-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation
p-ISSN: 2163-2405 e-ISSN: 2163-2413
2014; 4(3): 83-91
doi:10.5923/j.jmea.20140403.01
Modelling of Particle Behaviour in Shot Peening Process
Yuki Kato1, Masaki Omiya2, Hiroaki Hoshino3
1Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, 3-14-1, Hiyoshi, Kohoku-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa, 223-8522, Japan
2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Keio University, 3-14-1, Hiyoshi, Kohoku-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa, 223-8522, Japan
3Solver Technology Division, Altair Engineering Ltd., 43F Sunshine 60, 3-1-1, Higashi-Ikebukuro, Toshima-ku, Tokyo, 170-6043, Japan
Correspondence to: Masaki Omiya, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Keio University, 3-14-1, Hiyoshi, Kohoku-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa, 223-8522, Japan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this paper, the numerical modelling for particle behaviours in shot peening process is developed with taking account of interactions between particles and treated materials and between particles. Also, particle acceleration by compressive air is considered. The force acting on shot particles is calculated from the detail analysis of the compressive air flow. The developed model is implemented in multi-body dynamic simulator and the particle behaviours in shot peening process are analysed. The numerical results showed that the particle velocity of shot particles before collision is distributed due to the interactions between particles flying from the nozzle to the specimen. Also, the impact location on the specimen surface is distributed, which is the same trend with the experimental results. Therefore, the developed model is simulated the particle behaviours during shot peening. The particle velocities and the location of impingement obtained by the proposed approach are useful for the initial condition of the following collision analyses.
Keywords: Shot peening, Multi-body dynamics, Particle behavior, Compressive flow, Impact, Numerical simulation
Cite this paper: Yuki Kato, Masaki Omiya, Hiroaki Hoshino, Modelling of Particle Behaviour in Shot Peening Process, Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 83-91. doi: 10.5923/j.jmea.20140403.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Shot peening process has been widely used as one of the most common surface treatments for mechanical and structural components. In this process, a large number of hard shot particles are projected by compressive air at high speed and they impinge on the surface of processed materials. At that time, compressive residual stress and strain hardening are induced in the near surface of treated materials and this treatment improves the fatigue strength of mechanical components.Shot peening process is very complex phenomena, since a large number of particles hit the specimen surface in a short time. Therefore, the surface modification is difficult to estimate. Recently, numerical approach has been taken to predict the surface modification for shot peening processes. Numerical studies about compressive residual stress induced by shot peening process have been conducted by theoretical based analysis [1] and finite element analyses [2-12]. They focused on the collision behaviour between shot particles and treated materials. The study about shot velocities has been carried out by Ogawa et al. [13], and the analyses of modelling particle behaviours by discrete element method have been developed by Bhuvaraghan et al. [14] and Hong et al. [15]. However, they did not consider the forces from compressive air, which strongly affect the particle behaviour before collision. For the application of erosion testing and abrasive air jet machining, the particle collision and particle streams has been simulated by Ciampini et al. [16], Papini et al. [17] and Li et al. [18]. It is noted that the velocity and the size of shot particle in those application is different from the shot peening process.The purpose of this paper is to model shot particles before collision and implement the model into multi-body dynamics simulator. The particle behaviour before collision are modelled by considering all forces acting on shot particles, those are drug force from compressive air, the interactive forces between particles. Then, the motion of shot particles are implemented and calculated by multi-body dynamic simulator.The organization of this paper is followings. To investigate particle behaviours during shot peening in detail, shot peening experiments were carried out. Then, the effects of particle diameter, pressure and the number of particles on impingement behaviours were studied. The developed models were implemented in multi-body dynamics frame work and particle behaviours were simulated and compared with the experimental results.
2. Experimental
2.1. Experimental Set-up
- Shot peening experiments were carried out to investigate the effect of shot conditions such as particle diameter, air pressure and the number of particles on the particle behaviours. The specimen is JIS A5052 (ASTM 5052) aluminium alloy plate. The size of the specimen was 100 mm x 100 mm in plane, and the thickness of the specimen was 10 mm. Shot particles were JIS SUJ-2 (ASTM 52100) high carbon-chromium bearing steel and the sphericity of shot particles is 0.5. The experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 1 [19]. Pressure gauge was set at the upper side of compressor tank. The acceleration length in the nozzle, ln, is 40 mm, and its diameter, d, is 6 mm as shown in Figure 2. Distance from the nozzle tip to the specimen, l, is 100 mm. Shot particles are supplied from the supply inlet of the nozzle. The limitation of the experimental set-up is treated time because the particles are supplied from the inlet by hand. Usually, commercially available shot peening machine shot the particle continually for a long time. However, for this model apparatus, the number of particles in one shot is limited.
 | Figure 1. Experimental setup for shot peening process |
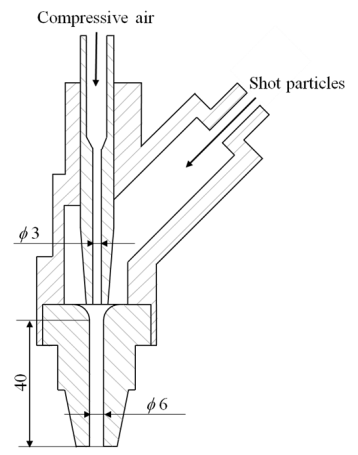 | Figure 2. Sectional view of the nozzle |
|
2.2. Experimental Results
- The distance from the indentation of the particle impingement to the centre of specimen was measured by image analyses. The experimental results were shown by histogram of 5 mm intervals from Figure 3 to Figure 5. Figure 3 shows the effect of air pressure on the impact location. Most particles hit the specimen surface within 20 mm from the centre of specimen. When the air pressure is lower, the surface impact location is broader. Figure 4 shows the effect of shot diameter on the impact location. When the diameter of the shot particle is smaller, the indentation of the particle impingement is broader. Figure 5 also shows the experimental results that single particle experiments and multi-particles experiments are compared. For multi-particles, the impact location is broader due to the collision between particles.
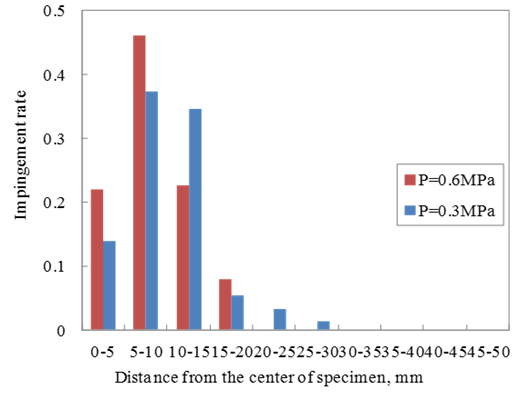 | Figure 3. The effect of air pressure on the impact location on specimen |
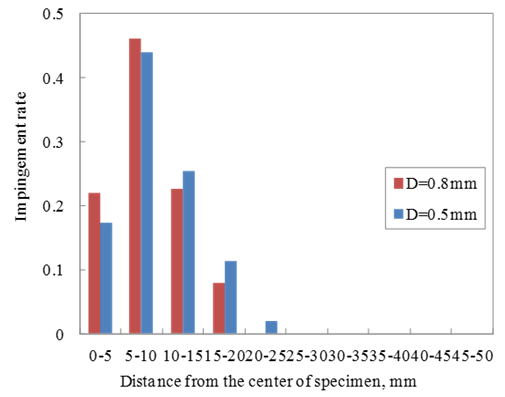 | Figure 4. The effect of shot diameter on the impact location on specimen |
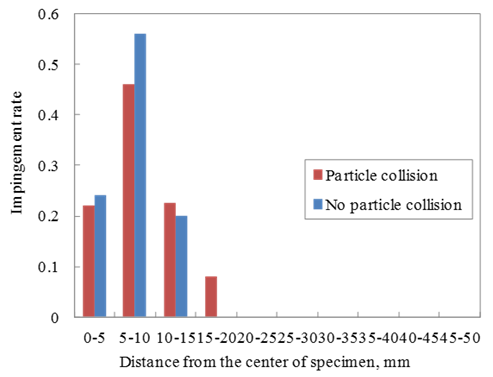 | Figure 5. The effect of particle collision on the impact location on specimen |
3. Modeling of Particle Behavior
- To make detail modelling about particle behaviours, the jet flow from the nozzle is considered. After blasting air from the nozzle, turbulent jets form three types of regions that are potential core region, mixing region and developed region [18, 20-22]. Particles are accelerated by the jet flow when they pass through these regions. We also focus on the interactive force between particle and specimen and between particles. The interactive force was modelled by using Hertzian contact theory [23, 24].
3.1. Equation of Motion for Shot Particles
- The structure of the turbulent jet flows is described in Figure 6 [20, 21]. In its initial stage of development, a region near the nozzle exit and along the center of the jet is called as the potential core region. In this region, mean velocity was assumed to be constant. The region that the potential core region is surrounded with is the mixing region. Over some distance from the nozzle, the jet becomes a fully developed and forms the developed region. The distance at the end of potential core region from the nozzle exit can be described as 5d, where d is the diameter of the nozzle [21].
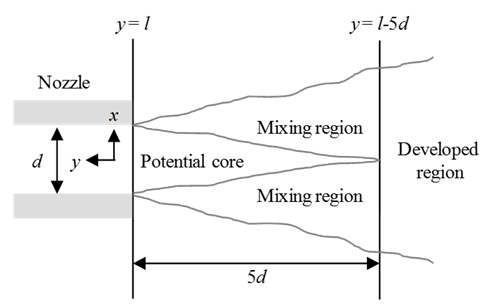 | Figure 6. The structure of turbulent jet flow |
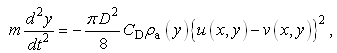 | (1) |
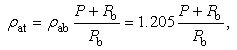 | (2) |
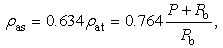 | (3) |
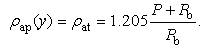 | (4) |
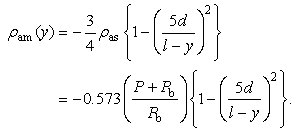 | (5) |
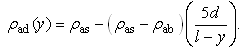 | (6) |
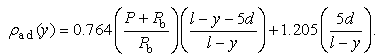 | (7) |
3.1.1. Air Velocity in Each Region
- If a0 is the speed of sound and the flow is isentropic, air velocity at the nozzle exit, ui, can be written as,
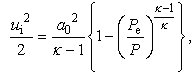 | (8) |
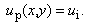 | (9) |
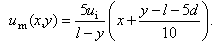 | (10) |
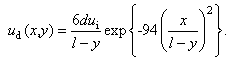 | (11) |
3.1.2. Governing Equations in Each Region
- The governing equation of particle motion in the potential core region can be obtained by substituting Eqs. (4) and (9) into Eq. (1) like,
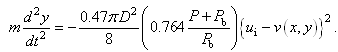 | (12) |
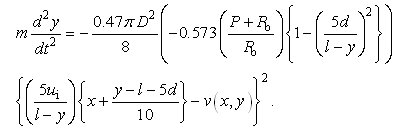 | (13) |
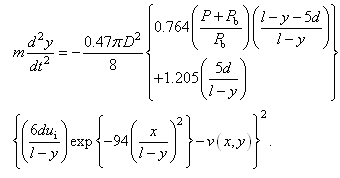 | (14) |
3.2. Horizontal Force Acting on Shot Particles
- Horizontal force acting on shot particles was considered after shot particles pass through the nozzle. Streamline of the jet is tilted toward horizontal direction. Angle αin Figure 7, which is the angle between path line and vertical line, means divergence angle. The magnitude of tanα can be obtained from the ratio of air velocity of horizontal direction ux divided by air velocity of vertical direction uy, and this is equal to 0.10.
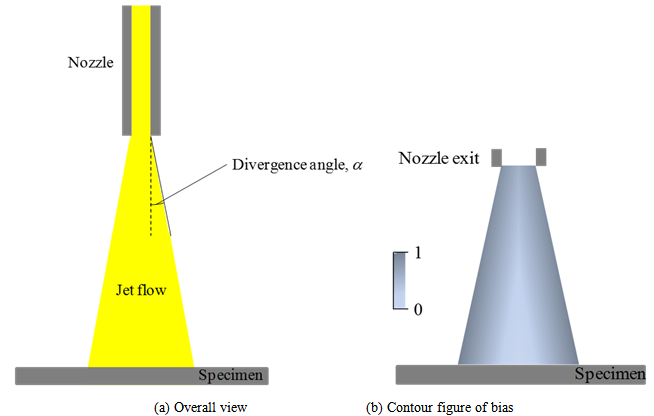 | Figure 7. The divergence of the jet |
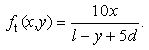 | (15) |
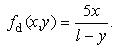 | (16) |
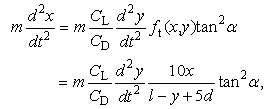 | (17) |
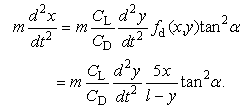 | (18) |
3.3. Interactive Force between Shot Particle and Specimen
- As mentioned above, interactive force between shot particle and specimen can be modelled by Hertzian contact theory [23, 24]. In Hertzian contact theory, contact force can be modelled by non-linear dashpot and non-linear spring as shown in Figure 8. The equation of motion for particles during collision can be described as,
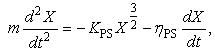 | (19) |
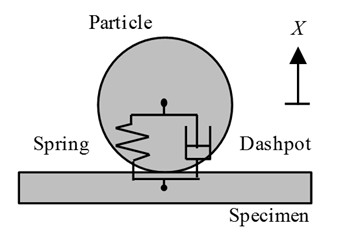 | Figure 8. Modelling of Hertzian contact between particle and specimen |
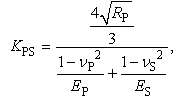 | (20) |
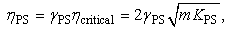 | (21) |
3.4. Interactive Force between Shot Particles
- Interactive force between shot particles can also be modelled by Hertzian contact theory [23, 24]. Colliding force between shot particles can also be modeled by dashpot and spring. The equation of motion for particles during collision can be described as,
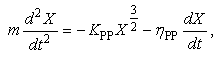 | (22) |
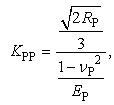 | (23) |
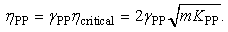 | (24) |
3.5. Numerical Model and Conditions
- The above forces acting on particles were implemented in Multi-body dynamics simulator, MotionSolve (Altiar Engineering) and the equation of motion was solved. Figure 9 shows the numerical model of particle projection. 30 particles set in the side of nozzle randomly. Because there assumed to be the effect of jet entrainment [31], particles were set in the x-direction from 1.5 to 3.0 randomly. The initial velocity of each particle is zero at the nozzle inlet. Governing equation of motion for particles in the nozzle is equal to Eq. (12). Parameters used in numerical simulation are shown in Table 2. Calculations were conducted more than 5 times by changing the initial location of particles.
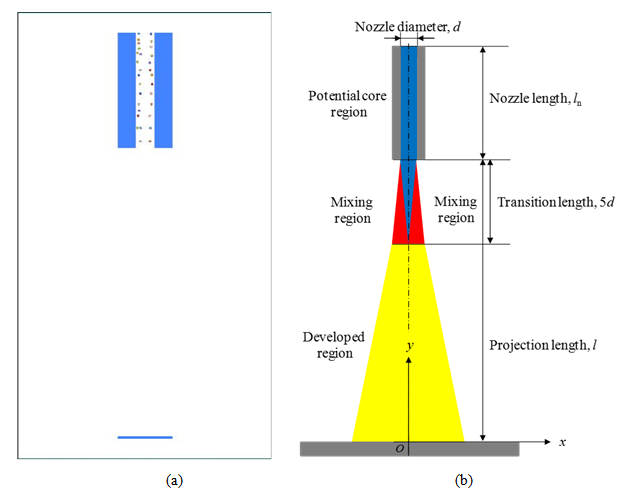 | Figure 9. (a) Initial distribution of shot particles in the nozzle. (b) Overview of turbulent jet |
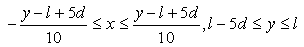 | (25) |
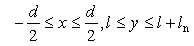 | (26) |
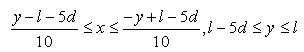 | (27) |
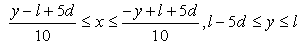 | (28) |
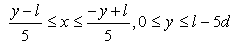 | (29) |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Particle Projection
- Figure 10 shows particle projection. Due to the interaction between particle and compressive air, particles were accelerated by compressive air depending on where particles pass through in the compressive air region. Figure 11 focuses on the velocity variation from the nozzle inlet to the specimen surface. This is the verification of velocity variation in each region. Similar velocities has been experimentally observed by Maeda et al. [32]. In this figure, the case of non-collision between particles and the case of collision among particles are also compared. Velocity of collision particles are varied by the collision between particles.
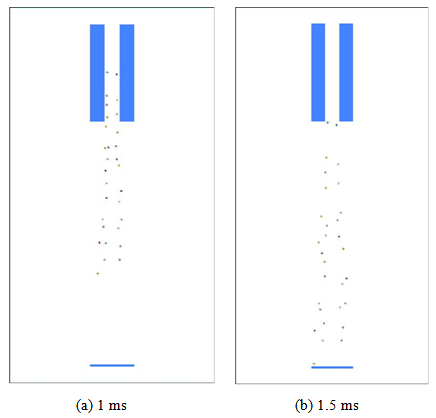 | Figure 10. Particle projection at (a) 1 ms and (b) 1.5 ms |
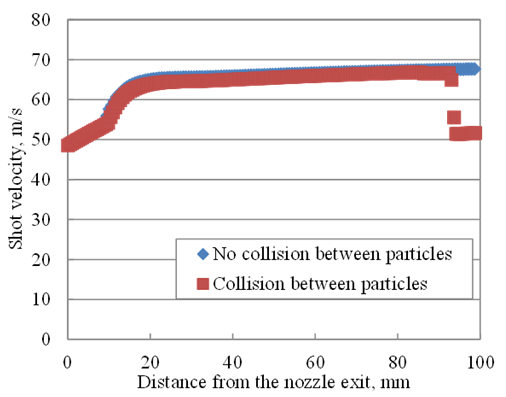 | Figure 11. Particle velocity variation |
4.2. Particle Velocity and Impingement Location
- The particle velocities for y-direction just before impingement are shown by histogram of 5 m/s intervals in Figure 12. About 65% of particles have the velocities between 60 and 80 m/s. But, about 16% of particles were slower than 60 m/s or higher than 80 m/s. Another 19% of particles did not collide with specimen, and their trajectories varied dramatically. This is the effect of the collision among particles. From the calculation of single particle shot, the impingement velocity was about 65 to 70 m/s. When the collisions between particles occur, the particle velocity was changed. Thus, it can be said that the distribution of impingement velocity is due to the collision between particles. Similar trend has been experimentally observed by Shipway and Hutchings [33].
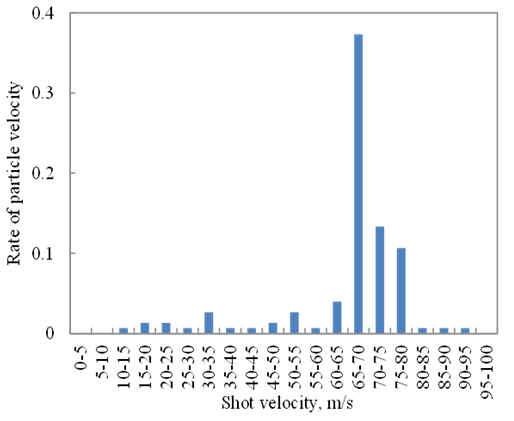 | Figure 12. Histogram of impingement velocities of particles |
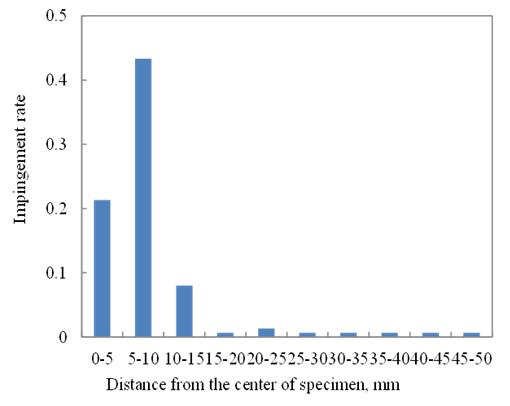 | Figure 13. Histogram of impact location of particles |
5. Conclusions
- In this paper, the numerical simulations of shot peening process by multi-body dynamics were carried out. Special contribution of this paper is the detail modelling about the interaction between shot particles and compressive air. Particle interactions are also modeled by Hertzian contact theory. The numerical results were compared with the experimental results. Results obtained in this paper are summarized as the followings.1. Considering acting forces on the shot particle from the jet flow of compressive air, equation of motion was derived and implemented in multi-body dynamics simulation.2. Distribution of impingement velocity can be found. This phenomenon is caused by the collision between particles.3. Distribution of particle impingement location can also be observed. The peak of the impingement rate is 5 to 10 mm from the center of the nozzle. This result is identical to the experimental results.The particle velocities and the location of impingement obtained by the proposed approach are useful for the initial condition of the following collision analyses, such as finite element analyses.The future work of this study is the direct comparison between experimental and numerical results. The shot particles can be observed by a high speed camera and the results will be reported elsewhere [34].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledge the Academic Open Program of Altair Engineering Inc. for using HyperWorks software.
References
| [1] | K. Ogawa, T. Asano, Theoretical Prediction of Residual Stress Induced by Shot Peening and Experimental Verification for Carburized Steel, Japan Society of Materials Science, 48 (1999) 1360-1366. |
| [2] | T. Hong, J.Y. Ooi, B. Shaw, A numerical study of the residual stress pattern from single shot impacting on a metallic component, Advances in Engineering Software, 39 (2008) 743-756. |
| [3] | M. Guagliano, Relating Almen intensity to residual stress induced by shot peening: a numerical approach, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 110 (2001) 277-286. |
| [4] | G.I. Mylonas, G. Labeas, Numerical modeling of shot peening process and corresponding products: Residual stress, surface roughness and cold work prediction, Surface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2011) 4480-4494. |
| [5] | B. Bhuvaraghan, S.M. Srinivasan, B. Maffeo, Numerical simulation of Almen strip response due to random impacts with strain-rate effects, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 53 (2011) 417-424. |
| [6] | B. Yildirim, S. Muftu, A. Gouldstone, Modeling of high velocity impact of spherical particles, Wear, 270 (2011) 703-713. |
| [7] | A. Gariepy, S. Larose, C. Perron, M. Levesque, Shot peening and peen forming finite element modeling – Towards a quantitative method, International Journal of Solids and Structures, 48 (2011) 2859-2877. |
| [8] | H.Y. Miao, S. Larose, C. Perron, M. Levesque, On the potential applications of a 3D random finite element model for the simulation of shot peening, Advances in Engineering Software, 40 (2009) 1023-1038. |
| [9] | T. Kim, J.H. Lee, H. Lee, S. Cheong, An area-average approach to peening residual stress under multi-impacts using a three-dimensional symmetry-cell finite element model with plastic shots, Materials and Design, 31 (2010) 50-59. |
| [10] | H.Y. Miao, S. Larose, C. Perron, M. Levesque, An analytical approach to relate shot peening parameters to Almen intensity, Surface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2010) 2055-2066. |
| [11] | G.H. Majzoobi, R. Azizi, A. Alavi Nia, A three-dimensional simulation of shot peening process using multiple shot impacts, Journal of Material Processing Technology, 164-165 (2005) 1226-1234. |
| [12] | S.M. Hassani-Gangaraj, M. Guagliano, G.H. Farrahi, Finite element simulation of shot peening coverage with the special attention on surface nanocrystallization, Procedia Engineering, 10 (2011) 2464-2471. |
| [13] | K. Ogawa; T. Asano; A. Saito; K. Kawamura; M. Ogino; H. Aihara: Measurement and Analysis of Shot Velocity in Pheumatic Shot Peening. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 60 C (1994) 1120-1125. |
| [14] | B. Bhuvaraghan, S.M. Srinivasan, B. Maffeo, R.D. McCLain, Y. Potdar, O. Prakash, Shot peening simulation using discrete and finite element methods, Advances in Engineering Software, 41 (2010) 1266-1276. |
| [15] | T. Hong, J.Y. Ooi, B. Shaw, A numerical simulation to relate the shot peening parameters to the induced residual stresses, Engineering Failure Analysis, 15 (2008) 1097-1110. |
| [16] | D. Ciampini, J.K. Spelt, M.Papini, Simulation of interference effects in particle streams following impact with a flat surface Part I. Theory and analysis, Wear, 254 (2003) 237-249. |
| [17] | M. Papini, D. Ciampini, T. Krajac, J.K. Spelt, Computer modelling of interference effects in erosion testing: effect of plume shape, Wear, 255 (2003) 85-97. |
| [18] | H.Z. Li, J. Wang, J.M. Fan, Analysis and modelling of particle velocities in micro-abrasive air jet, International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 49 (2009) 850-858. |
| [19] | ISO 26910-1:2009, Springs – Shot peening – Part 1: General procedures. |
| [20] | N. Rajaratnaum, Turbulent Jets, Elsevier, 1976. |
| [21] | T. Shakouchi, Jet Flow Engineering –Fundamentals and Application–, Morikita, 2004. |
| [22] | A. Sarkar, R.P. Singh, Air impingement technology for food processing: visualization studies, Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und-Technologie, 37 (2004) 873-879. |
| [23] | K.L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, 1985. |
| [24] | D. Maugis, Contact Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids, Springer, 203 (1999). |
| [25] | F.M. White, Fluid Mechanics, Six Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008. |
| [26] | K. Aoki, K. Muto, H. Okanaga, Effects of dimples for drag and lift on a sphere with rotation, Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 77 C (2011) 793-802. |
| [27] | J.B. Barlow, M.J. Domanski, Lift on stationary and rotation spheres under varying flow and surface conditions, AIAA Journal, 46 (2008) 1932-1936. |
| [28] | Y. Tsuji, T. Tanaka, T. Ishida, Lagrangian numerical simulation of plug flow of cohesionless particles in a horizontal pipe, Powder Technology, 71 (1992) 239-250. |
| [29] | C.X. Wong, M.C. Daniel, J.A. Rongong, Energy dissipation prediction of particle dampers, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 319 (2009) 91-118. |
| [30] | A. Aryaei, K. Hashemnia, K. Jafarpur, Experimental and numerical study of ball size effect on restitution coefficient in low velocity impacts, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 37 (2010) 1037-1044. |
| [31] | D.J. Tritton, Physical Fluid Dynamics, Second Edition, Oxford University Press, 1988. |
| [32] | H. Maeda, N. Egami, C. Kagaya, N. Inoue, H. Takesita, K. Ito, Analysis of Particle Velocity and Temperature Distribution of Struck Surface in Fine Particle Peening, Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 67 C (2001) 306-312. |
| [33] | P.H. Shipway, I.M. Hutchings, A method for optimizing the particle flux in erosion testing with a gas-blast apparatus, Wear, 174 (1994) 169-175. |
| [34] | Y. Aiba, K. Murai, M. Omiya, J. Komotori, Observation of Particle Behavior in Fine Particle Peening process, Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Shot Peening (ICSP2014), Goslar, Germany, September 15-18, (2014). |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML