-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Materials Science
p-ISSN: 2162-9382 e-ISSN: 2162-8424
2015; 5(2): 31-40
doi:10.5923/j.materials.20150502.02
Kinetic and Adsorption Behaviour of Aqueous Fe2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ Using a 30 nm Hydroxyapatite Based Powder Synthesized via a Combined Ultrasound and Microwave Based Technique
Sridevi Brundavanam, Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Derek Fawcett
Murdoch Applied Nanotechnology Research Group, Department of Physics, Energy Studies and Nanotechnology, School of Engineering and Energy, Murdoch University, Murdoch, Australia
Correspondence to: Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Murdoch Applied Nanotechnology Research Group, Department of Physics, Energy Studies and Nanotechnology, School of Engineering and Energy, Murdoch University, Murdoch, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
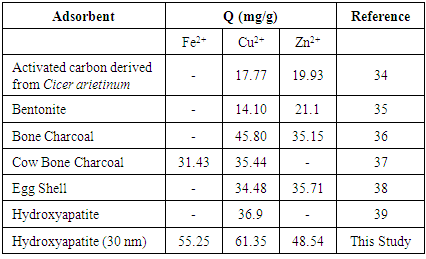
The present study reports the kinetic and absorption performance of novel nanometre scale hydroxyapatite (HAP) absorber synthesised from a combined ultrasound and microwave based technique for the removal of metal ions (Fe2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+) from aqueous solutions. After powder characterisation was carried out using XRD, SEM, EDS and FT-IR, batch adsorption studies were carried out. Kinetic studies established that Fe2+and Cu2+ ion adsorption tended to follow a pseudo-second order model, while Zn2+ ion adsorption tended to follow an intra-particle diffusion pattern. All three metal ion adsorption studies indicated an ion-exchange mechanism (metal ion → Ca2+) was a primary participant in the sorption process and was influenced by intra-particle diffusion. The Isotherm studies indicated the Langmuir isotherm modelled Fe2+ and Cu2+ ion adsorption, while the Freundlich isotherm was the better model for Zn2+ ion adsorption data. Maximum adsorption capacity of HAP determined via Langmuir isotherm was found to be 61.35 mg/g for Cu2+ ions, 55.25 mg/g for Fe2+ ions and 48.54 mg/g for Zn2+ ions. The study established HAP as an effective absorbent material for the removal of Fe2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ loaded aqueous solutions.
Keywords: Hydroxyapatite, Adsorption, Metal ion, Ultrasound, Microwaves
Cite this paper: Sridevi Brundavanam, Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Derek Fawcett, Kinetic and Adsorption Behaviour of Aqueous Fe2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ Using a 30 nm Hydroxyapatite Based Powder Synthesized via a Combined Ultrasound and Microwave Based Technique, American Journal of Materials Science, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 31-40. doi: 10.5923/j.materials.20150502.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The presence of heavy metal contaminants in the environment is a well-recognised problem that threatens the world today. Even in small concentrations, their high solubility in aquatic environments makes them extremely hazardous to living organisms [1, 2]. Once heavy metals enter the food chain their toxicity together with their tendency to accumulate beyond acceptable concentrations in the human body can result in serious health disorders [3]. Metals are generally considered heavy metals when their density exceeds 5 gcm-3 [4]. Metals and alloys with densities greater than 5 g cm-3 are widely used as biomaterials due to their superior mechanical properties. The majority of these metallic biomaterials are used in load-bearing implants such as bone plates, fixation pins and screws, hip and knee replacements. Metallic biomaterials are grouped into three distinct categories: 1) stainless steels; 2) cobalt-based alloys, and 3) titanium alloys. Individually, each category consists of a primary metallic biomaterial that is composed of a number of secondary metallic constituents. For example, the main constituents of stainless steels are iron (Fe), chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni). Most of the metal constituents used in the three metallic biomaterial groups like Cr, cobalt (Co), Fe, molybdenum (Mo), Ni, and tungsten (W) are used as alloying elements to improve the properties of the main constituent element [5]. For example, Fe based stainless steels have Cr (17-20%) added to improve corrosion resistance and Mo (2-4%) is added to improve resistance to pitting corrosion [6]. However, metallic constituents such as Cr and Mo are toxic and can only be tolerated in very small amounts in the body. Studies have shown that leaching of metallic surgical implants can result in the release of toxic metallic ions into surrounding cells, blood vessels and tissues [7-9]. The release of metallic ions can only be tolerated in very minute amounts, as in larger amounts they induce an unfavourable inflammatory response that significantly reduces the biocompatibility of the implant [8]. Importantly, exposure to heavy metals can lead to serious health problems such as cancer, nervous system and organ damage. For example, both Cr and Ni are known carcinogens and long-term exposure can lead to the development and growth of cancer. Metallic biomaterials used in orthopaedic applications will generally experience load-induced stresses in the inner core of the implant. Whereas, the surface of the implant is exposed to the surrounding physiological environment in the body. The interaction between exposed surface and physiological environment is very important in soliciting a favourable biological response. Because of the importance that biocompatibility plays in delivering a successfully implantation procedure, there have numerous studies into improving interfacial properties between the implant surface and the physiological environment [9, 10]. To this end, bioactive coatings based on calcium phosphate ceramics have been extensively investigated and used to coat a variety of biomedical metallic implants. These coatings have been found to improve biocompatibility, promote implant attachment and restrain the release of metallic ions into the physiological environment [10, 12]. In particular, hydroxyapatite (HAP) is a thermodynamically stable mineral phase at physiological pH and has a hexagonal crystal structure composed of calcium phosphate groups. Both crystallographic and chemical studies reveal synthetic HAP is similar in chemical composition to the naturally occurring mineral phase found in human bone and teeth [13]. Synthetic HAP has the advantages of being biocompatible, non-toxic, and has enhanced bioactive properties towards bone cells and other body tissues [14]. Another interesting property of HAP results from its complex hexagonal structure. The structure provides effective high capacity absorbance for a variety of pharmaceutical products such as antibiotics, drugs, enzymes, hormones and steroids. The use of HAP as a slow and sustained release drug delivery platform has proven to be effective in the treatment of diseases such as osteomyelitis, osteoporosis and osseous cancer [15-18]. Likewise, HAP used in orthopaedic applications also has the potential to act as an adsorption matrix. In this case, adsorption results from a mass transfer process by which metallic particles are transferred from the physiological environment (liquid phase) to the HAP matrix, and become bound by physical and/or chemical interactions. HAP makes an attractive absorbent because of its advantageous surface properties such as its hydrophilic nature, surface charge, pH, porous structure and 2.6 P-OH surface groups per nm2 which act as sorption sites [19, 20]. Generally speaking there are three steps involved in sorption of metallic particles onto the HAP absorber: (1) transfer of metallic ion particles from the physiological environment to the absorber surface; (2) adsorption on the metallic ion particles onto the surface, and (3) transport of the metallic ion particles within the absorber matrix. In the present work the adsorption of copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn) ions from aqueous solutions onto a solid nanometre scale HAP powder in agitated batch absorber vessels was studied. The nanometre scale HAP powder was synthesized via a combined ultrasound and microwave based technique to produce a spherical particle with a mean diameter of 30 nm. The main goal of this study was to examine the ability of the nanometre scale HAP powder to remove these ions from an aqueous solution and therefore evaluate its potential to store heavy metallic ions. The source of these metallic ions could arise from the corrosion and wear of surgical implants or by metabolic uptake via nutritional intake, drinking water and inhalation. The synthesized HAP powders were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). The metal ion adsorption capacity of the powders were investigated via the removal of Cu, Fe, and Zn ions from aqueous solutions using a batch equilibrium procedure. The kinetic behaviour of metal ion adsorption was investigated using Lagergren’s pseudo-first order, McKay & Ho’s pseudo-second order and intra-particle diffusion models. Furthermore, Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms were used to model the experimental data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Adsorption experiments were conducted using three different metal salts. The first, FeCl2.4H2O was supplied by Chem-Supply (Australia). The second, CuCl2.2H2O was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (United States) and the third, ZnCl2 was supplied by Scharlau (Barcelona, Spain). Each respective metal salt was dissolved in an aqueous solution to make up a 1000 ppm stock solution and lower solution concentrations were produced by successive dilution of the stock solution. HAP powders were synthesized from high purity calcium nitrate tetra-hydrate [Ca(NO3)2.4H2O] and potassium di-hydrogen phosphate [KH2PO4], while solution pH was controlled by the addition of ammonium hydroxide [NH4OH]. All chemicals used to synthesize HAP were supplied by Chem-Supply (Australia). During HAP synthesis an Ultrasound Processor [UP50H: 50 W, 30 kHz, MS7 Sonotrode (7mm diameter, 80 mm length)] supplied by Hielscher Ultrasound Technology was used to deliver the ultrasound irradiation. All aqueous solutions were made using Milli-Q® water (18.3 MΩ cm-1) produced by an ultrapure water system (Barnstead Ultrapure Water System D11931; Thermo Scientific, Dubuque, IA).
2.2. Synthesis of Nanometres Scale Hydroxyapatite
- Ultrasonic and microwave processing are two techniques that significantly influence and enhance the properties of materials. Ultrasound produces extremely rapid pressure and temperature variations that promote both physical effects and chemical reactions that directly influence particle size and morphology during synthesis. Microwave processing has the advantages of providing controlled volumetric heating, lower energy consumption, reduced reaction times, increased product yields, and improved material properties when compared to conventional heating methods [21]. A detailed synthesis procedure developed by the authors is given elsewhere [21, 22]. But a brief description is give here in the interest of completeness and begins by adding a 40 mL solution of 0.32 M calcium nitrate tetra-hydrate into a small glass beaker. The pH of the solution is then adjusted to 9.0 by adding approximately 2.5 mL of ammonium hydroxide. The solution was then subjected to 50 W of ultrasound irradiation for 1 h set and maximum amplitude. The second hour of ultrasound treatment included slowly adding 60 mL of 0.19 M potassium di-hydrogen phosphate solution. During the addition of potassium di-hydrogen phosphate the solution pH was maintained at 9.0 and the Calcium/Phosphate [Ca/P] ratio was maintained at 1.67. After ultrasonic treatment, the solution was centrifuged (15,000 g) for 20 minutes at room temperature to produce a solid white precipitate. The precipitate was collected, washed and centrifuged for a further 10 minutes. At the end of the second centrifugation, the precipitate was placed into a fused silica crucible and then loaded into a domestic microwave oven for thermal treatment [Set at 100% power for 40 minutes: 1100W at 2450 MHz-LG® Australia] [21]. The resultant agglomerated powder was collected and then subjected to ball milling until an ultrafine nanometre scale HAP powder was produced.
2.3. Advanced Characterisation Techniques
2.3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Spectroscopy
- XRD spectroscopy was used to study the synthesized powders, with the XRD patterns being used to identify the crystalline size and phases present. Spectroscopy data was recorded at room temperature, using a Siemens D500 series diffractometer [Cu Kα = 1.5406 Å radiation source] operating at 40 kV and 30 mA. The diffraction patterns were collected over a 2θ range of 20° to 60° with an incremental step size of 0.04° using flat plane geometry with 2 second acquisition time for each scan. The scan data was then used in conjunction with the Debye-Scherrer equation [Equation 1] to determine the crystalline size of each sample.
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
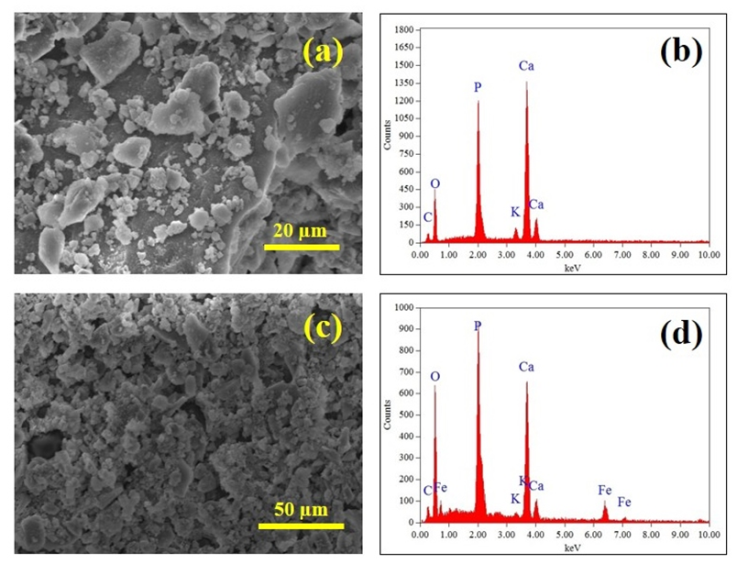
- The SEM technique was used to examine the size, shape and morphological features of absorbents before and after the batch adsorption studies. All micrographs were taken using a JCM-6000, NeoScopeTM with attached energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Samples were mounted on individual substrate holders using carbon adhesive tape before being sputter coated with a 2 nm layer of gold to prevent charge build up using a Cressington 208HR High Resolution Sputter coater.
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
- FT-IR spectroscopy was used to identify species and functional groups present in the HAP absorber before and after metal adsorption studies. Samples were examined using a Perkin–Elmer Frontier FT-IR spectrometer with Universal Single bounce Diamond ATR attachment. Both FT-IR spectra were recorded in the range from 525 to 4000 cm−1 in steps of 4 cm-1.
2.4. Batch Adsorption Studies
- All adsorption experiments were carried out using the batch equilibrium technique. During the experimental work the adsorption capacity of the HAP absorber for three metal ions, namely, Cu2+, Fe2+ and Zn2+ were investigated. The study also examined the influence of the initial metal ion concentration and contact time at 298ºC. The influence of contact time on metal ion adsorption on the absorber was examined using aqueous solutions containing 300 mg/L of metal ions (300 ppm) prepared from the three metal chlorides. HAP samples (0.1 g) were taken from the stock solution (1g/L) were added to each of the 300 ppm metal chloride solutions. The magnetic stirring speed for each metal suspension were set to 400 rpm, while the temperature of each suspension was maintained at 298 ± 1 K. In addition, the initial and final pH of the suspensions were recorded. Sample volumes were taken from the suspension during the mixing process at pre-determined time intervals (10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 90, 120, 180, 240 and 300 min) so that metal ion concentration in the respective solution could be measured. Once a sample volume was taken, an equivalent volume was added to maintain testing solution volume. Each solution volume was filtered using a Whatman® 0.22μm membrane syringe filter before being centrifuged at 15,000 g for 20 minutes. The concentration of Cu2+, Fe2+, Zn2+ and Ca2+ ions in the sample solutions were determined using atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). The instrument used was a Varian SpectrAA50 (Victoria, Australia) flame atomic absorption spectrometer operated in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. Elemental analysis of Cu, Fe and Zn was carried out using an air–acetylene flame and Ca analysis was carried using a nitrous oxide (N2O)–acetylene flame. Sample aspiration flow rate used was 5 mL min−1. During analysis hollow cathode lamps of Fe, Cu, Zn and Ca (Varian) were used. While Fe, Cu, Zn and Ca concentration were measured at the wavelengths of 248.3, 324.8, 213.9 and 422.7 nm respectively. In addition, the influence of initial metal ion concentration was studied by first preparing a series of Schott reagent bottles containing 100 mL aqueous solutions consisting of varying concentrations of metal ions (100, 150, 200, 250 and 300 mg/L). All initial metal ion concentration experiments were carried out in triplicate. The data collected from the adsorption experiments were then used in the subsequent kinetic and adsorption isotherm modelling studies.
3. Results and Discussions
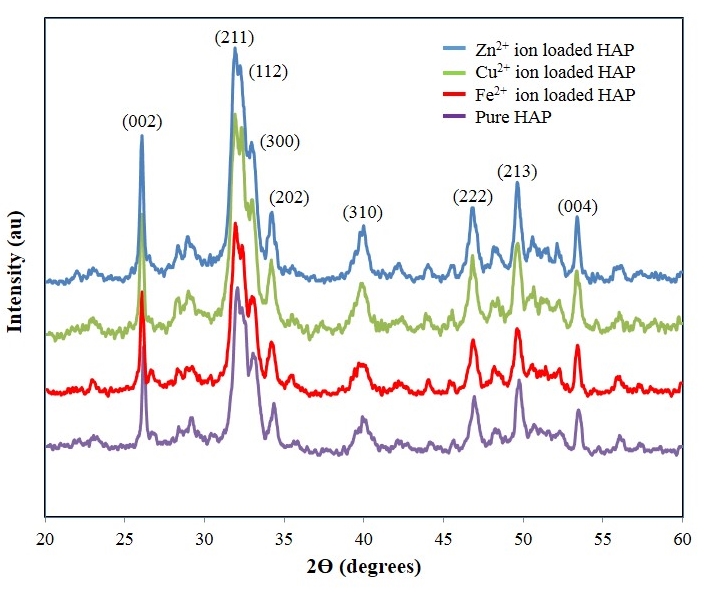
3.1. XRD Spectroscopy, SEM and EDS Analysis
- XRD spectroscopy was carried out on all HAP powders before and after adsorption studies. The resultant XRD patterns were used to determine crystalline size and phases present in the samples. An XRD pattern of a typical pure powder sample before adsorption testing is presented in Figure 1 and is indicated by the purple pattern. Examination of the pure HAP sample pattern reveals the presence of peaks that coincide with the known phases of pure HAP and is consistent with the phases listed in the ICDD database. The main (h k l) indices found in pure HAP, namely (002), (211), (112), (300), (202), (310), (222), (213) and (004) can be seen in the pattern for the synthesized HAP powder. In addition, the pattern showed no evidence of non-HAP phases. The crystalline size, t (hkl), of each sample was calculated from the respective XRD patterns using the Debye-Scherrer equation [23-25]
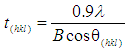 | (1) |
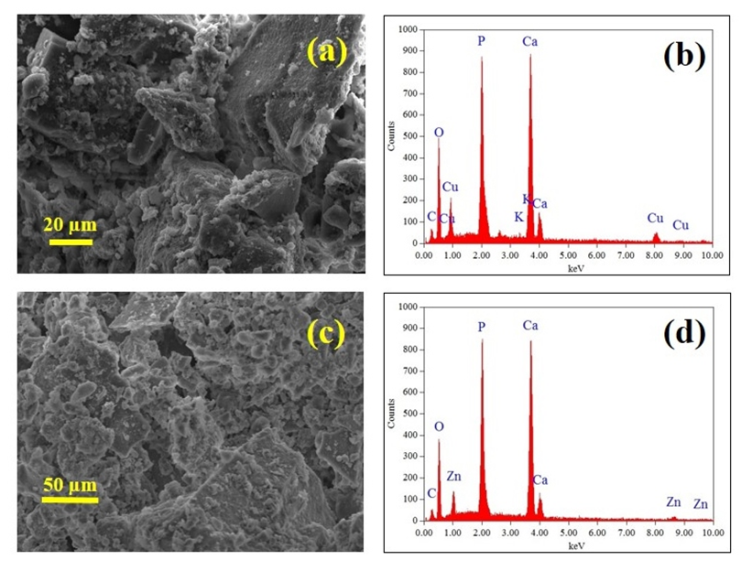 | Figure 3. (a) SEM micrograph of Cu2+ loaded sample; (b) EDS spectrum of Cu2+ loaded sample; (c) SEM micrograph of an Zn2+ loaded sample, and (d) EDS spectrum confirming the presence of Zn2+ ions |
3.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy Studies
- FT-IR spectroscopy was used to detect species and functional groups associated with peaks seen in sample spectra taken before and after adsorption studies. Figure 4 presents the results of a FT-IR spectroscopy study of HAP powder samples taken before and after metal ion adsorption studies. Starting from the right hand side of Figure 4 with a typical synthesized HAP powder sample (purple) prior to adsorption studies. The first three peaks encountered are 561 cm-1, 600 and 631cm-1 that are associated with v4 vibrations of the O-P-O modes. The peak located at 827 cm-1 indicates the presence of carbonates in the sample and is a consequence of atmospheric carbon dioxide interacting with HAP precursors during synthesis and has been reported in the literature by other researchers [29, 30]. The small peak located at 963 cm-1 is associated with v1 symmetric stretching vibrations associated with a P-O mode. While the much larger peak at 1026 cm-1 and the smaller peak located at 1090 cm-1 correspond to PO43- functional groups. While the peaks located at 1373 cm-1 and 1643 cm-1 correspond to CO32- functional groups. While the weak peak located at 3470 cm-1 corresponds to OH- ion vibrations in the HAP crystal lattice. The three remaining spectra are representative Fe2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ loaded powder samples taken after adsorption testing. The results for the metal ion loaded samples are very much the same as the pre-adsorption sample, except that both 872 cm-1 and 1373 cm-1 peak intensities have vanished from all spectra. Both the missing peaks correspond to CO32- functional groups and suggest that the low pH of the batch adsorption technique resulted in the loss of the carbonates. For example, equilibrium pH of the Fe2+ ion and HAP solution pH was 3.2, while Cu2+ was 3.8 and Zn2+ was 4.4.
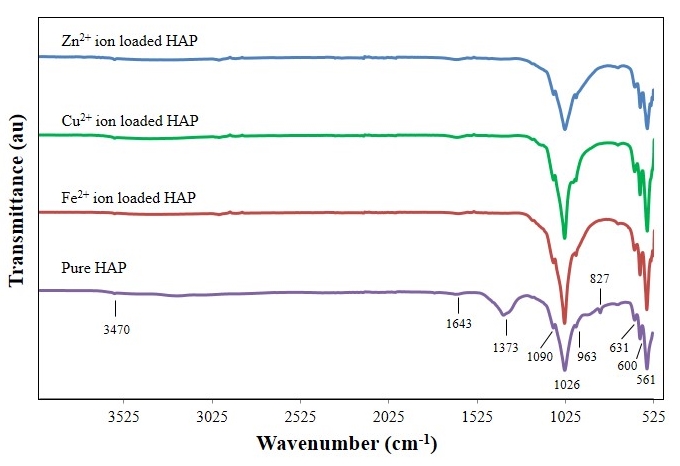 | Figure 4. FT-IR Spectroscopy analysis of synthesized pure nanometre scale hydroxyapatite powder and metal ion loaded samples after adsorption studies |
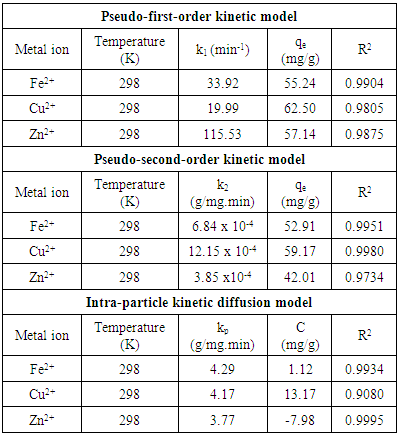
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
- A proper understanding of adsorption kinetics is important since sufficient residence time on the absorber surface is needed to complete the adsorption reaction. This is reflected in the metal ion concentration profiles encountered during the batch adsorption studies and presented in Figure 5. Inspection of the profiles reveals there is an initial rapid uptake of metal ions, but as time progresses the uptake slows and around the 150 minutes mark no further adsorption takes place. The quantity of metal ions adsorbed at equilibrium time (qe) was determined by equation 2 below:
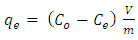 | (2) |
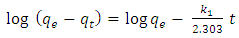 | (3) |
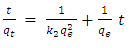 | (4) |
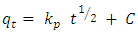 | (5) |
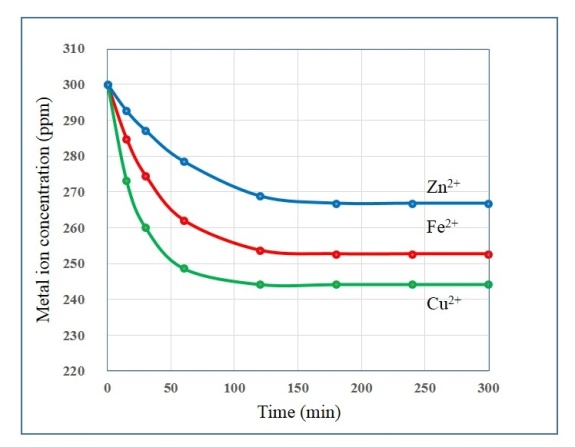 | Figure 5. Metal ion concentration profiles during batch adsorption studies over a period of 300 minutes using a nanometre scale HAP powder as absorber |
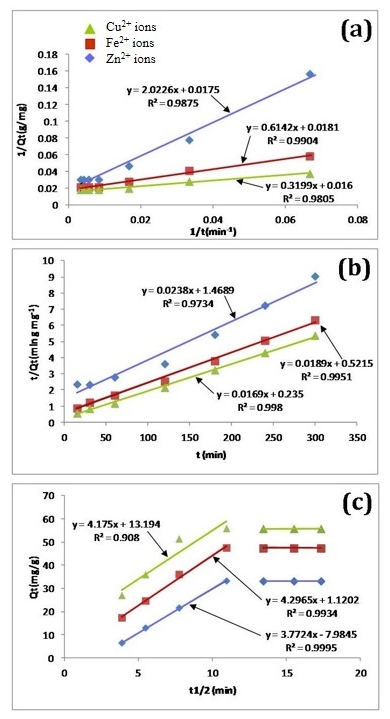 | Figure 6. Metal ion adsorption data modelled using three kinetic models: (a) Lagergren’s pseudo-first order law; (b) McKay and Ho’s pseudo-second-order law, and (c) the intra-particle diffusion model |
|
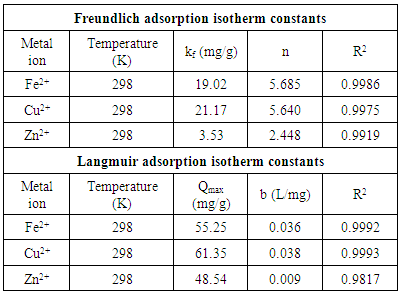
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
- There are two widely used equilibrium equations for modelling equilibrium data obtained from adsorption systems. The first model is the Freundlich and is purely an empirical equation that takes into account surface heterogeneity, the exponential distribution of active adsorption sites and their respective energies over a wide range of concentrations. The second model is the Langmuir equation and unlike the Freundlich, it assumes maximum adsorption occurs when the entire surface of the absorber is covered by a monolayer of adsorbate. The equilibrium data for metal ions in solution for initial concentrations consisting of 100, 150, 200, 250 and 300 mg/L at constant temperature of 298 K, 1 g/L absorbent dose and a contact time of 300 minutes were analysed using Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms. The linear form of the Freundlich isotherm used for modelling the data is expressed by in equation (6):
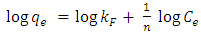 | (6) |
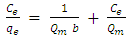 | (7) |
|
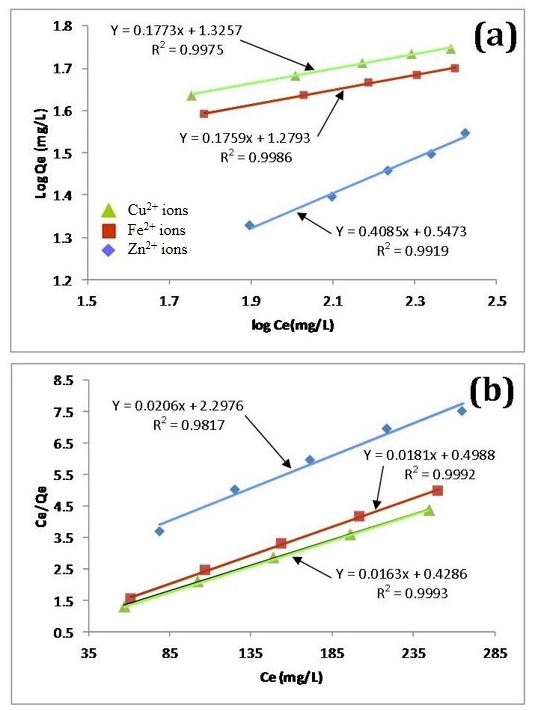 | Figure 7. Linear fits of experimental data using (a) Freundlich and (b) Langmuir isotherms |
|
4. Conclusions
- The results of the present study have revealed that a nanometre scale HAP powder synthesized using a combined ultrasound and microwave based technique was capable of producing a highly crystalline powder consisting of spherical particle morphology with a mean particle size of 30 nm. The powder was found to be an effective adsorbent for the removal of metal ions such as Fe2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ from aqueous solutions. Kinetic studies revealed the sorption process for Fe2+and Cu2+ ions closely followed pseudo-second order kinetics. While the slightly higher correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.9995 for Zn2+ ions indicated that the Intra-particle kinetic diffusion kinetics was more suited to modelling the experimental data. Overall, the sorption performance was found to be a function of initial metal ion concentration. With initial uptake rate of metal ions being high compared to the much lower uptake rates occurring in the later part of the absorption period. The ion-exchange mechanism (metal ion → Ca2+) was seen to be a participant in the sorption process which was influenced by intra-particle diffusion. Isotherm studies indicated the Langmuir isotherm modelled Fe2+ and Cu2+ ion adsorption data better than the Freundlich isotherm. However, the Freundlich isotherm modelled the Zn2+ ion adsorption data. The Langmuir isotherm was used to determine maximum adsorption capacity of the HAP absorber for each metal ion. The study found the metal ion with the largest maximum adsorption capacity was Cu2+ ions (61.35 mg/g). This was followed by Fe2+ ions (55.25 mg/g) and then Zn2+ ions (48.54 mg/g).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Mrs Sridevi Brundavanam would like to acknowledge Murdoch University for providing a Postgraduate Scholarship to undertake this hydroxyapatite synthesis study as part of her PhD project.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML