-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Materials Science
p-ISSN: 2162-9382 e-ISSN: 2162-8424
2012; 2(1): 5-13
doi:10.5923/j.materials.20120201.02
Shape Controlled Synthesis of Barium Carbonate Microclusters and Nanocrystallites using Natural Polysachharide – Gum Acacia
B. Sreedhar1, Ch. Satya Vani2, D. Keerthi Devi1, M. V. Basaveswara Rao3, C. Rambabu2
1Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Division, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research), Hyderabad 500607 Andhra Pradesh, India
2Department of Chemistry, Acharya Nagarjuna University P.G. Centre, Nuzividu-521201, Andhra Pradesh, India
3Department of Chemistry, Krishna University, Machilipatnam-521001,Andhra Pradesh, India
Correspondence to: B. Sreedhar, Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Division, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research), Hyderabad 500607 Andhra Pradesh, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Different morphosynthesis strategies for BaCO3 using natural polysaccharide-gum acacia (GA) as templating species are presented. The influence of GA with different functionalities such as –OH, –COOH and -NH2 on the crystallization and structure formation was investigated. Some interesting morphologies, including rods, dumbbell, double-dumbbell and flower like clusters, can be readily generated by using GA as cooperative modifier in the mineralization process, under the conditions of 0.5%, 1% of templating species and at ambient temperature. The modifier GA and its concentration is the key factor in this system. In continuation, morphology was also examined for mixed metal carbonates (Ba-LaCO3, Ba-TbCO3). The possible formation mechanism of the nanocrystallites is discussed. Structural characterization of the synthesized materials was investigated byPowder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Analysis (EDAX), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) coupled Mass (MS) and Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR).
Keywords: Biomaterials, Composite Materials, Crystal Growth, Electron Microscopy
Cite this paper: B. Sreedhar, Ch. Satya Vani, D. Keerthi Devi, M. V. Basaveswara Rao, C. Rambabu, Shape Controlled Synthesis of Barium Carbonate Microclusters and Nanocrystallites using Natural Polysachharide – Gum Acacia, American Journal of Materials Science, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 5-13. doi: 10.5923/j.materials.20120201.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The study of mineral formation in biological systems, biomineralization, provides inspiration for novel approaches to the synthesis of new materials. Biomineralization relies on extensive organic-inorganic interactions to induce and control the synthesis of inorganic materials. In recent years, bioinspired morphosynthesis of crystals with hierarchical forms in the presence of organic templates having complex functionalizing patterns have been explored widely so as to mimic natural biominerals[1-6]. Among a variety of construction methodologies of functional materials, patterned crystal arrays of organic[7], inorganic[8,9] and their hybrid crystals[10,11], have received considerable attention in recent years for their diverse application potential in areas such as catalysis, medicine, pigments, cosmetics, separation technology[12,13], nano-devices[14] and find diverse applications in nanotechnology[15,16].Nanostructural materials have become attractive because of their unique characteristics that can hardly be obtained from conventional bulk materials owing to their quantum size and surface effects. So, there has been considerable interest in fabrication of low-dimensional nanosized materials such as nanowires, nanorods and nanotubes. Several processes have been explored in the literature for the synthesis of nanomaterials. These processes involve both physical and chemical methods[17-20]. Various artificial complexations have been investigated as models of biomineralization using modifier agents , e.g., urease[21], nitrilo triacetic acid, citric acid[22], poly(acrylic acid) (PAA)[23], poly(methacrylic acid) PMMA, poly(ethylene glycol) PEG [24], poly(allylamine hydrochloride) PAH, poly (sodium 4-styrene sulfonate) PSS[25], (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) CTAB[26]. These modifying agents have also been thought to control the polymorph of the barium carbonate clusters. However, the characterization of these native and modifier agents on the crystal surface is still unclear.BaCO3 has attracted a lot of recent research[27-30] due to its close relationship with aragonite, a prevalent and important biomineral, with many important applications in the ceramic and glass industries as well as its use as a precursor for magnetic ferrites and/or ferroelectric materials[31]. Barium carbonate (BaCO3) is also used as a precursor for producing superconductor and ceramic materials[32] and other important applications in optical glass and electric condensers[33]. Therefore, in the present study, we report the synthesis and characterization of BaCO3 nanocrystallite using natural polymer, gum acacia.Polymer-mediated mineralization of inorganic materials has been the subject of intense research because polymers have been found to dramatically influence the characteristics of an inorganic precipitate. The ability to influence the morphology and phase of an inorganic precipitate has important technological implications[34], because some physical properties of crystalline materials such as the brilliance of color pigments or the dielectric function of electroceramics depend on crystal habit, grain size, grain size distribution, impurities, or content of polymorphous modifications. Control of nucleation, crystal growth, and organization of crystals to a superstructure (“texture”) make these physical properties tunable and are thus important for technical application[35]. The present investigation deals with the influence of Gum Acacia a natural polysaccaharide as templating species for the formation of BaCO3 nanocrystallites self- assembling into microclusters. Gum Acacia is a natural gum made of hardened sap derived from Acacia Senegal and Acacia Seyel. GA consists of mainly three fractions (1) The major one is a highly branched polysaccharide consisting of β-(1-3) galactose backbone with linked branches of D-galactose (38%), L-arabinose (45%), L-rhamnose (4%), which terminate in D-glucuronic acid (7%), and 4-O-methyl-D-glucuronic acid (6%). (2) A smaller fraction (~10 wt % of the total) arabinogalactan–protein complex (GAGP–GA glycoprotein) in which arabinogalactan chains is covalently linked to a protein chain through serine and hydroxyproline groups. The attached arabinogalactan in the complex contains ~13% (by mole) glucoronic acid. (3) The smallest fraction (~1% of the total) having the highest protein content (~50 wt %) is a glycoprotein which differs in its amino acids composition from that of the GAGP complex. Here the functional groups namely, hydroxyl (-OH) present in arabinose and rhamnose and carboxylic (-COOH) in glucoronic acid play a crucial role in the growth and formation of metal carbonates whereas the proteinaceous core in amino acids stabilizes the formed metal carbonates[36]. It not only acts as a stabilizer [37], but also acts as surfactant and templating agent for which the functional group moieties (–OH, COOH & -NH2) have been found to play a key role in mimicking the biomineralization process. The crystallization involves the formation of different hierarchical structures like rods through dumbbell to flower shaped which have never been seen before in natural biominerals. Proteins and polysaccharides with complicated patterns of various functional groups in GA selectively adsorb on to the metal ion thereby hindering the crystal growth, followed by the mesoscale self-assembly of nanometer-scale building block into hierarchial superstructures[38-42]. The key reaction of CO2 with Ba2+ ions entrapped within GA polymer leads to the growth of beautiful structures of witherite nanocrystalline, such an aggregated morphology not normally observed using other surfaces as templates. This templating species composed of many anionic moieties, which interacts strongly with ions, crystal surfaces. Functional, water- soluble polymers with the ability to bind ions and crystals play a major role as scale inhibitors crystal faces and thus, promotes the crystal growth. This species also strongly modify the morphology of growing crystals in an interesting manner. Indeed, in the presence of such templating species, the nucleated crystals may adopt a variety of shapes. The interacting part of the GA (–OH, COOH & -NH2) can be selected or designed in such a way that it specifically adsorbs to a certain crystal face. The proteins and inorganic ions regulate the phase of the deposited mineral[43,44].The aim of the study was to determine the effects of GA on the morphological and structural characteristics of the resulting different morphological structures, with special emphasis on different phases in the growth process. Our results demonstrate that by varying the reaction conditions the interaction of gum acacia (GA) with the precursors, results in controlling the shape, size, and microclusters of the inorganic crystals by means of a simple mineralization process.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
- Analytical grade chemicals of BaCl2, LaCl2, TbCl2, gum acacia, sodium bicarbonate were purchased from Merck, India and used as such without further purification. Double distilled water was used in all experiments.
2.2. Preparation of BaCO3 Microclusters
- In a typical procedure, at room temperature, 0.2442 g (1mM) of BaCl2 was taken along with different proportions of homogenized GA (0.5 % and 1.0%) in different 25 ml glass beakers. They were dissolved in 20 ml distilled water and the mixed solution was blended thoroughly with the help of magnetic stirrer. Then NaHCO3 (2mM; 2 ml) solution is added by vigorous stirring and the reaction mixture was kept for 24 h crystallization at room temperature. After 24 h, the crystals are filtered and washed several times with distilled water and dried at room temperature.
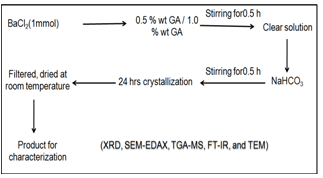 | Figure 1. Flow chart for the synthesis of microclusters of BaCO3 using gum acacia |
2.3. Characterization Methods
- X-ray diffraction measurements of barium carbonate clusters were recorded using a Rigaku diffractometer (Cu Kα radiation, λ = 0.1546 nm) running at 40 kV and 40mA (Tokyo, Japan). FT-IR spectra of BaCO3 structures were recorded with a Thermo Nicolet Nexus (Washington, USA) 670 spectrophotometer. TEM images were observed on TECNAI FE12 TEM instrument operating at 120 kV using SIS imaging software. The particles were dispersed in methanol and a drop of it was placed on Formvar-coated copper grid followed by air drying. Scanning electron microscopy (FEI Quanta 200 FEG with EDS) was used for morphology assessment of BaCO3 crystals. The crystals were collected on a round cover glass (1.2 cm), washed with deionized water and dried in a desiccator at room temperature. The cover glass was then mounted on a SEM stub and coated with gold for SEM analysis. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) coupled to Balzer Mass (MS) was carried out on a TGA/SDTA Mettler Toledo 851e system using open alumina crucibles containing samples weighing about 8–10 mg with a linear heating rate of 10℃ min-1. Nitrogen was used as purge gas for all these measurements.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization of BaCO3 Microclusters
- The phase structures of the obtained samples were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). Figure 2 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of BaCO3 synthesized without GA, with GA (1%) at room temperature, hydrothermal treatment at 90℃ and calcined product at 700℃. The XRD pattern of BaCO3 crystals obtained are pure orthorhombic BaCO3 crystals. All the observed peaks can be perfectly indexed to a pure orthorhombic witherite phase and no characteristic peaks from other impurities have been detected in the synthesized products. The observed diffraction peaks (2θ [°]): can be correlated to the (hkl) indices (110), (020), (111), (021), (002), (012), (112), (200), (220), (040), (221), (041), (202), (132), (113) and (222) respectively, of pure orthorhombic witherite (JCPDS card number: 85-0720). It may also be seen that the peak (111) is the strongest in all the BaCO3 crystals synthesized using various routes, suggesting that BaCO3 crystals are well oriented and grew mainly along the (111) face. The extra diffraction peaks (102) and (130) observed in the calcined product is due to increase in crystallinty. Along with (111) face several other strong diffraction peaks in the XRD pattern suggest that the crystallinity of BaCO3 nanocrystallites obtained is excellent, and can be correlated to TEM (SAED) micrograph. The diffraction spots can be indexed on the orthorhombic phase and those results are in good agreement with the results of XRD. It can be concluded that GA has major influence on the growth and size morphology of BaCO3 crystals formed. However, the addition of templating species has no effect on the internal crystal structure of the resulting BaCO3 crystals as no changes are observed in the XRD patterns.
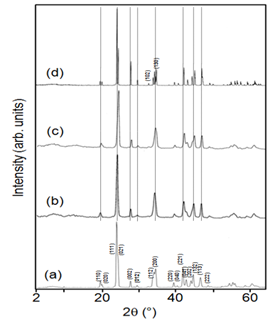 | Figure 2. XRD pattern of BaCO3 crystals (a) absence of GA, (b) presence of GA (1%), (c) hydrothermal at 90℃ (1%), and (d) calcined at 700℃ (1%) |
3.2. Effect of Gum Acacia on the Morphology of BaCO3
- The morphology of the obtained BaCO3 crystals was remarkably influenced by the synthetic protocol used such as hydrothermal treatment and varying concentration of GA. Morphologies of the formed crystal aggregates were investigated using SEM-EDAX and TEM. Under ambient conditions in the absence of any templating species only rod-shaped crystals of witherite in the form aragonite-type crystals (Figure 3a) with different sizes (700 nm to 20μm length, 200 nm to 2μm diameter) were formed as expected. Significant changes have been observed in the morphology of the products obtained in the presence of the templating species – GA. Bunch of rods, dumbbell, double-dumbbell and flower shaped BaCO3 clusters were observed for 0.5 % and 1.0 % GA concentration depending on the reaction conditions. These clusters are of sizes in several nanometers to several micrometers at both ambient (Figure 3b, c) and hydrothermal crystallization conditions (Figure 3d, e). SEM images of the products formed after 24h of reaction at various concentrations of GA (0.5 % and 1.0 %) in both the reaction conditions are shown in figure 3.At room temperature, when GA concentration was 0.5%, bunch of rods in the form of clusters are seen as shown in figure 3b. The length of the rods present in the clusters is in the size range from 100 nm to 400 nm. The enlarged image clearly shows that the rods aggregate in the form of bunch like clusters (Figure 4a). When the amount of GA added is increased to 1.0%, shorter assemblies of BaCO3 aggregates in the form of dumbbell, double dumbbell and flower like clusters are observed, as depicted in figure 3c. These clusters constitute nanosized subunits with size around 30nm. The enlarged SEM images of both the concentrations are separately shown in figure 4b. Similar morphological changes were observed in both the concentrations except variation in the size of the cluster and alignment of rods. With the increase in concentration of GA the size of the cluster increased but the nanocrystallite size decreased. This behavior can be attributed due to the effective passivation of the surfaces and suppression of the growth of the nanoparticles through strong interactions with the particles via there functional molecular groups of acacia namely, hydroxyl groups of arabinose, rhamnose and galactose and carboxylic groups of glucoronic acid moieties. Progressive changes in the assembled BaCO3 clusters indicated that the arrangement continued to grow principally in width rather than in length when the crystals interlinked. Although the individual rods observed in the absence of templating species are often disordered, they were structurally intact, suggesting that there are strong interparticle interactions between adjacent rods. Significantly, the HR-SEM images show that the BaCO3 crystals appear to be higher-order superstructures, exhibiting close morphological alignment of the rod shaped crystals into microclusters. Further, crystal growth of BaCO3 was monitored under hydrothermal crystallization at 60℃ and 90℃. Since there is no much variation in the morphology observed, the results obtained at 90℃ are shown in figure 3d, e. At 90℃ stacks of rods are arranged randomly and appear like flowers at lower gum acacia concentration (0.5%), whereas at higher concentration (1 %), more number of flower like clusters are seen but there is no change in the morphology as observed in figure 3d, e. From this it is evident that during hydrothermal crystallization, at two different concentrations common morphology i.e.; flower shaped clusters are seen except their number increased at higher ratio of metal/ligand concentration, and the size of the clusters is also almost similar. This attributes that increasing concentration does not have much effect on the crystal morphology during hydrothermal crystallization. Moreover, temperature variation also does not have any impact in the growth morphology except variation in size. On the other hand, synthesis of BaCO3 nanostructures at ambient condition show influence of concentration on the morphology and arrangement of the clusters formed. The schematic illustration of BaCO3 crystal morphology is shown in the table 1.
 | Figure 3. SEM images of BaCO3 clusters (a) rod shaped witherite (aragonite-type) crystals without gum acacia (b, c) room temp reaction using 0.5 and 1.0 % GA, and (d, e) hydrothermal (90℃) reaction with 0.5 and 1.0 % GA |
 | Figure 4. Enlarged SEM images of BaCO3 clusters at different reaction conditions (a) 0.5% GA at room temperature, (b) 1% GA at room temperature, (c) 0.5% GA at hydrothermal 90℃, and (d) 1% GA at hydrothermal 90℃ |
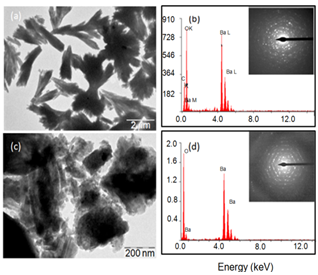 | Figure 5. TEM images and EDAX (SAED inserted) of BaCO3 (a, b) in the presence of 1% GA, and (c, d) calcined product at 700℃ |
3.3. Ba-LaCO3 System and Ba-TbCO3 System
- Other than barium carbonate, mixed metal carbonates such as Ba-LaCO3 and Ba-TbCO3 were synthesized at room temperature using higher GA (1.0 %) concentration. Figure 6a, c shows the SEM images of Ba-LaCO3 and Ba-TbCO3 mixed metal carbonates, respectively. As can be seen, there is a clear morphological difference between BaCO3 structures synthesized with and without the addition of rare earths. Ba-LaCO3 clusters are in the form of short rods whereas Ba-TbCO3 appears to be dendritic clusters. It would be instructive to understand the chemical composition of the different features observed for both Ba-LaCO3 and Ba-TbCO3 microstructures. This is conveniently done by spot-profile EDAX. In addition to the expected Ba, C and O signals, strong signals of La and Tb are seen for Ba-LaCO3 and Ba-TbCO3 mixed metal carbonates, respectively as shown in figure 6b, d.
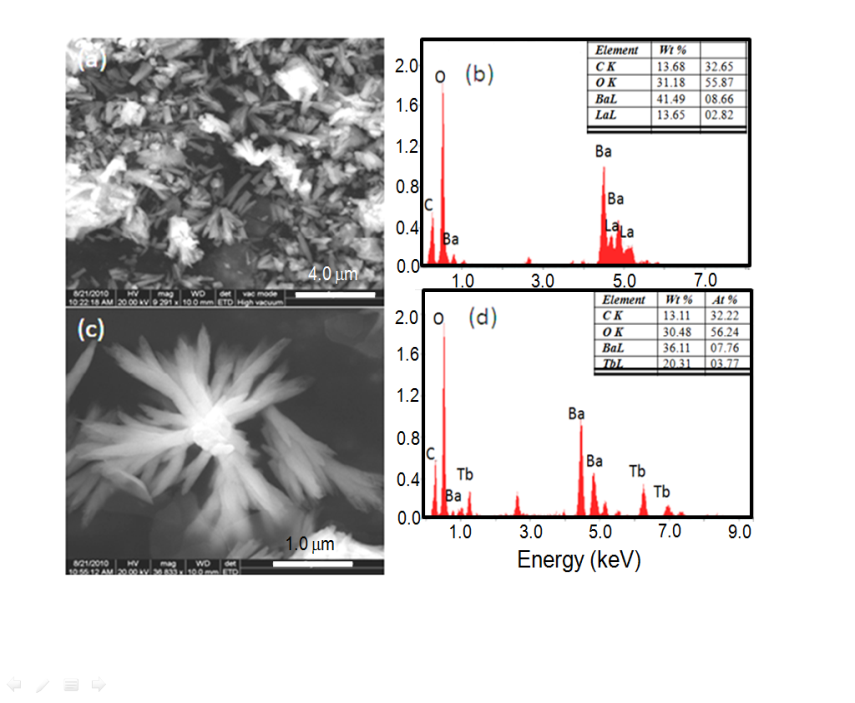 | Figure 6. SEM images of mixed metal carbonates (a) Short rod like clusters of Ba- LaCO3, (b) EDAX data of Ba-LaCO3, (c) Dendritic shaped clusters of Ba-TbCO3, and (d) EDAX data of Ba-TbCO3 |
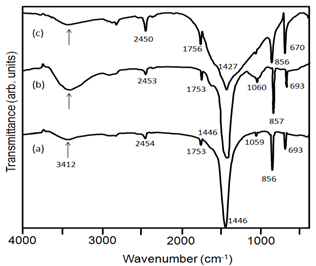 | Figure 7. FT-IR spectra of BaCO3 clusters (a) nucleated in the absence of GA, (b) nucleated in the presence of GA, and (c) calcined product at 700℃ |
3.4. FTIR Studies
- FT-IR spectra of BaCO3 have been studied to determine the effect of GA on the microstructure of nanocrystallites. The sharp peaks at 856, 693 cm-1 (Fig. 7a), 857, 693 cm-1 (Figure 7b) and 856, 690 cm-1 (Figure 7c) are in-plane and out-of-plane bending of CO32-. The IR bands at 1446 cm-1 (Figure 7a, b), and 1427 cm-1 (Figure 7c) correspond to the asymmetric stretching mode of C-O bond, while the weak band at 1059 and 1060 cm-1 (Figure 7a, b) is attributed to the symmetric C-O stretching vibration. The band at 3412 cm-1 can be attributed to OH stretching vibration due to hydrogen bonding and or N-H stretch of the –NH2 group from the protein present in GA (Figure 7b). In comparison with figure 8b the C-O stretching vibration peak around 1427 cm-1 in figure 7c shifts to lower frequency by 19 cm-1 (1446 cm-1), suggesting the influence of GA on the microstructure of barium carbonate. This is probably due to the GA molecules adsorb onto the surfaces of BaCO3 nuclei and influence the mode of crystal growth with a little change in superstructure. Increase in the intensity of the peak at 3412 cm-1 in figure 7b shows the presence of GA in the BaCO3 crystals resulting in the formation of inorganic-organic hybrid material.
3.5. TGA-Mass studies
- Thermogravimetric analysis coupled to mass helps us to understand the decomposition steps more precisely as we can know the evolved gas fragments as a function of temperature or time. As representative systems, the TG/DTG-MS thermograms of pure GA, BaCO3 synthesized without GA, as synthesized BaCO3 using GA and BaCO3 with GA calcined at 700℃ are shown (Figure 8a-d). TGA-MS thermogram of pure GA (Figure 8a) shows a major decomposition step (64.5% wt. loss) in the temperature range 260 - 400℃ and it is during this step the evolution of the gas with mass fragment 44 a.m.u characteristic of CO2 from the decomposition of –COOH functional groups in GA is observed. TGA profile of BaCO3 structures synthesized without gum acacia (Figure 8b) show a single step decomposition with the onset at 850℃. The mass fragment 44 a.m.u observed in this range clearly suggests that the BaCO3 nanocrystallites decompose into BaO and CO2 in this temperature range. Further, BaCO3 nanocrystallites synthesized using GA (Figure 8c) showed three step decomposition pattern. The first two steps in the temperature range are due to the decomposition of the GA component in the inorganic and organic hybrid material, and the third step with onset of decomposition at 920℃ can be attributed mainly due to the decomposition of BaCO3 nanocrystallites. The evolution of CO2 gas in the first two steps (mass fragment 44 a.m.u) can be attributed due to the decomposition of GA component in the inorganic and organic hybrid BaCO3 nanocrystallites and the percentage of mass loss was found to be 6.2. The absence of the first two decomposition steps in the calcined (at 700℃) BaCO3 synthesized with gum acacia (Figure 8d) clearly suggests that the as synthesized BaCO3 nanocrystallites are having both inorganic and organic components. As can be seen from figure 8c, the as synthesized BaCO3 nanocrystallites using GA show the temperature of maximum decomposition at 1120℃, which is less compared to the others and this can be attributed to the size effect of nanoparticles.Based on the above analysis, a possible growth mechanism for the formation of flower like BaCO3 clusters at air/solution interface is schematically shown in figure 9 that follows a rod-dumbbell-flower(R-D-F) progression. The exact growth mechanism of the micro clusters is not fully understood. Initially, the various functional groups in GA inhibit the crystal growth by the encapsulation of Ba2+ ions which in the presence of sodium bicarbonate forms BaCO3 nanocrystallites that act as building units stacking in parallel sequence, resulting in the formation of micro clusters. These particles are formed homogeneously in the solution and the crystallization is based on these BaCO3 clusters that are made up of nanocrystallites and are built up from individual nanocrystals and are aligned in a common crystallographic pattern.
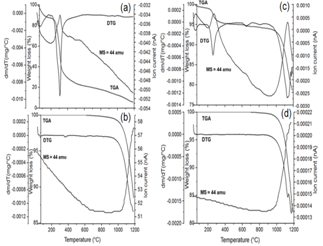 | Figure 8. TGA-DTG-MS thermograms (a) pure gum acacia, (b) BaCO3 synthesized without GA, (c) as synthesized BaCO3 using GA, and (d) as synthesized BaCO3 with GA calcined at 700℃ |
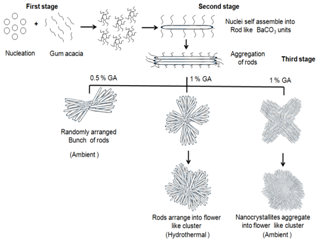 | Figure 9. Schematic mechanism of BaCO3 clusters at different reaction conditions |
4. Conclusions
- Using natural gums, a variety of crystal morphology could be produced when ambient and hydrothermal conditions were employed. In summary, we demonstrated that simple GA can be used as crystal growth modifier to template unusual complex morphologies of BaCO3 crystals. Micro clusters of barium carbonate are having different shapes such as bunch-like, dumbbell, double dumbbell and flowerlike arrangements, which are confirmed by SEM and TEM micrographs. The crystalline nature and spectral features of barium carbonate is confirmed by XRD and FT-IR spectra, respectively. TGA-MS study confirms that the as synthesized BaCO3 nanocrystallites using GA are having both inorganic and organic components resulting into the formation of inorganic-organic hybrid materials. The present results demonstrate that the crystallization methods using natural gums provide a new way to realize morphological control of biomineralisation for synthesizing different superstructures of minerals or inorganic-organic hybrid materials.
References
| [1] | D. B. Deoliveira, and R. A. Laursen., 1997, Control of calcite crystal morphology by a peptide designed to bind to a specific surface, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119(44), 10627-10631 |
| [2] | T. Kato, A. Sugawara, and N. Hosoda., 2002, Calcium carbonate–organic hybrid materials” Adv. Mater. 14(12), 869-877. |
| [3] | H. Colfen, and S. Mann., 2003, Higher-order organization by mesoscale self-assembly and transformation of hybrid nanostructures, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42(21), 2350-2365 |
| [4] | S. H. Yu, and H. Colfen., 2004, Bio-inspired crystal morphogenesis by hydrophilic polymers, J. Mater. Chem. 14(14), 2124-2147. |
| [5] | H. Colfen, and S. H. Yu., 2005, Biomimetic Mineralization/Synthesis of Mesoscale Order in Hybrid Inorganic–Organic Materials via Nanoparticle Self-Assembly, MRS Bull. 30(10), 727-735 |
| [6] | G. Falini, S. Albeck, and L. Addadi., 1996, Control of aragonite or calcite polymorphism by Mollusk shell macromolecules, Science. 271, 67-69 |
| [7] | D. D. Sawall, R. M. Villahermosa, R. A. Lipeles, and A. R. Hopkins., 2004, Interfacial polymerization of polyaniline nanofibers grafted to Au surfaces, Chem. Mater. 16(9), 1606-1608 |
| [8] | S.A. Morin, F.F. Amos, and S. Jin., 2007, Biomimetic assembly of zinc oxide nanorods onto flexible polymers, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(45), 13776-13777 |
| [9] | T. X. Wang, A. Reinecke, and H. Colfen., 2006, In situ investigation of complex BaSO4 fiber generation in the presence of sodium polyacrylate. 2. Crystallization mechanisms, Langmuir, 22(21), 8986-8994 |
| [10] | S. Tugulu, M. Harms, M. Fricke, D. Volkmer, H. and A. Klok., 2006, Polymer brushes as ionotropic matrices for the directed fabrication of microstructured calcite thin films, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45(45), 7458-7461 |
| [11] | S. Ludwigs, U. Steiner, A. N. Kulak, R. Lam, and F. C. Meldrum., 2006, Bioinspired polymer–inorganic hybrid materials, Adv. Mater. 18(17), 2270-2273 |
| [12] | M. P. Pileni, T. Gulik-Krzywicki, J. Tanori, A. Filankembo, and J. C. Dedieu., 1998, Template design of microreactors with colloidal assemblies: Control the growth of copper metal rods, Langmuir, 14(26), 7359-7363 |
| [13] | G. D. Rees, R. Evans-Gowing, S. J. Mammond, and B. H. Robinson., 1999, Formation and morphology of calcium sulfate nanoparticles and nanowires in water-in-oil microemulsions, Langmuir 15(6), 1993-2002 |
| [14] | A. L. Briseno, S. B. Mannsfeld, M. M. Ling, S. H. Liu, J. R. Tseng, C. Reese, M. E. Roberts, Y. Yang, F. Wudl, and Z. N. Bao., 2006, Patterning organic single-crystal transistor arrays, Nature, 444, 913-917 |
| [15] | Y. H. Li, V. P. Kotzeva, and D. J. Fray., 2006, Electrochemical performance of CdS nanomaterials synthesized by microemulsion techniques, Mater Lett. 60 (21-22), 2743-2746 |
| [16] | W. J. Liu, W. D. He, and Z. C. Zhang., 2006, Fabrication of CdS nanorods in inverse microemulsion using HEC as a template by a convenient γ-irradiation technique, J. Cryst. Growth 290 (2), 592-596 |
| [17] | J. E. Schaefar, H. Kisker, H. Kronmuller, and R. Wurschum. 1992, Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline nickel, Nanostruct. Mater. 1(6), 523-529 |
| [18] | S. Komarneni, M. C. D. Arrigo, C. Leionelli, G. C. Pellacani, and H. Kotuku., 1998, Microwave-hydrothermal Synthesis of nanophase ferrites, J Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 3041-3044 |
| [19] | P. P. Phule, and D. C. Grundy., 1994, Pathways for the low temperature synthesis of nano-sized crystalline barium zirconate, Mater Sci Eng B. 23(1), 29-35 |
| [20] | A. Chatterjee, D. Das, S. K. Pradhan, and D. Chakravorty., 1993, Synthesis of nanocrystalline nickel-zinc ferrite by the sol-gel method, J Magn. Magn. Mater. 127 (1-2), 214-218 |
| [21] | I. Sondi, and E. Matijevic., 2003, Homogeneous precipitation by enzyme-catalyzed reactions. 2. Strontium and barium carbonates, Chem. Mater. 15 (6), 1322-1326 |
| [22] | D. M. Sun, Q. S. Wu, and Y. P. Ding., 2006, A novel method for crystal control: synthesis and design of strontium carbonate with different morphologies by supported liquid membrane, J. Appl. Cryst. 39 (4), 544-549 |
| [23] | T. Wang, A.W. Xu, and H. Colfen., 2006, Formation of self-organized dynamic structure patterns of barium carbonate crystals in polymer-controlled crystallization, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45 (27), 4451-4455 |
| [24] | S. H. Yu, H. Colfen, and M. Antonietti., 2003, Polymer-controlled morphosynthesis and mineralization of metal carbonate superstructures, J. Phys. Chem. 107 (30), 7396-7405 |
| [25] | S. H. Yu, H. Colfen, A. W. Xu, and W. Dong., 2004, Complex spherical BaCO3 superstructures self-assembled by a facile mineralization process under control of simple polyelectrolytes, Cryst. Growth and Des. 4(1), 33-37 |
| [26] | L. Chen, Y. Shen, A. Xie, J. Zhu, Z. Wu, and L. Yang., 2007, Nanosized barium carbonate particles stabilized by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide at the water/hexamethylene interface, Cryst. Res. Technol. 42 (9), 886-889 |
| [27] | K. Konno, M. Koide, and A. Kitahara., 1984, Preparation of barium carbonate particles using a W/O microemulsion, J. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 6, 815-822 |
| [28] | K. Kandori, K. Kon-no, and A. Kitahara., 1988, Preparation of BaCO3 particles in ionic w/o microemulsions, J. Disp. Sci. Technol. 9(1), 61-73 |
| [29] | L. Qi, J. Ma, H. Cheng, and Z. Zhao., 1997, Reverse micelle based formation of BaCO3 nanowires, J. Phys. Chem. B. 101(18), 3460-3463 |
| [30] | M. Dinamani, P. V. Kamath, and R. Seshadri., 2003, Electrodeposition of BaCO3 coatings on stainless steel substrates, Cryst. Growth Des. 3 (3), 417-423 |
| [31] | P. Balaz, and B. Plesingerova., 2000, Thermal propertie of mechanochemically pre-treated precursors of BaTiO3 synthesis, Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 59 (3) 1017-1021 |
| [32] | B. F. Allen, N. M. Faulk, S. C. Lin, R. Semiat, D. Luss, and J. T. Richardson., 1992, A continous coprecipitation process for the production of 1-2-3 precursors, AIChE Symp. Ser. 88, 76-87 |
| [33] | J. J. Macketta., 1977, Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design, Marcel Dekker, New York, 51 |
| [34] | A. Taubert, G. Glasser, and D. Palms., 2002, Kinetics and particle formation mechanism of zinc oxide particles in polymer-controlled precipitation from aqueous solution, Langmuir 18(110), 4488-4494 |
| [35] | J. Norwig, W. H. Meyer, and G. Wegner., 1998, Control of ZnO crystallization by a PEO-b-PMAA diblock copolymer, Chem. Mater. 10(2), 460-463 |
| [36] | D. K. Devi, S. V. Pratap, R. Haritha, K. S. Sivudu, P. Radhika, and B. Sreedhar., 2011, Gum acacia as a facile deducing, stabilizing, and templating agent for palladium nanoparticles, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 121(3), 1765-1773 |
| [37] | B. Sreedhar, P. S. Reddy, and D. K. Devi., 2009, Direct one-pot reductive amination of aldehydes with nitroarenes in a domino fashion: catalysis by gum-acacia-stabilized palladium nanoparticles, J. Org. Chem. 74(22), 8806-8809 |
| [38] | H. Colfen, and M. Antonietti., 1998, Crystal design of calcium carbonate microparticles using double-hydrophilic block copolymers, Langmuir 14(3), 582-589 |
| [39] | N. A. J. M. Sommerdijk, and G. de. With, 2008, Biomimetic CaCO3 mineralization using designer molecules and interfaces, Chem. Rev. 108(11), 4499-4550 |
| [40] | H. Colfen., 2001, Double-hydrophilic block copolymers: Synthesis and application as novel surfactants and crystal growth modifiers, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 22(4), 219-252 |
| [41] | L. M. Qi, H. Colfen, M. Antonietti, M. Li, J. D. Hopwood, A. J. Ashley, and S. Mann., 2001, Formation of BaSO4 fibres with morphological complexity in aqueous polymer solutions, Chem. Eur. J. 7(16), 3526-3532 |
| [42] | L. M. Qi, H. Colfen, and M. Antonietti., 2000, Crystal design of barium sulfate using double-hydrophilic block copolymers, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39(3), 604-607 |
| [43] | A. M. Belcher, X. H. Wu, R. J. Christensen, P. K. Hansma, G. D. Stuky, and D. E. Morse., 1996, Control of crystal phase switching and orientation by soluble mollusc-shell proteins, Nature 381, 56-58 |
| [44] | S. Mann, B. R. Heywood, S. Rajam, and J. D. Birchall., 1988, Controlled crystallization of CaCO3 under stearic acid monolayers, Nature 334, 692-694 |
| [45] | H. Colfen, and L. Qi., 2002, The mechanism of the morphogenesis of CaCO3 in the presence of poly(ethylene glycol)- b -poly(methacrylic acid), Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 117, 200-203 |
| [46] | R. Kniep, and S. Busch., 1996, Biomimetic growth and self-assembly of fluorapatite aggregates by diffusion into denatured collagen matrices, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 35(22), 2624-2626 |
| [47] | S. Busch, H. Dolhaine, A. DuChesne, S. Heinz, O. Hochrein, F. Laeri, O. Podebrad, U. Vietze, T. Weiland, and R. Kniep., 1999, Biomimetic morphogenesis of fluorapatite-gelatin composites: Fractal growth, the question of intrinsic electric fields, core/shell assemblies, hollow spheres and reorganization of denatured collagen., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1999(10), 1643-1653 |
| [48] | S. Sindhu, S. Jegadesan, R. A. Edward Leong, and S. Valiyaveettil., 2006, Morphosynthesis of mixed metal carbonates using micellar aggregation., Crystal Growth & Design. 6(6), 1537-1541 |
| [49] | N. H. De Leeuw,, 2002, Molecular dynamics simulations of the growth inhibiting effect of Fe 2+ , Mg 2+ , Cd 2+ and Sr 2+ on calcite crystal growth., J. Phys. Chem. B. 106(20), 5241-5249 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML