-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Wireless Networking and Communications
p-ISSN: 2167-7328 e-ISSN: 2167-7336
2014; 4(1): 7-17
doi:10.5923/j.jwnc.20140401.02
A Survey on Middleware for Wireless Sensor Networks
Bhaskar Bhuyan 1, Hiren Kumar Deva Sarma 1, Nityananda Sarma 2
1Dept of IT, Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology, Mazitar, Rangpo, Sikkm, 737136, India
2Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Tezpur University, Napaam, 784028, India
Correspondence to: Hiren Kumar Deva Sarma , Dept of IT, Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology, Mazitar, Rangpo, Sikkm, 737136, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The wireless sensor network is an emerging field and it offers a wide variety of applications that include habitat monitoring, object tracking, environmental surveillance, military systems, health care, precision agriculture, building monitoring etc. However, due to their unique characteristics and the constraints they suffer from, sensor networks pose considerable challenges and make application development quite complicated .There is a necessity of an intermediate software layer between the sensor hardware and the sensor network applications that may be termed as middleware. Middleware is necessary in order to fully meet the design and implementation challenges of wireless sensor networks. In this paper, we highlight the main design challenges of wireless sensor networks and present a study on the existing middleware approaches for wireless sensor networks. We also discuss the scope of Quality of Service support at middleware layer for wireless sensor networks. The paper is concluded with future research directions in the middleware level to meet the requirements of emerging applications of wireless sensor networks.
Keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks, Middleware, Quality of Service
Cite this paper: Bhaskar Bhuyan , Hiren Kumar Deva Sarma , Nityananda Sarma , A Survey on Middleware for Wireless Sensor Networks, Journal of Wireless Networking and Communications, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 7-17. doi: 10.5923/j.jwnc.20140401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have emerged as a rapidly growing field in the recent years. It has attracted significant attention from the researchers involved in both academic and industrial communities. A typical wireless sensor network consists of a collection of tiny inexpensive sensor nodes. This collection may be in the tune of hundreds or thousands of sensor nodes and these nodes communicate through wireless media, i.e., radio. The sensor nodes are deployed randomly and typically in harsh environments. Depending on the application type, a sink node may be located in a remote corner which is connected to the sensor nodes through wireless channels. A typical sensor network setup is shown in Figure 1. The sensor nodes are resource constrained whereas the sink node is generally resourceful. Such an arrangement of sensor nodes and the sink node can be used for building distributed systems for data collection and processing. Thus, a wireless sensor network involves the tasks like on-field signal sensing and processing, in-network data aggregation and wireless communication. The wireless sensor networks are self starting and self organized in nature[1][36]. The technical advancements in the field of hardware and wireless communication are significant in recent times. Therefore, the features provided by computing and communication hardware require to be matched by an appropriate software layer in the wireless sensor network system. This should enable programmers to easily and efficiently exploit the capabilities of the underlying hardware and other opportunities provided by the current communication technologies. The wireless sensor networks support a wide range of applications such as habitat monitoring, object tracking, environmental surveillance, military systems, health care, precision agriculture, building monitoring etc[1].
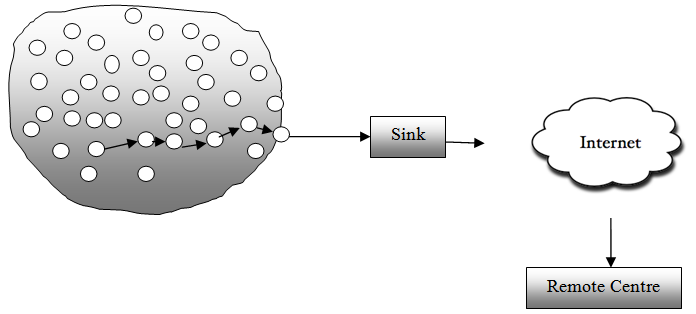 | Figure 1. Wireless sensor network architecture |
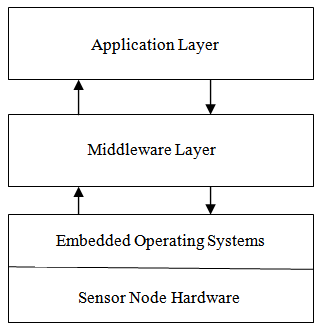 | Figure 2. Logical organization of middleware |
 | Figure 3. Purposes of middleware |
2. Related Work
- There are some reported works with respect to middleware technology in wireless sensor networks. W.B. Heinzelman et al presented the study related to the necessity of middleware support in wireless sensor network in[13], (2004). Salem Hadim and Nader Mohamed presented a study on middleware approaches in wireless sensor networks in[23], (2006). Wasim Masri et al presented a comparative study of different middleware technologies applicable to wireless sensor networks in[16], (2007). M.M. Wang et al reported a survey on middleware in wireless sensor networks in[3], (2008). N. Mohammed et al presented a survey on service oriented middleware for wireless sensor networks in[35], (2011).
3. Challenges in Designing Middleware for Wireless Sensor Networks
- The traditional middleware used in distributed systems are generally heavy weight in the sense that they require huge memory space and also computation requirements are very high[4]. Since the sensor nodes are resource constrained, these solutions are not suitable for wireless sensor networks. The sensor networks suffer from limited energy, limited processing power and also limited memory. Therefore, the middleware solutions for wireless sensor networks should be light weight and these solutions should address the unique constraints such networks suffer from. Some of these constraints the wireless sensor networks suffer from are ad-hoc deployment of the nodes, limited computing and communication resources and also dynamic operating environments[1]. Some of the differences between traditional middleware used in distributed systems and the middleware used in wireless sensor networks are mentioned below:● Most of the distributed system middleware techniques proposed in[5][6] aim at providing transparency by hiding the context information. In contrast, wireless sensor network based applications should usually be context aware.● Although many mobile computing middleware[7] support context awareness, their major concern is how to satisfy the interest of individual mobile node continuously taking into consideration the node mobility factor. On the other hand, wireless sensor network based systems are data centric and it reflects the whole application interest but not a single portion of it.● Data aggregation or data fusion has no significance in traditional distributed system middleware. On the other hand, data aggregation in the intermediate nodes of the forwarding path in a wireless sensor network is highly desirable. ● The traditional distributed systems may be resourceful. Therefore, the middleware designed for such systems can be heavyweight which demands large memory space and high computing capability in the nodes. Unlike the nodes in such traditional distributed systems, the sensor nodes are simple with limited processing power, limited storage and finite as well as limited onboard battery power. Therefore, the middleware for resource constrained wireless sensor networks should be light weight so that these can be implemented in the simple sensor nodes. The middleware solution for wireless sensor network should be energy efficient. Moreover, the design of the middleware for wireless sensor networks should also take into consideration the factors like sensor node hardware, operating systems, routing protocols and applications[8][9][10].The design and development of successful middleware solutions for wireless sensor networks need to address several challenges. Figure 4 shows different challenges in the middleware design for wireless sensor networks.
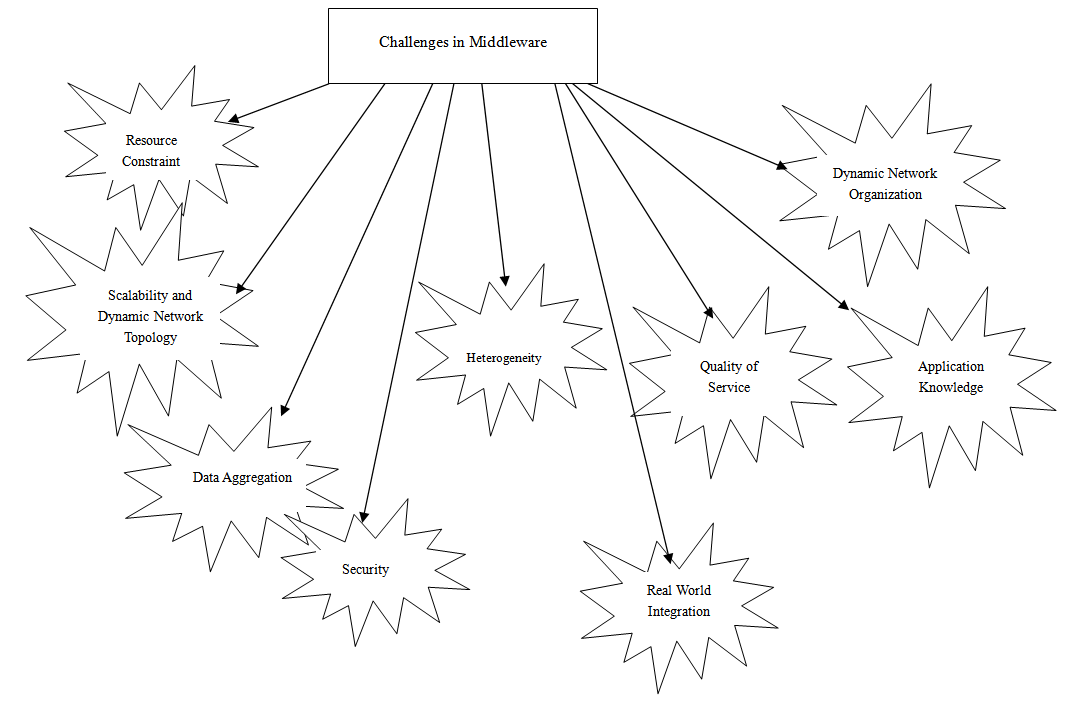 | Figure 4. Challenges in middleware design for wireless sensor networks |
4. Classification of Different Middleware Approaches for WSN
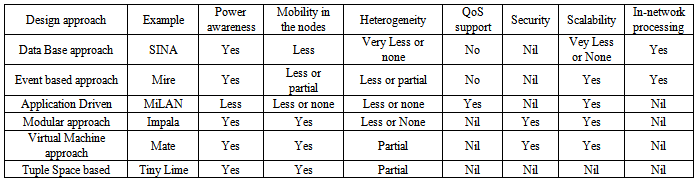
- In this section, different classes of middleware approach followed for wireless sensor networks are discussed. There have been several research projects undergoing all around the world for design and development of middleware for wireless sensor networks. The classification of various middleware approaches for wireless sensor networks along with respective examples are enlisted below. Table 1 summarizes some major classes of middleware design approaches.
4.1. Database Approach
- In this approach, the whole sensor network is considered as a database. An application can make query to the database using structured query language (SQL) like language. This approach facilitates a simple and easy communication scheme between users and the network, but generally it lacks time space relationships between events[16].An example of database approach based middleware is SINA (Sensor Information Networking Architecture). It was designed as part of a research project at University of Delaware, USA. In SINA[17], the sensor applications can make queries to the network and get the replies back from the network. It can monitor changes in the network. It basically comprises of three functional components namely hierarchical clustering, attribute based naming and location awareness. The hierarchical clustering consists of grouping of nodes based on their proximity or energy levels. The groups of nodes are called clusters. The attribute naming replaces the standard id-based naming by attributes of the data. This mechanism is used for data centric routing in wireless sensor networks. Location awareness of the sensor nodes is achieved by using GPS (Global Positioning System) based techniques. When querying the network, collision may result from the large number of responses coming from different parts of the network. All such responses propagate to the enquirer node during a short span of time and it may create response implosion problem. To overcome this problem, SINA introduces the following three techniques: First, sampling operation, in which a node may not respond to a query when its neighbor is responding. Second, self orchestrated operation, in which some nodes may defer their responses for a certain period of time reducing the number of collisions. Third, diffused computation operation, which uses data aggregation to reduce the amount of data exchanged over the network. SINA provides scalability through hierarchical clustering. Some other examples of database approach based middleware for wireless sensor network are as mentioned below.● Cougar developed by Cornel University[18],● DsWare developed by University of Virginia[19],● TinyDB developed by University of California, Berkeley[20].
4.2. Event Based Approach
- Event based, message oriented middleware provides asynchronous communication based on publish/subscribe paradigm[21]. In event based approach data acquisition support is focused on event definition, event registration/ cancel, event detection and event delivery. The interest of the applications lies in certain changes of states of data. When such an event is detected, the middleware sends the event notification to the interested application. Publish/subscribe paradigm is the typical way of implementing event based middleware[3]. The basic entities of publish/subscribe system are event subscriber and event publisher. The event subscriber is the sink node and the sensor nodes are the event publishers. An example of publish/subscribe based middleware is Mires[21], which was developed at University of Pernambuco. Mires middleware is built upon TinyOS[22]. TinyOS is an operating system built for wireless sensor network nodes. Mire is basically composed of the publish/ subscribe service which has two main key services: routing services and aggregation service. The communication between the sensor nodes is consisting of three phases. Initially, the sensor nodes in the network advertise their available topics such as humidity, temperature etc. Next, the advertised messages are routed to the sink node. User applications connected to the sink node can now subscribe the desired application topics to be monitored. Finally, the subscribed messages are broadcasted to the sensor nodes in the network. In Mires, only the messages referring to the subscribed topics are sent and as a result, it reduces the number of transmissions and thus subsequent energy consumptions.
4.3. Application Driven
- In this approach, the applications are given more privileges by providing an architecture which reaches the network protocol stack and tunes the network on the basis of application requirements[23]. Therefore, the application dictates the management of the network by considering the Quality of Service issues as a matter of high priority. MiLAN (Middleware Linking Application and Networks) is an example of application driven middleware. It was developed at the University of Rochester, USA. In MiLAN[13], application specifies its requirements, monitors network conditions and optimizes sensor network configurations. In order to do these tasks, an application specifies its requirements through some specialized graphs. MiLAN receives the application variables and the required Quality of Service parameters through these graphs. Then it determines which sensor or set of sensors can provide what level of Quality of Serie for each variable. MiLAN can determine the set of sensors which can satisfy all the Quality of Service requirements. Due to energy constraints and dynamic network topology, the feasible set is constrained to subset of sensors. Subsequently MiLAN chooses the most suitable one to fulfill the required Quality of Service level. Although MiLAN supports Quality of Service and scalability, it has no support for node mobility. Moreover, due to its tight coupling with the network stack it does not support platform heterogeneity.
4.4. Modular Approach
- In this approach, application is divided into some small program modules which save energy by allowing simple and lightweight software updates. This approach uses mobile agents or codes that are injected to sensor network for collecting local data. The agents can also move from one node to other.An example of modular approach based middleware is Impala[24]. It was specially designed as a part of ZebraNet project, a wildlife monitoring project at Princeton University, USA. Impala is a middleware architecture that supports application adaptability, modularity and repairability in wireless sensor networks. It supports multiple applications by using event based modular programming model and provides a user friendly interface. It ensures application adaptation. The Impala middleware consists of two layers. The upper layer contains all the applications and protocols developed for ZebraNet project. These applications use various strategies to collect environmental information and to rout the information to the base station. The lower layer has three middleware agents namely event filter, application adapter and the application updater. The event filter controls different operations which trigger a chain of processing. These events are timer event, packet event, data event and device event. The application adapter is armed with Application Finite Sate Machine (AFSM). The AFSM handles application adaptation based on different scenarios such as energy efficiency and other attributes determined by the applications. On the other hand the updater agent is responsible for getting effective software updates by taking into account the tradeoff such as high node mobility, constrained bandwidth, wide range of updates and code management. In the case of software updates, as the first step, the nodes first exchange an index of application modules and then request the changed modules for transmission which saves network bandwidth. This happens before the actual software exchange. A program module is compiled into binary instructions before being injected into the network. The module is not linked to the main program for installation until the whole update is received. Although, Impala addresses issues like adaptability, software updates, energy efficiency, security but it does not give support for hardware heterogeneity and Quality of Service issues[16].
4.5. Virtual Machine Approach
- Virtual Machines (VM) are used in sensor networks for various reasons. One of the advantages of implementing VMs in wireless sensor networks is that it allows the programmer the semantic like write-once and execute many times across a range of heterogeneous sensors. The modularity of VM code allows for concise bytecode.This reduces memory footprint and power consumption when dynamically updating applications via the network[25]. On the other hand the virtual machine based approach intrinsically provides security and synchronization models which simplify the programming task.An example of virtual machine based middleware for wireless sensor network is Mate[25]. This project was developed at the University of California, Berkeley. It provides an abstraction layer to implement its operations and mainly focuses on a new programming paradigm to overcome the issues like limited bandwidth and higher energy consumption. Mate proposes a method of reprogramability from simple parameter adjustments to upload complete updates using VM approach. It uses a byte code interpreter built on top of TinyOS[22]. The programs are broken into capsules of 24 instructions, each of which fits in to a single byte. This limitation allows a capsule to fit into a single TinyOS packet. There are five key components in Mate. Those are VM, Network, Logger, Hardware and Boot scheduler. Mate uses a synchronous model that begins execution in response to an event such as packet transmission or timer going off. With this it avoids message buffering and larger storage requirements. The synchronous model makes application level programming easier and less prone to error than dealing with asynchronous event. The concept of version number is used in this approach. In the event of network update, the update is carried out by adding a version number in the capsule and then comparisons are made with neighbors. Then if necessary, a new version capsule can be installed. Mate is energy efficient for simple and short running applications. But it incurs high CPU overhead for long running applications. Mate also has mechanisms to deal with security related issues. Moreover, it can prevent programs from causing system failure[16].
4.6. Tuple Space Approach
- A tuple space is an implementation of the shared memory paradigm used for distributed computing. It provides a repository of tuples that can be accessed concurrently. As an example, let us consider that there is a group of processors that produces pieces of data (i.e., producer). Again there is another group of processors that uses the data (i.e., consumer). Producers post their data as tuples in the space, and the consumers then retrieve data from the space that match a certain pattern. The tuple space model was pioneered by Gelernter and co-workers[26] in the Linda programming system for coordinating objects across a distributed computing environment.An example of a tuple space based middleware developed for wireless sensor network is Tiny Lime[27]. It is a data sharing middleware built on TinyOS. Tiny Lime extends Lime[28]. Lime is a middleware developed for mobile ad-hoc networks. Lime breaks up the Linda tuple space into multiple tuple spaces. Each of these multiple tuple spaces is attached to a mobile component. The rules for sharing of their contents i.e., tuple content, are defined. It is considered that the components are able to communicate. In a sense, the static global tuple space of Linda is rearranged as federated tuple space, which changes now dynamically. Tiny Lime is an extension of Lime which incorporates some suitable features required for sensor networks. For instance, reactions in Tiny Lime give the ability to specify the data freshness [27]. Tiny Lime reactions also accept conditions based on which a particular set of data can be fetched from the sensor nodes. Tiny Lime is designed for environments in which clients typically only need to query data from local sensors. Interestingly, Tiny Lime does not support multi-hop propagation of data through the sensor network. TS-Mid is another example of tuple space based middleware designed for sensor networks. Details of TS-Mid can be found in literature[29].
5. Comparative Study
- In this section a comparative study is presented considering the major design approaches of middleware. The comparison based on our study about the different middleware approaches is shown below in the Table 2.
|
6. Middleware Layer Based Quality of Service Support in WSNs
- Quality of Service in wireless sensor networks is application dependent. Suitable design of middleware may be helpful in achieving application specific Quality of Service in wireless sensor networks. Middleware based Quality of Service (QoS) support is a very new and an open area of research in the field of wireless sensor networks[3]. If the required application specific Quality of Service can not be supported by underlying wireless sensor network then the middleware can play a role. The middleware may negotiate between the application and underlying sensor network to provide appropriate Quality of Service. Figure 4 shows such a scheme between the middleware and the application level Quality of Service. Middleware based Quality of Service supports may also give an implementation framework in order to simplify the development of wireless sensor network applications[3]. Some of the important Quality of Service parameters at the middleware and the application layer are accuracy, aggregation degree, aggregation delay, coverage, and optimum number of sensor nodes in a region. On the other hand the Quality of Service parameters at the network layer are delay, jitter, bandwidth, and packet loss[30]. In[14], it is emphasized that for wireless sensor networks the collective Quality of Service metrics should be considered. This is because, the wireless sensor networks are generally densely deployed and single sensor accuracy or time delay between two sensor respective sensor nodes may not be meaningful. Therefore, collective behavior and effect of a group of logically related sensor nodes may be more meaningful. During middleware design, it is necessary to consider collective behavior of the sensor nodes and implement collective QoS metrics in the middleware layer. Quality of Service (QoS) support at wireless sensor network middleware depends on the middleware services[3] for example, resource discovery and resource management service. QoS support at the middleware may also have impact on some other services such as data acquisition in the data management service. In[31] a framework is proposed which uses services and function for fault detection without recovery. It is framework with fault tolerant algorithms. MiLAN[16], discussed in the previous section is a middleware approach to provide QoS between the application and the underlying sensor network. MiLAN allows the applications to specify their quality requirements and adjust the network characteristics for longer lifetime of the application and also meeting the QoS requirements. In[32] a middleware architecture called MidFusion, is proposed which makes use of Bayesian theory to support information fusion by the sensor network application. It selects and discovers the best possible set of sensor nodes based on the QoS requirements and the QoS that can be provided for the applications. In[33] a reflective and service-oriented middleware is proposed. It provides an abstraction layer between application layer and the underlying sensor network infrastructure. It uses QoS parameters such as data accuracy and energy awareness in its evaluation. It keeps a balance between application QoS requirements and the network life time. The main features of this middleware are divided into three parts[33] as shown in Figure 5. Firstly, an interoperable layer is provided by the system between different applications and the wireless sensor network. Secondly, the services provided by the middleware are accessed in a flexible way by some standard high level languages. And finally, the provided service for network configuration and adaptation increases the overall lifetime of the network meeting the application requirements. In[30] a cluster based mechanism of QoS support at the middleware level is proposed. The middleware is based on publish/subscribe[21] model of communication and provides real time and fault tolerant services to its application. i) part I, interoperable layer between application and underlying sensor network, ii) part II, service access by standard high level languages,iii) part III, increase in lifetime by network configuration and adaptation services meeting the application requirements.
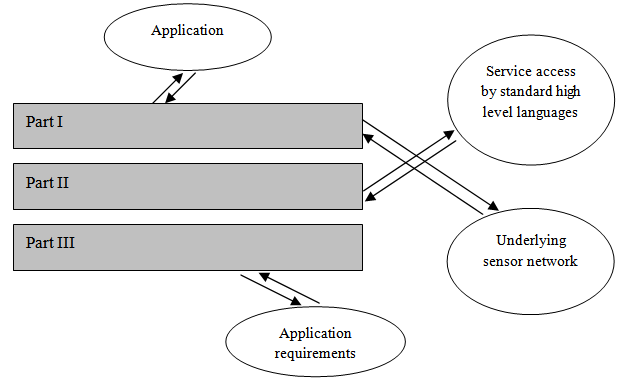 | Figure 5. Three parts of service oriented middleware proposed in[33] |
7. Future Research Directions
- Based on our study it is observed that there are very little work that have been reported for middleware layer based QoS support in wireless sensor networks. In the previous section (section 6), we have cited some of the middleware based QoS support examples in wireless sensor networks and most of the projects we have mentioned here are at their initial stages. QoS provisioning at middleware layer is an open area of research and needs significant contributions from the research community. Another important observation is that almost all the middleware we have discussed are application specific. However, designing a middleware for a particular application has certain limitations such as limited reusability, tight coupling between application and the sensor network etc. Current state of the art middleware for sensor network have several drawbacks. This is why such middleware solutions can not be used for emerging pervasive applications[34]. Some of the drawbacks are:i) It is assumed that in most of the cases wireless sensor networks consist of homogeneous and resource constraint sensors. ii) Lack of Quality of Service management and control. To overcome these drawbacks, the design and development of service oriented generic middleware for wireless sensor networks can be adapted as a solution. Service oriented generic middleware is a new direction of research in the middleware level. MiSense[34] is an example of service oriented component based middleware for wireless sensor networks. Again provisioning Quality of Service in such a service oriented middleware for wireless sensor network is yet another promising area of research. Defining and implementing collective Quality of Service metrics in wireless sensor networks is another open research issue.
8. Conclusions
- In this paper, we have discussed the main challenges faced by the designers during the design and development of middleware for wireless sensor networks. We surveyed the existing middleware design approaches for wireless sensor networks. Suitable examples of these approaches are mentioned and a comparative study among them is presented. We also stated the scope and status of QoS support at the middleware level for wireless sensor networks and cited some of the examples in this direction. Though middleware is a stable technology in distributed systems and distributed computing environments, there is scope and need to develop this technology for wireless sensor networks. Finally, we highlighted the limitations of the current middleware technologies in wireless sensor networks and outlined a new direction of research based on the concept of Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) for the design and development of middleware in wireless sensor networks to meet the requirements of emerging pervasive applications.
References
| [1] | I.F. Akyildiz, W. Su, Y. Sankarasubramaniam and E. Cayirci, “Wireless sensor networks: a survey”, IEEE Communication Magazine, 40(8), 2002, pp. 102-114. |
| [2] | Cecilia Mascolo, Stephen Hailes, “Survey of middleware for networked embedded systems”, Technical Report for Project: Reconfigurable Ubiquitous Networked Embedded Systems, University College London, 2005. |
| [3] | M.M. Wang, J.N. Cao, Jing Li, Sajal K.Das, “Middleware for Wireless Sensor Network: A Survey”, Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 23(3), May 2008, pp. 305-326. |
| [4] | Yang Yu, Bhaskar Krishnamurthy, V.K. Prasanna, “Issues in Designing Middleware for Wireless Sensor Network”, IEEE Network, Jan-Feb 2004. |
| [5] | Java Soft., “Java Remote Invocation specification”. Revision 1.5, JDK1.2 Edition, Oct. 1998, http://java.sun.com /j2se/ 1.4.2/docs/guide/rmi/. |
| [6] | OMG,”The common object request broker: Architecture and specification”, Rev. 2.2, 1998,http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CORBA. |
| [7] | Licia Capra, Wolfgang Emmerich, Cecilia Mascolo, “Middleware for mobile computing, Technical Report”, Department of Computer Science, University College London, 2005. |
| [8] | Kay Roomer, Oliver Kasten, Friedemann Mattern, “Middleware challenges for wireless sensor networks”, Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 6(1), 2002, pp. 12-17. |
| [9] | Matthew Wolenetz, Rajnish Kumar, Junsuk Shin, Umakishore Ramachandran, “Middleware guidelines for future sensor networks”, Technical Report 30332-0280”, College of Computing, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta Georgia 2004. |
| [10] | Bartolome Rubio, Manuel Diaz, Jose M. Troya “ Programming approaches and challenges for wireless sensor networks”, in proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Systems and Networks Communications (ICSNC’07), Cap Esterel, French Riviera, France, August 25-31, 2007. |
| [11] | D. Estrin et al., “Next Century Challenges: Scalable Coordination in Sensor Networks”, in proceedings of 5th Annual ACM/IEEE Int’l. Conf. on Mobile Computing and Networking (Mobi Com’99), ACM Press, 1999, pp. 263–270. |
| [12] | B. Krishnamachari, D. Estrin, and S. Wicker, “Impact of Data Aggregation in Wireless Sensor Networks,” in proceedings of 22nd Int'l Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCSW 02), IEEE CS Press, 2002, pp. 575–578. |
| [13] | W.B. Heinzelman et al., “Middleware to Support Sensor Network Applications”, IEEE Network, vol. 18, no. 1, 2004, pp. 6–14. |
| [14] | D. Chen and P.K. Varshney, “QoS Support in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey,” in proceedings of Int’l Conference on Wireless Networks (ICWN 04), CSREA Press, 2004, pp. 227–233. |
| [15] | A. Perrig, J. Stankovic, and D. Wagner, “Security in Wireless Sensor Networks,” Communications ACM, vol. 47, no. 6, 2004, pp. 53–57. |
| [16] | Wassim Masri, Zoubir Mammeri, “Middleware for Wireless Sensor Networks: A comparative Analysis”, IFIP International Conference on Network and Parallel Computing Workshops, September 18-21, 2007, pp. 349-356. |
| [17] | C.C. Shen, C. Srisathapornphat, C. Jaikaeo, “Sensor Information Networking Architecture and Applications”, IEEE Personal Communications, August 2001, pp. 52-59. |
| [18] | P. Bonnet, J. Gehrke, and P. Seshadri, “Towards Sensor Database Systems,” in proceedings of 2nd Int’l Conf. on Mobile Data Management (MDM’01), 2001, pp. 314–810. |
| [19] | S.R. Madden, M.J. Franklin, and J.M. Hellerstein, “TinyDB: An Acquisitional Query Processing System for Sensor Networks,” ACM Trans. Database Systems, vol. 30, no. 1, 2005, pp. 122–173. |
| [20] | S. Li, S. Son, and J. Stankovic, “Event Detection Services Using Data Service Middleware in Distributed Sensor Networks,” in proceedings of 2nd Int’l Workshop on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN 03), LNCS 2634, Springer, 2003, pp. 502–517. |
| [21] | E. Souto, G. Guimaraes, G. Vasconcelos, “A message- oriented middleware for sensor networks”, in proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Middleware for Pervasive and Ad-hoc Computing 2004, (MPAC’04), pp. 127-134. |
| [22] | J. Hill, et al., “System architecture directions for networked sensors”, ACM SIGPLAN Notices, vol. 35, issue 11, November 2000, pp. 93-104. |
| [23] | Salem Hadim, Nader Mohamed, “Middleware: Middleware Challenges and Approaches for Wireless Sensor Networks”, IEEE Distributed Systems Online, vol. 7, no. 3, March 2006. |
| [24] | T. Liu and M. Martonosi, “Impala: A Middleware System for Managing Autonomic, Parallel Sensor Systems,” in proceedings of ACM SIGPLAN Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming (PPoPP’ 03), 2003, pp. 107–118. |
| [25] | P. Levis and D. Culler, “Mate: A Tiny Virtual Machine for Sensor Networks,” in Proceedings of 10th Int’l Conf. on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (ASPLOS-X), ACM Press, 2002, pp. 85–95. |
| [26] | David Gelernter. “Generative Communication in Linda”, In ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, vol. 7(1), January 1985, pp. 80-112. |
| [27] | C. Curino, M. Giani, M. Giorgetta and A. Giusti, “TinyLIME: bridging mobile and sensor networks through middleware”, in proceedings of 3rd IEEE Int. Conf. on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Hawaï, March 2005. |
| [28] | A. L. Murphy, G. P. Picco, and G.-C. Roman, “LIME: A middleware for physical and logical mobility”, in proceedings of the 21st Int. Conf. on Distributed Computing Systems, Phoenix, April 2001. |
| [29] | Rita de Cassia Acioli Lima et al, “TS-Mid: Middleware for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Tuple Space”, in proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, March 25-28, 2008, pp. 886-891. |
| [30] | M. Sharifi, M.A.Taleghan, A.Taherkordi, “A Middleware Layer Mechanism for QoS Support in Wireless Sensor Netwroks”, in proceedings of ICN/ICONS/MCL, 23-29 April 2006. |
| [31] | Ruiz L B, Siqueira I G, Oliverira L B, “Fault management in event-driven wireless sensor networks”, In Proc. the 7th ACM/IEEE Int. Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, Italy, 2004. |
| [32] | Alex H., Kumar M., Shirazi B., "MidFusion: An adaptive middleware for information fusion in sensor network applications," Information Fusion, vol. 9, issue 3, July 2008, pp. 332-343. |
| [33] | F.C. Delicato et al., “Reflective middleware for wireless sensor networks”, in proceedings of ACM Symposium on Applied Computing 2005, (ACM SAC’05), pp. 1155-1159. |
| [34] | K.K. Khedo, R.K. Subramanian, “A Service-Oriented Component Based Middleware Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks”, International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, vol.9, no.3, March 2009, pp. 174-182. |
| [35] | N.Mohamed, J. Al-Jaroodi, “A survey on service-oriented middleware for wireless sensor Networks”, SOCA, vol. 5, no. 2, 2011, pp. 71-85. |
| [36] | Feng Zhao, Leonidas Guibas, Wireless Sensor Networks an information processing approach, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, An imprint of Elsevier, 2005, ISBN 81-8147-642-5. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML