-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Basic Sciences of Medicine
p-ISSN: 2167-7344 e-ISSN: 2167-7352
2014; 3(4): 85-100
doi:10.5923/j.medicine.20140304.03

The Protective Effect of Pumpkin Seed Oil on Azathioprine – Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats: Histological and Immunohistochemical Study
Fatma Sayed Abdel Aal
Histology Department, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Fatma Sayed Abdel Aal, Histology Department, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Pumpkin is an herbal medicine rich in unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs), which represent about 84% of the total fatty acids. It is also rich in minerals and antioxidants as tocopherols and carotenoids. It has many medicinal properties like anti-diabetic, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogens. Azathioprine (AZ)(imuran) is an immunosuppressive drug used to treat autoimmune diseases in the skin, blood, and multiple body systems. On the hand it also causes damage to remote organs. Material and Methods: Twenty four adult male albino rats were used in the present study. They were divided into four equal groups. Group I, was untreated and used as a control group. Group II, group III and group IV were treated with pumpkin (4ml/day), azathioprine (15mg/day) and pumpkin/azathioprine (4 ml/15mg/day) orally respectively for four weeks. At the end of the experiment blood was collected for biochemical study. Tissues samples from the liver were collected from all rats for histological and immunohistochemical study. Aim of the work: to evaluate the possible protective role of pumpkin seed oil on hepatic injury induced by AZ treatment in male albino rats. Results: Azathioprine injection elevated plasma level of SGPT, SGOT and ALP compared to control group. Pumpkin seed oil improved these results to some extent.Light microscopic examination showed hepatic tissues with hemorrhage, cellular vacuolation, and dilation of blood vessels, cellular infiltration and intense immune reaction for caspase-3. The ultrastructure showed the cytoplasm of hepatocytes appeared rarified with marked vacuolation and destroyed organelles. The rats treated concomitantly with both AZ and pumpkin seed oil showed significance attenuation of the histological and immunohistochemical alternations. Conclusions: These results suggest that Pumpkin seed oil has a protective effect against Azathioprine induced toxicity, may be via its antioxidant role.
Keywords: Pumpkin, Imuran {Azathioprine}, Liver, & Rat
Cite this paper: Fatma Sayed Abdel Aal, The Protective Effect of Pumpkin Seed Oil on Azathioprine – Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats: Histological and Immunohistochemical Study, Basic Sciences of Medicine , Vol. 3 No. 4, 2014, pp. 85-100. doi: 10.5923/j.medicine.20140304.03.
1. Introduction
- Liver disease is one of the serious health problems. The use of hapatotoxic drug is a major cause of hepatic dysfunction.Azathioprine (AZ) is an immunosuppressive drug belongs to the chemical class of purine analogues used in organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases [1]. It has been widely used as an immunosuppressant for more than 50 years [2]. Synthesized originally as a cancer drug and as a prodrug for mercaptopurine in 1957 by inhibiting an enzyme that is require for the synthesis of DNA, thus it most strongly affects the proliferating cells, such as the T and B cells of the immune system. [3]. The main adverse effect of azathioprine is bone marrow suppression, which can be life-threatening, especially in people with a genetic deficiency of the enzyme thiopurines S-methyltransferase. [4] It is also listed by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as a Group 1 carcinogen (carcinogenic to humans) [5]. Azathioprine is produced by a number of manufacturers under different brand names, Imuran by GlaxoSmithKline in Canada, the U.S., Australia, Ireland and the United Kingdom [6].It is available as 50 mg oral tablets. Azathioprine is used alone or in combination with other immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection following organ transplantation, and to treat an array of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Behçet's disease and other forms of vasculitis, autoimmune hepatitis, atopic dermatitis, myasthenia gravis, neuromyelitis optica (Devic's disease), restrictive lung disease, and others. [7]It is used as a "steroid-sparing" agent for reducing the dose of corticosteroids. [4] [8] [9] It was shown to be very effective in eczema and atopic dermatitis in researches, even though it is not commonly used. [4]Azathioprine, like other thiopurines, can also cause liver injury, nodular regenerative hyperplasia and varying amounts of sinusoidal dilation, central vein congestion and injury to the sinusoidal endothelial cells [10]. Typically, serum aminotransferase levels and alkaline phosphatase levels are minimally elevated, even in the presence of hyperbilirubinemia and other manifestations of hepatic dysfunction. It had a high incidence of serious adverse drug reaction including hepatotoixty in rats and elevation of reactive oxygen species leading to mitochondrial injury and cell death due to necrosis [11]. SGPT is cytoplasmic enzyme, SGOT is a cytoplasmic and mitochondrial enzyme in hepatic cells, whereas ALP also synthesized by hepatic cells. An increase activity of those enzymes is a very sensitive index of hepatic damage [12]. C-reactive protein (CRP) is member of acute phase reactants synthesized by the liver, its level rise dramatically in liver disease [13].The use of herbal medicine individually or in combination with standard medicines has been used in various medical treatises for the cure of different diseases.Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.; Cucurbitaceae) is one of the well-known edible plants and has many medicinal properties as Anti-diabetic, Antioxidants, Anti- inflammatory, Anti-carcinogens and Phytochemical [14]. Pumpkin seed oil (PSO) is rich in unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs), which represent about 84% of the total fatty acids. Rich in minerals and antioxidants as tocopherols and carotenoids [15]. It contains remarkably high proportions of essential amino acids, and polysaccharides, and its relatively large amount of various essential micro-elements such as K, Cr, Na, Mg, Cu, and Se [16].Pumpkin seeds have a high content of vitamin E (tocopherol; an antioxidant). Pumpkin extract administration significantly increases the hepatic activities of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and reduce the concentration of malonaldehyde in tumour-containing mice serum [17].They also contain conventional mineral antioxidants like zinc and manganese. Phenolic antioxidants are found in pumpkin seeds in a wide variety of forms, including the phenolic acids hydroxybenzoic, caffeic, coumaric, ferulic, sinapic, protocatechuic, vanillic, and syringic acid. Antioxidant phytonutrients like lignans are also found in pumpkin seeds, including the lignans pinoresinol, medioresinol, and lariciresinol [18] [19].
2. Material and Methods
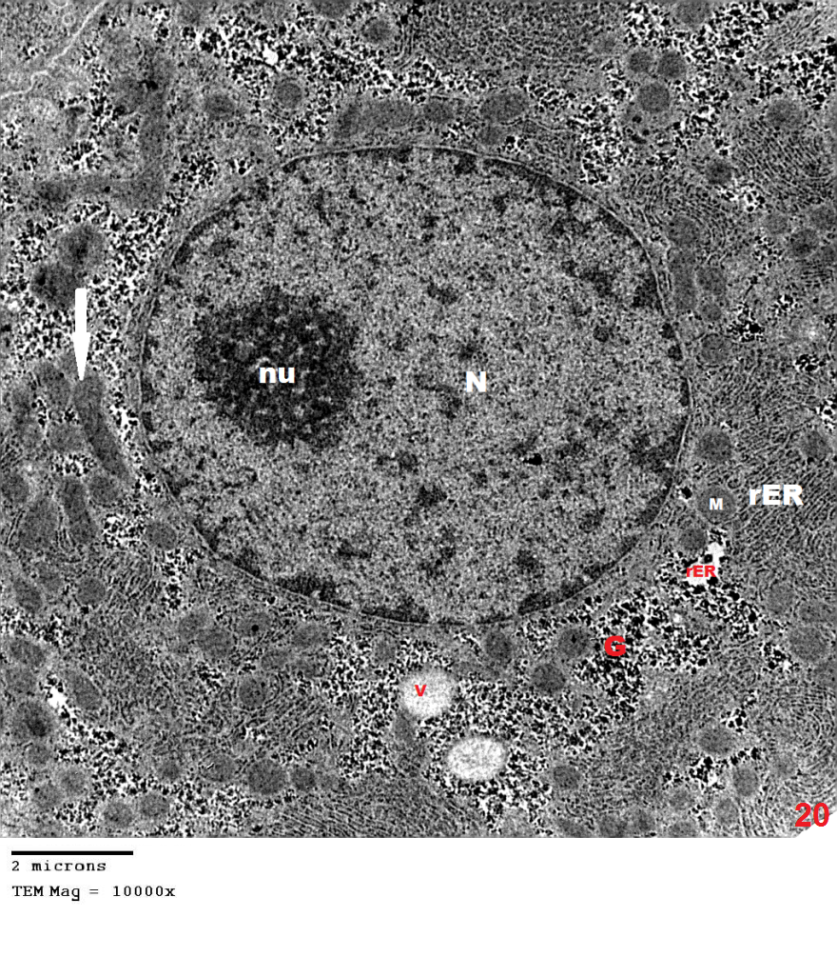
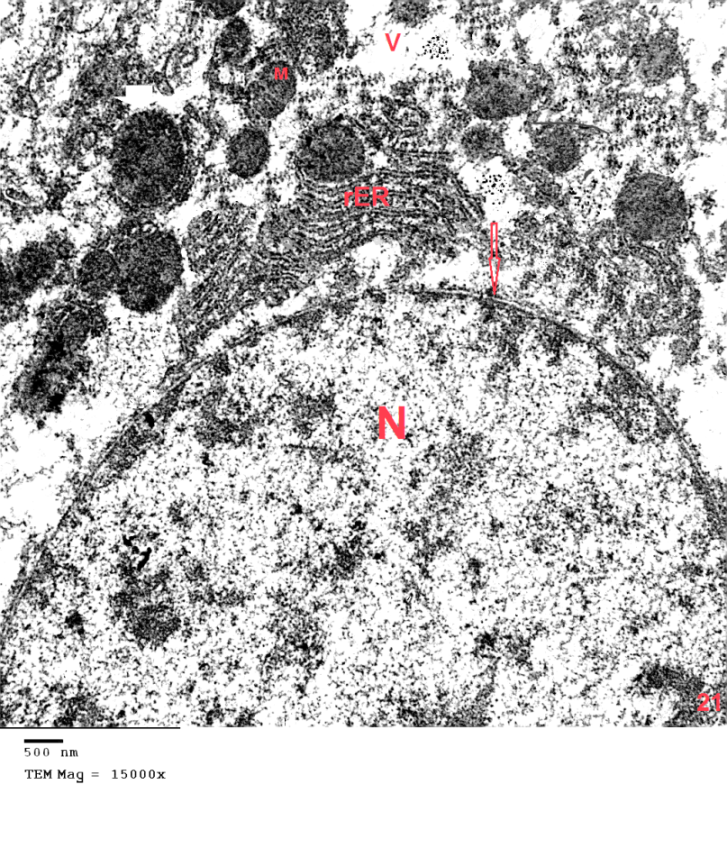
- DrugsImuran (Azathioprine): Imuran (Azathioprine), manufacture by Excell Gmbh Numberger12.90537 Feucht, Germany, was dissolved in normal saline (0.9% NaCl). Pumpkin seed oil (PSO): Pumpkin seed oil; manufactured by Imtenan, health shop company, Cairo, Egypt. Experimental animalTwenty- four adult male albino rats weighting 150-180 gm. were used in this study. The animals were housed in clean cages in animal house of the faculty of Medicine for Girls, Al Azhar University. Animals were maintained in a room temperature range of 25 ± 5°C under a 12:12h. light- dark cycle. They had fed free access to food (chow and water). They were fasted 12 houres (9:00p.m - 9:00a.m) before the experiment, but they allowed water.Experimental procedures One week acclimatization period was allowed before initiation of the experiment. On the start of the second week, the animals were divided equally into four groups as follows: I- control group. II - pumpkin seed oil group: the animals were given pumpkin seed oil by daily oral dose 4 ml/kg/day for four weeks [20]. III- azathioprine group rats: animals were injected intraperitoneally with azathioprine at dose 15mg/kg b. wt. for four weeks [21]. IV azathioprine/pumpkin seed oil group: animals were concomitantly administrated both azathioprine and pumpkin seed oil at the same dose and duration of group II and III. Hematological study:At the end of the experiment, animals were fasted for 12-16 hours before collection of blood samples. Blood was collected from retro –orbital sinus by heparin zed capillary tubes under ether anesthesia. The serum concentrations of Liver transaminases AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were estimated in the faculty of Medicine for Girls, Al Azhar University, Center for Virus Research and Studies.Statistical Analysis: All statistical analysis was performed using the statistical software package SPSS. The obtained data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA). The statistical significance level was defined as p< 0.05 [22]. Histological study:At the end of the experiment, animals were anaesthetized by ether inhalation and liver samples of the right lobe were collected from all animals. Each specimen was divided into two parts. The first part was immediately fixed in 5% glutaraldehyde for electron microscopic study while the other part was fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for light microscopic study.1. Light microscope study: one part was fixed 10% neutral buffered and processed for paraffin thin sections of 5um thickness. The sections were stained with haematoxylin & Eosin (H & E) for routine histological examination and Periodic acid Schiff's reaction (PAS) stain for glycogen demonstration [23].2. Imunohistochmical study: Caspase-3 (diluted 1:50) was used for detection of apoptosis in hepatic cells. Paraffin sections of the liver were cut at 5µm thickness on positively charged slides and incubated at 42°C in an oven for 24 h. Sections were deparaffinized in xylene (1h), hydrated in descending grade of alcohol, and incubated in hydrogen peroxide (5 min). They were thin washed twice in PBS (5 min each). Primary antibody was applied to the sections, which were incubated for (1.5 h). Then the specimens were washed in PBS for 5 minute each. Secondary antibody was applied and the sections were again incubated for 20 min, followed by washing 3 times in PBS for 5 min each. Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrocholride solution was applied to the sections and they were further incubated for 10 min [23]. The sections were washed in distilled water and countered stained with Mayer’s hematoxylin (2 min). Thereafter washed in tap water, cleared, and mounted by DPX. 3. Electron microscope study: t the specimens (1x1mm) were immediately fixed in 5% glutaraldehyde for 20 h, and then washed with cacodylate buffer and fixed in 1% osmium tetraoxide. Ultrathin sections of 50 nm were cut by an ultramicrotome, stained with uranyle acetate and lead citrate. The grade was examined and photographed with transmission electron microscope (Jeol-JEM-100CXII; Toyo, Japan) in the Electron Microscope Unit of Al-Azhar University [24].
3. Results
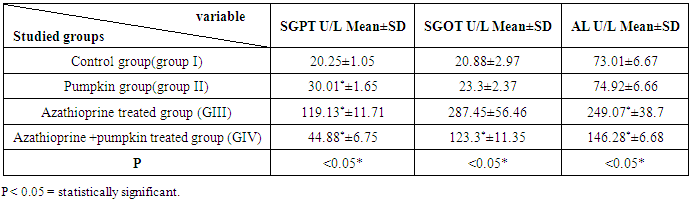
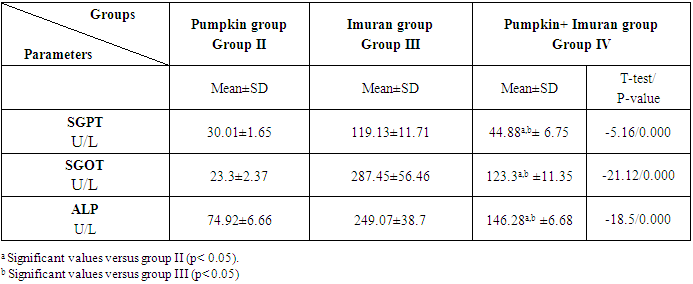
- HEMATOLGICAL RESULTSRegarding the liver function tests; serum SGPT was significantly increased in Imuran group and pumpkin + Imuran group compared to control group (table 1, histogram 1). Serum SGOT was significantly increased in Imuran group & pumpkin + Imuran group, while it was insignificantly changed in pumpkin group compared to control group (table 1, histogram 2). Serum ALP was significantly increased in Imuran group and pumpkin+ Imuran group, while they were insignificantly changed in pumpkin group compared to control group (table 1, histogram 3).
|
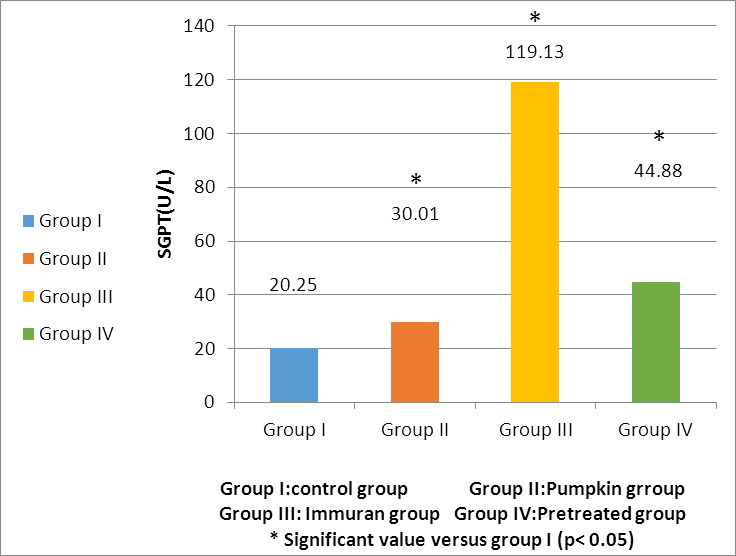 | Histogram 1. Changes in SGPT (U/L) level within all studied groups |
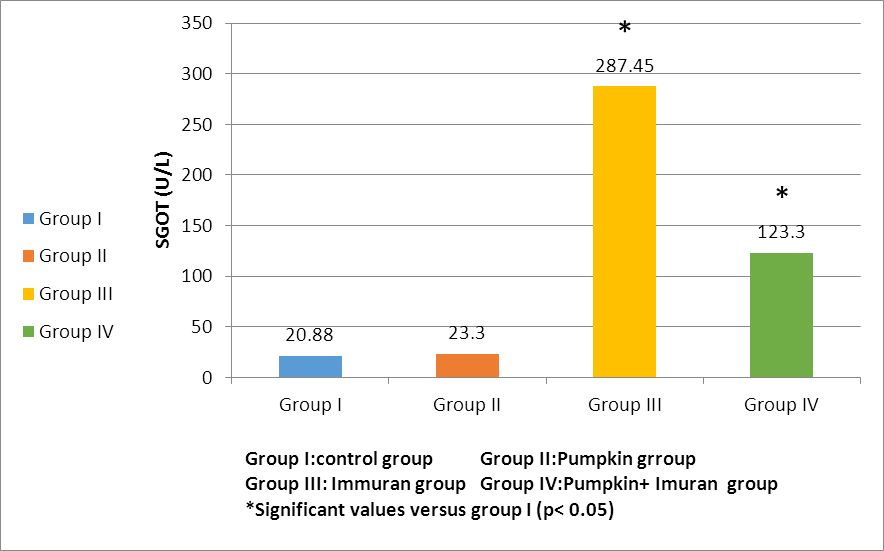 | Histogram 2. Changes in SGOT (U/L) level within all studied groups |
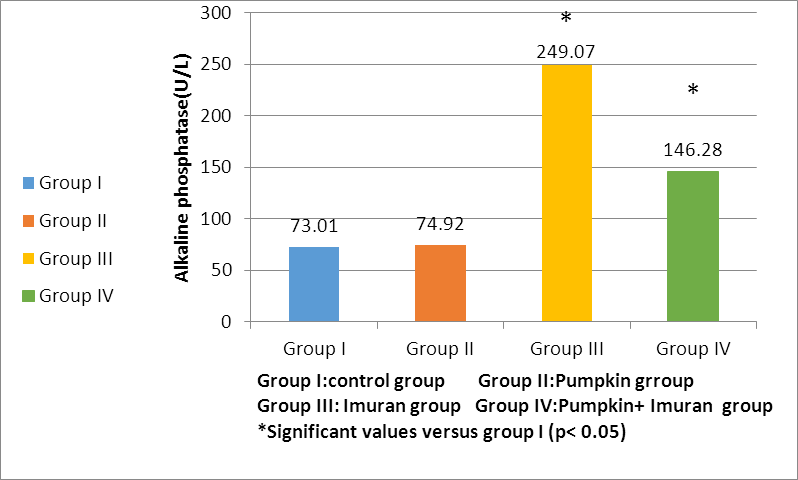 | Histogram 3. Changes in ALP (U/L) level within all studied groups |
|
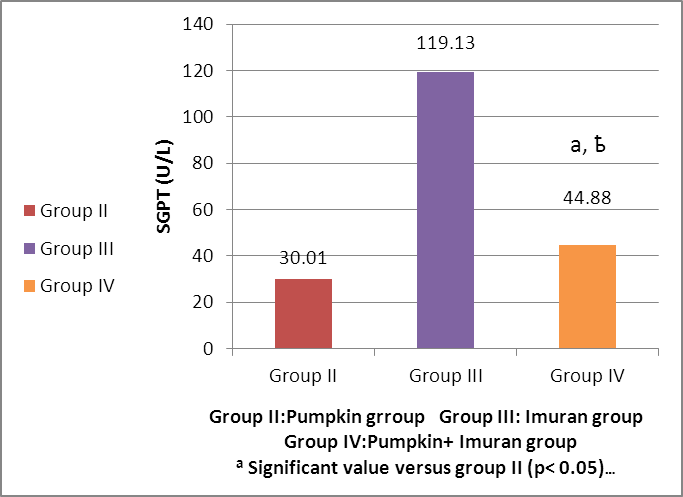 | Histogram (4). Changes in SGPT (U/L) level in group IV versus group II and group III |
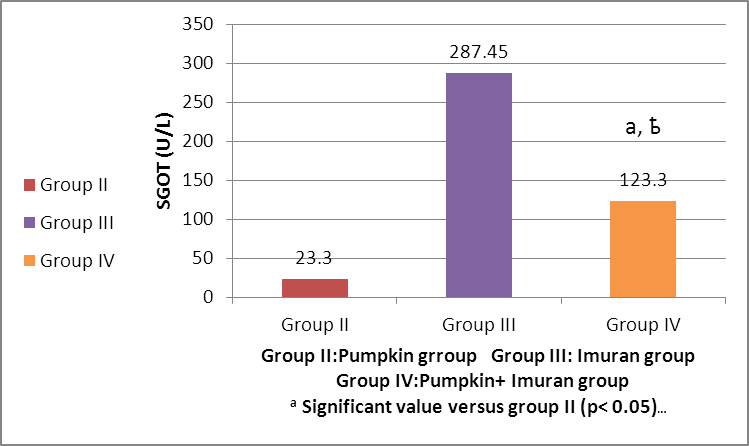 | Histogram 5. Changes in SGOT (U/L) level in group IV versus group II and group III |
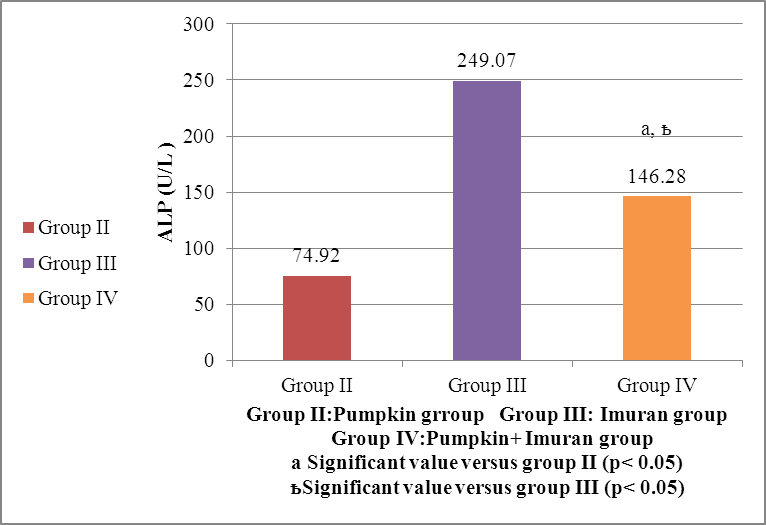 | Histogram 6. Changes in ALP (U/L) level in group IV versus group II and group III |
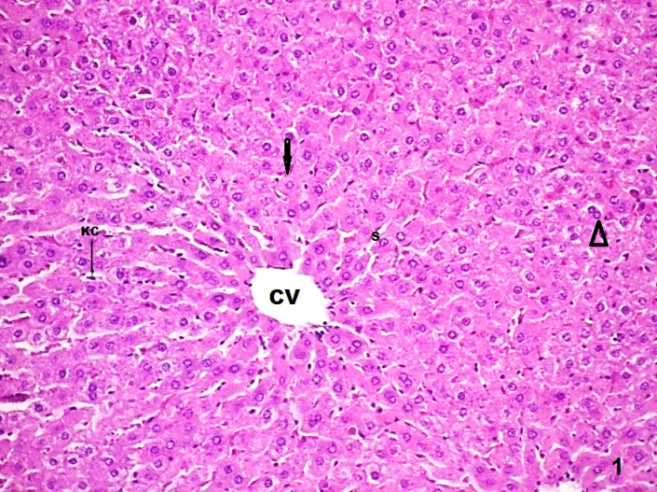
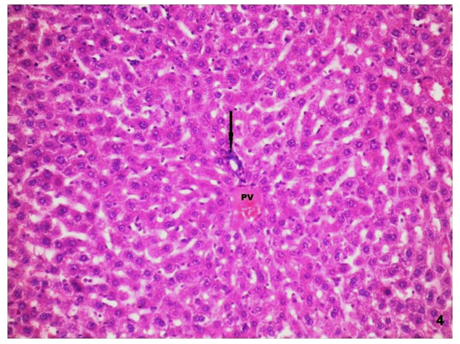
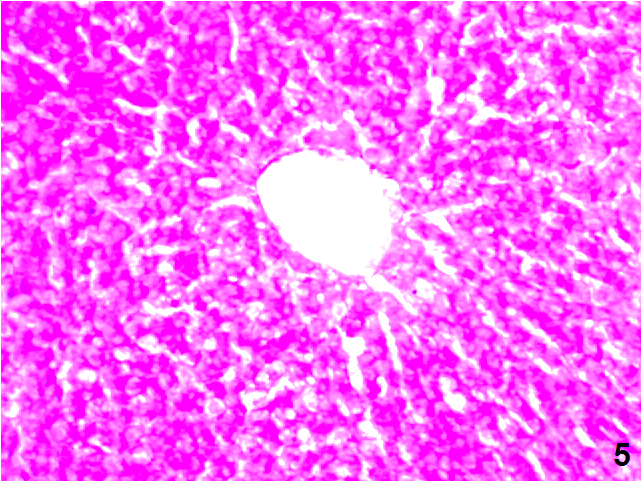 | Figure (5). A photomicrograph of a liver section control group (GI), showing, and the normal distribution of the PAS + ve materials within the hepatocytes. (PAS stain, X200) |
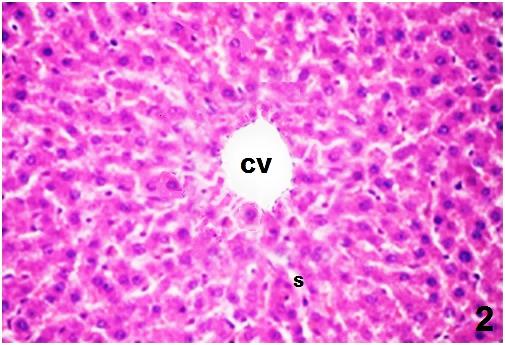
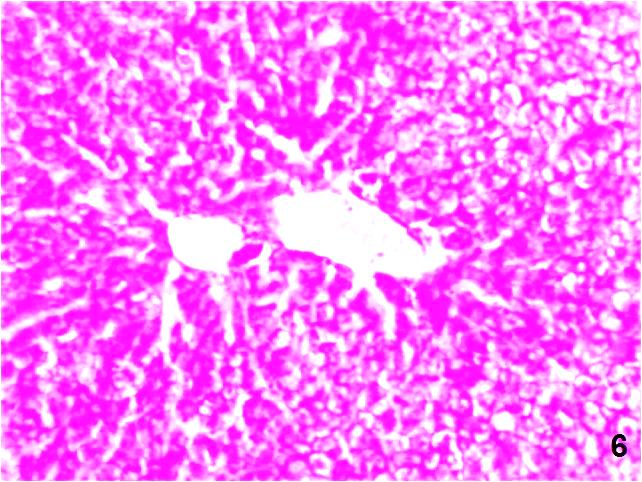 | Figure (6). A photomicrograph of a liver section (GII) showing, normal distribution of the PAS +ve materials within the hepatocytes. (PAS stain, X200) |
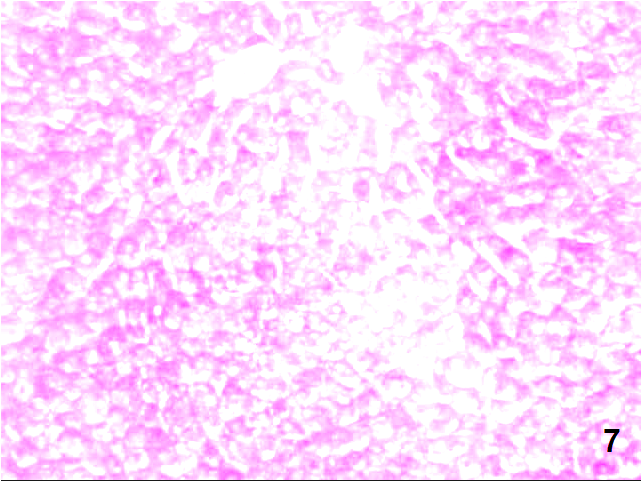 | Figure (7). A photomicrograph of a liver section (GIII) showing, decrease in the PAS+ve density in the majority of the hepatocytes. (PAS stain, X200) |
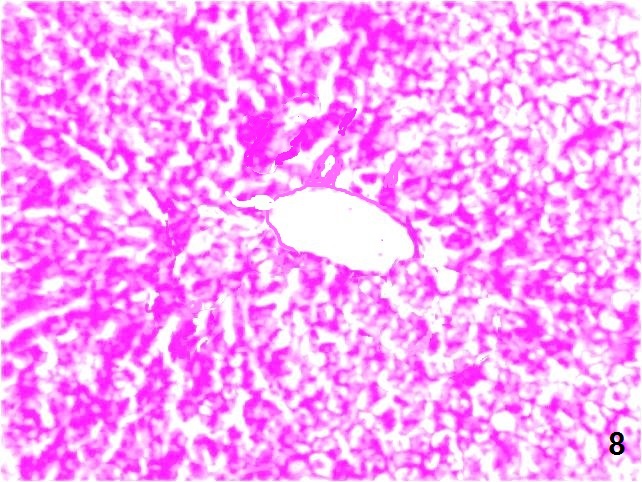 | Figure (8). A photomicrograph of a liver section (GIV) showing mild decrease in the distribution of the PAS+ve materials within the hepatocytes. (PAS stain, X200) |
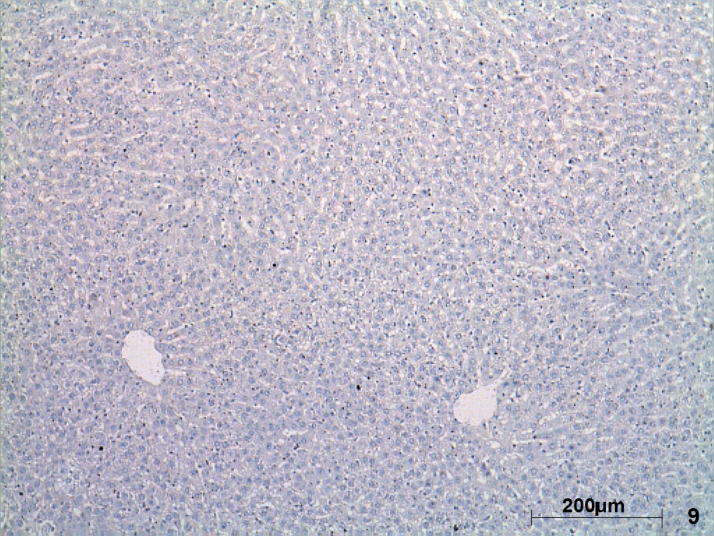 | Figure (9). A photomicrograph of a liver section control rat liver (GI) showing, hepatocyte with negative caspase-3 reaction. (Caspase-3, X100) |
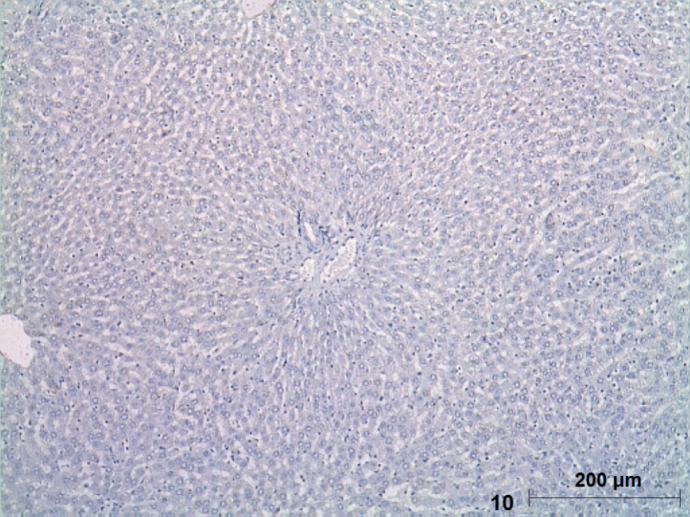 | Figure (10). A photomicrograph of a liver section (GII) showing, hepatocytes with negative caspase-3 reaction. (Caspase︱-3, X100) |
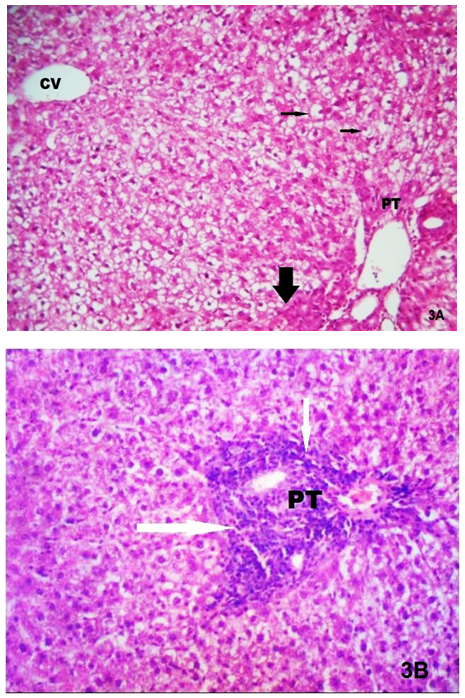
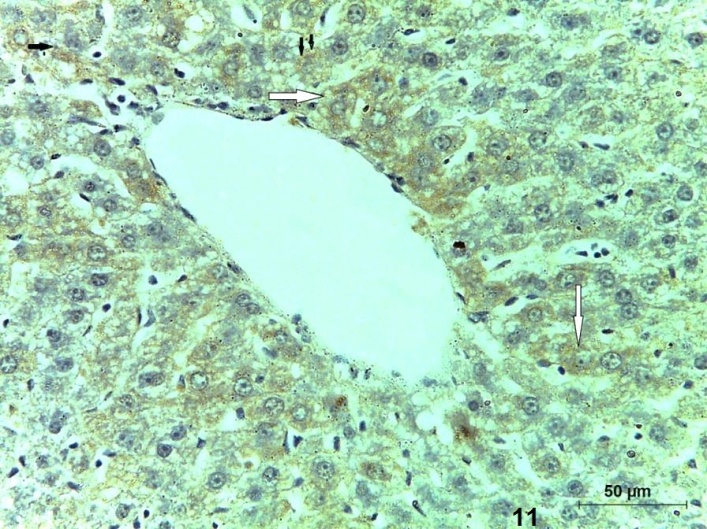 | Figure (11). A photomicrograph of a section (GIII) showing multiple apoptotic hepatocytes with an intense immune reaction for caspase-3 (arrow) (Caspase-3, X400) |
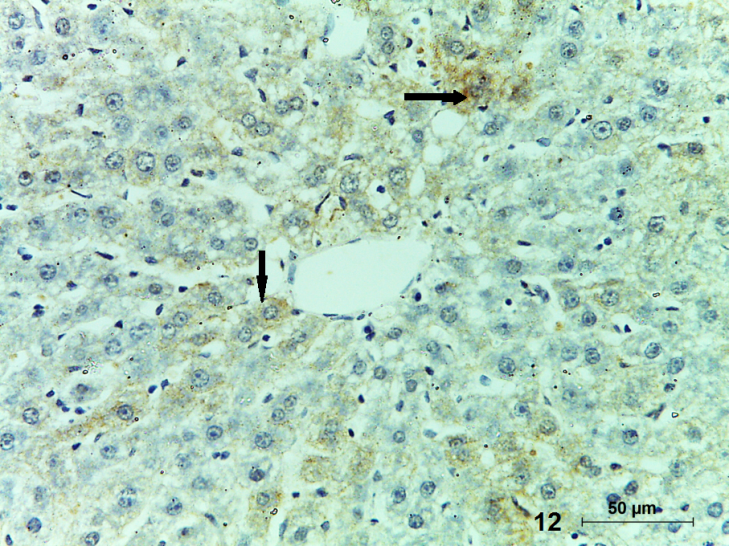 | Figure (12). A photomicrograph of a section (GIV) showing some apoptotic hepatocytes with positive caspase-3 reaction (arrow). (Caspase-3, X400) |
4. Discussion
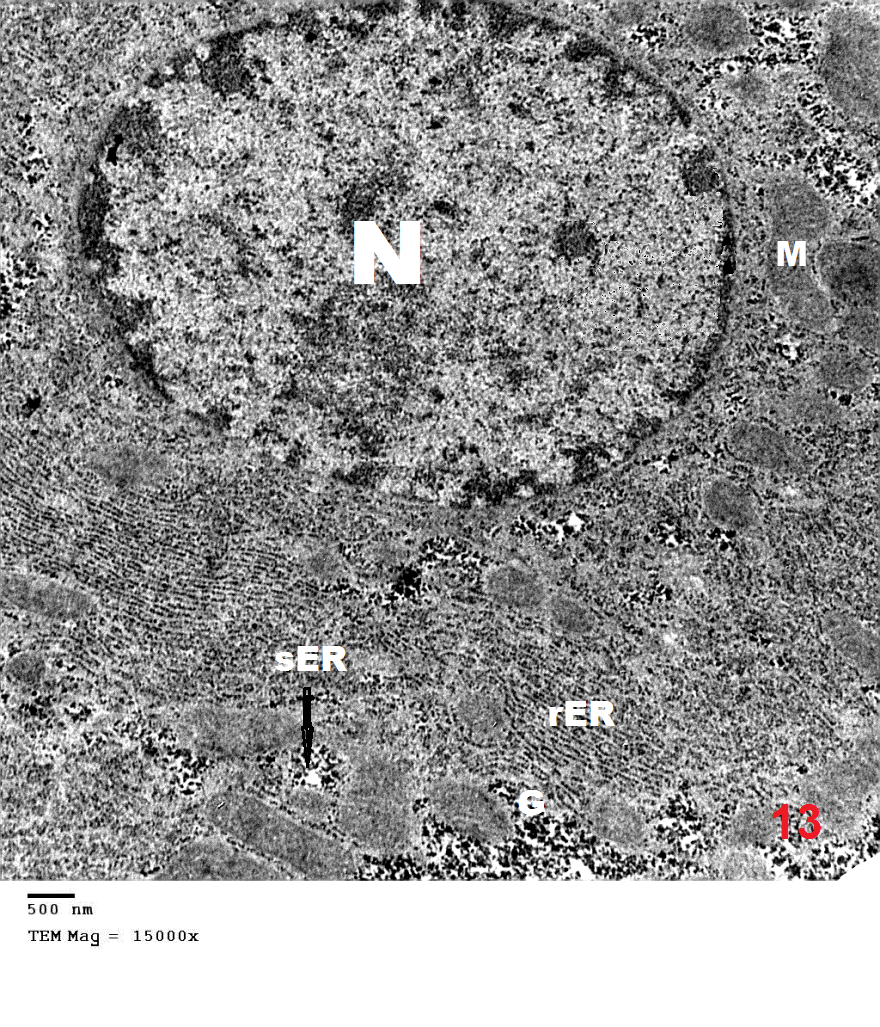
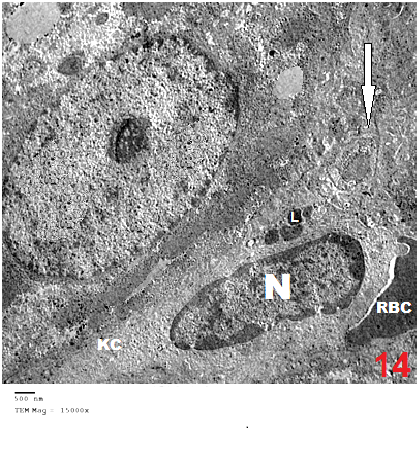
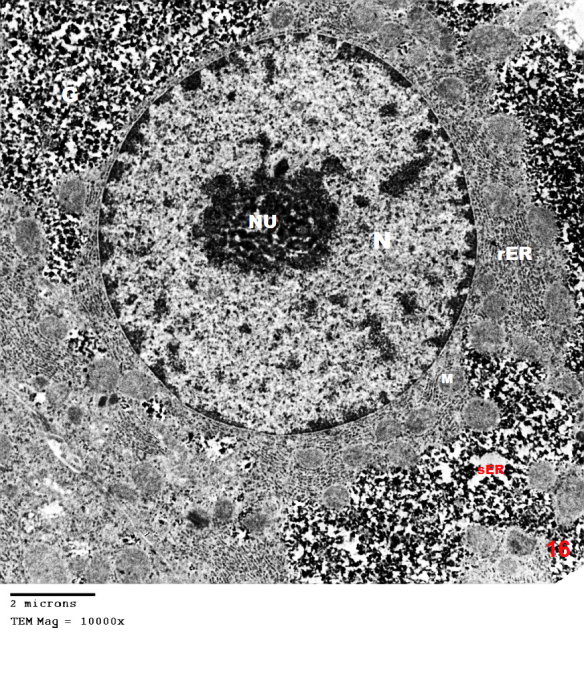
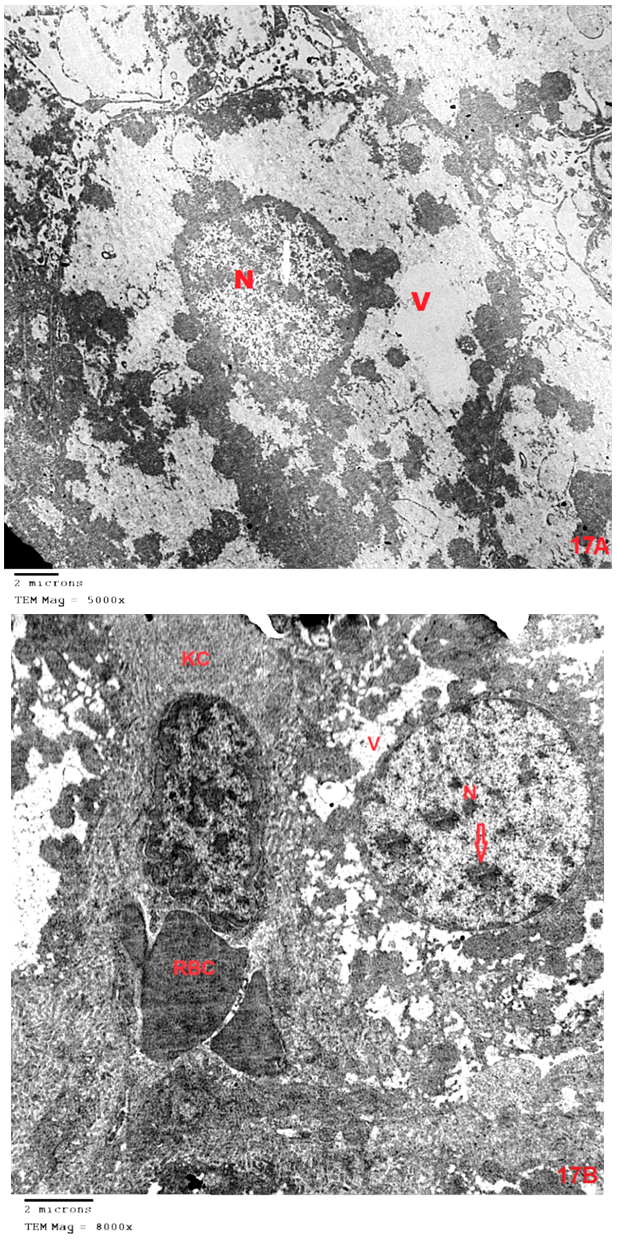
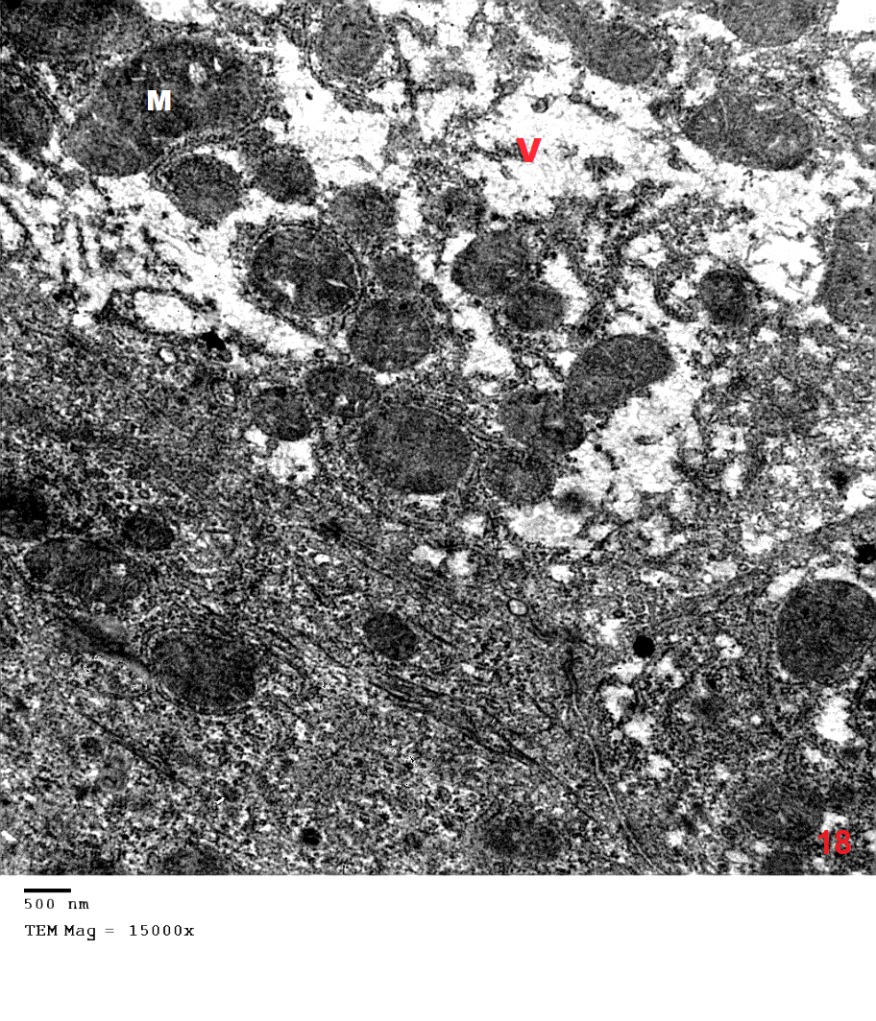
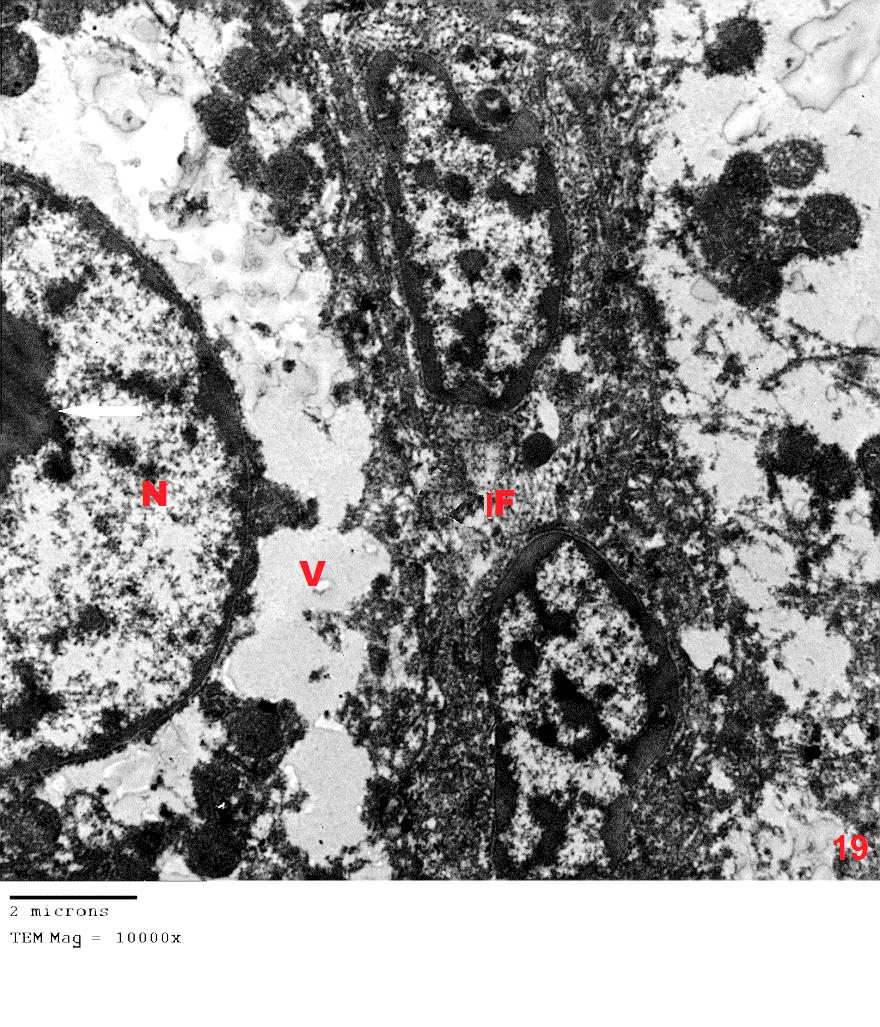
- Although azathioprine is an immunosuppressant used in the treatment of several diseases, it has been reported to be hepatotoxic. Intraperitonial injection of azathioprine resulted in not only lymphocyte suppression, but also toxicity to bone marrow and liver [25].The present work was carried out to evaluate the protective role of pumpkin seed oil in remote liver in rates by biological and histological study.SGPT is cytoplasmic enzyme & SGOT is cytoplasmic and mitochondrial enzyme in hepatic cells, whereas ALP also synthesized by liver. An increased activity of this enzyme is very sensitive index of hepatic damage [26].In the present study, the results revealed that rats treated with azathioprine exhibited a significant increase of SGPT, SGOT, ALP compared to control group.The results were in agreement with those of [27] who explained the occurrence of hepatic enzyme elevation may be attributed to endogenous protein breakdown due to possible increase tissue wasting.Light microscopic examination in this work of group III revealed that the hepatocytes had cytoplasmic vacuolation with darkly stained nuclei. Darkly stained cells with ill-defined nuclei were noted and this cell was most properly apoptotic hepatocytes. In addition the immunostained sections of this group revealed multiple apoptotic hepatocytes with an intense immune reaction for caspase 3. This in harmony with other studies which reported an increase in caspase 3 in the kidney after azathioprine treatment [28].The apoptotic changes observed in the present work were explaned by others investigators who proved that early injury of the cells occurred mainly in the form of apoptotic cells. They reported that cytochrome c and others apoptosis-promoting substances are released in great amount, leads to apoptosis of the cells [29]. The present results were also supported by other investigators who stated that hapatocellular injury and hepatocyte death were occurs as azathioprine administration [30]. Hepatocytes injury lead to production of oxygen free radicals (OFRs) which caused cellular damaged by oxidizing membrane lipids, essential cellular proteins and DNA [31].In this study, inflammatory cellular infiltration can be observed in per portal area. In accordance with the present finding, some investigators reported extensive cellular infiltration and neutrophil accumulation after azathioprine treatment [32].In this work, there were impairment in glycogen metabolism in liver appeared as decrease in glycogen material in hepatocytes in group III. This finding was explained by investigator who observed that the glycogen content in the liver decrease as the result daily administration of azathioprine (20 mg/kg body weight) intraperitoneally for 2 weeks caused significantly lower liver glycogen content [33]. In the current study, pumpkin seed oil improved the histological picture to be appeared more or less like that of the control group. Pumpkin is an important medical plants, it composed of polysaccharide & protein [34]. The extracted protein from this plant has an essential role in decreasing the harmful effects of protein malnutrition [35]. Such protein leads to an elevation in the level of hepatic enzymes and decreasing in the toxic effect of azathioprine because it contains anti oxidative compounds [36]. The extraction from the green leaves of pumpkin was used in treatment of many diseases and due to its higher ant oxidative activity, it can remove cellular toxicity of hepatic tissue [37]. The present investigation demons treated that pumpkin reduced the toxic effect of azathioprine on liver male rats and this might be due to high content of B. carotene, which agreed with [38] who discussed the antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of active groups treated with pumpkin due to it B-carotene content. This was augmented by some investigator who stated that B-carotene had been proved to be a powerful anti-oxidant and profound protective action against oxidative stress [37].Furthermore, some studies demonstrated that the role of pumpkin as a powerful anti-oxidant and protective actions against tissue damage because the role of antioxidant vitamins like B- carotene. [39] Added that B- carotene help in neutralization of free radicals and overtly aggressive oxygen species [36]. Electron microscopic findings of group III in the present study demonstrated some hepatocytes with marked shrunken (pyknotic) nucleus contained clumps of chromatin. The cytoplasm appeased rarified with marked vacuolation, swollen mitochondria and ill-defined organelles. These cells were most properly apoptotic hepatocytes. Other studies explained that, damage of mitochondrial structure and function in cells due to release of active substance including cytochrome c which released into cytoplasm. low amounts of Cyt c are capable enough to activate procaspase-9, activated caspase-9 then activate of caspase-3, which lead to intense generation of ROS and cell apoptosis [40], [41].The present investigation demonstrated that pumpkin seed oil reduced the toxic effect of azathioprine on liver tissues of rats. This might be due to its highly content of B-carotene, which agreed with [32] who said that the antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of pumpkin due to properties of polyphenol and B carotene content which had been proved to be a powerful antioxidant and protective actions against cell injury [42]. [43] Described the role of antioxidant vitamins like B-carotene in neutralizing free radicals and overtly aggressive oxygen species. B-Carotene was among the most efficient substance known for quenching the excitation energy of single oxygen and also for trapping certain organic free radicals, thus offering another mechanism of its anticancer nature [44].The anti-inflammatory activity of pumpkin seed oil may be attributed to promising proportions of ω-6 and ω-9 UFAs present in it, due to either their individual activity or the synergistic effect of these bioactive molecules [45].
5. Conclusions
- It is concluded that pumpkin extract was effective in preventing the toxic effect of azathioprine on liver of male albino rate.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML