-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Basic Sciences of Medicine
p-ISSN: 2167-7344 e-ISSN: 2167-7352
2012; 1(5): 34-39
doi: 10.5923/j.medicine.20120105.03
Receptor Binding Proteins: the Promise of theAngiotensin type 2 (AT2) Receptor
Erwin J Landon 1, Tadashi Inagami 2
1Dept of Pharmacology Vanderbilt University Medical School, Nashville, TNUSA
2Dept of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University Medical School, Nashville, TNUSA
Correspondence to: Erwin J Landon , Dept of Pharmacology Vanderbilt University Medical School, Nashville, TNUSA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The purpose of this review is to document the significance of several proteins that bind with the angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2), with emphasis on the first to be identified, the transcription factor PLZF.In this context the therapeutic potential of an AT2 agonist under current investigation is considered.Yeast two hybrid screening identified PLZF and two cytosolic proteins, ATIP and ATB50, as AT2 binding proteins.Chronic angiotensin II infusion in the AT2 gene deleted mouse did not result in cardiac hypertrophy.To determine the AT2 contribution to cardiac hypertrophy an AT2signaling pathway was identified.AT2 activated PLZF, which translocated to the nucleus.PLZF induced the formation of p85α, the coactivator of PI3K.The downstream pathway led to enhanced protein synthesis.In addition PLZF directly induces the major cardiac transcription factor GATA4.AT2 and PLZF are also widely distributed in brain and function in the kidney. ATIP and ATB50 were found to be a family of ATIP isoforms, some with tumor suppressing activity.ATIP interacts with the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to translocate to the nucleus and induce MMS2 a ubiquitin ligase with cellular protective effects.Phenotypes of both ATIP and SHP-1 deleted mice suggest their role as anti proliferation agents.A nonpeptide AT2 agonist under development, C21, shows most promise as an anti-inflammatory agent.It also holds promise for the central nervous system in stroke and in cognitive impairment.
Keywords: AT2, PLZF, ATIP, ATB50, SHP-1, C21
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The AT2 receptor is a seven transmembrane receptor interacting with the G proteins Gαi or Gαo.It was at first thought to have little apparent function.Current studies find that beyond classical interaction with G proteins, its interaction with receptor binding proteins opens a new conceptual universe of membrane receptor function[1].The purpose of the present review is to document the significance of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2) interaction with the apparently unrelated transcription factor PLZF and with the ATIP proteins and also to consider the potential of the new AT2 agonist C21 to broaden the range of pharmacotherapy.Initial yeast two hybrid screening for AT2 binding proteins led to the discovery of AT2 interaction with the transcription factor PLZF.Studies that followed in other laboratories revealed an AT2 interaction with ATIP and ATB50[2],[3].ATIP and ATB50 were found to be identical but several ATIP transcription variations were found.ATIP was subsequently also found to be identical to a tumor suppressor protein MTUS1[4].Angiotensin II mediates most of its known cardiovascular effects through the AT1 receptor acting on heterotrimeric G proteins.These effects include blood pressure elevation, EGF activation and the generation of reactive oxygen species.The AT2 receptor although abundant in the fetus is limited in its distribution in the adult but its expression is increased under pathological conditions such as cardiac hypertrophy.The AT2 receptor had been less frequently studied compared with the decades of study of the initial angiotensin II receptor (AT1).An important AT2 function is the stimulation of eNOS mediated in part by bradykinin and in part independently[5].Most recently additional NOS stimulation has been found to occur in mitochondria and this is apparently activated by intracellular AT2[6].NO in turn activates cGMP formation leading to blood vessel relaxation and potential reduction of blood pressure.AT2 also directly activates the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 by releasing it from AT2 bound form independently of classical heterotrimeric G protein activation.SHP-1 inhibits several growth promoting kinases[2],[7],[8].Initially this seemed to generalize AT2 as an antagonist of AT1 receptor function.
1.1. PLZF (Promyelocytic Leukemia Zinc Finger Protein)
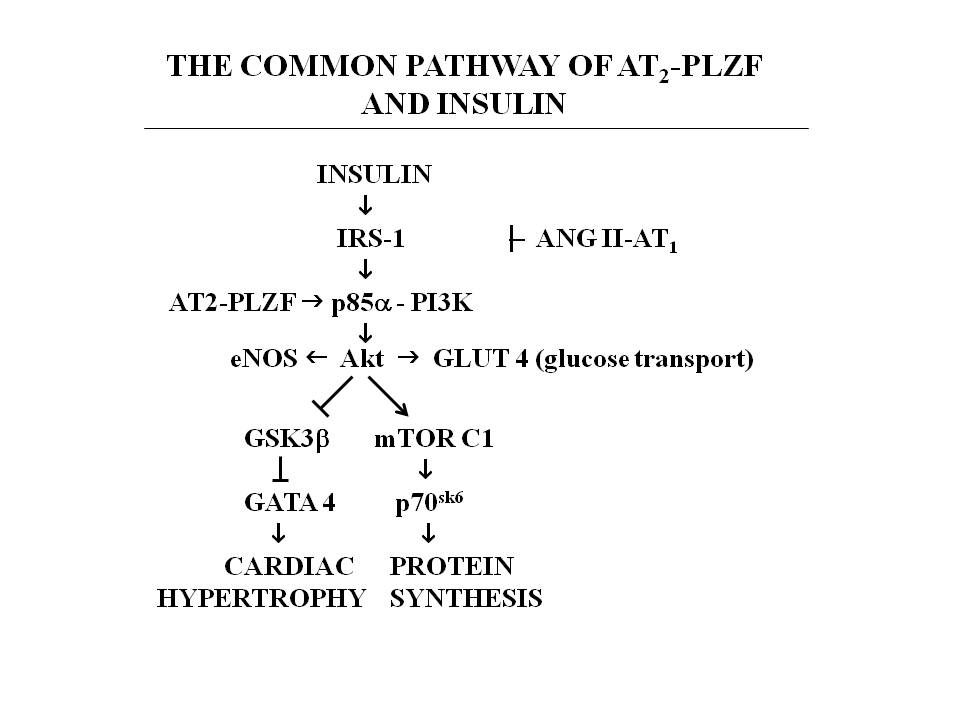
- Senbonmatsu and Ichihara et al[9],[10] found that angiotensin II infusion, which caused a sustained blood pressure rise and resulted in cardiac hypertrophy in a wild type mouse, failed to cause cardiac hypertrophy in a mouse strain with the AT2 receptor deleted, although a blood pressure response was observed.This absence of response occurred with aortic banding pressure overload as well as angiotensin II infusion. This implied that the AT2 receptor played a positive role in the hypertrophic response.It had been previously observed in several studies that deletion of the AT1 gene did not alter the cardiac hypertrophic response to pressure overload[11-13].In addition AT2 receptor blocker PD123319 prevented cardiac wall thickening and hypertrophy found in wild type mice infused with angiotensin II[14] which provides further support for the role of AT2 in cardiac hypertrophy.This contradicted the perspective of the AT1 receptor as the indispensable growth promoting receptor in the heart.Employing a yeast two hybrid assay, Senbonmatsu et al. searched for a binding partner for the AT2 receptor that could help to explain the observations in the heart.The unanticipated answer was the transcription factor PLZF binding to the AT2 C-terminal tail[15].Angiotensin II stimulation of the AT2 receptor resulted via pertussis toxin sensitive Gαi/o in tyrosine phosphorylation of PLZF at its carboxy terminal region resulting in PLZF activation.PLZF translocated from the cytosol to the plasma membrane colocalizing with the AT2 receptor.Both molecules slowly endocytosed over a 60 minute period with AT2 localizing in the perinuclear area and PLZF entering into the nucleus.In this study the nuclear PLZF binds to the gene promoter of p85α, the co-activator of PI3Kα.This enhances PI3K activity and time dependently activates the downstream pathway.Specifically documented increases were Akt (4 fold), p70s6k (3 fold) protein synthesis 40% and cardiac hypertrophy.Newer data from the laboratory confirms this work.Mice with PLZF gene deletion fail to respond to angiotensin II infusion with cardiac hypertrophy.In addition, cardiac fibrosis or wall thickening found in the wild type mouse infused with angiotensin II is absent in the PLZF gene deleted mouse after angiotensin II infusion.PLZF was also shown to bind and activate the gene promoter of the major cardiac hypertrophic gene GATA 4[14].The phosphatase SHP-1 when activated by AT2 is inhibitory to growth factors such as EGF and insulin.However, SHP1 was not detected in the heart except after myocardial infarction[16].In addition (unpublished) in R3T3 cells with endogenous AT2 and SHP-1 but no PLZF, SHP-1 is activated by angiotensin II.When these cells are transfected with PLZF, there is no activation of SHP-1.PLZF is involved in fetal development.Its initial discovery related to its involvement in promyelocyticleukemia.It is both a transcription repressor and activator e.g. coactivator of interferon induced genes[17].Like AT2 it is highly expressed in the fetus and diminishes in the adult.Northern blot analysis in the Senbonmatsu study indicates its highest expression in the heart of adult mice[15].
1.2. ATIP (Angiotensin II type 2 Receptor Interacting Protein)
- AT2 is similarly involved with the AT2 receptor binding protein ATIP[2] as it is with PLZF.There are four specifically identified isoforms of ATIP.Common to all of them is a coiled coil C terminal domain allowing dimerization.It is the site of the AT2 interacting domain.ATIP inhibits growth factors.Although AT2 activates SHP-1, tyrosine dephosphorylation is apparently not involved.Inhibitory activity requires ATIP interaction with the AT2 receptor but not the activation of the receptor by angiotensin II.AT2 as noted activates the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 independently of classical G-protein activation.In neuronal cells AT2 activates a protein complex of ATIP and SHP-1 that translocates to the nucleus where it leads to the induction of the protein MMS2[31].This is an ubiquitin ligase involved in DNA repair and neuronal differentiation.Gene deletion of ATIP in mice[32] resulted in cardiac hypertrophy in 28% of the mice (independent of blood pressure), nephritis in 12% and lymphoid hyperplasia in more than 37%.These are symptoms consistent with B cell lymphoproliferative disease; this confirms ananti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory role for MTUSI (ATIP in its identity as a tumor suppressor).The isoform 3 of ATIP is associated with microtubules[33] and may point to a mechanism of its antiproliferative action.SHP-1 deficient mice have enhanced proliferation of hematopoietic cells. Their lymphocytes exhibithyper-response to antigens[34].This seems to resemble ATIP gene deletion and suggests that the ATIP gene deletion report may involve ATIP interaction with SHP-1.ATB50identical to ATIP is localized in the Golgi and functions in export of AT2 to the cell membrane[3].MTUS1 is identical to ATIP and is localized in the mitochondria[33].
1.3. C21
- A newly developed nonpeptide AT2 agonist (C21) is awaiting phase 1 clinical trials in the year 2012.Earlier experimental studies employed AT2 gene deletion, PD 123319 (an AT2 receptor antagonist) and CGP42112A a peptide AT2 agonist.There has been a need for a clinically useful AT2 specific agonist.The most striking finding in the initial studies is the anti-inflammatory response to the AT2 agonist.Both in vitro and in vivo C21 inhibits nuclear translocation of NFκB, the transcription factor involved in cytokine activation. The molecular anti-inflammatory mechanism of C21 is presented in Fig. 2.In absence of angiotensin II NFκB is trapped in the cytosol by the binding protein IκB.Activation e.g. by the cytokine TNFα leads to IκB phosphorylation by the kinase IKK.IκB is then degraded.NFκB translocates to the nucleus to promote synthesis of cytokines.It also self regulates by promoting synthesis of IκB and the deubiquitinase A20.In Fig. 2 angiotensin II via AT1 activates Cyp 4A/4F to form 20 HETE (20 hydroxytetraeicosoenoic acid) from arachidonic acid.This activates NFκB.C21 via AT2 activates Cyp 2C/2J to form 11,12 EET (11,12 epoxyeicosotrienoic acid) from arachidonic acid.This inhibits NFκB.C21 also activates phosphatases that inhibit NFκB.Affirmation of C21’s anti inflammatory action is seen in the two kidney/one clip (2K1C) rat model[36].Early renal inflammation from the procedure includes increases in cytokines TNFα, IL6 and TGFβ and a decrease in NO and cGMP. C21 reversed this without an effect on the 2K1C induced hypertension.Of interest, the AT2 receptor via NO and cGMP also mediates inhibition of renin biosynthesis[37].
 | Figure 2. shows the molecular mechanism of NFkBregulation by angiotensin II and C21 |
2. Conclusions
- In summary, the initial study with AT2 and PLZF demonstrated a relatively new aspect of G-protein function, a G-protein mediated receptor binding to a transcription factor.It also demonstrated that AT2 receptor endocytosis unlike AT1 does not involve βarrestin and is much slower.The critical interaction with the co-activator of PI3K is at the crossroads of major metabolic pathways.It appears to explain why AT2 is an essential contributor but not the likely cause of angiotensin II induced cardiac hypertrophy.This AT2-PLZF interaction appears to extend beyond the heart and may play a major role in our understanding of the central nervous system.The findings with AT2-PLZF require the presence of both of them at significant levels. This at present holds for the brain and heart. The potential interaction with the insulin pathway in the heart needs to be evaluated in terms of insulin resistance. The tyrosine phosphatase Shp-1 has a complex relationship with AT2. AT2, when activated by angiotensin II, directly activates SHP-1 and it anti-growth factor activities. PLZF appears to prevent AT2 interaction with SHP-1. ATIP also interacts with AT2 and SHP-1. The ATIP-SHP-1 complex goes to the nucleus and exerts biological effects such as reduced vascular senescence. The anti-inflammatory activity of AT2 is its most consistent experimental finding. This and the enhancement by AT2 of angiotensin receptor blocker activities may be where the potential of a clinically effective AT2 agonist lies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors thank Tina Stack for typing the manuscript..This work was supported by Research Grant HL58205 from the National Institutes of Health.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML