-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
p-ISSN: 2168-457X e-ISSN: 2168-4588
2015; 3(2): 35-45
doi:10.5923/j.m2economics.20150302.03
Taxes Performance Analysis as a Source of Local Revenue in the City of Pekanbaru
Syapsan1, Munawar2, Multifiah2, David Kaluge2
1Doctoral Program of Economics Science, Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
2Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was conducted to analyze the influence of taxation services, awareness and extortion taxpayers on tax compliance. In addition, to analyze the influence of tax compliance on the performance of the hotel tax in the city of Pekanbaru. The unit of analysis in this study, hotel and lodgement which has more than 10 rooms. Total samples 102 respondents with hotel owners and lodgement owners. The analysis tool used is Structural Equation Modeling (SEM).Results of this study explained that the hotel tax compliance behavior is influenced by variables of service tax, hotel tax payer awareness and extortion. Formatting dominant indicator in service variable is organizational culture. Indicators dominant form of consciousness is characteristic variables and indicators taxpayer dominant form of bribery is variable transaction costs of the dominant form while the indicator variable tax compliance is the timeliness of paying taxes. Results of this study support the theory of Gunadi and strengthen the Theory of Planned Behaviour through illegal levies due to the shadow norms.
Keywords: Tax Services, Awareness taxpayer, Illegal Payments, Taxpayer Compliance and Performance Hotel Tax
Cite this paper: Syapsan, Munawar, Multifiah, David Kaluge, Taxes Performance Analysis as a Source of Local Revenue in the City of Pekanbaru, Microeconomics and Macroeconomics, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2015, pp. 35-45. doi: 10.5923/j.m2economics.20150302.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
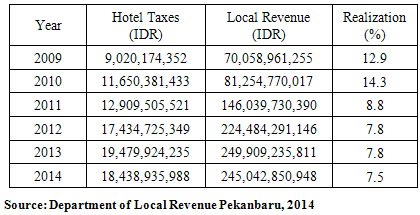
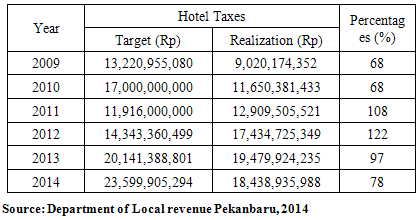
- Decentralization is an instrument of achieving the purpose of the state within the framework of democratic national unity. Therefore, attention to the balance between the need for the decentralization with the need to strengthen national unity is a must to be considered. HAW (2005) argues that there are two main objectives to be achieved in the decentralization policy that the political and administrative objectives.The implication is for the district and the city, to not only focus on the financial balance, but rather the excavation and develop the economic potential of the region so that the source of funds for the development of local Revenue derived from the area can be further optimized and be a contributor to regional development funds in the future. Then, based on Law No. 33 of 2004 which explains the Financial Balance Between Central Government and Local Government Finance, Local Revenue (PAD) have resources in the form of tax revenue, retribution and advantages of the Regional Owned Enterprises (BUMD) and other revenue areas that are considered legitimate by the regulations.Soemarsono (2007) formulated a theory that explains the devotion that the state has the right to tax. The theory states that every person can not stand alone so that they formed an alliance (organization) which later became the basis for the establishment of a state. Guild or organization has the right to the members and one of those rights is the collection of taxes. According to this theory, the tax is the embodiment of devotion marks the citizens of the state. The rationale of the tax according to this theory is the concept of the relationship between the people and the country in which the formation of the country is the will of the people. The settings in the alliance has the rights and obligations of each party where one of the state's right to collect taxes is a close relation in fulfilling the needs of their own people so that it is known that in the fulfillment of required financing needs of the people and in this case borne by the people in the form of taxes.Pekanbaru city, as an area which has been implementing autonomy, has some obstacles in the implementation of regional autonomy that is the low portion of the PAD and the magnitude of the budget's dependence (APBD) on donations and Assistance Section and Tax Revenue/Non-Tax. This barrier will directly affect the future implementation of regional autonomy. Tambunan (2001) argues that the constellation of central and local financial relations prevailing since the new order until the enactment of the Regional Autonomy (OD) in January 2001 which then led to the role of Local Revenue (PAD) in the local budget be relatively small. This makes the government very dependent on the central government.It also Pekanbaru City is strategically located geographically located on the border of the neighboring countries (Malaysia and Singapore) causes Pekanbaru a trading town and has a special attraction for the various groups. Pekanbaru city to be able to realize it can not be separated from the role of human resources owned by the city. Population into human resources that were most responsible, because the population is an asset for the city that gives color and expectations as well as a threat if not managed properly. Pekanbaru City residents from year to year continues to increase. Based on data from Central Bureau of Statistics (BPS) Pekanbaru total population of 964,558 inhabitants in 2012 and in 2013 as many as 999,031 people, have added as many as 34,473 people (3.57%), this means higher when compared with the national population growth rate that is 1.17% per year.PAD is relatively small as illustrated in Table 1 to the total local revenue for local causes in the race to achieve improved PAD conducted intensification and extension. The presumption that the PAD become a regional benchmark for the cause of independence of the above. Many occurred avoidance of tax payment obligation (tax evasion/avoidance), weakness in calculating the tax potential, as well as rigidity in the determination of tax rates allow the opportunity of doing tax intensification is still very large.Table 1 it can be seen that there are fluctuations in tax revenue which the hotel reception in 2014 was lower than the previous year. Then when viewed potential of the city of Pekanbaru hotel is large enough it can be seen from the number of the hotel with several classification and number of rooms. It also contributed to a hotel tax revenue reached 7.5% Pekanbaru City in 2014, for more details can be seen in the following table:
|
|
2. Research Methods
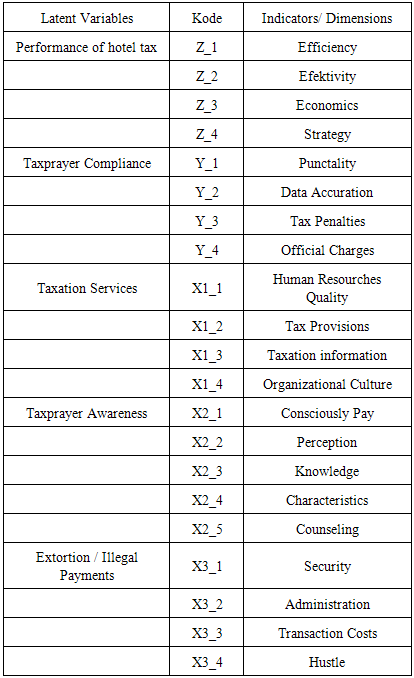
- This research was conducted in Pekanbaru City Riau Province. Pekanbaru City chosen as a test site for the reason that as the capital city of Pekanbaru in Riau Province which is expected to be an example for the districts and cities in the province of Riau. The study used taxpayer in Pekanbaru as a population, a total of 172 taxpayers who are scattered in several groups of 1-5 star hotels, budget hotels and Lodgement/boardinghouse. Probability sampling method with the number 100 as a condition of SEM but for reasons of strata representativeness of the sample into the sample 102. With the sampling technique stratified random sampling technique to follow the terms SEM analysis of samples in which samples 100-200 (Sugiyono, 2014). This study uses a quantitative research methods. The variables in this study were taxation services, awareness of the taxpayer, extortion and variables between (intervening) is the endogenous variable is compliance and tax performance. Measurement of these variables using a Likert scale, ie a score of 1 to 5. Score 1 means' strongly disagree 'or 0% (for intensity) or' very unsure '(confidence level), a score of 2 means' disagree' or ' not sure ', a score of 3 means' doubtful', a score of 4 means' agree 'or' unsure ', a score of 5 means' strongly agree' or 'very confident'.Hair (1998) in Sugiono (2013) explains that the Structural Equation Modeling commonly abbreviated as SEM has several designations, such as structural analysis of covariance (Covariance Structure Analysis), analysis of latent variables. SEM can be drawn into an analysis of merging approach factor analysis and structural models as well as path analysis. So that SEM can do three kinds of activities simultaneously, namely checking the validity and reliability of the instrument (confirmatory factor analysis), model testing relationships between variables (path analysis) and a suitable model for prediction (analysis of the structural model). (Sugiyono, 2013). Path analysis techniques used in the analysis of relationships and influence in this study. In analyzing the pattern of relationships between variables used path analysis with a direct or indirect influence of the independent variables (exogenous) on the dependent variable (endogenous) can be known.The use of path analysis techniques to be applied in testing the magnitude of the contribution shown by the path coefficient in each diagram the path of causal influence on the variables X1, X2, X3, to Y and Y to Z, correlation and regression analysis which is the basis for the calculation of structure equation model (SEM) then in its calculations using AMOS 21 software. Furthermore latent variables, codes and indicators/dimensions are presented in Table 3 as follows.
|
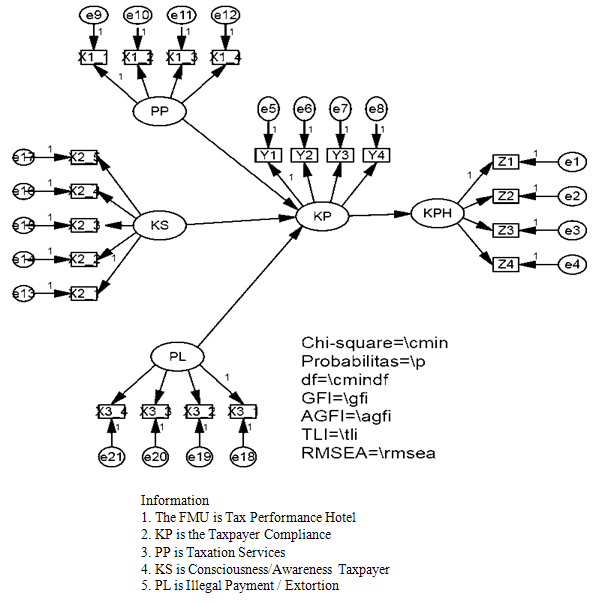 | Figure 1. |
 | Figure 2. Research Location Map |
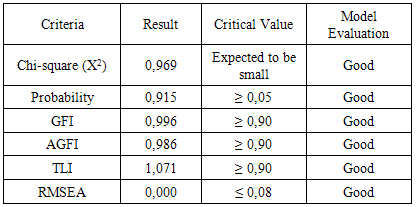
3. Empirical Result
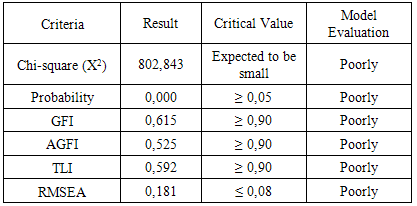
- Construction in this study begins with determining the value of the model, variable model testing. Exogenous variables in this study were taxation services, awareness, extortion and taxpayer compliance. While endogenous variable is the performance of the hotel tax. The model said to be good if the theoretical model development hypothesis is supported by empirical data. Results of SEM analysis at this stage is complete can be seen in Figure 3.
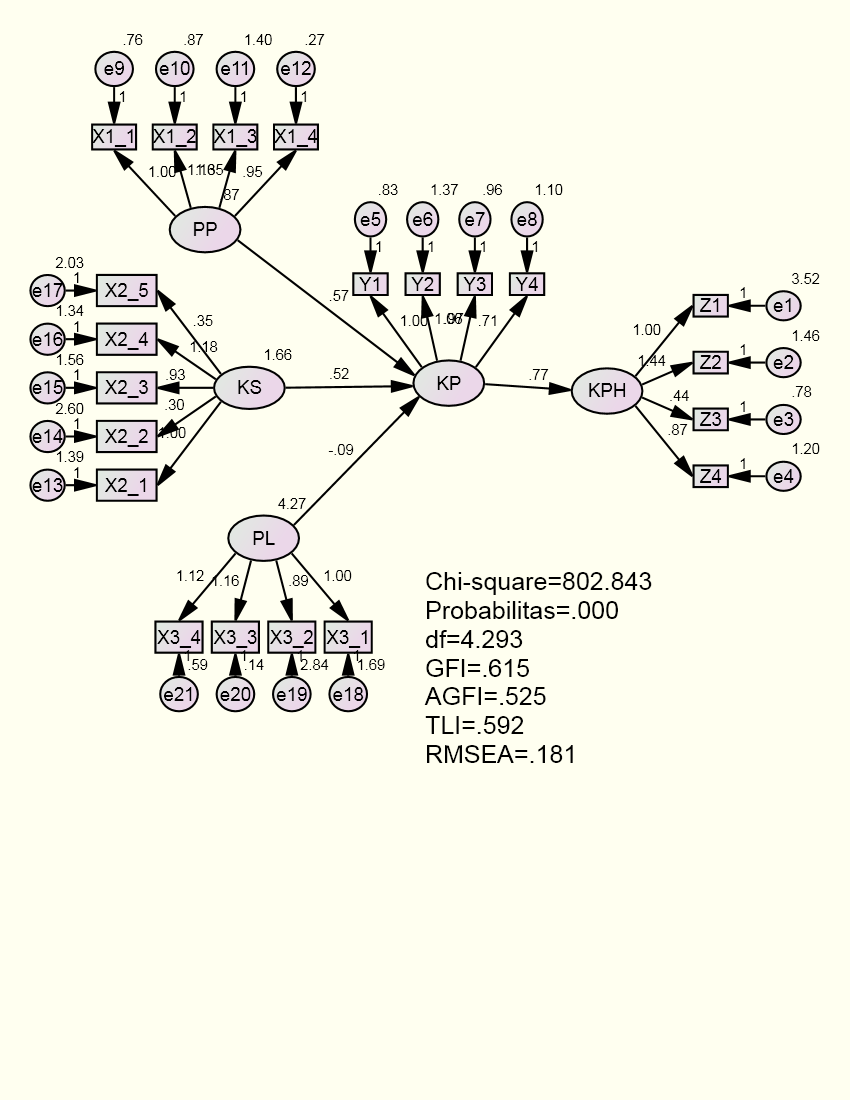 | Figure 3. Testing Structural Model Full Beginning |
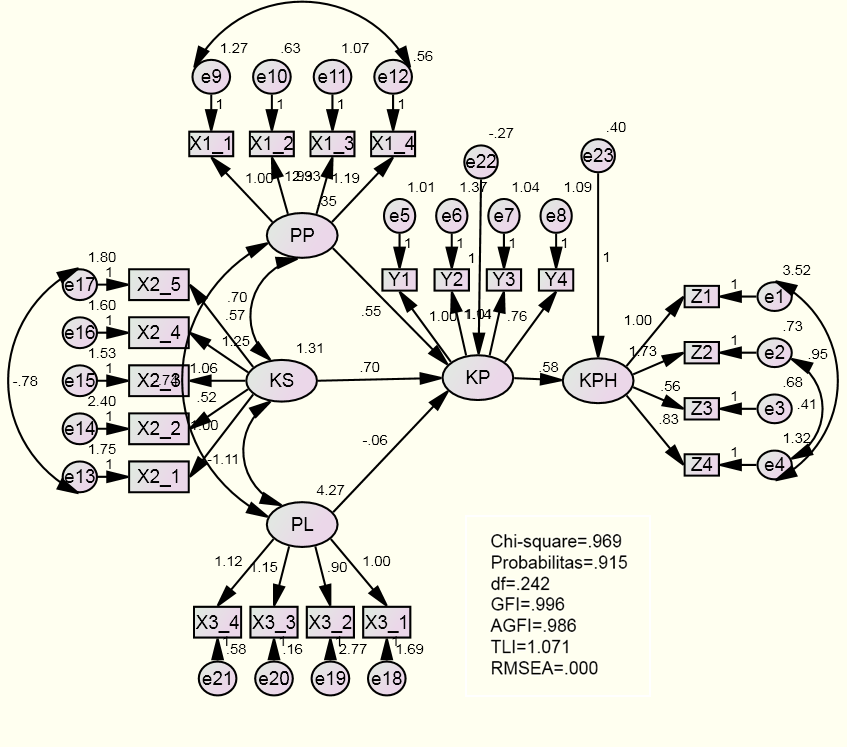 | Figure 4. Testing Structural Model Full Final Stage |
|
|
3.1. Tax Performance Hotel
- Results of the study explained that the perception of respondents on the performance of the hotel tax (Z) is considered sufficient with an average score of 3.38. This means that in general, the hotel tax has been quite performing as one source of revenue in the city of Pekanbaru. If the comparison between the indicators in this variable, economic indicators were the lowest hotel tax be seen from the mean score of the indicator. Economical rate tax with a score of 3,21. This shows the tax payments from the taxpayer less hotel quality with a form of accountability and a clear designation for the community and the use of hotel tax levy costs are relatively not comparable to the tax paid taxpayer when seen from the naked eye is still low.The average score of the effectiveness indicator highest response with an average value of 3.39. This means that the government agency is considered quite successfully achieved the goal to collect taxes to taxpayers with no problems. Agencies always receive tax payments from hotels to increase over time. Agencies can sufficiently explore the potential tax with a detailed description of the tax object. According to respondents from year to year, there was an increase in taxes to local income is relatively high. Indicators of efficiency as measured by government agencies to collect taxes efficiently within the hotel (with a fixed time each period); Agencies then have the energy tax collectors and reliable service and tax services agencies have adequate facilities for tax payments is still relatively low with a score of 3.35.Indicators of the strategic plan, the lack of socialization of strategic planning knowledge affect the taxpayer in tax planning lays the hotel, because it does not know clearly what is being planned by the revenue and will affect taxpayers in planning. Score this indicator is of 3.42.This study also produced that tax performance is influenced by factors of compliance as an intervening variable that directly affects the performance of taxation significantly and positively. Then the tax service factors affecting adherence variables significantly and positively, variable taxpayer awareness significantly affect adherence variables and variable positive and extortion affecting compliance variables significantly and negatively where this indicator variable as the variables affecting indirect tax performance.
3.2. Taxation Services
- The results also show that the government's national tax service in order to collect taxes is quite good hotel with a score of 3.61. This is because the quality of taxation, provisions and taxation information system is good enough. The first indicator variable tax service quality of human resources with a score of 3.38 (good enough). This is due to the government have tax officials technically proficient in providing services and the hotel tax for tax officials to uphold the ethics of taxation with no room to perform service learning with the taxpayer.Indicators of tax provisions with a score of 3.76 (good enough) is due to the government made tax provisions, especially the hotel tax that can be understood taxpayer. Then the taxpayer can easily apply the existing tax provisions and tax provisions currently impacting the well once issued to the taxpayer in paying taxes. Indicators taxation information system with a score of 3.69 (pretty good), this means that the government has a clear service procedures are applied to taxpayers and government hotels have data accurate enough tax bill to the taxpayer as well as the information systems used can accelerate payments work tax and computerized systems also facilitate services to taxpayers who are good.Cultural organizations are asked to respondents is responsive to taxpayer complaints, the results of the field and the interview concluded relative speed of response of the officer reasonably well and in giving an explanation on the taxpayer's good enough, the above due to the attitude of officers not professional. The culture of the organization 3.76.According to Suryadi, 2006. awareness of taxpayers and tax services are not significant to the performance of the tax. While tax compliance have a significant effect on the performance of taxation. Bawazier (2011) has introduced the principle of self-assessment, simplification and reduction in tariff of income tax and the implementation of VAT. Tax reform in 1994 made changes to the Income Tax Act tariff that was introduced back lowered and the start of final income tax, local tax structuring starts and eventually be accepted by society and achieve success against targets and objectives. While the post-1997 tax reform despite the expensive cost, due to not having good planning as well as politically charged gives an indication of failure.
3.3. Taxpayer Awareness
- Indicators consciously paying with a score of 4.21 (good), this means that always wanted to take the time to pay taxes according to the time of maturity. Always want to report tax data truthfully and always deposit the hotel tax in accordance with applicable regulations. Perception indicator with a score of 3.54 (good enough), this is due to consider that taxes for local development and ultimately have an impact on the development of the hospitality itself and considers the tax used to finance the implementation of the wheels of government in order to always be able to run smoothly and also considers that the use of taxes for the welfare of many.Indicators of knowledge with a score of 3.84 (good enough), this is due to find out who the object of hotel tax set by the government under the rules. Knowing who the subject of hotel tax levied according to the rules and determine the amount of hotel tax rate levied according to the rules and to know the time of hotel tax payment in each period and then determine the tax payment procedures in this area and also know the risks of late or do not pay hotel taxes.Indicators characteristics with a score of 4.08 (good), this means that it is always trying to record what the pay hotel taxes, always trying to calculate the tax that is borne pursuant hotel, always trying to discipline in recording and reporting tax dependents with counseling hotel. Indikator a score of 3.11 (good enough), this is due to get information about the search for his own hotel tax themselves through reading a book or open internet and get counseling about the hotel tax from local governments as well as get information about the hotel tax of media through advertising.Based on the above description of the taxpayer's awareness can be concluded that the awareness of the taxpayer with a score of 3.76 (good enough). This means taxpayers have enough awareness to pay taxes in the city of Pekanbaru.
3.4. Illegal Payments (Extortion)
- Indicators used for extortion is on the security of money, money administration, transaction costs, and the cost of the crowds. Security is a form of levy imposed on the owner of the hotel that guarantees guests from physical violence and also the problem of theft of goods belonging to guests, such as: security of thugs or future organization, guarantees and warranties faced physical violence against threats.Indicators security with a score of 2.58 (enough) is due to pay a security deposit of thugs or organization routinely future, pay protection money to face physical violence from organizations and local police officers as well as to pay protection money to the threat posed in the competition to certain elements.Administration assurance indicators with a score of 2.27 (enough) is due to pay the administrative officers of government officials in addressing the problem of taxation which is not in accordance with the wishes, to pay administrative ease in dealing with the security forces and pay more money the administration in order to establish relationships with government officials.Indicators of transaction costs with a score of 2.50 (enough) is due to always pay extra money to facilitate dealings with the government, to spend more in a relationship with the authorities and are always looking for the best way in the context of the efficiency of business transactions.Indicators permission crowd with a score of 3.46 (enough) is due to always pay the money crowd to local security forces in any activity at the hotel, the event always get the protection of local authorities to pay certain benefits and have long cooperated with local authorities in the affairs ease crowds held at this hotel.Of all the indicators, we can conclude that the extortion with a score of 2.70 (enough) which means that there is quite a lot of bribery in running hospitality business ranging from security, administration, transaction costs, and permits the crowds. According Ikhsan, M, 2012, the Local Revenue has a strong relationship with security, community awareness, extortion, human resources and natural resources, reaching 67%.
3.5. Taxpayers Compliance
- Indicators of punctuality with a score of 3.62 (pretty good), is due to always pay taxes based on the timeliness with which payments have been set by the government, trying to comply with the provisions of the tax payment time hotel and once tolerance for delays pay hotel tax. Indicators of data accuracy with a score of 3.96 (pretty good), is due to always contain all the elements relating to the taxes and all the elements that exist in the reporting in the notice. Always clear in providing clarity in reporting about the source and origin of the object of taxation as well as the clarity of the elements involved in reporting on the notice.Indicators tax penalties with a score of 3.89 (pretty good), is due to sanction violations in hotel tax payment was printed in the existing provisions, lack of firmness sanctions by the hotel tax officers and the deterrent effect of sanctions to the taxpayer. Punggutan other official, an indicator that also affect compliance, where many types of charges are made in accordance with the rules.Scores indicators other official levies are 3.96 and well.Of the four indicators can be concluded that the taxpayer compliance in paying taxes in the city of Pekanbaru with a score of 3.82 in the category quite well. This is because the taxpayer is quite timely, accurate enough data given and also quite adherent to tax sanction. Viewed from other official levies, the hotelier was weighing on their business. According to Suryadi, 2006. awareness of taxpayers and tax services are not significant to the performance of the tax. While tax compliance have a significant effect on the performance of taxation.
3.6. Effect Taxation Services to Hotel Taxprayer Compliance
- In this research, taxation services using 4 indicators of quality of human resources, tax regulations, tax information systems and organizational culture. The fundamental differences in organizational culture. Cultural organizations in providing services also affect taxpayer compliance in line with what was said Damayanti, 2011, compliance was influenced by the culture of paying taxes.Indicators of the most dominant influence is the hotel tax service organizational culture (X1_4) of 0.863. Organizational culture, according to respondents relative officials responsive to the complaints of taxpayers, of the results of the field and the interview concluded responsiveness of relatively good officers and to provide the required explanation. The better the culture of the organization that applied to such rapid response officer, the clerk was friendly and courteous, the more shape better services. Subsequently, followed by the quality of human resources (X1_1) of 0.731. In general, the apparatus Revenue already has sufficient ability in the field of each, however the presence of mutations cause problems, because employees were not placed on a new post or field control of the existing rules. So it is not yet formed via cooperation between employees between fields or Courant section, therefore it does not happen cohesiveness between each section. Revenue employee morale is quite good, however there is a lack of some things like in terms of fairness and equality that impact on the truth.Indicators tax provisions (X1_2) establish tax services for 0757. Fairly good indicator of the tax provisions, according to the respondents the government made tax provisions, especially the hotel tax that can be understood taxpayer. Taxpayers can easily apply the existing tax provisions and tax provisions currently impacting the well once issued to the taxpayer in paying taxes.Indicators taxation information system (X1_3) forming services for 0,729. Taxation information obtained by the respondents are generally based on friends and read books, and very little comes from the Dispenda. Results of the research that has been conducted shows that the services performed taxation organizations in this regard is the Revenue Pekanbaru City in order to increase tax compliance is the preferred implementation of the organization's culture to be friendly, attentive, rules are subjective in nature in the form of local wisdom of the Indonesian nation in the sense of more invites taxpayers to pay taxes persuasively in the hotel.
3.7. Effect of Taxprayer Awareness to Hotel Taxpayer Compliance
- Indicators of the most dominant form of consciousness variable taxpayer is abiding characteristics (X2_4) of 0.794. Because the taxpayer always trying to record what the pay hotel taxes, taxpayers are also always trying to count the hotel tax in accordance with the provisions of, and are always trying to discipline in recording and reporting tax dependents hotel. The higher the characteristics indicate higher consciousness.Other indicators such as indicators consciously pay (X2 _ 1) of 0.738. Timeliness of payment of taxes in general the respondents (the hotel) pay the hotel tax in accordance with the payment due time, if there is a delay, due to a contract with another party which has not paid, and usually negotiated with the Dispenda, so no forfeiture. Knowledge of taxation (X2_3) of 0.691. Tax knowledge is good enough, the taxpayer know the requirements, procedures and risk of late or paying taxes. Indicators extension (X2_5) forming a variable awareness of 0.299 socialization conducted by the Revenue how to call the hotel with the same party at a new place and socialization, socialization is a new one. The hotel suggest counseling or socialization should be done several times and when there are changes to the rules to be socialized. With frequent meetings conducted counseling and communication between Revenue and the hotel goes well. Positive perception indicator (X2_2) forming a variable awareness of 0.232. The hotel (in this case the respondent) to realize that the tax they pay is indispensable in financing regional development. The results showed that the higher the tax paying public awareness in the more obedient to the realization of the tax paid. This awareness is predominantly due to the characteristic indicator which means abiding characteristics, such as: notes it is, calculate the appropriate rules and discipline. This is in line with what was presented by Karyoto 2011 that the taxpayer awareness proven effective in improving taxpayer compliance by explaining that consciousness taxpayer is aware of the conditions when wajb tax obligations to pay taxes because they have tax knowledge, receive counseling taxation, has the characteristics required good tax and determine the function of the tax. Then suryadi, 2006, said awareness of the taxpayer that can be measured from the perception of taxpayers, tax knowledge, the characteristics of the taxpayer and the tax extension is no real difference between the tax paid consciousness of large taxpayers was higher awareness than the small taxpayer. This study using five indicators that combines Karyoto opinion and the opinion suryadi prove that the better the characteristics of the taxpayer in the form of notes it is in paying taxes, calculating tax in accordance with the provisions and tried to discipline in recording and reporting tax dependents which in essence is characterized by honest taxpayers and obey the rules.
3.8. Effect of Extortion to Hotel Taxpayer Compliance
- Indicators of the most dominant influence of extortion hotel tax is a transaction fee (X3_3) of 0.988 is the unofficial cost incurred while taking care of the tax service and this is done in order to get the ease of settlement and to reduce the tax affairs. The larger the transaction costs in the form of additional money to facilitate dealings with the government, a relationship with the authorities, seeking the best way in order to indicate the efficiency of business transactions, the higher the extortion.Moreover indicator administrative costs (X3_2) formed extortion by 0.736. Administrative costs are paid by the taxpayer to the smooth administration officers to tackle the problem of tax administration which is not in accordance with the wishes, ease in dealing and establish relationships. Indicators crowds costs (X3_4) forms of illegal levies at 0.950. Hotel costs for the activities carried out at police forces apparatus extortion occurs for example at the time of license crowds and a certain time for security reasons. And indicator variables form the security costs amounted to 0.846 extortion. Extortion was carried out by military personnel paid to security, in particular to the existing hotel pub, karaoke, life music, because the members of the military or police who visited, usually frequent commotion fellow members. Based on the results of research on the illegal fees associated with tax compliance proven that the illegal levies in particular in the form of transaction costs and a significant negative impact on tax compliance to pay hotel taxes. The more the transaction costs incurred, the lower adherence to pay taxes. The results are consistent with what is delivered by Ikhsan M. (2012), which states that illegal payments made local revenue (PAD) decreases. In this study, a hotel tax revenue is one source of this means that the illegal levies can affect taxpayer compliance.Related to transaction costs as the costs for the negotiation process, and the imposition of exchange measurements. Williamson in Yustika (2008) explained that the costs in running an economic system (the cost of running the economic system) and the cost of adjustment to changes in the environment. Rachbini (2002) in Yustika (2008) argues that public choice theory can also perform further transformation of the basic concepts of classical economics into the political field. In this case, the concept of earnings (income) transformation into a concept of rent seeking. This concept is very important for the science of political economy in explaining the behavior of employers, political behavior and interest groups. Rent-seeking theory was first introduced by Krueger (1974), further development of the theory by Bhagwati (1982) and by Srinivasan (1991). Extortion in the form of a security deposit, money administration, transaction costs, and the money crowd, occurred because the unwritten rules that run and run in such a manner. If not given the money at the time to deal with the officer feels someone doing strange and this provision is considered reasonable. Extortion occurs because the rules are not clear, the rules are not clear, the writer called shadow norm (norm shadow), therefore it is normal this shadow come affect hotel submissive behavior taxpayer. Norm shadows that occur during the time that the extortion is ingrained in society. The point is that, this condition has been going on since a long time and left or the situation omission committed by certain elements because it regarded it as a form of compensation or additional to those (persons) because they are instrumental in helping to ease the affairs or conduct negotiations with the taxpayer hotels for ease of payment.In addition, in the crowd held usually hotel often conducting activities as requested by the customer. They like parties and other events that cause road conditions to be jammed and avoids anything that is not accompanied by events in the form of disruption to guests and unsettling, usually held security costs. Also related to the hustle and hustle of the necessary permits certain elements usually given money in issuing the permit. The rules seemed to have become accustomed applied, though no formal provisions that govern them. The behavior of taxpayer in pay or give security money, crowd money and administration money as well as money transactions. This occurs because of the norm shadow, which form the required behavior of taxpayer compliance in paying taxes. The more charges are paid, the more disobedient taxprayer in the form of reports and records as well as the calculation of the expected reporting delivered correctly.The taxpayer should pay taxes normally, with the actual number. However, the presence of illegal charges can cause taxes paid by the taxpayer to be more reduced. The behavior of this relieve the taxpayer for the taxpayer because if implemented in accordance with applicable tax regulations, the amount of the tax burden to be incurred to be larger. Based on the above, it is known that the taxpayer hotels follow the flow of extortion in the operations because there is shadow norm that they must follow.
4. Conclusions
- This study describes the performance of the tax in Pekanbaru as follows.1. Compliance taxpayer paying taxes in hotels, especially in the timeliness of payments shown to be affected significantly by variable taxation services, awareness of the taxpayer and extortion. Of three variable taxation services most dominant influence is taxpayer compliance. Here are some of the conclusions drawn each variable, namely:a. Taxation services proven to have a significant effect on tax compliance in paying taxes. Indicators of the most dominant form of tax services is a form of organizational culture values that support the achievement of the vision that has been set, proficiency officer, a good organizational system of taxation.b. Awareness taxpayer in paying taxes proved significant effect on tax compliance. Indicators of the most dominant form of consciousness taxpayer in paying taxes is characteristic of the taxpayer.c. Extortion to hotel taxpayers proved to have a significant effect on tax compliance. Indicators of the most dominant form of bribery is transaction costs.2. Compliance taxpayer proven to have a significant effect on the performance of the hotel tax. Indicators of the most dominant form of taxpayer compliance is punctuality of pay taxes while the indicator most dominant form of hotel tax is an effective performance.This study provides recommendations on the performance of hotels in Pekanbaru City tax as follows:1. In order to improve taxpayer compliance is expected to pay hotel taxes to the government in this case is the Department of Regional Revenue Pekanbaru City and taxpayers to increase tax services and taxpayer awareness and remove the extortion. In detail things that can be done Pekanbaru city government, among others:a. Build an organizational culture that is responsive, friendly and courteous in accordance with the values of local wisdom of Indonesia through the implementation of a value system that is rooted in the vision, mission and strategic objectives, and provide appropriate remuneration and reward sustainable and improve supervision.b. Build character and discipline honest taxpayer in recording, calculating and reporting of hotel tax through character development training (character building) to the taxpayer.c. Applying the hotel tax payment system that efficiently by shortening the payment process through the implementation of online tax payment system to avoid transaction costs because of the shadow norm causes of illegal fees.2. In order to improve the performance of the hotel tax is expected to increase taxpayer compliance in paying taxes, especially the timeliness of payment of taxes in accordance with the provisions through the implementation of reward and punishment by the Department of Regional Revenue Pekanbaru. Surveillance material is expected to Department of Regional Revenue Pekanbaru create object data base in accordance with the development of hotel tax and Law No. 28 Year 2009 on Regional Taxes and Regional retributions.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML