-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
p-ISSN: 2168-457X e-ISSN: 2168-4588
2018; 6(1): 1-8
doi:10.5923/j.m2economics.20180601.01

Household Catastrophic Health Expenditure: Evidence from Nigeria
Ibukun Cleopatra, Komolafe Eunice
Obafemi Awolowo University, Department of Economics, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Ibukun Cleopatra, Obafemi Awolowo University, Department of Economics, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study examined the incidence and intensity of catastrophic health expenditure; and, its determinants among Nigerian households. Secondary data was drawn from the Nigeria - General Household Survey conducted between 2015 and 2016. The detailed information provided in the survey was used to classify households as not having or having catastrophic health expenditure using the methodology proposed by the World Health Organization in 2005. Descriptive statistics and logistic regression was applied across various thresholds. The results showed that the incidence and intensity of catastrophic health expenditure is high especially among households in the poorest quantile, households located in rural areas, female headed households, households with uneducated household heads, households with unemployed heads, and those without health insurance; but, it is lowest among households located in South West Nigeria. In addition, the risk of incurring catastrophic health expenditure reduced among households in the richest quantile, households headed by an employed person, households located in urban areas, households with no hospitalized member and households who utilized private hospitals. It is therefore important to establish financial and social intervention mechanisms that can protect households from incurring catastrophic health expenditure.
Keywords: Catastrophic Health Expenditure, Out-of-Pocket Payments, Nigerian-General Household Survey, Non-food Expenditure, Nigeria
Cite this paper: Ibukun Cleopatra, Komolafe Eunice, Household Catastrophic Health Expenditure: Evidence from Nigeria, Microeconomics and Macroeconomics, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.5923/j.m2economics.20180601.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The burden of health care costs and the economic effect on households depend on the country’s health care system and the ability of individual households to pay (Wyszewianski, 1986). Globally, an average of about 32% of each country’s health expenditure comes from out-of-pocket payments, while 100 million people are pushed into poverty every year. Also, 150 million people suffer financial catastrophe because of out-of-pocket expenditure on health services (World Health Organisation, (WHO), 2016). Healthcare spending is considered catastrophic, if the out-of-pocket healthcare expenses incurred are large relative to the resources available to the household and this disrupts the material living standard of the household. Therefore, in developing countries like Nigeria where prepayment mechanisms such as taxing and health insurance do not play a major role in health financing, households face a risk of incurring large health care expenditures when members fall ill.Healthcare financing is the branch of finance that helps patients and healthcare beneficiaries pay for healthcare. It is the process by which funds are mobilized, allocated and utilized to purchase goods and services from private and public healthcare providers for the specific needs of the population (Hsaio and Liu, 2001). Like many other developing countries, healthcare in Nigeria is broadly financed through private expenditure, public expenditure and external aid. Private expenditure includes private insurance, donations, direct service payments by private corporations and out-of-pocket (OOP) payments while public expenditure includes funds spent by the government, external borrowing and grants which are paid for by taxes, donations or compulsory (social) health insurance funds. External aid can be sourced through non-governmental organizations and bilateral aid programme. Consequently, the methods used to finance healthcare influence the types of healthcare provided, access and allocation of services; which is a critical determinant for reaching universal health coverage (UHC).Despite this health financing options, achieving a successful health care financing system in Nigeria continues to be a challenge. Based on the 2010 World Health Report, a country’s public health spending of about 6% of GDP will limit OOP payments and make the incidence of catastrophic health expenditure (CHE) negligible. Contrarily, Nigeria’s total health expenditure (THE) as a percentage of the gross domestic product (GDP) was 3.7% in 2014 and it has fluctuated between 2.8% in 1995 (the lowest) and 4.5% in 2007 (the highest) over the years, which is well below many developing countries. Public health expenditure (PHE) as a percentage of GDP, accounted for 0.7% in 1996, reached a maximum value of 1.5% in 2007/2008 but also decreased steadily over the years to 0.9% in 2014. However, private health expenditure as accounted for at least 68% since 2009 and reached 74.9% of total health expenditure in 2014; the bulk of which comes from out-of pocket expenditure which has been over 95% of PHE since 2004 (World Bank, 2017). Ultimately, whether through OOP payments, taxation or health insurance, Nigeria’s healthcare financing system stems mostly from the households (Uzochukwu et al. 2015).A fundamental function of a healthcare system is to provide affordable health services to the entire population while protecting them against the financial risks associated with ill health (WHO, 2000). This reduces the possibility that an individual will be unable to pay for healthcare or face financial catastrophe as a result of minor healthcare costs. Consequently, the hypotheses under study are that Nigerians who are uninsured and those with low-income do not have the economic capacity to pay for unexpected healthcare costs. In the same vein, certain characteristics of household heads, households living in rural regions, households with at least one hospitalised member, households with at least one elderly member and households without treated bed-nets are more likely to incur catastrophic healthcare expenses. To confirm or reject these hypotheses, data from the Nigeria - General Household Survey (GHS) 2015/2016 was analysed. As studies related to the incidence, intensity and determinants of catastrophic health expenditures in Nigeria are few, this research will shed light on the features that can make households in Nigeria more vulnerable to catastrophic health expenses, in order to confirm or reject the hypotheses under study.
2. Brief Review of Literature
- The concept of catastrophic health expenditure can be traced to the study of Berki (1986), who explained the catastrophic financial implications of a disease as one which has high productivity loss (also known as indirect costs by economists); and results into premature mortality and high morbidity for the working population. Wyszewianski (1986) described catastrophic health expenditure as a situation in which the household’s expenditure is large relative to ability to pay (for instance, when out-of-pocket health expenditure exceeds 15% of annual household income). In another study, Russell (1996) explained catastrophic health expenditure by focusing on its opportunity cost (such as food and education) and the consequences on households and individuals within it. This implies that household living standards and consumption of other goods and services will be affected by a large health expenditure.Several studies (Gotsadze, Zoidze and Rukhadze, 2009; Kim and Yang, 2011; Li et al. 2012) have used different thresholds in examining catastrophic health expenditure in different countries. While some other studies (Wagstaff and Doorslaer, 2003; Yardim, Cilingirogiu and Yardim 2010; Arsenijevic, Pavlova, and Groot 2012; Minch et al., 2013) included in their study the impoverishment effect of health expenditure on the household in developed and developing counties. Amongst these is Xu et al. (2003) who carried out an international survey on 59 countries. Their study considered health expenditure as catastrophic if a household’s financial contribution to health exceed 40% of the income remaining after subsistence needs have been met. They discovered that an improvement in financial risk protection (such as health insurance) and less reliance on OOP can protect households, particularly poor ones from CHE. In addition, studies such as Su, Kouyaté and Flessac (2006); Chuma and Maina (2012); David, Kimani and Kinyanjui (2017) who examined catastrophic health expenditure in Africa buttressed that each year, most households spend over a tenth of their budget on healthcare payments; while, the poorest households spend a third of their resources on healthcare payments each year. Most of the studies mentioned above revealed a set of possible factors that may influence the probability of a household incurring/experiencing CHE and impoverishment problems due to OOP health expenses. Among such factors are the type of healthcare facility visited, health insurance, households with more elderly people, socio-demographic conditions, economic situation of the household and some characteristics of the household head. In addition, Buigut, Ettarh, and Amendah (2015) discovered that the proportion of households facing catastrophic health expenditure and its level of influence depends on the method of estimation, the level of development of the country under investigation and the threshold used.Furthermore, some Nigerian studies related to CHE were carried out using primary data collected at state levels (Onoka et al., 2011; Ukwaja et al., 2013; Ilesanmi, Adebiyi and Fatiregun 2014) but they concentrated on the southern part of Nigeria and the catastrophic impact of healthcare payment on a particular disease such as tuberculosis. Their findings indicated high levels of CHE in Southeast Nigeria and households in the lowest wealth quintiles were at a higher risk of CHE. Other studies carried out using a nationally representative household survey (Adisa, 2015; Omotosho and Ichoku, 2016; Aregbesola and Khan, 2017) focused on elderly households, financial protection and universal health coverage in Nigeria. These studies discovered that irrespective of the threshold used, poorer households and those with at least one elderly member were most at risk. Also, many households experience catastrophic health payments due to factors such as the type of health event that required for health service payments, the economic situation of the households, characteristics of the head of household, socio-demographic conditions, and their health insurance status.In summary, most studies on catastrophic health expenditure have employed the same threshold levels for both rich and poor households using food expenditures and income in measuring the incidence of CHE. However, the capacity to pay should allow for the consumption of various necessities and not just food. Therefore, this paper assesses the incidence and intensity of catastrophic healthcare spending and its determinants in Nigeria, particularly utilizing the methodology proposed by WHO in 2005 and a more recent nationally representative household survey.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data
- This study used the information obtained from the Nigeria-General Household Survey Panel (GHS) 2015-2016. This survey is representative of the 37 states in Nigeria and it is the third wave of a panel survey of households fielded by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) in partnership with the Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (FMA&RD), the National Food Reserve Agency (NFRA), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), and the World Bank (WB). A multi-stage stratified sample design was used to obtain information from 5,000 households; however, some households had moved from their location during this survey resulting in a smaller sample of 4,581 households. This survey contains information on demographics, education, labour, food and non-food expenditure, household nonfarm income-generating activities, food security and shocks, safety nets, housing conditions, assets, information and communication technology, and other sources of household income. The data was administered to all households in the sample in two visits: post-planting (September - November 2015) and post-harvest (February - April 2016).
3.2. Definition of Key Variables
- The dependent variable in this study is a dummy variable on catastrophic health expenditure. This is defined as a certain percentage of healthcare costs that endangers the household’s ability to maintain its customary standard of living (Berki, 1986). In this paper, catastrophic health expenditure is expressed as a certain percentage of monthly per-capita OOP expenditure to monthly non-food consumption expenditure of a household. Since there is no standard threshold level to define catastrophic health expenditure, alternative catastrophic thresholds are considered in this paper to demonstrate sensitivity to different measures.Out of pocket payments: These refers to the direct payments made by households to healthcare providers at the point of receiving healthcare services and it includes cash payments reported in the survey. Spending on alternative or traditional medicine is incorporated while prepayments for healthcare services in form of taxes, insurance premiums or reimbursements are excluded.Household capacity to pay: This is defined at household level as effective income remaining after spending on basic subsistence needs and it is a measure of the non-subsistence effective income of the household (Xu et al., 2003). Since household’s consumption or expenditure is used as a proxy for effective income in order to reduce short-term fluctuations in income data, this study uses the non-food expenditure as a proxy for household’s capacity to pay based on WHO Word Health Report, 2000.The independent variables include socioeconomic indicators of household heads such as education level of household head which was recategorized into no education, primary education, secondary education, and post-secondary education; employment status of household head categorized as employed and unemployed; age of household head; sex of household head which was categorized into male and female according to the survey. Other independent variables include household size which was recoded as less than five members and more than five members; area of residence (urban/rural) and geo-political zone (north central, north east, north west, south east, south west, and south south); if a member in the household uses a treated bed-net or not; health insurance which was categorized as insured/uninsured; number of elderly people in the household; type of healthcare facility visited (recoded as public or private); and the household’s socio-economic status (recategorized into quantile groups based on the list of household assets owned).
3.3. Data Analysis
- This study employed univariate analysis (percentage) in determining the incidence and intensity of CHE in Nigeria. To examine the determinants of catastrophic health expenditure, the study employed logistic regression of the form:
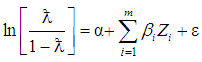 | (1) |
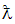 probability for a household with catastrophic expenditure and Zero (CHE=0) with probability
probability for a household with catastrophic expenditure and Zero (CHE=0) with probability 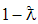 for households without catastrophic expenditure. Z is a vector of the independent variables, while
for households without catastrophic expenditure. Z is a vector of the independent variables, while 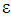 represents the error term. The data was analysed using Stata statistical software version 14.
represents the error term. The data was analysed using Stata statistical software version 14. 4. Results
- Descriptive statistics of explanatory factors for CHE and logit model (adjusted and unadjusted) were used to identify the probability of incurring CHE in Nigeria.
4.1. Incidence and Intensity of Catastrophic Health Expenditure
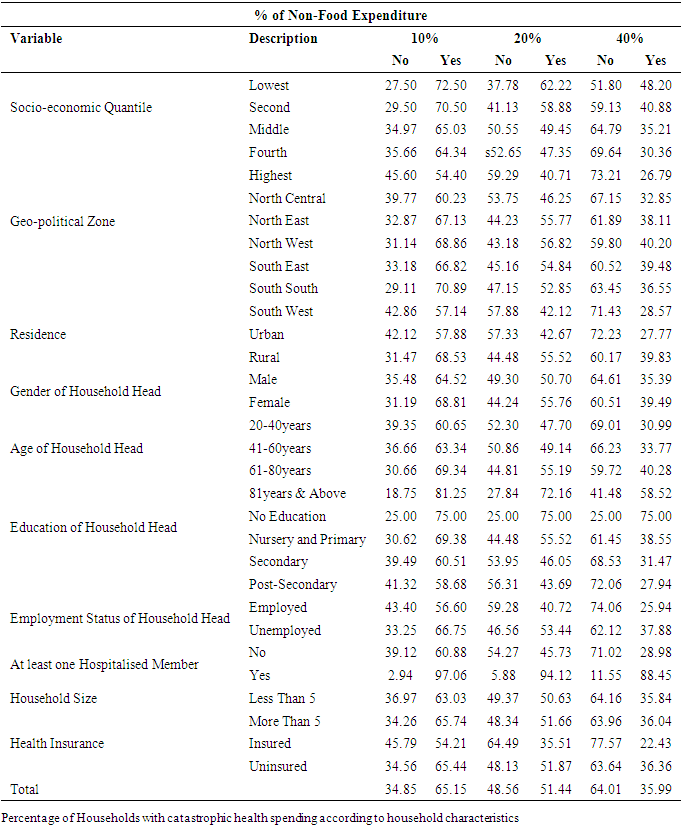
- The analysis of possible explanatory factors for CHE in Table 1 shows the population from which the percentage of households with CHE is calculated. The result shows that 72.5%, 62.2% and 48.2% of Nigerian households in the lowest quantile incurred CHE at 10%, 20% and 40% threshold respectively; while 65%, 49.5% and 35.2% of the households in the middle quantile incurred CHE at these different thresholds. At the 40% threshold, about 27% of households in the richest quantile experienced CHE and the highest incidence of CHE was amongst the poorest household. Table 1 also shows an inverse association between CHE and the age of household head. About 59% of households headed by an individual who is 81 years and above incurred CHE using a threshold of 40% of non-food expenditure and this increased to 81% if the threshold was set at 10%. Households headed by unemployed individuals also indicated a higher incidence of CHE at the three levels. Irrespective of the threshold used, 75% of households headed by individuals with no education incurred CHE, while about 59%, 44% and 28% incurred CHE at 10%, 20% and 40% of non-food expenditure respectively. At levels of 10%, 20% and 40% of non-food expenditure, the level of CHR was higher for households in rural communities at 68.5%, 55.5% and 39.8% respectively. At these levels the households in South West Nigeria had the lowest proportion of CHE while a higher percentage of female headed households faced CHE.Households with at least one hosiptalised member during the reference period and households with more than five members incurred more CHE at the three threshold levels. The availability of health insurance also played a significant role in reducing the intensity of CHE in Nigeria, as seen in Table 1. To buttress this, Figure 1 shows that at the 40% threshold level, the incidence of CHE among insured households was lowest in the South West and highest in the North Central zone of Nigeria, while the highest incidence of CHE among the uninsured households was highest in the Northwestern zone of the country. In total 65.2%, 51.4% and 36% of households studied experienced catastrophe when the threshold level was set at 10%, 20% and 40% of non-food expenditure.
|
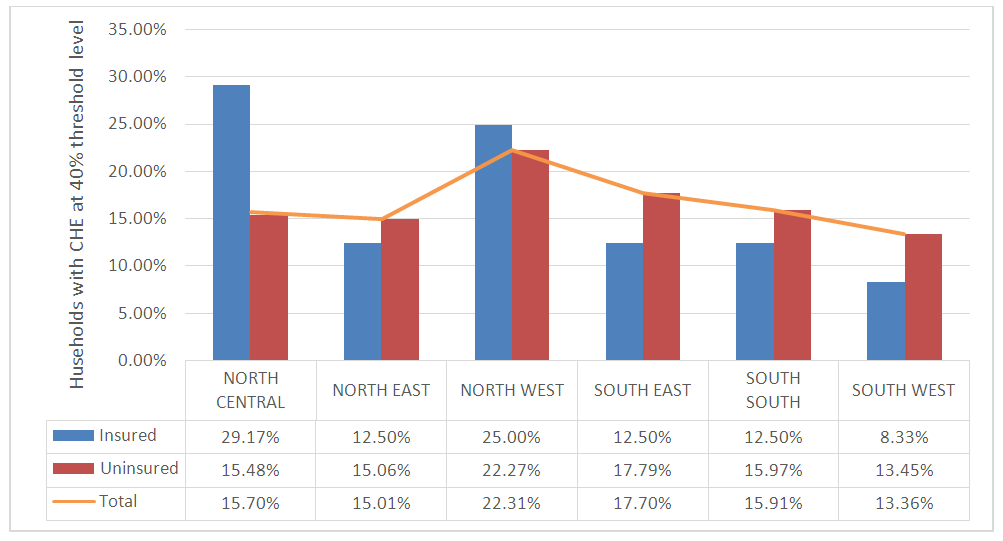 | Figure 1. Percentage of Households with CHE, According to the Geo-Political Zone and Health Insurance Status |
4.2. Determinants of Catastrophic Health Expenditure
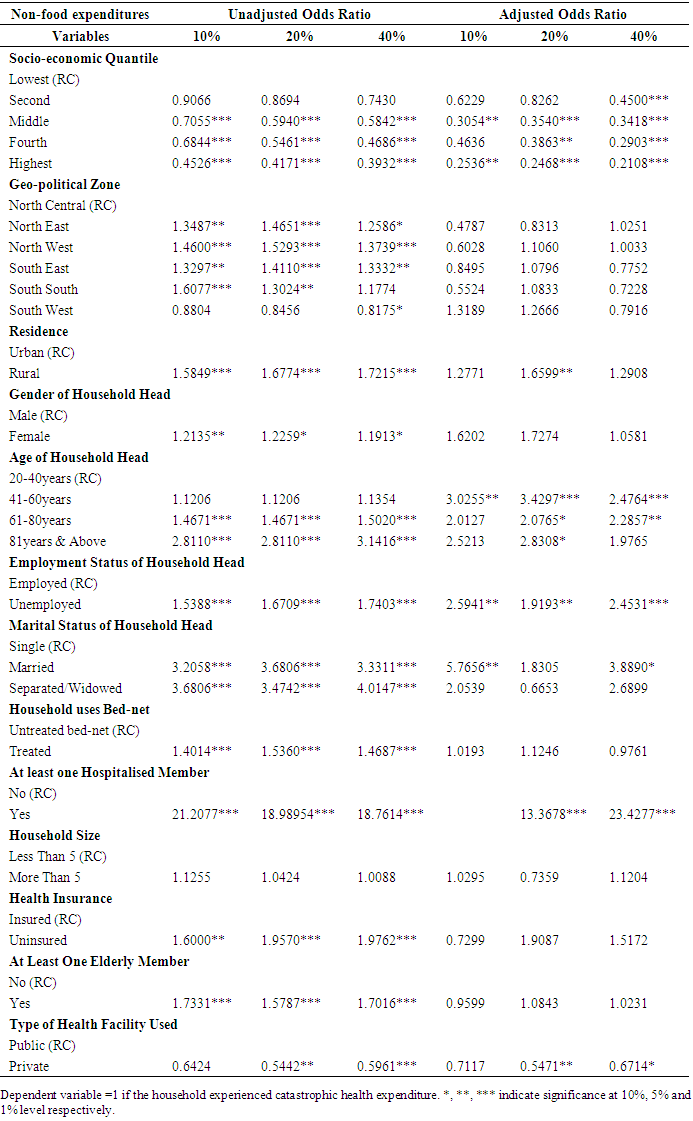
- The logistic regression on Table 2 yields a wide range of determinants associated with the occurrence of CHE and its magnitude. Irrespective of the threshold used, all household factors apart from the household size were found to be statistically significant when the model was unadjusted. The determinants of CHE using the adjusted model revealed a statistically significant relationship between CHE and variables such as the economic status of the household, age of household head and employment status of household head. The association between CHE and household’s area of residence was statistically significant at 20% but not significant at 10% and 40% thresholds of non-food expenditure. Furthermore, variables such as households with at least one hospitalized member and the type of healthcare facility were found to have a statistically significant association with CHE at 20% and 40% threshold of non-food expenditure.At the 10% threshold, Table 2 shows that the economic status of the household has a statistically significant but negative association with the occurrence of CHE. That is, compared with households in the first quantile (poorest households), the odds that households in the second quantile (poorer households) will incur CHE decreases by 38%. The odds for households in the third, fourth and fifth quantile incurring CHE decreased by 69%, 53% and 75% respectively. Hence, the wealthier the household, the lower the odds of incurring CHE. Compared with households headed by an employed individual, a household headed by an unemployed individual increases the odds of CHE by 203%. Furthermore, age and marital status of the household head showed a positively significant association with CHE. After adjusting for other variables in the model, the results at the 20% threshold indicted that as households move from the lowest (poorest) to the highest (richest) quantile, the odds of CHE decrease by 18%, 65%, 61%, 75% respectively. The odds of incurring CHE was more than 3 times as high among households headed by individuals aged between 41 and 60 years and it reflects a statistically significant association between the age of household head and CHE. Compared with households residing in urban areas, residing in a rural area increases the odds of incurring CHE by 66%, while an unemployed household head also increases the odds of incurring CHE. The odds of incurring CHE was more than 13 times as high between households with at least one hospitalised member and households with no hosiptalised member; and it decreases by 45% when an household uses a private healthcare facility.Furthermore, the results of the logistic regression at the 40% threshold confirmed the statistically significant effects of household’s economic status on CHE, using households which are in the lowest quantile as the reference category. Table 2 also shows that the odds of incurring CHE increased by 148%, 129% and 198% among household headed by an individual whose age is between 41-60 years, 61-80 years and, 81 years and above. The odds of incurring CHE also increased by 145% among households headed by an unemployed person. In the same vein, the odds of incurring CHE was more than 23 times as high among households with at least one hospitalized member than households with no hospitalized member. Interestingly, the odds of incurring CHE decreased by 13% among households who utilized a private health facility as compared to those who used a public health facility.
|
4.3. Discussion
- The results presented throughout this paper indicates that the incidence, intensity and the determinants of CHE is sensitive to the threshold used. Across the three threshold levels used, the incidence of CHE was very high among the poorest quantile but reduces as the socio-economic status improves. This paper also shows that the lowest incidence of CHE in households is found in Southwestern Nigeria and households residing in urban areas. This high level is expected because there is no mechanism to protect the poor against healthcare cost even when there is a 68% prevalence of poverty in rural communities as compared with 50% in urban communities. Also, over 80 million of the population live below the poverty line, while prevalence ranges from approximately 47% in the South West to over 70% in North West and North-East Nigeria (NBS, 2015). Sadly, the Nigerian Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) which is a form of risk protection covers only about 10% of the Nigerian population, which buttresses the high incidence of CHE among uninsured households in Nigeria. This is consistent with the findings of Onoka et al. (2011).With respect to the determinants of CHE, it was observed in both models that an improvement in the socio-economic status of households from the poorest to the richest quantile decreases the odds of incurring CHE, since both the poor and the rich pay huge amounts for healthcare in the absence of health insurance. This is supported by the study of (Adisa, 2015) who discovered that richer households are less likely to incur CHE when compared to poorer households in Nigeria. At the 40% threshold of non-food expenditure, area of residence and the geopolitical zone of the household did not show any significant association with CHE after adjusting for other variables, which contradicts the findings of Omotosho and Ichoku (2016) and, Aregbesola and Khan (2017). Gender of the household head was also not a significant determinant of CHE which is similar to the findings of Su et al. (2006) and, Aregebsola and Khan (2017) but inconsistent with the findings of Adisa (2015) and Ukwaja et al. (2013) who revealed that men are the major income earners in the household. This study also revealed that households headed by an individual who is above 40 years of age are at a higher risk of CHE than those headed by individuals below 40 years old. Hence the age of the household head is strongly associated with CHE. This may be because human’s health deteriorates with age. Also, the employment status of the household head is a determining factor of CHE occurrence because employed individuals are expected to be in a better position financially and be able to finance healthcare costs better than the unemployed. Households with at least one hospitalised member at the period of survey significantly influenced the occurrence of CHE at all levels, but using a private healthcare facility reduces the odds of CHE. This is unexpected and contrary to the findings of Aregbesola and Khan (2017) because private healthcare facilities in Nigeria are more costly than public health facilities. However, this may be because public healthcare facilities (especially tertiary facilities) provide specialized treatments which most private hospitals in Nigeria do not provide, hence households patronize and pay more at public healthcare facilities than private facilities. In addition, variables such as the use of bed-nets, household size, households with at least one elderly member and health insurance did not significantly determine CHE after adjusting for other variables.This study has some limitations related to the data, because it is based on the remembrance of expenses in different time periods (weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly) which was taken to a monthly unit for analysis. Despite these limitations, the study provides some useful insights into the catastrophic effects of health expenditure in Nigeria while examining its incidence, intensity and determinants. In addition, this study uses variable thresholds for robustness check.
5. Conclusions
- This study indicates the existence of a high incidence and intensity of CHE in Nigeria. Although this varies according to the threshold used and it reduces as the threshold increases, the large proportion of CHE is expected due to the high rate of poverty in the country. The analysis of the determinants of CHE indicates that having a better socio-economic status, residing in an urban area, age of the household head, an employed household head and having no hospitalised member reduces the risk of incurring CHE; however, seeking healthcare services from public hospitals still proves catastrophic. It is therefore necessary for the government to establish intervention mechanisms in order to ensure that healthcare services are both accessible and affordable; thereby protecting the Nigerian population against the financial risk and reduce the incidence of CHE. The study also discovered that the incidence and intensity of CHE reduces among those covered by health insurance. This suggests that the existing national health insurance scheme should be extended to more Nigerians especially the poor, in order to reduce the financial burden of healthcare on households.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML