-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Materials Science
p-ISSN: 2162-9382 e-ISSN: 2162-8424
2012; 2(4): 110-118
doi: 10.5923/j.materials.20120204.03
Ferroelectric Relaxor Behavior and Spectroscopic Properties of Ba2+ and Zr4+ Modified Sodium Bismuth Titanate
B. Tilak
Department of Materials Science, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Correspondence to: B. Tilak , Department of Materials Science, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Polycrystalline ceramics (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3, (BNBZT) (for x=0.10, 0.12; y=0.04), has been synthesized by conventional solid-state sintering. X-ray diffraction analysis indicates the formation of a single phase with tetragonal symmetry with pure perovskite structure. Scanning electron micrograph of the studied materials shows a distribution of grains. A broad dielectric peak with maximum permittivity has been observed near 1200 (for x=0.10, y=0.04) and 1600 (for x=0.12, y=0.04) respectively in the temperature range, RT–600℃. This result indicates that these materials may have great potential for a variety of high temperature applications. These ceramics show diffuse phase transition and the transition temperature shifting toward higher temperature with increasing frequency, which represents the relaxor behvaiour. The relaxor materials obey modified Curie–Weiss law and Vogel–Fulcher relationship. The values of the diffuseness parameter γ=2 for x = 0.10 and 1.67 for x = 0.12, obtained from the fit of a modified Curie-Weiss law established the relaxor type nature. For a more detailed interpretation of the ac data, the complex impedance (Z*) and electric modulus (M*) as a function of frequency f (i.e., 45 Hz–5 MHz) has been simultaneously analysed. Impedance study reveals that there exists a temperature dependent electrical relaxation phenomenon in the materials. Modulus represents hopping of ions and localized motion in studied compositions. Conductivity obey’s Jonscher law
Keywords: Polycrystalline, lead-Free relaxors, Vogel-Fulcher relation, Impedance, Modulus , Conductivity
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Lead-based complex perovskite relaxor ferroelectrics, such as Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 (PMN), Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3, and the derived compounds, are widely used in the fabrication of multilayer ceramics capacitors, hysteresis-free actuators, and high performance sensors because of their excellent dielectric and piezoelectric properties.[1–4] However, these lead based relaxor ferroelectrics contain more than 60 wt % lead.[5,6] Lead is a very toxic substance, which can cause damage to the kidney, brain, and nervous system, especially the intelligence of the children.[7] In recent years, therefore, some countries have required all new electronic products to be lead-free for the environmental protection and human health.[8] Hence, many studies are focused on the BaTiO3-based materials such as BaTiO3–BaZrO3,[9] BaTiO3–BaSnO3,[10] BaTiO3–BiAlO3,[11] and BaTiO3– CaTiO3–SrTiO3[12] because these BaTiO3-based lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics show relatively high dielectric and piezoelectric properties among the lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics. Unfortunately, these BaTiO3-based lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics show low temperature of the maximum dielectric permittivity (Tm). This temperature (<100℃) is not high enough to use these materials in high temperature fields, such as automotive, aerospace, and related industrial applications.[13] Therefore, currently, much effort has been placed on the study of searching and developing the new lead-free or lead-reduced relaxor ferroelectrics for high temperature applications[14–16]. The NBT is an excellent example of lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics in order to develop for high temperature applications. In literature review, the dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of typical lead-free perovskite ferroelectric ceramics such as BaTiO3 (BT)-based, (Na0.5Bi0.5) TiO3 (NBT)-based and KNbO3 (KN)-based systems for actuator and high- power applications and also BLSF ceramics such as Bi4Ti3O12 (BIT)-base, Bi3TiTaO9 (BTT) –based and (Sr Ca)2 Bi4 Ti5 O18(SCBT) systems for ceramic resonator applications are desired as superior candidates for environmental friendly, lead-free piezoelectric materials to reduce some damage to earth. Among the NBT based system, (1-x)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–xBaTiO3 posses rhombohedral (FR) – tetragonal (FT) morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) at x=0.06-0.07[17]. Gao et al reported the composition (1-x)BaTiO3 -xBi0.5Na0.5TiO3 with x >0.3mol start to exhibit the relaxor ferroelectric properties[18]. (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3, BNBZT is another most promising NBT based material posses rhombohedral – tetragonal phase with morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) at x=0.07-0.08. The aim of this paper is to investigate the phase structure, microstructure, dielectric, complex impedance, electric modulus and conductivity behavior of (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3 ( abbreviated as BNBZT) ceramics. NBT modified with barium at A-site and zirconium at B-site, i.e., (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3, (x=0.10, 0.12; y=0.04), (abbreviated as 0.10 BNBZT, 0.12 BNBZT). These are the promising candidates for device applications. We expect to provide an alternative direction for searching and developing high temperature lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics through this study. In addition, the mechanisms of the relaxor behavior in the BNBZT ceramics are discussed in detail.
2. Experimental
- The BNBZT Ceramic samples were prepared by a conventional solid state sintering. AR grade powders of oxides or carbonates with 99% purity were used as the starting materials. These materials were grounded for 10 h and calcined at 850℃/2h. After calcination, the grounded powders were pressed into disks with 12mm diameter and about 2mm in thickness. The disks were sintered at 1180℃/3hrs in air. The phase structure was examined using x-ray powder diffraction analysis using a Phillips diffractometer using CuKα radiation wavelength, λ =1.5406Ao for wide range of bragg’s angle, 2θ (100≤2θ ≤70℃) with a scanning rate of 20/min. Lattice parameters have been calculated through POWD software. For the observation of the microstructure samples were polished and thermally etched. Finally, the microstructures were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM: JEOL_JY: Model 5800F).The permittivity (ε*), impedance (Z*), electrical modulus (M*), and conductivity (σ*) as a function of temperature (35-600℃) and frequency (45Hz to 5MHz) were performed with computer interfaced LCR Hi-Tester (HIOKI 3532-50, japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Phase Structure of (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3, (x=0.10, 0.12; y=0.04), (Abbreviated as 0.10 BNBZT, 0.12 BNBZT) Ceramics
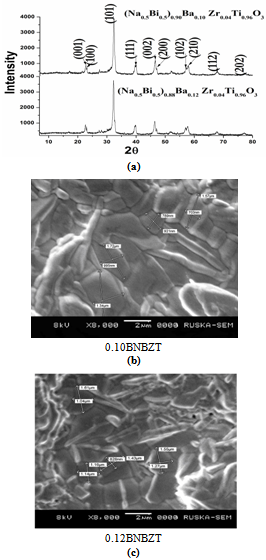
- Figure 1(a) shows that X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3, (x=0.10, 0.12; y=0.04) ceramics at room temperature. It is observed from the patterns; that all samples show pure perovskite phase and there is no traces of secondary phase. This indicates that both Barium and zirconium have completely diffused into NBT lattice to form new solid solution. The orthorhombic phase is characterized by (202)/(020) peak splitting by about 45 o[6].The tetragonal phase is characterized by (002)/(200) peak splitting by about 45o[6]. According to Figure 1(a), the phase structure of 0.10BNBZT, 0.12BNBZT ceramic is pure perovskite phase with tetragonal symmetry. It is also observed that as Ba concentration increases, lattice parameters and cell volume increases. In the perovskite structure of (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3, the substitution of Ba2+ for Na+ and Bi3+ on the A-site increases the crystal plane spaces and causes the increase of lattice constant and lattice distortion and ultimately causes the appearance of tetragonal ferroelectric phase at room temperature as shown in Table.1. The increase in lattice parameters and cell volume are also reported in PZT system[19]. The density of the sintered materials has been measured by Archimedes method. The Experimental density achieved above 90% to that of theoretical density, which is tabulated in table.1.Figure 1 (b), (c) shows the microstructures on sintered BNBZT ceramics with different x content and at constant zirconium concentration. Grain shapes are clearly visible, indicating the existence of polycrystalline microstructure. Grains of unequal size appear to be distributed in the studied materials. The average grain size of the studied materials is estimated by line intercept method. Grain size for 0.10BNBZT is found to be 1.15 μm and for 0.12BNBZT is found to be 1.29μm. The average grain size is found to be increased with increase in Ba content.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.2. Dielectric Properties of (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3 Ceramics
- Figure.2 (a) shows the temperature dependence of the dielectric permittivity (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3 ceramics at a temperature range of 35℃ -600℃. For 0.10BNBZT and 0.12BNBZT, the transition temperatures are shown in Table.2. It is observed that from Figure 2(a) that the Tm increases from 343℃ (0.10BNBZT) to 360℃ (0.12BNBZT) ceramics with increase of Barium content; this result is consistent with the above XRD analysis, and the phase transition temperature range around Tm become more and more broader with increasing addition of Barium, which can be called the diffuse phase transition. In addition, it can be observed that BNBZT ceramics show a broad dielectric peak with maximum permittivity maximum and low dielectric loss. This result may be used for high temperature applications.
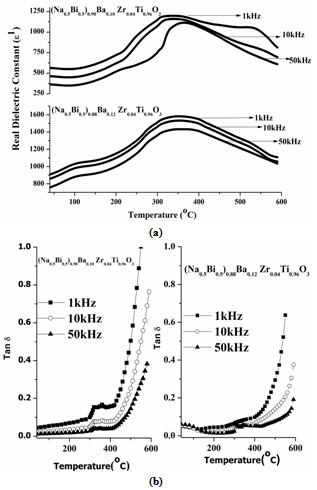 | Figure 2. Temperature dependence of the dielectric constant and Tan δ for 0.10BNBZT and 0.12BNBZT |
|
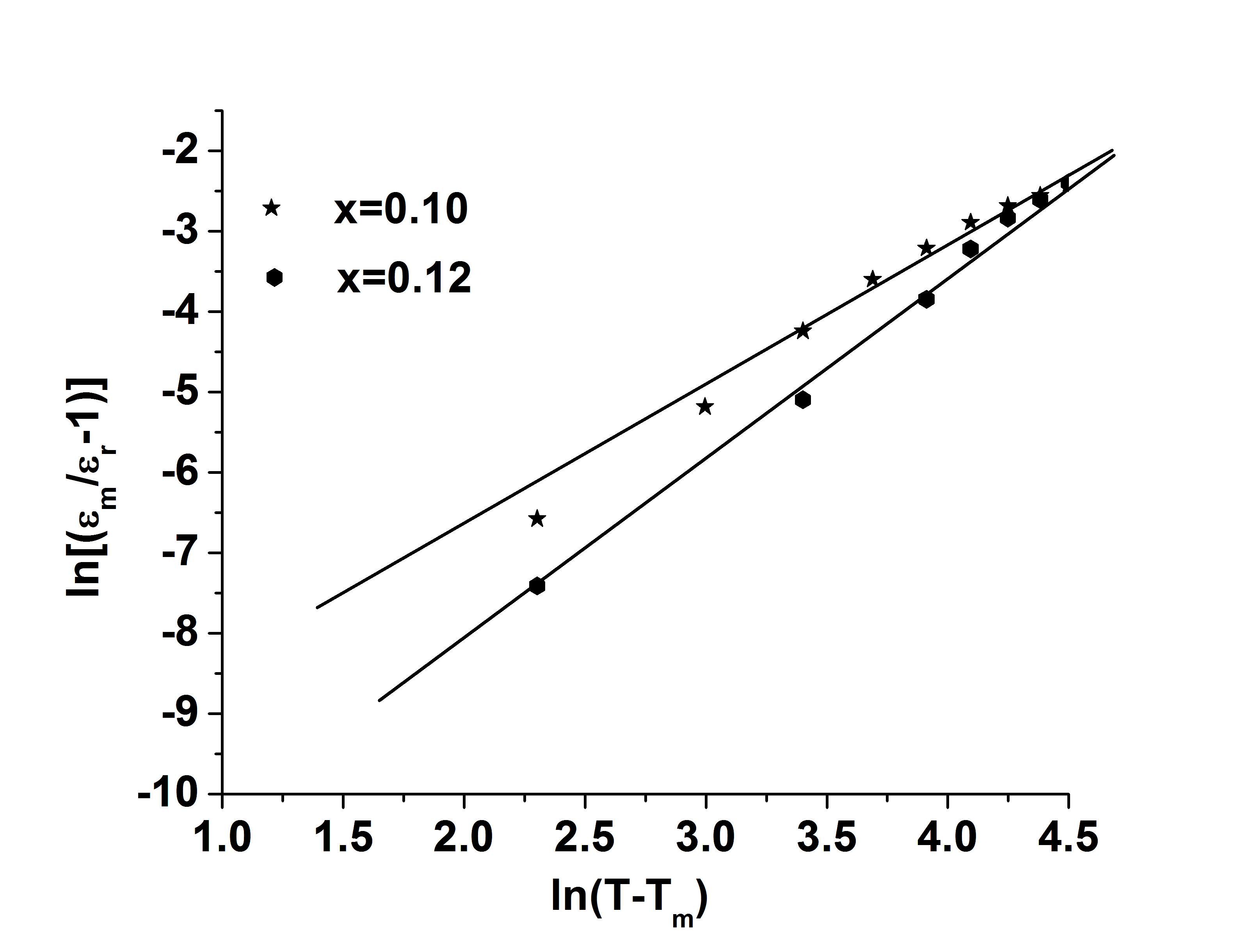 | Figure 3. ln[(εm/ εr-1)] Vs ln (T-Tm) at 1kHz |
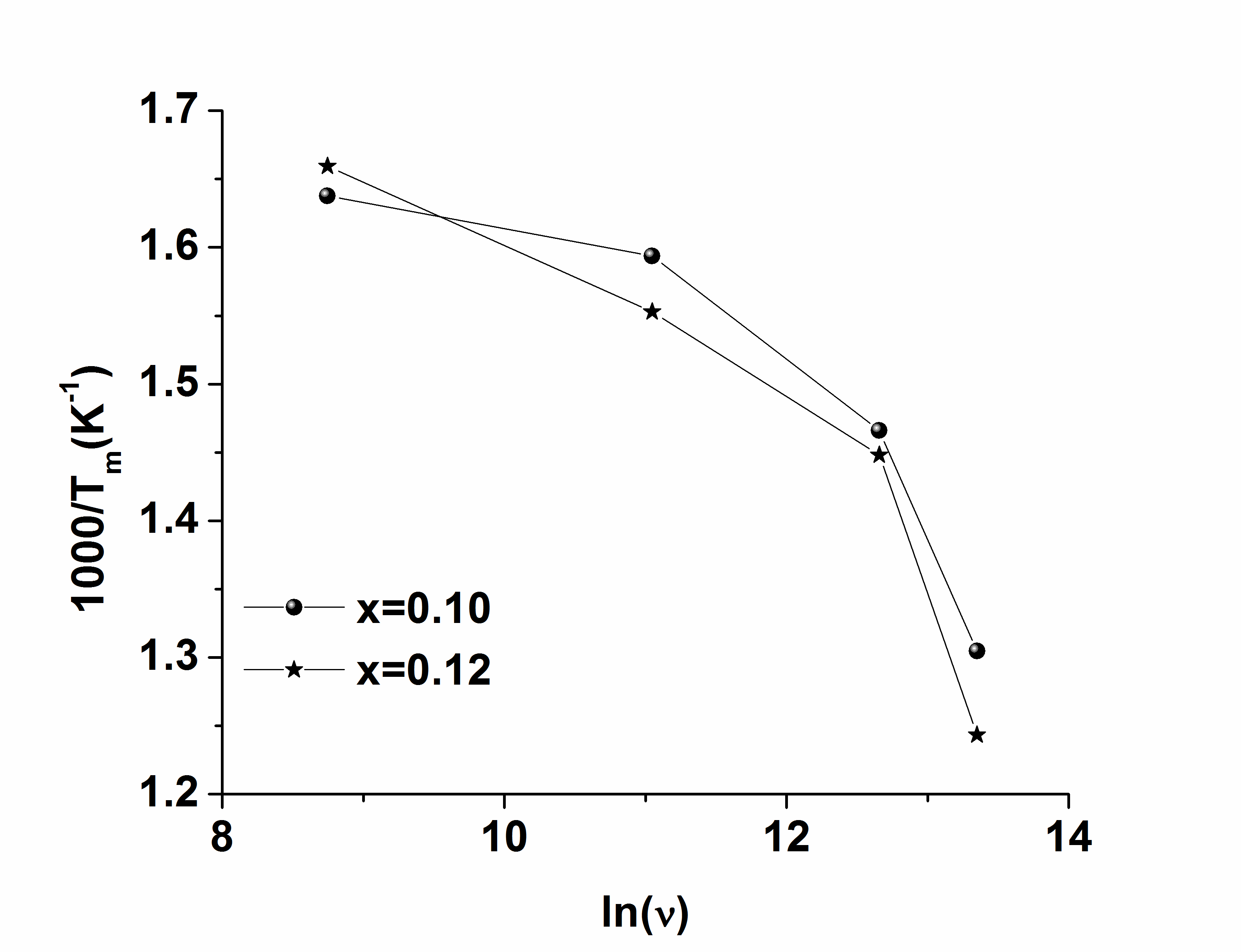 | Figure 4. Verifying Vogel-Fulcher Relation |
3.3. Relaxor Behavior of (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3 Ceramics
- It is well known that the dielectric permittivity of a normal ferroelectric should obey the Curie-Weiss law when the temperature exceeds the Curie temperature,
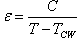 | (1) |
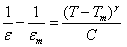 | (2) |
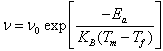 | (3) |
3.4. Impedance and electrical Modulus analysis
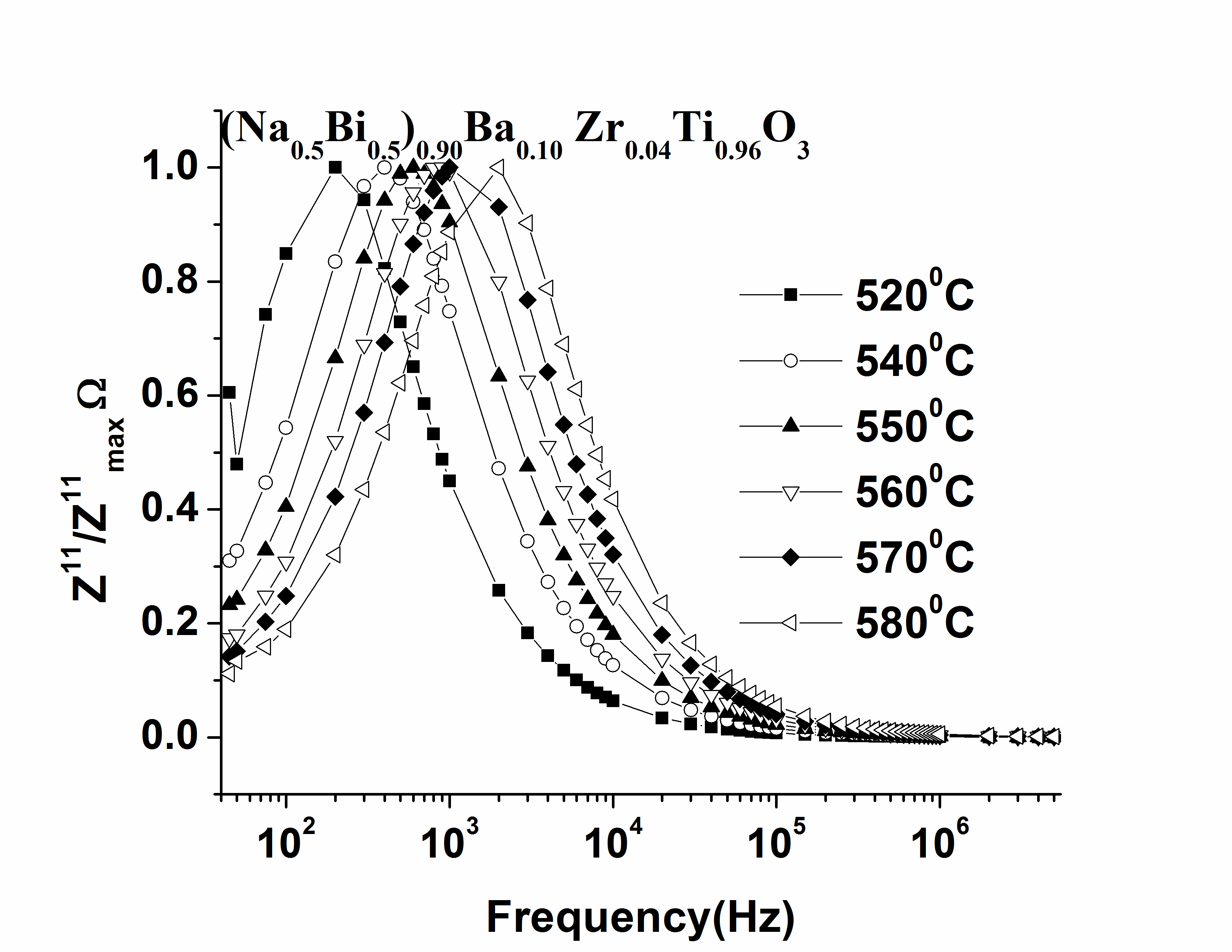
- The electrical behaviour of the compound has been studied over a range of temperature and frequency using the ac technique of complex impedance spectroscopy (CIS). This technique enables us to separate the real and imaginary components of the electrical parameters and hence provides a true picture of the material properties. Each representation can be used to high light a particular aspect of the response of a sample. Figure 5(a) shows the variation of the real part of the impedance (Z1) as a function of frequency at various temperatures for 0.10BNBZT. It is observed that the magnitude of Z1 decreases with the increase of frequency and temperature, indicating an increase in ac conductivity. The merging of Z1 curves at all temperatures above 10 kHz is ascribed to be the release of space charges as a result of reduction in the barrier properties. This may be due to the enhancement of ac conductivity of material with temperature at higher frequencies. Similar behaviour has been observed in the composition for 0.12BNBZT.Figure 5(b) shows the variation of imaginary part of impedance Z11 as a function of frequency at different temperatures for 0.10BNBZT. At low temperatures (below 3000C), Z11 decreased monotonically, suggesting that relaxation is absent in the measured frequencies. This means that the relaxation species in the material are immobile species/ electrons and orientation effects may be involved in the sample. Above 3000C, the nature of the Z11 starts attains a maximum value at a particular frequency and the peak position varies with temperature which indicated the defects or the vacancies appearance at a high temperature.
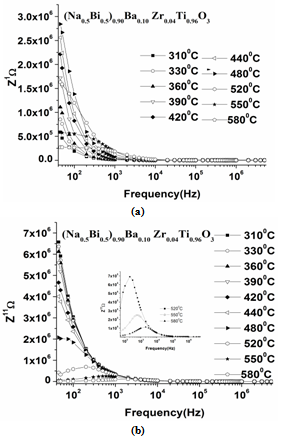 | Figure 5. Variation of the Z1 and Z11 with frequency at different temperatures for 0.10BNBZT |
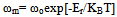 | (4) |
 | Figure 6. Variation of normalized imaginary part of the impedance (Z11/Z11max) as a function of frequency at different temperatures for 0.10BNBZT |
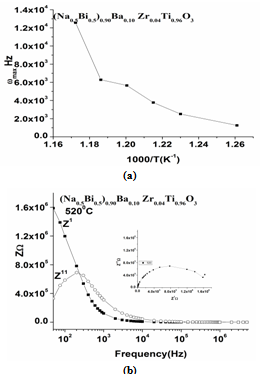 | Figure 7. a: Arrhenius plot of Z11 peak frequencies for 0.10BNBZT; b: Frequency dependence of Z1 and Z11, corresponding Argand diagram(insert) for 0.10BNBZT |
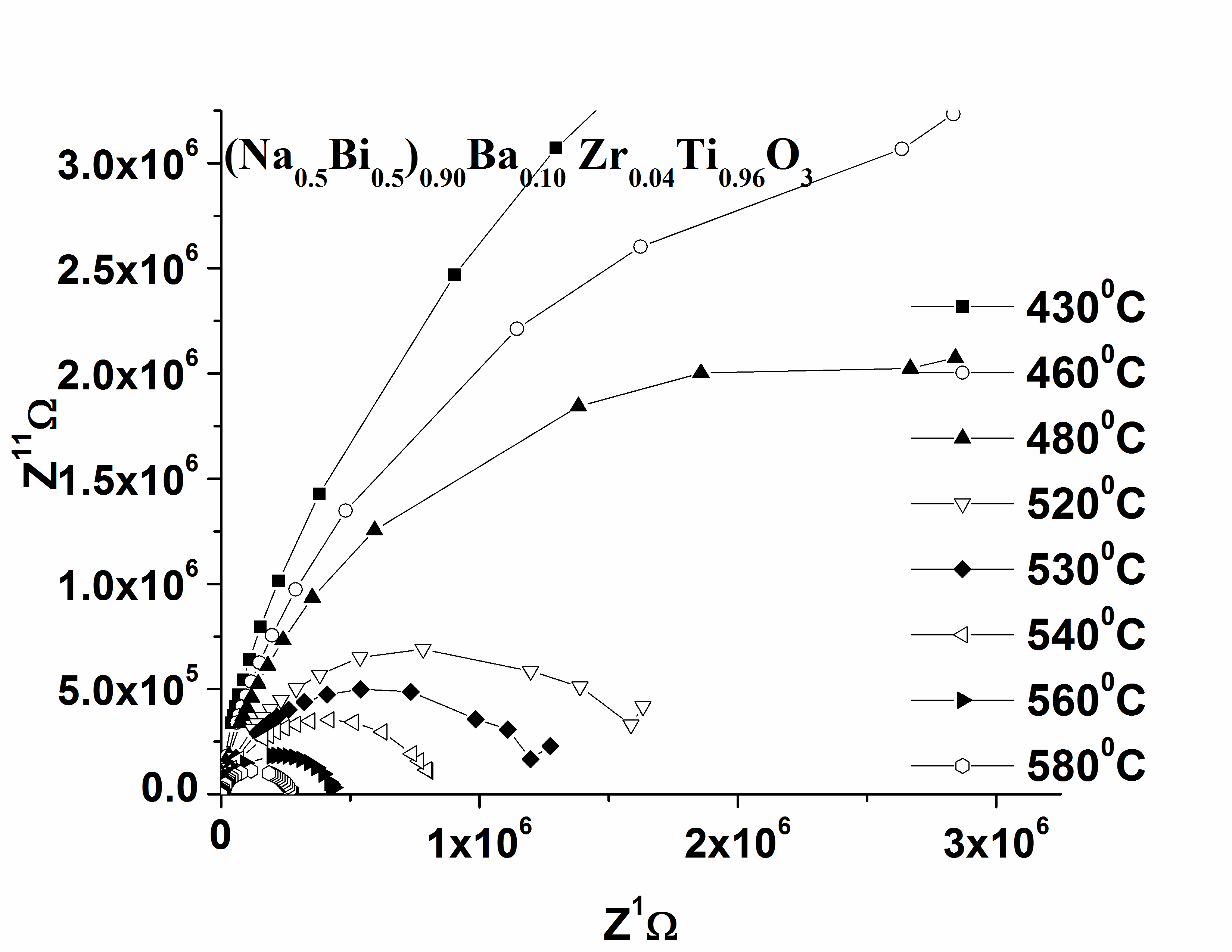 | Figure 8. Complex impedance plots (z11VsZ1) at several temperature of 0.10BNBZT (a similar behaviour was found for 0.12BNBZT) |
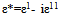 | (5) |
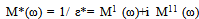 | (6) |
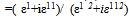 | (7) |
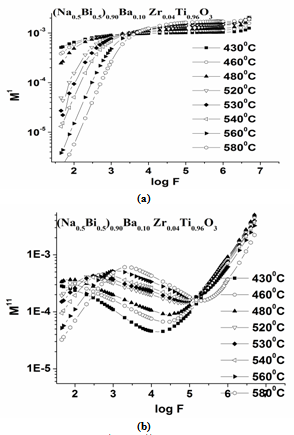 | Figure 9. Variation of M1 and M11 with frequency for 0.10BNBZT |
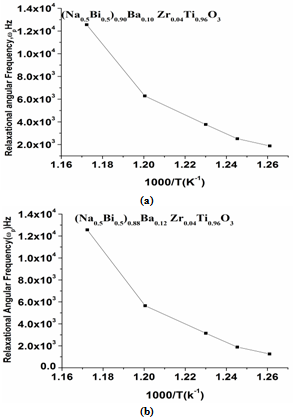 | Figure 10. M″-Peak frequency showing Arrhenius behavior for 0.10BNBZT and 0.12BNBZT |
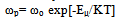 | (8) |
3.5. Conductivity
- Figure 11(a) shows the electrical conductivity σ(ω) as a function of frequency at different temperatures for 0.10BNBZT (results for the 0.12BNBZT ceramic show similar and omitted for briefness). In the present materials, the ac conductivity is found to increase with increase in frequency suggesting the bound carriers trapped in the sample. Conductivity varying at lower frequencies corresponds to space charge polarization[30]. Also, a change in slope has been observed at a particular frequency is related to ion hopping frequency[31-33]. This trend represents the conductivity in the present materials for 0.10BNBZT and 0.12BNBZT obeys Jonscher law[34],
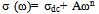 | (9) |
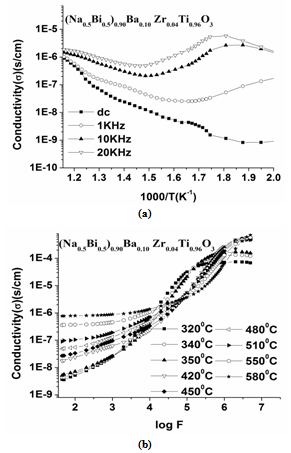 | Figure 11. a: Frequency dependence of conductivity; b: Arrhenius plot of conductivity for x=0.10 |
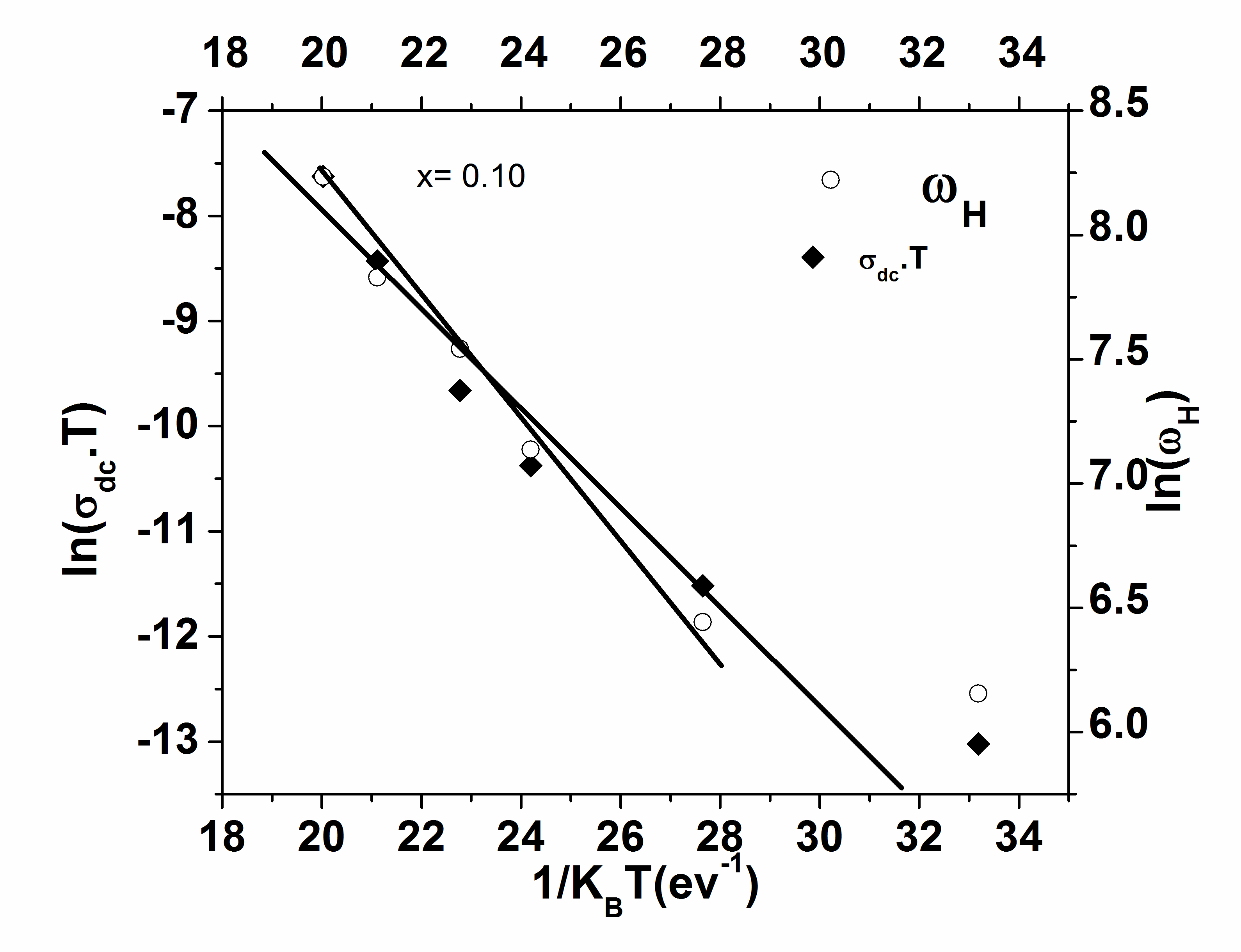 | Figure 12. Arrhenius dependence of dc conductivity (σdc) and the hopping frequency (ωHz) for 0.10BNBZT |
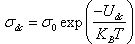 | (10) |
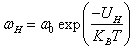 | (11) |
4. Conclusions
- Perovskite type (Na0.5 Bi0.5)1-xBax ZryTi1-yO3 (BNBZT) (with x= 0.10, 0.12 and y=0.04) ceramics have been prepared through conventional solid-state sintering. At room temperature, XRD studies suggest that the studied compositions have single phase with tetragonal structure. As Ba concentration increases keeping Zr concentration constant lattice parameters and cell volume are found to increase. Microstructure studies reveal that the studied compositions are highly dense with a polycrystalline nature. Dielectric studies (ε1 Vs temperature) at various frequencies exhibit a peak broadening with diffused phase transition. It is observed that transition temperature(Tm) shifted towards higher temperatures accompanied by a decrease in the magnitude of the dielectric maximum (εm) reveals a relaxor type nature. The values of the diffuseness parameter γ=2 for x = 0.10 and 1.67 for x = 0.12, obtained from the fit of a modified Curie-Weiss law established the relaxor type nature. Frequency dependence of maximum permittivity of the studied compositions has been modelled by using Vogel-Fulcher relation., the observed values are activation energy (Ea), freezing temperature (Tf) and operating frequency (νo), Where Tf = 2730C, Ea = 0.0346 eV, and ν0 = 4.60 x109 Hz for x = 0.10; Tf = 258℃, Ea = 0.007 eV, and ν0 =5.03 x108 Hz for x = 0.12, which provides the evidence of the relaxor behavior in BNBZT ceramics. Variations of Z1/ Z11 with frequency at different temperature are found to merge above 10 kHz in both materials revealing the reduction in space charge polarization. In electrical modulus, real part of electrical modulus (M1) with frequency at high temperature, it is observed that M1 tends to zero, confirms the electrode and/or ionic polarization. The low and high frequency side of imaginary Part of electrical Modulus i.e., M11 curves, (M11 Vs F) represents hopping of ions and localized motion respectively in studied BNBZT compositions. The observed dispersion in σ(ω) at low frequencies is due to the electrode polarization. It is also observed that at low frequency, high temperature region reveals the transition from long range hopping to short range ion motion and conductivity relaxation phenomena.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors thank to Naval Science and Technology Laboratory (NSTL), Govt of India, Visakhapatnam, for funding the research project and University Grants commission, Govt of India for Research fellowship.
References
| [1] | L. E. Cross, Ferroelectrics., 76 (1987) 241-67 and reference therein |
| [2] | L. E. Cross, Ferroelectrics., 151 (1994) 305-20 and reference therein |
| [3] | Z-G Ye, Key Engineering Materials., 155-156(1998) 81-122, |
| [4] | Chen, I. W., J. Phys. Chem. Solids., 61(2000) 197-208 |
| [5] | L. E. Cross, Nature (London), 432(2004) 24-25 |
| [6] | M. Kosec, V. Bobnar, M. Hrovat, J. Bernard, B. Malic, and J. Holc, J. Mater. Res., 19(6) (2004) 1849-54 |
| [7] | M. D. Maeder, D. Damjanovic, N. Setter, J. Electroceram., 13, (2004)385-392 |
| [8] | Y. Li, K. Moon and C. P. Wong, Science., 308(2005) 1419-1420 |
| [9] | T. Maiti, R. Guo, and A. S. Bhalla, J. Appl. Phys., 100(11) (2006) 114109-1–6. |
| [10] | C. Lei, A. A. Bokov and Z. G. Ye, J. Appl. Phys., 101(2007) 084105-1-9 |
| [11] | H. Yu and Z. G. Ye, J. Appl. Phys, 103(2008) 034114-1-5 |
| [12] | L. Zhang, X. Wang, W. Yang, H. Liu and X. Yao, J. Appl. Phys., 104(2008) 014104-1-5 |
| [13] | J. Ryu, S. Priya nd K. Uchino, Appl. Phys. Lett., 82(2003) 251-253 |
| [14] | H. L. Du, W. C. Zhu, F. Luo, D. M. Zhu, S. B. Qu, Y. Li and Z. B. Pei, J. Appl. Phys., 104(2008) 044104-1-5 |
| [15] | C. J. Stringer, T. R. Shout and C.A. Randall, J. Appl. Phys., 101,(2007) 054107-1-6 |
| [16] | H. Ogihara, C.A. Randall and T. M. Susan, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 90(1) (2009) 110–118 |
| [17] | T. Takenaka, K. Maruyama, and K. Sakata, J. JAP, Part 1-Regular Papers Short Notes & Review Papers., 30[9B](1991) 2236-9 |
| [18] | L. Gao, Y. Huang, Yan hu, hongyan Du, CeramicInternational., 33 (6)(2007) 1041-1046 |
| [19] | Liu Yunfie, XUMing, SHI shuzhe, XUHanqiao, YANG Xiaodong, J. Wuhan University of technology-materials Science dition., 22(2) (2007)315-319 |
| [20] | A. A. Bokov and Z. G. Ye, J. Mater. Sci., 41(1) (2006) 31-52 |
| [21] | B. Beleckas, J. Grigas, S. Stefanovich, Litovskii Fizicheskii sbornik., 202(1989) 29 |
| [22] | B. E. Vugmeister, M. D. Glinichuk, Rev. Mod. Phys., 62(1990) 993–1026 |
| [23] | T. Badapanda, S. K. Rout, S. Panigrahi, T. P. Sinha, J. Current Applied Physics., 9(4) (2009) 727-731 |
| [24] | T. A. Nealon, Ferroelectrics., 76(1)(1987), 377-382 |
| [25] | S. A. Ahmed, E. M. M. Ibrahim, S. S. Saleh, Applied Physics A: Materials Science and Processing., 85(2)(2006) 177-184 |
| [26] | A. k. Jonsher, K. L. Deori, J. M. Reau and J. Moali, J. Mater. Scien., 14(6)(1979) 1308-1320 |
| [27] | P. B. Macdo, C. T. Moynihan, and R. Bose, J. Phy. Chem. Glass., 13(6)(1972) 171-179 |
| [28] | J. Liu, Ch-Duan, W. G. Yin, W. N. Mei, R. W. Smith, J. R. Harday, J. Chem. Phys., 119(2003) 2812-19 |
| [29] | N. Hirose, A. R. West, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 79(1996) 1633-164 |
| [30] | B.V.Bahugunasaradhi, K. Srinivas, G. Prasad, S. V. Suryanaryana, T. Bhimasankaram, Mat Sci Eng B.,98(2003) 10- 16 |
| [31] | Lily, K. Kumar, K. Prasad, R. N. P. Choudary, J. Alloys and Compounds., 453(1-2)(2008) 325-33 |
| [32] | R. Y. Sun, S. J. Fan, J. D. Wu and Y. F. Lin., Proc. IEEE. Int. Frequency. Contr. Symp.,(1996) 113 – 117 |
| [33] | S. Sen, P. Pramanik, R. N. P Choudary, J. Applied Physics A: Materials Science & Processing., 82(3)(2006) 549-557 |
| [34] | R. M. Hill, C. Pickup, J. Mater. Scie., 20(12)(1985) 4431-4444, |
| [35] | M. M. Kumar, Z. G. Ye, J. Appl. Phys., 90(2011) 934-4 |
| [36] | V. Hornebecq, J. M. Reau and J. Ravez, Solid State Ionics., 127(2000) 231–240 |
| [37] | V. Hornwbecq, Personal communication |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML