches were observed bilaterally. On right side, common trunk arose from femoral artery 4 cm distal to inguinal ligament. Instantly the common trunk gave medial circumflex femoral artery. The common trunk descended further for 2 cm and trifurcated into lateral circumflex femoral, profunda femoris arteries and muscular branches. Such branching pattern of profunda femoris artery is unique. On the left side, femoral artery gave common trunk on medial aspect at a distance of 4 cm from inguinal ligament. This common trunk bifurcated into medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries. Then femoral artery gave origin to profunda femoris artery at a distance of 6 cm below the inguinal ligament. Such branching pattern of profunda femoris and femoral artery is also rare. Variations in the branching pattern of femoral and profunda femoris arteries have clinical implications while performing various therapeutic and diagnostic procedures around femoral triangle. Hence the case has been reported.
Keywords: Variation, Femoral artery, Profunda femoris artery, Lateral circumflex femoral artery, Medial circumflex femoral artery
Cite this paper: Rajani Singh , Munish Wadhwan , Aberrant Configuration and Branching Pattern of Circumflex and Profunda Femoris Arteries, Basic Sciences of Medicine , Vol. 5 No. 1, 2016, pp. 8-10. doi: 10.5923/j.medicine.20160501.03.
1. Introduction
- Normally profunda femoris artery arises on the posterolateral aspect of femoral artery about 3.5 cm distal to inguinal ligament in femoral triangle. Lateral circumflex femoral artery (LCFA) originates from profunda femoris artery near the root and medial circumflex femoral artery (MCFA) emanates below the lateral circumflex artery on the medial aspect of profunda femoris artery. The MCFA and LCFA branches anastomoses with the internal and external iliac arteries (1). Interventional radiology is new technique to study the variations of the courses of the PFA. The anatomical knowledge of the site of origin of PFA is useful in avoiding iatrogenic femoral arterio-venous fistula formed during puncture of femoral artery (2). Rare variant configuration of PFA were observed in present study and are reported for rarity and clinical implications associated with these variations.
2. Case Report
- During dissection of femoral triangles in a female cadaver of 70 years preserv in 10% formalin in department of Anatomy, AIIMS Rishikesh for teaching purpose some rarely known and other unique variations in the branching pattern of femoral and profunda femoris arteries were observed on both sides. On the left side, femoral artery gave a common trunk on medial aspect at 4 cm distal to inguinal ligament. After travelling for 1.5 cm, this common trunk bifurcated into lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries (Fig.1).
 | Figure 1. Showing variations of femoral artery and profunda femoris artery on left femoral triangle |
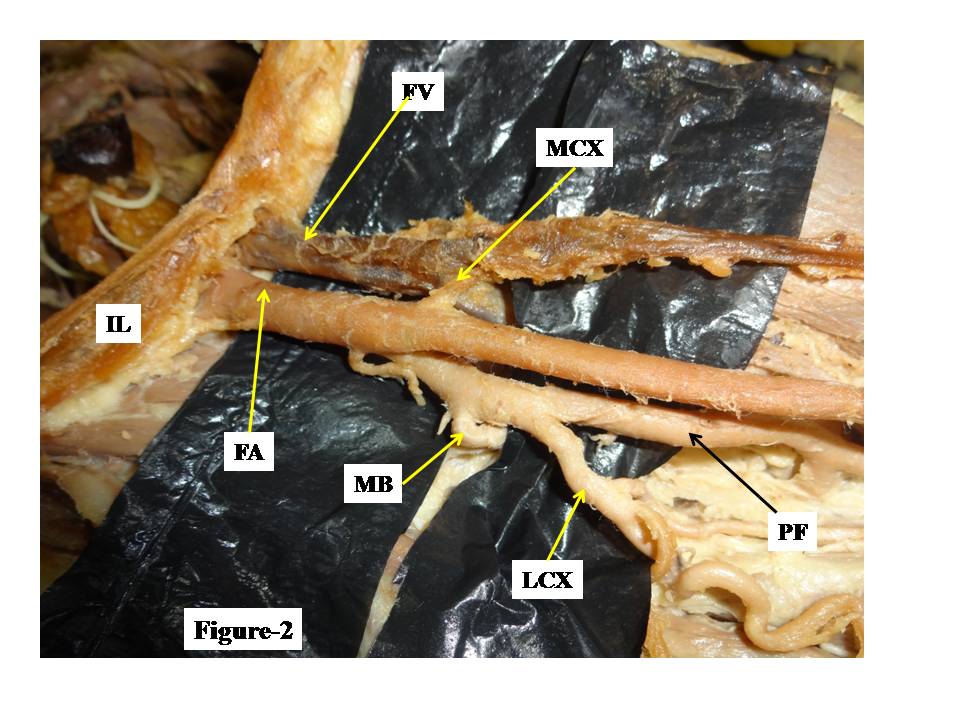 | Figure 2. Showing variations of femoral artery and profunda femoris artery in right femoral triangle |
3. Discussion
- Femoral artery is commonly used for various therapeutic and diagnostic procedures like catheterization, angiography etc. Moreover PFA and its branches are used for various surgical procedures like anterolateral thigh flap, plastic and reconstructive surgeries. Hence knowledge of variation in the origin of PFA and its branches is very important for preventing flap necrosis, particularly tensor fascia latae, when used in plastic and reconstructive surgery and also very relevant for the vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists [2, 3].Bifurcation of common trunk from femoral artery into medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries was observed by Evans et al similar to present study (on left side). But Evans et al [4] did not mention the arising side of common trunk from femoral artery whereas in the present case, common trunk arose on the medial aspect of FA. The normal distance of origin of profunda femoris artery from the midpoint of inguinal ligament is 35-40 mm [1]. This distance was between 31-40 mm on right side and between 41-50 mm on the left side [5]. High origin of PF arteries has been described by few authors [6, 7]. But present case describes a very lower origin PFA on left side arising at distance of 6 cm (60 mm) from inguinal ligament. Such low origin of PF artery is not described in literature and is new and unique. Profunda femoris artery arising from medial aspect of FA has been described by Chitra [8] similar to present study. But in our case, this variation is associated with low origin of PF. Origin of MCF and LCF arteries originating from FA directly has been reported by few authrs [9]. Sahin et al [10] reported the origin of LCFA directly from the FA at 4.9 cm distal to inguinal ligament. Vishal et al [7] also reported LCFA originating from FA directly. Profunda femoris artery arising from femoral artery as common stump with lateral circumflex femoral artery was also reported by Atulya et al., [11] Sangeeta et al., [12]. The common trunk splitting from FA, instantly gave MCX artery. Then it travelled further for 2 cm and trifurcated into LCX, PF and muscular arteries. No Literature describing such variation is available and this abnormality is new, unique and rare. The anatomical knowledge of the level of origin of PFA is of utmost use in avoiding iatrogenic femoral arterio-venous fistula formed during puncture of femoral artery [2]. PFA is used for haemodialysis, vascular reconstructive procedures and various radio imaging techniques like Ultrasound Doppler Imaging and MRI [8, 13].
4. Conclusions
- Knowledge of variations in the branching pattern of FA and PF artery are very essential for surgeons for carrying out various surgical procedures in and around femoral triangle, radiologists for diagnosis and interpretations of radiographs coupled with new variations for anatomists.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML