-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics
p-ISSN: 2167-6895 e-ISSN: 2167-6909
2021; 11(1): 1-6
doi:10.5923/j.jnpp.20211101.01
Received: Dec. 15, 2020; Accepted: Jan. 6, 2021; Published: Feb. 6, 2021

Radionuclide Depth Profile Baseline and Radiation Hazard Indices of the Reclaimed Old Nekede Mechanic Village, Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria
Chijioke M. Amakom1, Amarachi U. Nkwoada2, Chidiebere I. Nwaogbo1, Nneka O. Iheonu3
1Department of Physics, Federal University of Technology, Owerri
2Department of Chemistry, Federal University of Technology, Owerri
3Department of Mathematics, Federal University of Technology, Owerri
Correspondence to: Chijioke M. Amakom, Department of Physics, Federal University of Technology, Owerri.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

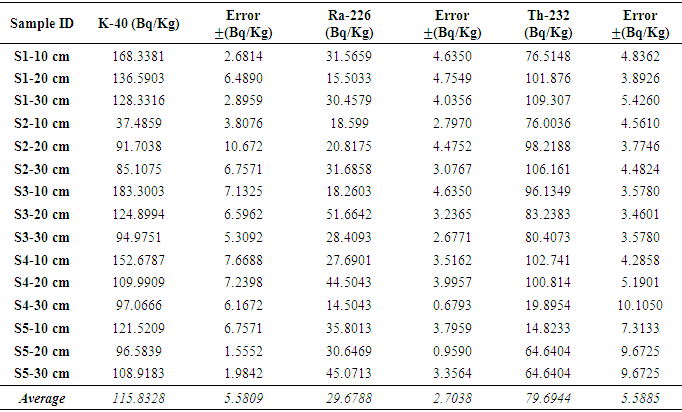
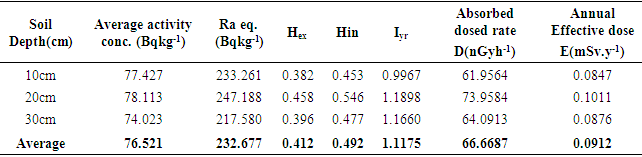
Radionuclide concentration in soil samples collected at the old Nekede auto-mechanic village in Owerri were determined using gamma spectroscopy. A total of 15 soil samples were collected at depths of 10-cm, 20-cm and 30-cm at 5 different sites respectively. From the results, the mean activity concentrations of 40K, 226Ra, and 232Th were 132.66±5.61 Bq/Kg, 26.38±3.88 Bq/Kg, and 73.24±4.91 Bq/Kg respectively for samples collected at 10cm depth. At 20cm depth the mean values obtained were 111.95±6.51 Bq/Kg, 32.63±3.48 Bq/Kg, and 89.76±5.20 Bq/Kg for 40K, 226Ra, and 232Th respectively, while 102.88±4.62 Bq/Kg, 30.03±2.77 Bq/Kg, and 76.08±6.65 Bq/Kg were obtained at the 30 cm depth for 40K, 226Ra, and 232Th respectively. The calculated absorbed dose rate and annual effective dose have an average value of 66.6687 nGyh-1 and 0.0912 mSv.y-1. The 10cm depth presented the lowest dose rate and annual effective dose rate with values of 61.9564 nGyh-1 and 0.0847 mSv.y-1 respectively. While the highest values were obtained at 30cm depth with values of 64.0913 nGyh-1 and 0.0876 mSv.y-1 respectively. The value of the annual effective dose lies within the world average value of 1.0 mSvy-1 annual effective dose equivalent rate. The hazard indices corresponding to the collected samples was also estimated to have a mean value of 0.142, which is below the recommended world average.
Keywords: Radionuclide concentration, External and Hazard indices, Mechanic village, Annual effective dose
Cite this paper: Chijioke M. Amakom, Amarachi U. Nkwoada, Chidiebere I. Nwaogbo, Nneka O. Iheonu, Radionuclide Depth Profile Baseline and Radiation Hazard Indices of the Reclaimed Old Nekede Mechanic Village, Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria, Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 1-6. doi: 10.5923/j.jnpp.20211101.01.
1. Introduction
- Several studies have reported on the effects of effluents discharged from anthropogenic activities to contain toxic substances that cause adverse effects to the environment and its inhabitants; such studies were reported by [1], [2]. In Nigeria, mechanic village is a place where various automobile repairs are carried out – such as, welding and fabrication, soldering, car battery recharging, scrapping, spraying, and painting of vehicle parts, gear box recycling, panel beating of scratched vehicles, discharge of condemned petroleum products (oils, greases, hydraulics fluids)” [3]. In a study on the impact of such activities on the physicochemical and microbial behavior of the soils from three mechanic villages in and around Abuja, Nigeria; the authors from their findings showed a high level of heavy metal concentrations which exceeded the recommended levels for industrial areas. [4] Also, another research carried on radiation levels within a mechanic village in Abuja, showed a background radiation that was less than the 1 mSv/yr provided by the Basic Safety Standards (BSS). Furthermore, research work by [5], found that Neem, Cashew and Mango trees takes up heavy metals from a contaminated Mechanic village. These trees in turn produce edible parts that are consumed by the local dwellers, thus exposing the inhabitants to secondary uptake of heavy metals and radionuclides. Several other studies have also shown that radionuclides can easily be transferred from contaminated soil into the food chain. This is because the plants naturally take up mineral contents within the shoot system. Sometimes these radionuclides are concentrated in the plants in levels higher than what is obtainable in the contaminated soil, such results were obtained by [6]. This uptake of radionuclides by plants are described through the soil-to-plant transfer factors [7].Naturally occurring radionuclide materials (NORM) are ubiquitous in our environment and can in most cases can be concentrated in amount which may pose health concern to the public. These enhanced concentration because of technological activities are regarded as technological enhanced natural occurring radionuclide materials (TENORM). Many non-nuclear industrial processes have been observed to concentrate NORM to TENORM, as suggested by [8], the intent of those activities was not designed for such purposes. In so many places, little attention is given to NORM related activities, but as suggested by [9], the environmental and regulatory implications of NORM sites deserve more attention; they argued that this is so because in many cases, the diffused NORM wastes are produced a long time ago and most time is treated as non-radioactive remnant materials; and some industries who produce NORM wastes are not even aware of such production. Radiation monitoring and regulation is well established in the oil and gas sector in Nigeria, but this is not the case in many other sectors like mineral sand processing, quarry sites, scrap yards, etc. In a recent research, the NNRA conducted a survey on occupation dose for nuclear energy related activities [10], such surveys are rarely seen amongst non-nuclear energy related activities. In our area of study, the state government has recently relocated the Nekede mechanic village, and the place is being reclaimed for private settlements. In our previous study [2] on the soil and water physicochemical water parameters and heavy metals, the study shows that the reclaimed land would not be suitable for agricultural and recreational purposes due to the high level of heavy metal contamination. There have been several documentations on the accumulation of NORM to TENORM due to human activities; this concentration poses radiation risks not only to the human population within the affected area but also to the flora and fauna within such area; some of these radionuclides have been found to accumulate in earthworms within such areas [11]. The enhanced radiation due to NORM has become an issue of importance in radiological protection of humans and biota. As such, source characterization, comprising the radionuclide speciation, distribution and mobility analysis, is crucial in the environmental risk and impact assessment [12]. In this study, we intend to establish the radionuclide baseline concentration with at 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm depth profile within the reclaimed mechanic village and assess the radiation hazard indices, this, when combined with our previous study, will provide a holistic view of both radionuclide, heavy metal, and physicochemical parameters state of the reclaimed mechanic village. This will invariably provide a robust data for environmental impact assessment within the area under investigation.
2. Materials and Methods
- Study AreaThe study area is as described in our previous study [2].Sample Collection A total of 15 soil samples were collected within the reclaimed Nekede auto-mechanic village. The soil samples were taken at depths of 10, 20 and 30 cm at each site respectively, using hand – driven soil auger; this was done to determine the radionuclide profiling with depth in the area under investigation. 400 g of each sample were collected with a polythene bag and taken to the laboratory for preparations. The samples were labeled as S1-10 cm, S2-10 cm and S3-10 cm, representing samples from first, second and third locations at 10 cm depth respectively. Another sampling site was chosen as S1-20 cm, S2-20 cm and S3-20cm, representing samples from the three locations at the depth of 20 cm respectively, and lastly S1-30 cm, S2-30 cm and S3-30 cm which represents samples from the three locations at the depth of 30 cm respectively.Sample Preparation for Gamma SpectroscopyAll the samples were sun dried in constant humidity condition for 15 days until a constant weight was achieved. The samples were then sieved using 0.6 mm sieve to remove extraneous materials and sealed in cylindrical plastic containers with appropriate labels and was kept for 30 days to attain secular equilibrium. The gamma spectroscopic analysis was carried out as reported in [7], at the well-established laboratory located at the Centre for Energy Research and Training, Zaria, Nigeria.The gamma-ray spectrometry set-up is made up of a 7.62 cm by 7.62 cm NaI (Tl) detector housed in a 6 cm thick lead shield (to assist in the reduction of the background radiation) and lined with cadmium and copper sheets [13]. The samples were placed on the detector surface and each counted for about 29,000 seconds in reproducible sample detector geometry. The configuration and geometry were maintained throughout the analysis, as previously characterized based on well-established protocol of the laboratory (at the Centre for Energy Research and Training, Zaria). A computer based Multichannel Analyzer (MCA) MAESTRO Programme from ORTEC was used for data acquisition and analysis of gamma spectra. The 1764 keV Gamma-line of 214Bi for 238 U was used in the assessment of the activity concentration of 226Ra, while 2614.5 keV Gamma-line of 208Tl was used for 232Th. The single 1460 keV Gamma-line of 40K was used in its content evaluation. The activity concentration (C) in Bq/kg of the radionuclides in the samples was calculated after decay correction using the expression [14].
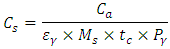 Where
Where 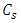 is sample activity concentration,
is sample activity concentration, 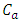 = net peak area,
= net peak area, 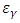 = efficiency of the detector for γ-energy of intensity,
= efficiency of the detector for γ-energy of intensity, 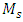 = sample mass,
= sample mass, 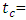 total counting time,
total counting time, 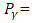 the abundance of the γ-line in a radionuclide.Data AnalysisThe data analysis was performed using MS-EXCEL.Assessment of Radiological HazardTo evaluate the radiation hazard of the gamma rays, due to the occurring radionuclides, the radiation hazard index used is the radium equivalent activity (Raeq) [8]. It provides a useful guideline in regulating the safety standard in dwellings. The radium equivalent concentration
the abundance of the γ-line in a radionuclide.Data AnalysisThe data analysis was performed using MS-EXCEL.Assessment of Radiological HazardTo evaluate the radiation hazard of the gamma rays, due to the occurring radionuclides, the radiation hazard index used is the radium equivalent activity (Raeq) [8]. It provides a useful guideline in regulating the safety standard in dwellings. The radium equivalent concentration 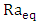 is given by the following relation.
is given by the following relation.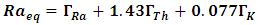 | (1) |
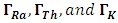 are the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K, respectively.The relation in equation 1 is based on the estimation that 1 Bq/kg of 226Ra, O.7 Bq/kg of 232Th and 13 Bq/kg of 40K produce the same radiation dose rates [13].Estimation of Hazard IndicesActivities carried out in the past at the study area may have contributed to external gamma dose rates. To limit the external gamma-radiation dose due to naturally occurring radionuclides, the following criteria must be satisfied [15].
are the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K, respectively.The relation in equation 1 is based on the estimation that 1 Bq/kg of 226Ra, O.7 Bq/kg of 232Th and 13 Bq/kg of 40K produce the same radiation dose rates [13].Estimation of Hazard IndicesActivities carried out in the past at the study area may have contributed to external gamma dose rates. To limit the external gamma-radiation dose due to naturally occurring radionuclides, the following criteria must be satisfied [15].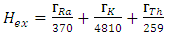 | (2) |
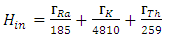 | (3) |
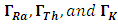 are the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K, respectively.The value of these radiation hazard indices must be less than unity respectively for the radiation hazard to be negligible [16]. When individuals are exposed to these radiations internally, they encounter significant health threats, like certain respiratory diseases like cancer and asthma.Estimation of Radiation dosesEquations 4 and 5 were used to estimate the outdoor annual radiation dose and external outdoor absorbed gamma dose from the radionuclides respectively [17], [18].
are the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K, respectively.The value of these radiation hazard indices must be less than unity respectively for the radiation hazard to be negligible [16]. When individuals are exposed to these radiations internally, they encounter significant health threats, like certain respiratory diseases like cancer and asthma.Estimation of Radiation dosesEquations 4 and 5 were used to estimate the outdoor annual radiation dose and external outdoor absorbed gamma dose from the radionuclides respectively [17], [18].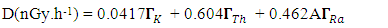 | (4) |
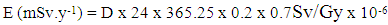 | (5) |
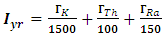 | (6) |
3. Results and Discussion
- The results generated from the spectroscopic analysis of the soil samples from the five selected sites are shown in Table 1. Only the primordial radionuclides—Potassium-40, Radium-226, and Thorium-232 (i.e 40K, 226Ra and 232Th) were observed, thereby suggesting that the auto repair activities did not introduce any anthropogenic source of radiation. The data obtained shows variations in the mean activity concentrations of the analyzed radionuclides with depths. The average Activity profile of 40K were 132.66 ± 5.61 Bqkg-1, 111.95 ± 6.51 Bqkg-1, and 102.88±4.62 Bqkg-1 for 10, 20 and 30 cm depths, respectively. 226Ra average values were 26.38 ± 3.88 Bqkg-1, 32.63 ± 3.88 Bqkg-1, and 30.03 ± 2.27 Bqkg-1 10, 20 and 30 cm depths, respectively.
|
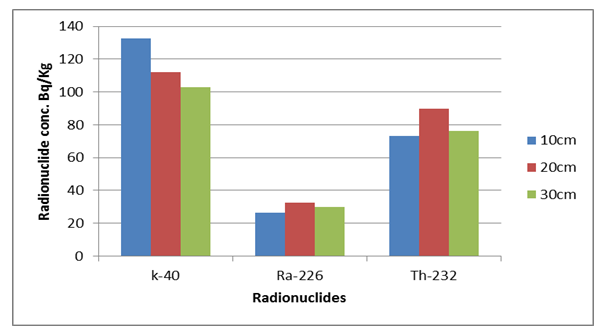 | Figure 1. Average activity profile of the radionuclides with soil depth profile |
|
|
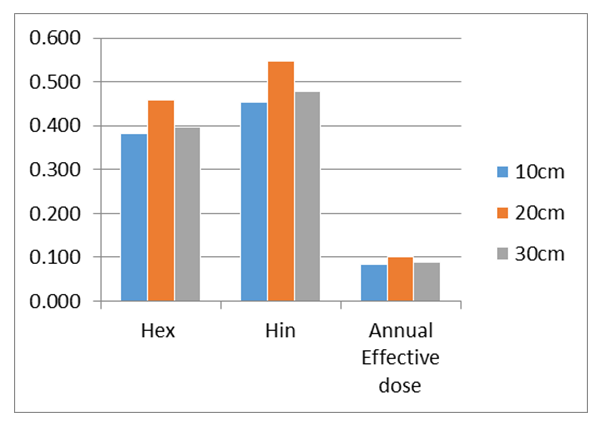 | Figure 2. Distributive pattern of hazard indices with soil depth profile |
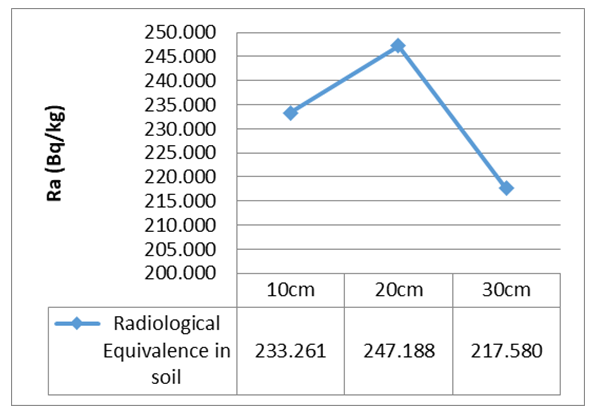 | Figure 3. The calculated Raeq for different lithology of the soil sample |
4. Conclusions
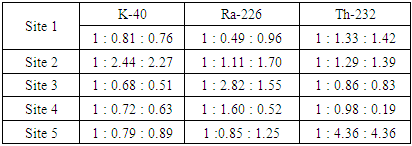
- The profiling of identified radionuclide concentration with depth in the reclaimed auto-mechanic village in Nekede, Imo state Nigeria, has been carried out. It was observed that 40k has relatively high concentration compared to other two identified radionuclides. In terms of depth, relatively high concentration of the natural radionuclides, was observed in 10 cm depth, while 20 cm and 30 cm were just moderately concentrated. However, the radionuclides were observed to be distributed at an irregular pattern down soil lithology, which could be attributed to the mineralogy, carbonate content in the lithology. The average radionuclide levels and calculated health hazard indices of the soil was estimated to be lower than the world standards for such environment and as such exposure to the environment pose no significant health threat to human lives especially those who now dwell within the study area. Hence, the environment is said to be radiologically habitable.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML