-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Mechanics and Applications
p-ISSN: 2165-9281 e-ISSN: 2165-9303
2017; 7(1): 1-13
doi:10.5923/j.mechanics.20170701.01

Design Optimization of Angular Extrusion for Severe Plastic Deformation of Tubular Specimens
Madaraka Fredrick Mwema1, Kiptoo Mathew1, Shagwira Harrison1, Obiko Japheth2
1Mechanical Engineering Department, Dedan Kimathi University of Technology, Nyeri, Kenya
2Mining, Materials and Petroleum Engineering Department, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture & Technology, Nairobi, Kenya
Correspondence to: Madaraka Fredrick Mwema, Mechanical Engineering Department, Dedan Kimathi University of Technology, Nyeri, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The purpose of this work is to optimize angular extrusion for sever plastic deformation of tubular specimens. A finite element model (FEM) was built in Deform-3D® for three extrusion dies and analyzed. The dies were ECAP (135°), TCAP with external groove of 90° (denoted as TCAP-e) and TCAP with internal groove of 90° (denoted as TCAP-i). The analysis for process parameters (such as coefficient of friction-µ, die angles-ѱ and φ, temperature - T, and radius ratio-R) showed that TCAP-i was the optimal die in processing Al6063 tubes based on strain and load distribution of the model.The TCAP-i die model was further optimized for different parameters namely die angles, coefficient of friction, deformation ratio and temperature. The results showed that at constant process temperature of 25°C, the optimal TCAP-i has the following parameters: φ2= 80°, Ψ1 = 30°, Ψ2 = 80°, Ψ3 = 30°, µ = 0.4 and R = 1.5.
Keywords: ECAP, Tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP), Finite element, Severe plastic deformation, Strains
Cite this paper: Madaraka Fredrick Mwema, Kiptoo Mathew, Shagwira Harrison, Obiko Japheth, Design Optimization of Angular Extrusion for Severe Plastic Deformation of Tubular Specimens, International Journal of Mechanics and Applications, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 1-13. doi: 10.5923/j.mechanics.20170701.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Severe Plastic deformation (SPD) is one of the widely used techniques in achieving nanostructured and ultrafine grains (UFG) in materials [1]. It has been used numerically to produce UFGs tubes of AZ91 magnesium alloy material [2], pure aluminium materials [3] and tubular copper [4]. This is because SPD imparts very high deformations to the material to attain exceptional refinement of the grains [5]. This deformation occurs without significant change in the overall dimension and shape of the specimen due to the paths of plastic deformation [6]. The commonly employed SPD techniques include equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) [7], high-pressure torsion (HPT) [8], accumulative roll bonding (ARB) [9] and tubular channel angular extrusion (TCAP) [10].Severe plastic deformation reduces the grain size of the material to nano (less than 100 nm) or ultrafine range size (100 nm-1 µm) which improves the strength of the material [11]. Therefore, producing materials with UFG will increase hardness and yield strength of the material. The enhanced mechanical performance is so because of the intersection of short and long-range intersecting shear bands produced by plastic deformation and local dynamic recovery and recrystallization process, which take place simultaneously in the material during processing [12]. UFG structure of the material obtained by SPD technique leads to superplastic behaviour of these materials at lower temperature and yet with high deformation rate [13].Although extensive research has been carried out on solid materials, there is limited research on SPD processing of tubular materials known as Tubular Channel Angular Pressing (TCAP). In this research, the effort is concerted in the less researched field of tubular extrusion since tubular specimens have found great applications in engineering. TCAP is one of the technique, which deals with the extrusion of tubular materials by subjecting them to very high strains [14]. These strains in turn result into refinement of grain structures of the material [15]. TCAP is mostly preferable over other tubular SPD processes because it can be used to process large specimens [16]. Despite being a promising technique for processing tubes, there is very little research on TCAP processing of tubular samples. This can be attributed to the challenges associated with the already existing methods of severe plastic deformation of tubes. Whereas researchers have developed different techniques for severe plastic deformation processing of tubular materials, little work has been reported on optimization of the die design for homogenous strain distribution during deformation of tubes. Post-processing optimization, such as heat treatment, of tubular materials, has also not been widely reported as compared to solid metal alloys. Furthermore, most of the existing methods have been developed for severe plastic deformation of copper [17], aluminium [18] and steel solid materials [19]; little has been reported on severe plastic deformation of tubular samples despite their increase in high-strength applications. As such, this work focuses on the design and optimization of TCAP for processing Al-6063 tubes. The reason for choice of this material is that it has wide industrial applications as architectural and structural material due to its attractive properties. Therefore, the material would be an appropriate model for the present study.
2. Finite Element Simulation
- To conduct ECAP and TCAP process simulation, the dies and work-piece were first modeled using Inventor® Professional software 2014, before being exported as STL file to commercial Deform-3D® finite element software. The work piece was assumed plastic while the die and press ram were modeled as rigid bodies. Constant ram speed of 1 mm/sec was used based on experimental press data available. Djavanroodi et al. [20] used similar conditions in an earlier study.In TCAP process, the number of meshes does not have any effect on the material being processed but instead it increases the simulation time and therefore the simplest number of mesh elements (10000 elements) is chosen to simplify the simulation [21].These simulations were all performed in isothermal and adiabatic under room temperature conditions to prevent recrystallization [22]. Coefficient of friction, die angles and deformation rations were investigated to study their effect on deformation behavior of the Al6063 material. The effective von Misses criteria was used to study the severe plastic deformation characteristics.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extrusion Technique Analysis
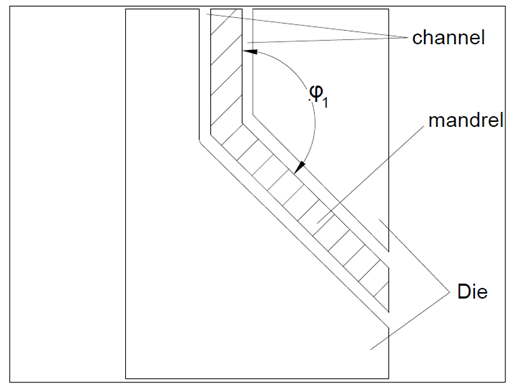
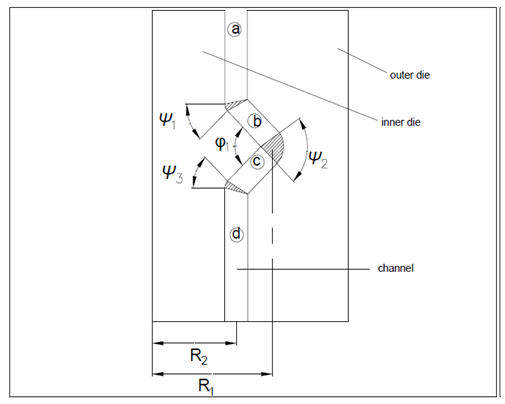
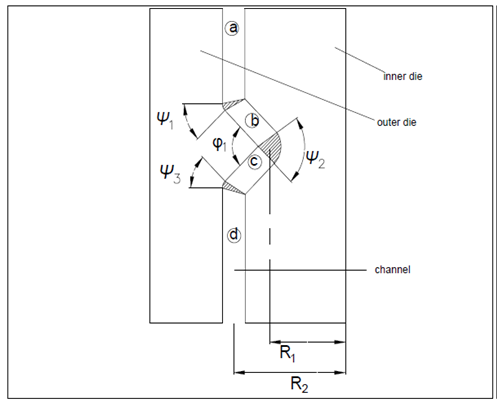
- To determine the most suitable extrusion process for severe plastic deformation of tubular samples, three die configurations namely ECAP die angle of 135°, TCAP with external groove (indicated as TCAP-e) and TCAP with internal groove (indicated as TCAP-i) were analysed. Appendix 1 is an illustration of the three die configurations. For all the dies, analysis was carried out at the same conditions using the DEFORM-3D® software. The results generated for each die are equivalent strain contours (equivalent strain distribution), equivalent strain variation along the thickness of the tubular sample and load variation with time.
3.1.1. Equivalent Strain Distribution
- Fig. 1 shows the equivalent strain contours for the FEM model of Al-6063 tubular samples SPD-processed. As shown in Fig. 1, the FEM model for the three dies was able to predict equivalent strain distribution within the length and cross-section of the tube during the severe plastic deformation. The maximum effective equivalent strain of 1.3 was achieved through the ECAP process as shown in Fig. 1(a). Furthermore, it can be seen that this equivalent strain is nearly homogeneously distributed within a considerable length of the sample after processing. Through the TCAP-e processing, as shown in Fig. 1(b), the maximum effective equivalent strain of about 3.0 is achieved. However, the equivalent strain inhomogeneity is significant along the sample length. As shown in Fig. 1(c), a maximum effective equivalent strain of about 2.36 is achieved through the TCAP-i. The equivalent strain distribution along the sample length, as it can be observed, is uniform compared to TCAP-e and less uniform compared to ECAP process in Fig 1(a). These results reveal that higher grain refinement can be achieved through processing of Al-6063 tubes through TCAP-e since large equivalent strains are imparted whereas the lowest grain refinement can be achieved through ECAP processing. However, large property disparities (hence anisotropy) are imparted to the Al-6063 tubes by processing through TCAP-e.
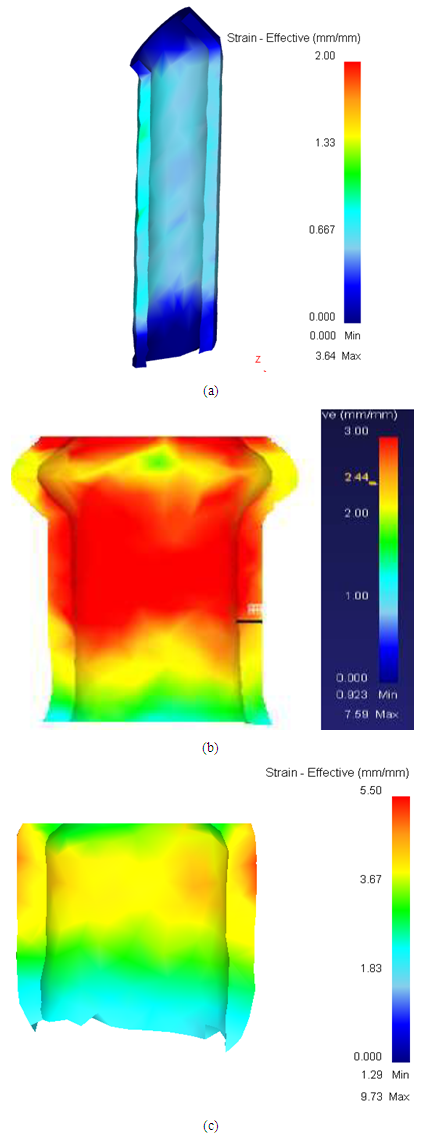 | Figure 1. Effective plastic equivalent strain contours for SPD processing to Al-6063 tubes through (a) ECAP (b) TCAP-e and (c) TCAP-i |
3.1.2. Equivalent Strain Variation Along the Thickness of Tubes
- Fig. 2 shows the graphs of effective equivalent strain versus distance along the thickness of the tube for the three dies. This length is defined as the distance from internal to the external wall thickness of the tube. As shown in Fig. 2(a), the equivalent strain variation along the thickness of the tube has gentle gradient from distance 1.0 to 1.8 mm; this means that there is some strain homogeneity within that thickness section. However, beyond 1.8 mm thickness the equivalent strain decreases considerably. It is important to note that the maximum equivalent strain is observed at 1.0 mm while the minimum equivalent strain occurs at the outer region of the tube. This is because of the superimposed compressive and tension equivalent strains coming from the outer and inner walls respectively on the upper side of the die. The minimum equivalent strains are experienced in the outer region of the tube; this can be explained using quantum mechanics approach. Similar results have been reported in experimental studies on severe plastic extrusion [23]. Fig. 2(b) shows a sharp decrease in gradient of equivalent strain with distance from the interior of the tube thickness; maximum equivalent strain is observed at the interior of the tube thickness while the minimum at the exterior region of the tube circumference when the sample is processed through TCAP-e. This means that equivalent strain variation across the tube thickness is very significant hence; there is a lot of equivalent strain inhomogeneity during TCAP-e processing as indicated in Fig. 2(b). Fig. 2(c) shows that the maximum equivalent strain occurs at the interior while the minimum occurs at the exterior of the tube thickness during processing through TCAP-i die. However, there is considerable gradual gradient in strain variation, which means that there is significant uniformity of distribution of equivalent strain within the tube thickness as compared to the tube processed through TCAP-e. The general inference from these results is that maximum equivalent strain occurs within the regions, which are in contact with the die although as observed from Fig. 1(a), there is a region within the tube thickness where a maximum equivalent strain occurs. It can also be deduced that higher equivalent strain inhomogeneity is observed along the tube thickness processed through TCAP-e whereas the lowest inhomogeneity is observed in specimen processed through ECAP. It is also observed that TCAP-i gives the highest maximum strains whereas the ECAP die gives the lowest maximum strain for the same processing conditions of the Al-6063 alloy.
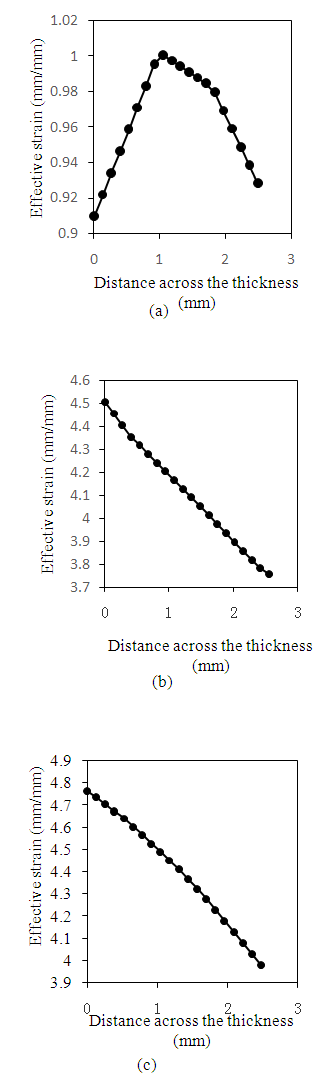 | Figure 2. Effective equivalent strain versus distance (mm) from the internal thickness of the tube after processing through (a) ECAP (b) TCAP-e and (c) TCA-I dies |
3.1.3. Load Variation with Time
- Fig. 3 illustrates the graphs of load versus time depicting variation of load with time during ECAP, TCAP-e and TCAP-i processing of the Al-6063 tube specimens. Load-time relationships are used in studying the power requirements for a severe plastic deformation process [24]. As from Fig. 3(a), the pressing force increases variedly with time because of different deformation rates, which means that the backpressure keeps on changing. At earlier processing stage, minimal force is used. This is because the front of the material is still experiencing bending in the channel and the backpressure is still small. This can be seen from Fig. 1(a), where the front part of the work-piece has almost zero equivalent strain meaning the material did not experience any stain until complete bending had took place. At later processing stage, the force increased considerably to a maximum of 50.5 kN, and then the force keeps varying with time. Three reasons can explain this observation. First, during the initial stage, the amount of material subjected to plastic deformation is progressively increased and therefore the loading increases progressively. Secondly, the presence of backpressure during pressing resulting from the change in the die channel geometry causes the material to expand and tends to resist flow of the material. Thirdly, the process induces some strain hardening making the material harder to deform thereby increasing the pressing load. Boroujeni and Saniee [14] provide a similar explanation in a related study. At the final processing stage, pressing force decreases noticeably. This is due to final extrusion of the work piece after passing through the deformation region where less material is subjected to deformation and as such, there is reduction in the backpressure. Experimental studies [20, 21] have reported similar observations. Fig. 3(b) and Fig. 3(c) show similar observations although in Fig. 3(b), the workpiece experiences a drop in pressing force up to 19.2 kN at processing time of around 130seconds. This is due to a reduction in back pressure and hence the material is not subjected to any pressing force. This could be the reason for equivalent strain inhomogeneity in the material. From Fig. 3(c), the material is subjected to loading that is somehow uniform. This could be the reason why there is homogeneous equivalent strain in the TCAP-i material as compared to TCAP-e material. TCAP-e and TCAP-i both experience large amount of maximum pressing load of about 87.1 kN and 174 kN respectively. This is why both processes have large equivalent strains as compared to ECAP, which experiences a maximum pressing load of about 50 kN. Large pressing force means large deformation rates are imposed on the material and therefore large equivalent strains are achieved.
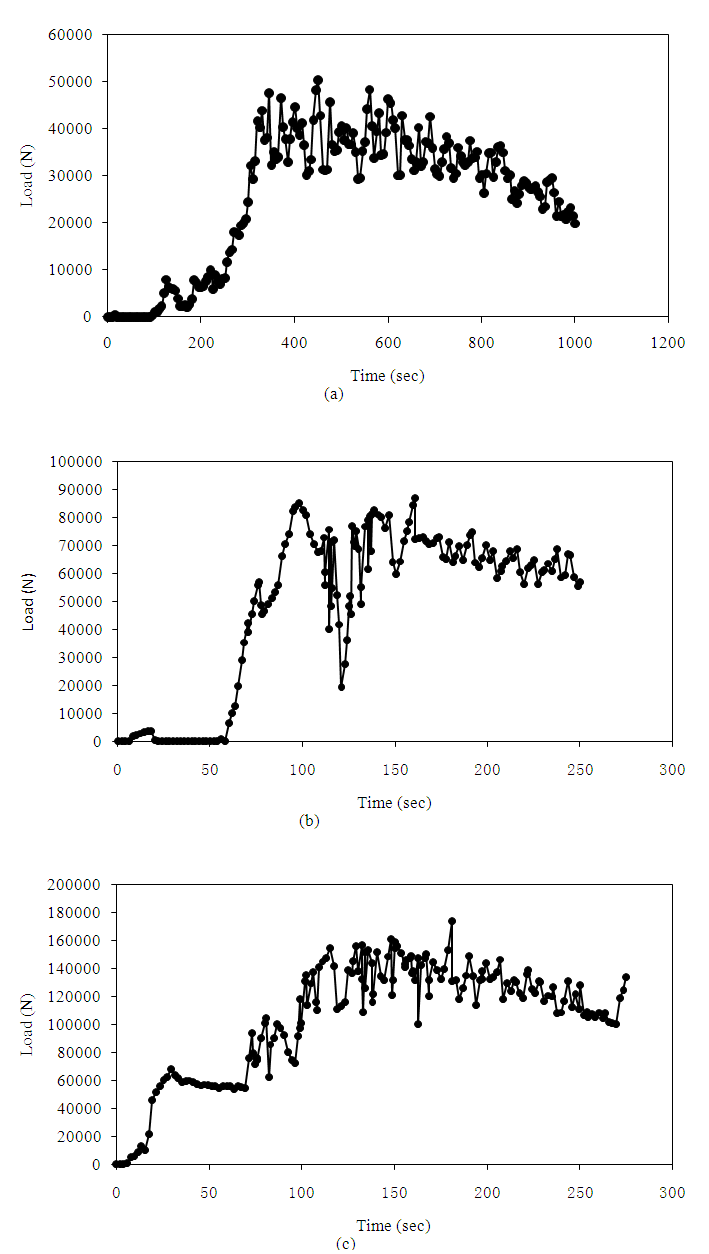 | Figure 3. Pressing load versus time during (a) ECAP (b) TCAP-e and (c) TCAP-i processing |
3.2. TCAP-i Die Optimization
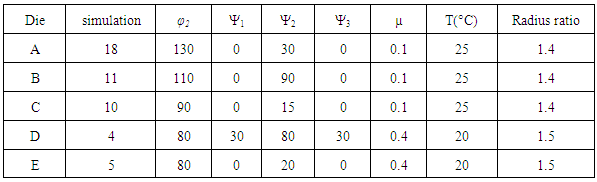
- Fig. 4 shows the tubular channel angular pressing die with internal groove used in the optimization in this work. The die parameters are also shown. The analysis in Deform-3D software was conducted for several die angles, coefficient of friction (µ) and radius ratio (R) combinations. Generally, for several combinations of parameters, it was observed that for the same die angles, the equivalent strains increases with increase in coefficient of friction. Additionally, as the channel angle increases, the equivalent strains decrease. It was also observed that for high radius ratios, high equivalent strains are achieved. Furthermore, varying the corner angle 2, while keeping all other die parameters constant leads to achievement of high equivalent strains when the corner angle is small and small equivalent strains when the corner angle is large. The best die angle conditions selected from the various simulations are show in Table 1.
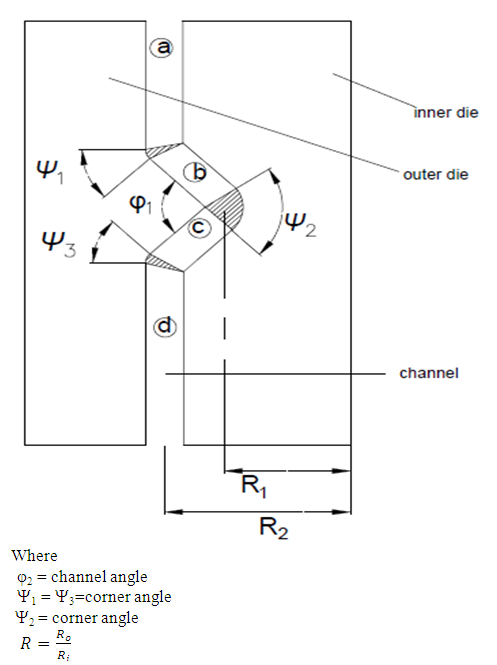 | Figure 4. Die configuration and process parameters |
|
3.2.1. Equivalent Strain Distribution Contours
- The Fig. 5 displays equivalent strain distribution over the surface and equivalent strain distribution across the thickness of a processed Al-6063 material. It was possible to predict the equivalent strain distribution along the length of the material subjected to severe plastic deformation. The contour diagrams display regions within the material that experiences high as well as low equivalent strains and furthermore the degree of their distribution over the surface and across the thickness of the processed material. These results are very important when analyzing the strength of a material since it represents the distribution of the material properties. The variables used in the research were the channel angle (φ2), the corner angles (Ψ1, Ψ2 and Ψ3), the radius ratios (R) and the coefficient of friction (µ) as indicated in Table 1.From Fig. 5 (a) above, the equivalent strains are distributed uniformly over both the inner and the outer surface as well as across the thickness of the material. However, it produces low equivalent strains and therefore the material strength is expected to be low. This is because the channel angle φ2 is large and therefore the amount of deformation imposed on the material is minimal. From Fig. 5 (b), contour diagram displays a uniform equivalent strain distribution. Furthermore, compared to die A the equivalent strains achieved using this die is much higher and the material processed will be much stronger. This is can be attributed to a smaller channel angle and larger corner angle. This finding agrees well with experimental and other numerical results [20, 21]. According to Fig. 5 (c), higher equivalent strains are induced in the material compared to dies A and B. However, its equivalent strain is not uniformly distributed as it can be seen from the contour diagram. High strains are induced in the inner surface compared to the outer surface. This is because the channel angle is smaller, which results in higher strains induced onto the sample. The corner angle 2 is much smaller hence, high deformation occurs in the inner region than the outer region. In Fig. 5 (d), the equivalent strains are distributed uniformly along the length. This means that the strength of the processed material is also uniform and high. High strains are due to small channel angle and homogeneity is because of high corner angles hence smooth flow of material during deformation. The die in Fig. 5 (e) induces the highest equivalent strains along the length of the material. However, the distribution of these equivalent strains is not uniform. This is because the small corner angles of the die restrict the flow of the material and therefore smooth flow of the material does not occur during deformation.
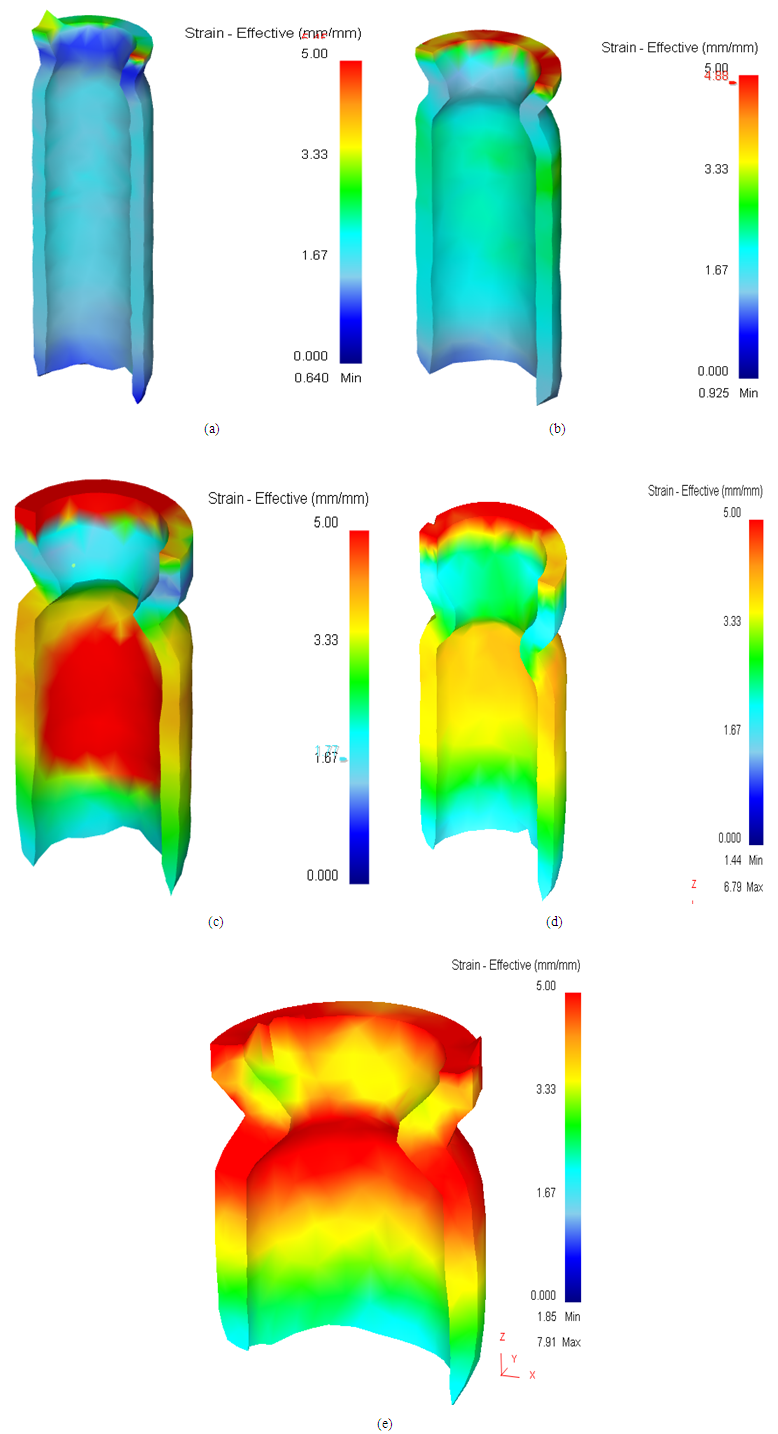 | Figure 5. Effective plastic equivalent strain contours for TCAP-i for Al-6063 tubes processed through (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D (e) E dies |
3.2.2. Equivalent Strain Variation across the Thickness of the Tubes
- The Fig. 6 shows the equivalent strain distribution across the thickness of the processed Al-6063 material. Small equivalent strain range means the degree of homogeneity in the material is high and therefore the die is reliable. From Fig. 6 (a), uniformly distributed strains of 1.7 mm/mm are achieved. This can be explained by the fact that the large channel angle of 130° causes a smooth flow of material. In Fig. 6 (b), maximum equivalent strain experienced is 2.97 mm/mm with uniform strain distribution and the material is stronger than that processed using die A. From Fig. 6(c), a maximum equivalent strain on the material processed is 3.97 mm/mm. The material is highly strained on the inner surface compared to the outer surface. This is because the die corner angles are small hence there is much resistance to flow of material on the inner radius. As seen from Fig. 6 (d), the maximum equivalent strain induced in the material is 4.05 mm/mm, which is higher compared to dies A, B and C. However, the strain distribution across the thickness of the material is quite inhomogeneous. This can be explained by small channel angle of 80° used that causes resistance to material flow. From Fig. 6 (e), maximum equivalent strain induced in the material is 4.19 mm/mm on the inner surface. Additionally, the strain distribution across the thickness of the material is not uniform. This is due to both small channel angle and corner angles hence there is no smooth flow of the material causing non uniform deformation.
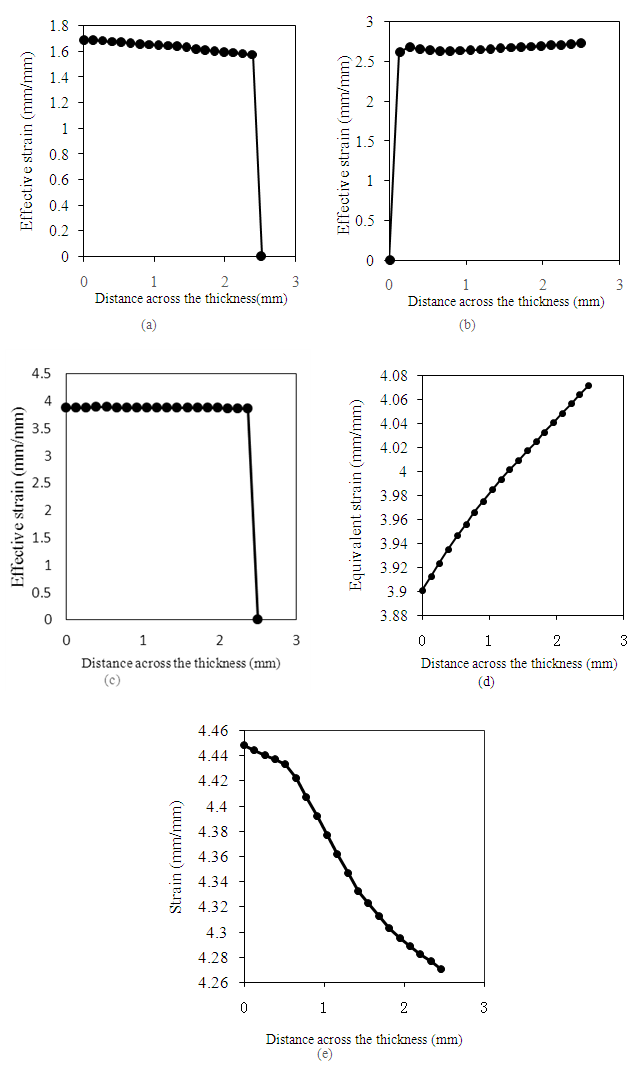 | Figure 6. Effective strain versus distance across the thickness of the tube after processing through (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D (e) E dies |
3.2.3. Load Variation with Time
- Fig. 7 illustrates the graphs of load prediction versus time during TCAP-i processing of the Al-6063 tube specimens subjected to various processing conditions and geometries of the die. The maximum pressing force is experienced when processing under die C as shown in Fig. 7 (c). This is attributed to the large channel angle of 130°, which imposes small stresses in the material such that small equivalent strains are achieved in the material. This occurs despite the fact that it has small pressing load variations meaning the pressing load is quite constant. Large pressing loads are also observed in Fig. 7 (a) (b) (d) and (e). However, as the graphs indicate, there is a sharp increase in pressing load. This is because the work-piece has reached the groove and has started following through the designed channel. Fig. 7 (a) and (b) experience large pressing force variations as compared to the others. This behavior could be due to two reasons: (i) Due to an increase in hydrostatic backpressure because each time the material is pressed, the change in geometry and an increase in the amount of material subjected to plastic deformation produces an opposite force to counter pressing load hence causing these variations. (ii) Due to the hardness imposed in the material. As the material is extruded, different scales of hardness are induced into the material, which cause the pressing force to keep on changing. It is also observed that Fig. 7 (a) and 7 (b) have small load variations during processing. The pressing load relates to the hydrostatic backpressure and the induced hardness into the material. This therefore means that these dies have good geometries and hence produce less backpressure and produce material that has uniform hardness. It can be concluded that die D (Fig. 7 (d)) produces a better load-time relationship compared to the others.
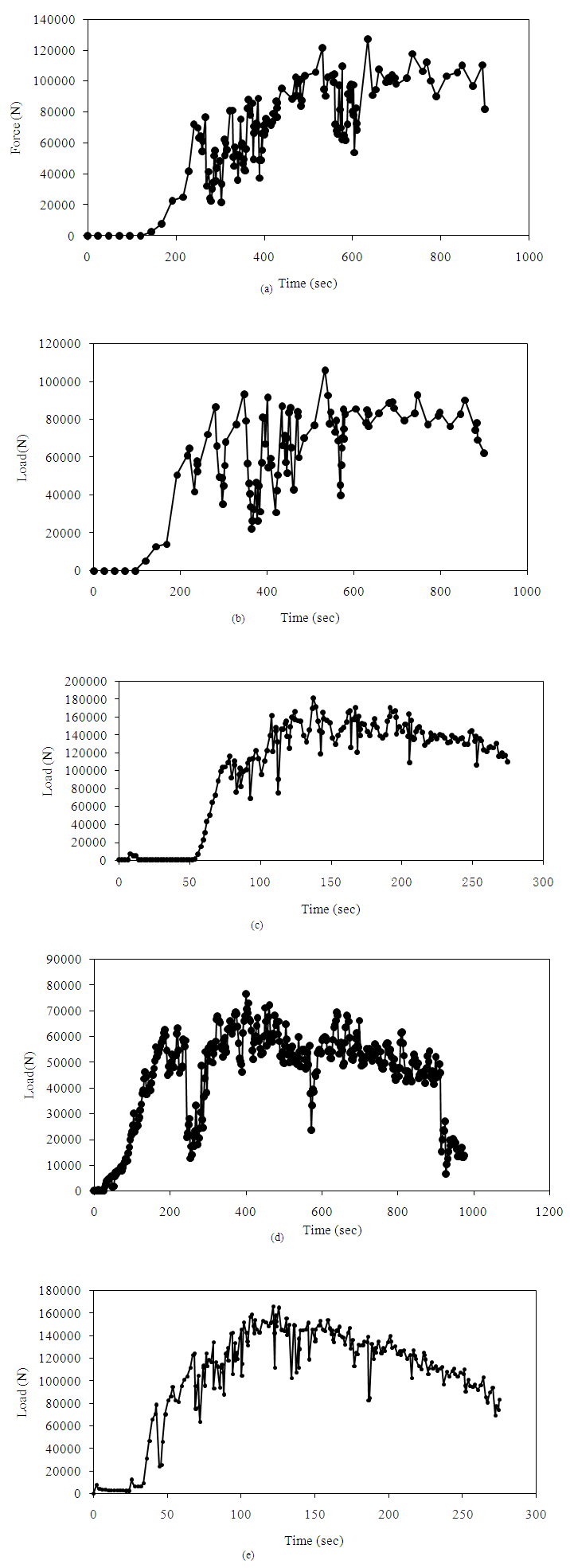 | Figure 7. Pressing load versus time for (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D (e) E dies |
4. Conclusions
- Several simulations of TCAP-i were necessary to obtain the optimal die design, which can produce a homogenous deformation in the workpiece. This makes it possible to select the suitable and optimal processing parameters. Of the three die configurations analysed, tubular channel angular pressing with internal groove, denoted as TCAP-i, was determined as the best die for severe plastic deformation of tubular Al-6063 samples. The choice was based on strain distribution and load-time relationships. Then, the TCAP-i was optimized and the results have showed that at constant process temperature of 25°C optimal TCAP-i has the following parameters; φ=80°, Ψ1 = 30°, Ψ2 = 80°, Ψ3 = 30°, µ = 0.4, and radius ratio (R) =1.5, which corresponds to die D in Table 1.However, this research did not analyze the high strains achieved at the interface between the punch and the die interface. Moreover, it does not explain the material loss and thermal generation during processing. Further research is therefore recommended in these areas.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to acknowledge the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dedan Kimathi University of Technology, DeKUT, for the financial support during this research work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML