-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Materials Science
p-ISSN: 2162-9382 e-ISSN: 2162-8424
2012; 2(2): 11-14
doi: 10.5923/j.materials.20120202.03
Capacitive Behavior of Manganese Dioxide/Stainless Steel Electrodes at Different Deposition Currents
Sameh Hassan 1, Masaaki Suzuki 2, Ahmed Abd El-Moneim 3
1Energy Resources and Environmental Engineering Department, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El Arab City, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt
2Department of Chemical Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2-12-1 O-okayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, 152-8552, Japan
3Material Science and Engineering Department, Egypt- Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El Arab City, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt
Correspondence to: Sameh Hassan , Energy Resources and Environmental Engineering Department, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El Arab City, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Amorphous manganese dioxide thin films were prepared by galvanostatic cathodic deposition at current densities of 0.5-1 mA/cm2 on etched stainless-steel substrate from KMnO4 solution. The structure of the deposited oxides was investigated using X-ray diffraction analysis. The capacitive behavior of the manganese dioxide electrodes was characterized by cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in Na2SO4 electrolyte. The capacitive performance was found to increase with the increase in the deposition current density. The electrode deposited at current density of 1 mA/cm2 showed specific capacitance of 174 F/g at a scan rate of 10 mV/s, equivalent series resistance of 3.53 Ω, and charge transfer resistance of 1.39 Ω. The improvement in the capacitive behavior of the electrode with the increase in the deposition current density was attributed to the increase in the electronic properties of the deposited oxides.
Keywords: Manganese Dioxide, Supercapacitor, Energy Density, Electrodeposition
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Energy storage devices have become more demanded due to the fast growing market of portable electronic devices and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs)[1]. Supercapacitors, also known as electrochemical capacitors or ultracapacitors, are an energy storage devices capable of storing charges in the electrode/electrolyte interface, have received much attention due to their unique properties, such as pulse supply of high power, longer cycle life and higher energy density[2]. However, the energy density of supercapacitors (< 10 Wh /kg) is lower than that of batteries (> 100 Wh/kg) but their power is significantly higher with lifetime longer[3]. On the basis of the energy storage mechanism, supercapacitors can be classified into two categories[4,5], namely the electrical double-layer capacitor (EDLC) and the pseudocapacitor. EDLCs store charge electrostatically through the charge accumulation at the electrode/electrolyte interface, therefore strongly depending on the surface area of the electrode accessible to the electrolyte. Pseudocapacitors store charge Faradaically through the transfer of charge between electrode and electrolyte. There are two electrode materials that are used to store charge in pseudocapacitors, conducting polymers and metal oxides[3, 6,7]. The latter is of interest in our work.Because of their high conductivity, metal oxides have also been explored as a possible electrode material for pseudocapacitors[8-12]. The most of relevant research concerns ruthenium oxide. This is because other metal oxides have yet to obtain comparable capacitances. A very high specific capacitance of up to 750 F/g was reported for RuO2 prepared at relatively low temperatures[2]. The capacitance of ruthenium oxide is achieved through the insertion and removal, or intercalation, of protons into its amorphous structure. Furthermore, the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of hydrous ruthenium oxide is lower than that of other electrode materials. As a result, ruthenium oxide pseudocapacitors may be able to achieve higher energy and power densities than similar EDLCs and conducting polymer pseudocapacitors. However, the high cost of this noble metal material limits its further commercial application. Hence, much effort has been aimed at searching for alternative inexpensive electrode materials with good capacitive characteristics, e.g., transition metal oxides, such as MnOx, NiOx, CoOx[2], etc. Thus, a major area of research is to utilize cheap metal oxide and/or the development of fabrication methods to reduce the cost of ruthenium oxide, without reducing the performance[8,9]. MnOx has been considered as a promising electrode material for electrochemical capacitors because of its low cost and excellent capacitive performance in the aqueous electrolytes. Manganese dioxide is generally produced by anodic deposition at a high current density onto metallic conductive substrate using acidified MnSO4 solution. However, this method usually leads to the dissolution of the conductive substrate and/or build up an insulating oxide layer at the interface of the active oxide and substrate, which negatively affect the value of specific capacitance as well as the resistance of developed manganese oxide electrodes. To improve the capacitive behavior and resistance of the deposited manganese dioxide, the present study is undertaken to deposit manganese dioxide thin film onto stainless steel substrate from KMnO4 aqueous solution using galvanostatic cathodic deposition technique. Special attention is given to study the effects of deposition cathodic current density on the structure properties as well as capacitive performance of MnO2 thin film.
2. Experimental
- Stainless-steel (SS) sheet of grade 316 LN, thickness and surface area of × was used as substrate material for the electrodeposition. The substrate was first etched in a mixture of hydrofluoric acid 40 %: nitric acid 69 %: distilled water with ratio 1:1:1 for 1 hour, then washed and dried in air. MnO2 thin films were galvanostatically deposited from KMnO4 solution at a cathodic current density of 0.5, 0.75, and 1 mA/cm2 onto SS substrate for 0.5 hour. The weight of the deposited manganese dioxide film was measured by means of a Sartorius micro-balance (Model BP211D). The structure was characterized by means of X-ray diffractometer (Shimadzu, XRD-7000) using Cu Kα radiation.All electrochemical measurements were performed at 30±1.0C using two compartment three electrodes electrochemical cell with platinum foil as an auxiliary electrode and a saturated Ag/AgCl reference electrode. The electrochemical impedance investigations and the cyclic voltammtery (CV) polarisation measurements were carried out in Na2SO4 electrolyte using VersaSTAT4 potenitostat/galvanostat. The CV measurements were carried out at potential ranges of 0–0.9 V vs. Ag/AgCl (sat.) at scan rates of 10–100 mV/s. The excitation amplitude for impedance measurements was 10 mV root mean square in a frequency domain of 10-1 to 105 Hz.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure
- Figure1 shows typical X-ray diffraction pattern of MnO2 film galvanostatically deposited onto etched SS substrate at 1 mA/cm2. The XRD pattern shows sharp peaks corresponding to crystalline stainless steel substrate. No reflection peaks typical to the formation of crystalline or nanocrystalline MnO2, indicating to the formation of amorphous MnO2 film. It’s worth mentioning that the amorphous phase of the oxide material is generally necessary to have an electrode with large surface area for supercapacitor applications[13]. Meanwhile, XRD results revealed that the value of deposition current density has insignificant effect on the recorded XRD patterns of the deposited films.
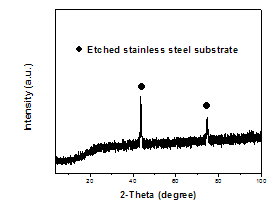 | Figure 1. XRD pattern for MnO2 film galvanostatically deposited at 1 mA/cm2 on etched SS substrate |
3.2. Supercapacitive Behavior
3.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
- Figure 2 shows the CV curves in Na2SO4 electrolyte for MnO2 films obtained at different deposition current densities.
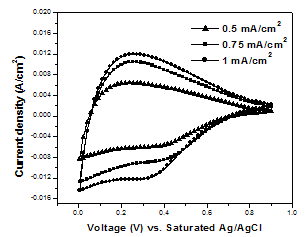 | Figure 2. Cyclic voltammetric curves of MnO2 films measured in Na2SO4 solution at a scan rate of 100 mV/s as a function of deposition current density |
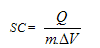 | (1) |
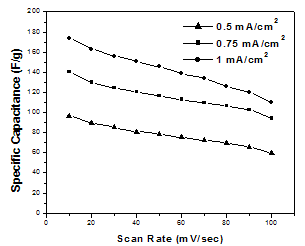 | Figure 3. Dependence of the specific capacitance on the scan rate of CV measurement for MnO2 films deposited at different deposition current densities |
3.2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
- The initial non-zero intersect with the real impedance axis at the beginning of the semicircle indicates the typical ESR value of all system[14,17]. The estimated ESR values for the deposited oxide films at deposited current densities of 1, 0.75, and 0.5 mA/cm2 are 3.53, 3.54, and 3.91 Ω, respectively. The results indicate that the variation in the ESR value with the deposition current density is insignificant.
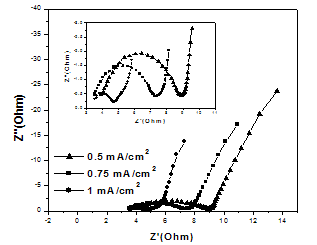 | Figure 4. Nyquist plots of MnO2/SS electrodes prepared under different deposition current densities |
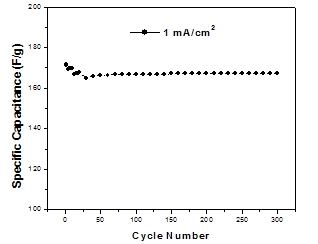 | Figure 5. Life-cycle data of MnO2/SS electrode at discharge current density 5.5 mA/cm2 |
3.2.3. Cyclic Stability using Galvanostatic Charge–Discharge
- The life-cycle test of the deposited MnO2 film at 1 mA/cm2 was performed at discharge current density 5.5 mA/cm2 and the result is presented in Fig. 5. As it can be seen, there is a little decrease in the value of specific capacitance in the first 10 cycles and then the specific capacitance value remained almost constant. A decrease of about 2.3 % in the initial specific capacitance was observed after 300 cycles. This decrease in the specific capacitance is very less compared to the value reported in the literature[19] and indicates the high stability of the deposited film.
4. Conclusions
- In an attempt to develop a novel electrode with low cost, high capacitive performance and long cyclic stability, amorphous manganese dioxide thin films were galvanostatically deposited onto etched SS electrodes from KMnO4 solution at different cathodic current densities in range of 0.5-1 mA/cm2. The capacitive performance of the films was found to increase with the increase in deposition current density. The MnO2 film deposited at current density of 1 mA/cm2 has the highest SC of 174 F/g at a scan rate of 10 mV/s and the smallest charge transfer resistance of 1.39 Ω. The excellent capacitive performance suggests that the amorphous MnO2 films obtained by cathodic deposition from KMnO4 solution has the potential to be used as an electrode material for high performance supercapacitors.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors gratefully acknowledge the Missions Sector-Higher Education Ministry, Egypt for financial support through this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML