-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics
p-ISSN: 2167-6895 e-ISSN: 2167-6909
2014; 4(1): 25-30
doi:10.5923/j.jnpp.20140401.04
Nuclei at or Near Drip-Lines
1Department of Appleid Sciences, RBCEBTW, Mohali-140 104, India
2King's Group of Institutions, Barnala-148 101, India
Correspondence to: M. S. Mehta, King's Group of Institutions, Barnala-148 101, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The magic number and halo and /or skin (neutron) of the nuclei at or near neutron drip-line are studied using axially deformed relativistic mean field model with NL3 and NL3* parameter sets. The density profiles of some of selected nuclei in the light mass region of nuclear landscape are plotted for the purpose. A considerable difference in the densities of neutron and proton can be seen easily in all the cases studied. Also, single particle energy levels show the visible shell gaps at N = 28 and 40 which corresponds the sudden decrease in the two neutron separation energy. The two results are consistent with each other, while the shell gaps corresponding to the numbers N = 32 and 34 seem not to be supporting the magicity at these numbers in the isotopes considered here.
Keywords: Relativistic Mean Field, Shell Structure, Magic Number, Halo, Skin, Drip-line, Quadrupole Deformation
Cite this paper: Harvinder Kaur, M. S. Mehta, Nuclei at or Near Drip-Lines, Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 25-30. doi: 10.5923/j.jnpp.20140401.04.
1. Introduction
- The study of neutron-rich nuclei with unusually large N/Z ratios is challenging the conventional view of nuclear structure. In the recent decades nuclear structure physics has made a considerable progress by the discovery of new phenomena and the emergence of new frontiers. The availability of more energetic beams of short-lived (radioactive) nuclei of the rare isotopes or exotic nuclear beams, has opened up the way for the exploration of the structure and dynamics of nuclei in drip-line regions, where very limited information is available. The advancement in the radioactive ion beam facilities enables us to study the behavior of nuclei near or even beyond the neutron and proton drip-lines and to investigate the emergence of new modes of nuclear behavior.The most fascinating phenomena found in exotic nuclei are the nuclear halo, skin and the new sequence of magic numbers than the nuclei on the beta-stability line of the nuclear landscape. The other interesting features in nuclei close to neutron drip-line are for example largely extended spatial density distribution, coupling of the bound states to the continuum, the Borromean structure etc. The experimental observation of large nuclear matter distribution of 11Li[1] nucleus started the chapter of the exotic properties of the nuclei in the region away from beta-stability line. This new phenomenon was termed as the halo. The definition of a halo nucleus is still being debated, but at least three basic conditions must be fulfilled[2]: (i) low separation energy of the valance particle (or particle clusters); (ii) a wave function be in a low relative angular momentum state (preferably s-wave); (iii) decoupling from the core. The halo structure in nuclei can develop when the system approaches the threshold and the relative motion is not constrained by a strong long-range repulsive force. As a result the tail of the wave function extends out well beyond the region of nuclear interaction, generating an unusual outer region of low nuclear density. The physics of neutron-rich nuclei is one of the current topics in nuclear science. In the past, several theoretical model in relativistic kinematics such as Hartree Bogoliubov with or without the Fock term, Relativistic mean field model with hartree approximation have been developed for a self-consistent description of spherical as well as deformed halo nuclei[3,4]. The reaction cross sections of certain nuclei 6,8He, 11Li[1] and 11,14Be[5] have been found anomalously large. The matter radius of such nuclei is much larger than that of neighboring nuclei. These are the two neutron halo nuclei. Recently, the measurement of nuclear reaction cross-section for 19,20,22C[6] shows that the drip-line nucleus 22C has halo structure. Also, the isotopes of 42,44Mg nuclei close to neutron drip-line also have been predicted[7, 8] to be halo. The nucleus 11Be, 19C, 31Ne are the examples of one-neutron halo nucleus[9, 10]. The density distribution showing an extended tail with a diffused neutron skin and neutron halo can be seen in references[11, 12].The change in magic number is another interesting feature of the nuclei in the drip-line region. It is now established that the dynamic effects of nucleon-nucleon interaction result in the evolution of shell structure and hence the new magic number sequence in drip-line region. The motivation for the present work is the investigation of dynamism of the magic numbers in neutron drip-line to the conventional ones at stability line. The halo structure of nuclei is another property of the nuclei at neutron drip-line. The extent of halo character in the isotopes is varying for different calculations.
2. Formalism
- We use axially deformed relativistic mean field (RMF) model to study the properties of the nuclei. The RMF model has been proved to be a very powerful tool to explain the properties of finite nuclei and infinite nuclear matter[13, 14, 15] for the last two decades. We start with the relativistic Lagrangian density for a nucleon-meson many-body system,
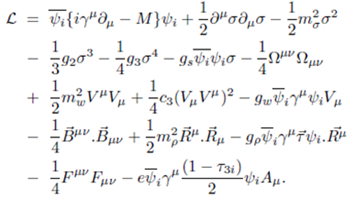 | (1) |
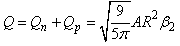 | (2) |
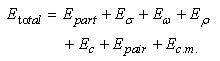 | (3) |
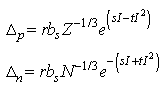 | (4) |
3. Results and Discussion
- In the present calculations we make use of axially deformed relativistic mean field (RMF) model with NL3 (non-linear coupling) and NL3* parameter sets. There are a number of parameter sets used in RMF, out of which NL3[17] and newer set NL3*[18] are found to be producing better results for the calculations of the ground state properties of nuclei. The detail of the parameter sets is shown in Table 1. The parameters are obtained by fitting the nuclear matter properties for closed sell nuclei such as 16O, 40Ca, 48Ca and 208Pb etc.
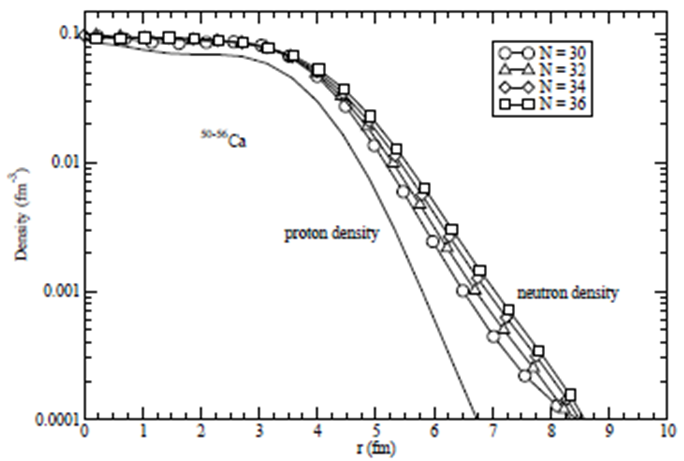 | Figure 1. The density distribution of 50-56Ca nuclei with NL3 parameter set |
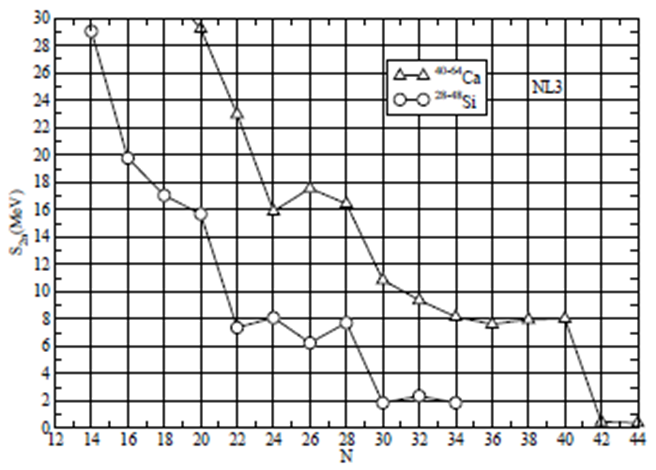 | Figure 2. The two neutron separation energy for Si and Ca-isotopes using NL3 parameter set |
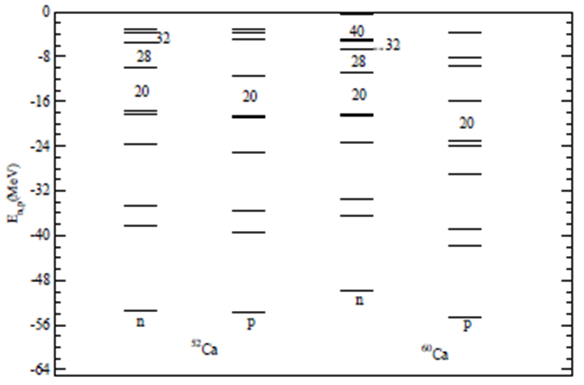 | Figure 3. The single particle energy levels of neutrons and protons for 52,60Ca nuclei using NL3 parameter |
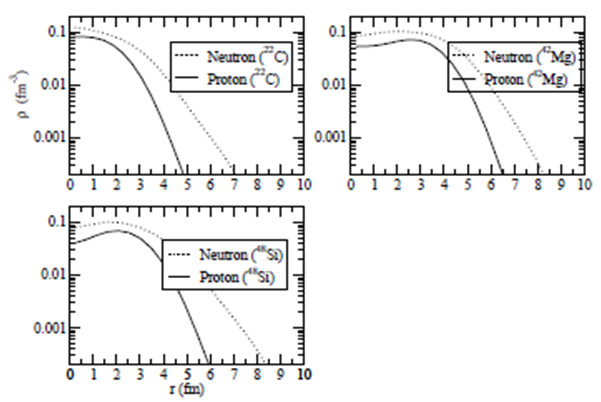 | Figure 4. The density distribution of 22C, 42Mg and 48Si nuclei with NL3 parameter set |
4. Conclusions
- In conclusion, we investigate the quite dramatic changes in the shell structure on nuclei in the neutron drip-line region using axially deformed relativistic mean field model with NL3 and NL3* parameter sets. Here, we investigate the halo character and the magic number in the nuclei close to or on the neutron drip-line. The density profiles show that the nuclei considered here are having considerable difference in the densities of neutron and proton, which is a clear indication of halo structure. The other part of investigation is magic number in this mass region. The figure 3, shows the single particle energy levels of 52Ca and 60Ca for both neutron and proton. There are visible shell gaps at N = 28 and 40 which correspond to the sudden decrease in two neutron separation energy in figure 2. The two results are consistent with each other. The shell gap corresponding to the numbers N = 32 and 34 seem not to be supporting the magicity in these isotopes. The shells at N = 32 or 34 are separated by energy ~1.6 MeV only, as compared to the gaps of ~4.5 MeV at N = 28. The shell gap of ~1.6 is small enough to create the stability required for the number to be a magic number. Therefore, these numbers do not seem show the magic number character.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- One of the authors HK thanks Rayat Bahra Group of Institutes for partial financial support of the present work. MSM thanks Dr. S. K. Patra for the discussion and valuable suggestions.
References
| [1] | I. Tanihata et al., Measurements of Interaction Cross Sections and Nuclear Radii in the Light p-Shell Region, Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 2676 (1985). |
| [2] | J. S. Al-Khalili, An Introduction to Halo Nuclei, Lect. Notes Phys. 651,77 (2004). |
| [3] | J. Meng and P. Ring, Relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov Description of the Neutron Halo in 11Li, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3963 (1996); W. H. Long et al., Relativistic Hartree-Fock-Bogoliubov theory with density dependent meson-nucleon couplings, Phys. Rev. C 81, 024308 (2010). |
| [4] | Y. K. Gambhir, P. Ring and A. Thimet, Relativistic Mean Field Theory for Finite Nuclei, Ann. Phys. 198, 132 (1990). |
| [5] | Tanihata I. et al., Determination of the density distribution and the correlation of halo neutrons in 11Li, Phys. Lett., B 287, 307 (1992). |
| [6] | K. Tanaka et al., Observation of a Large Reaction Cross Section in the Drip-Line Nucleus 22C, Phys. Rev. Lett., 104, 062701 (2010). |
| [7] | L. Li et al., Halos in a deformed Relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov Theory in Continuum, Phys. Rev. C 85, 024312 (2012). |
| [8] | Zhou et al., Odd systems in deformed relativistic Hartree Bogoliubov Thery in Continuum, Phys. Rev. C 82, 011301R (2010). |
| [9] | T. Nakamura et al., Experimental Program on Halo Nuclei with non-accelerated beams, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 262501 (2009). |
| [10] | A. Di Pietro, et. al., Elastic Scattering and Reaction Mechanisms of the Halo Nucleus 11Be around the Coulomb Barrier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 022701 (2010). |
| [11] | I. Tanihata, J. Phys. G, Neutron halo nuclei, 22, 157 (1996); I. Tanihata et al., Measurements of Interaction Cross Sections and Nuclear Radii in the Light p-Shell Region, Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 2676 (1985). |
| [12] | K. Riisager, Nuclear halo states, Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1105 (1994); Tanihata I. et al., Revelation of thick neutron skins in nuclei, Phys. Lett. B 289, 261 (1992); Tanihata I., Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 35, 505 (1995). |
| [13] | R. Machleidt, The meson theory of nuclear forces and nuclear structure, Adv. Nucl. Phys. 19, 189 (1989). |
| [14] | S. K. Patra and C. R. Praharaj One neutron removal reaction using relativistic mean field densities, Phys. Rev. C 44, 2552 (1991). |
| [15] | M. Del Estal, M. Centelles, X. Vi\~nas and Patra S. K., Versatility of field theory motivated nuclear effective Lagrangian approach, Phys. Rev. C 63, 024314 (2001). |
| [16] | D. G. Madland and J. R. Nix, New model of the average neutron and proton pairing gaps, Nucl. Phys. A 476, 1 (1988). |
| [17] | G. A. Lalazissis, J. Konig and P. Ring, Phys. Rev. C 55, 540 (1997). |
| [18] | G. A. Lalazissis, S. Karatzikos, R. Fossion, D. Pena Arteaga, A. V. Afanasjev, and P. Ring, Phys. Lett. B 671, 36 (2009). |
| [19] | Sorlin O. and Porquet M. -G., Nuclear magic numbers: new features far from stability, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 61, 602 (2008); Sorlin O., et al., 68284040: Magicity versus Super fluidity, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 092501 (2002). |
| [20] | R. Krücken, New magic numbers, arXiv:1006.2520 v1[phys.pop-ph], 2010. |
| [21] | A. Ozawa, et al., New Magic Number, N = 16, near the Neutron Drip Line, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5493 (2000); R. Kanungo, I. Tanihata and A. Ozawa, Observation of new neutron and proton magic numbers, Phys. Lett. B 528, 58 (2002). |
| [22] | R. Kanungo, I. Tanihata and A. Ozawa, Observation of new neutron and proton magic numbers, Phys. Lett. B 528 58 (2002); J. I. Prisciandaro et al., Observation of new neutron and proton magic numbers, Phys. Lett. B 510, 17 (2001). |
| [23] | M. Honma, T. Otsuka, B. A. Brown, Mizusaki T., Effective interaction for pf-shell nuclei, Phys. Rev. C 65, 061301(R) (2002). |
| [24] | E. K. Warburton, J. A. Becker, and B. A. Brown, Mass systematics for A=29–44 nuclei: The deformed A∼32 region, Phys. Rev. C 41}, 1147 (1990); A. Poves et al., Nucl. Phys. A 694, 157 (2001). |
| [25] | T. T. S. Kuo, G. E. Brown, Nucl. Phys. A 114, 241 (1968). |
| [26] | H. Nakada, One neutron removal reaction using relativistic mean field densities, arXiv:1003.572v2[nucl-ph], 2010. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML