-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Laboratory Chemical Education
2014; 2(2): 28-32
doi:10.5923/j.jlce.20140202.05
Noble Metal Nanoparticles Synthesized by Chemical Reduction: Undergraduate Experiments for Nanomaterials
Ning Sui1, Xinghua Li1, Manhong Liu1, Hailian Xiao1, Yingjing Jiang1, Jun Zhao1, 2, William W. Yu1, 2
1College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042, China
2Department of Chemistry and Physics, Louisiana State University Shreveport, LA 71115, USA
Correspondence to: William W. Yu, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Several noble metal nanoparticles were prepared using simple chemical reduction of the corresponding metal salts with proper stabilizers and solvents. The formation process for metal nanoparticles was monitored by ultraviolet–visible absorption spectra. The morphology and particle size of the metal nanoparticles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy. Data and error analyses were practiced for the average particle size measurements.
Keywords: Nanomaterial, Nanoparticle, Chemical reduction, Metal colloid
Cite this paper: Ning Sui, Xinghua Li, Manhong Liu, Hailian Xiao, Yingjing Jiang, Jun Zhao, William W. Yu, Noble Metal Nanoparticles Synthesized by Chemical Reduction: Undergraduate Experiments for Nanomaterials, Journal of Laboratory Chemical Education, Vol. 2 No. 2, 2014, pp. 28-32. doi: 10.5923/j.jlce.20140202.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Nanoscience deals with materials with nanometer scale, that is, approximately 1 to 100 nm. Properties of metal nanoparticles are different from those of bulk materials made from the same atoms. The experiments described are meant to be a resource that allows students with chemistry background to understand some of the foundations and exciting advances in the area of nanoscience. Applications of nanotechnology, which are already emerging, are highly interdisciplinary and include virtually many fields in engineering and the natural sciences. Therefore, this project also constitutes an effort to stimulate faculty collaboration in program and curriculum development.The work presented here aims at the development of an integrated research-education activity on noble metal nanoparticles. In recent years, there has been great interest and significant progress in the synthesis of various shapes and sizes of nanosized metal nanoparticles dispersed in solution. [1] Metal nanoparticles exhibit unique properties and potential applications in several areas such as catalysis, optoelectronics, microelectronics, magnetics and others, [2–8] which cannot be achieved by their bulk counterparts. For example, nanoscale gold metal particles often have reddish colors due to their absorption of light by their plasma (collective free-electron oscillations within the particles). [9] The reddish colors associated with small gold particles have been known for centuries, for example, in aqueous suspensions used for medicinal purposes and in glass objects where the particles were used for pigmentation [9-12]. Silver nanoparticles often have yellowish colors and have also been used to color glass. [11, 12] Solution dispersible metal nanoparticles stabilized by polymers, surfactants, organic ligands, and polyoxometallates have been adopted as effective quasi-homogeneous catalysts for many catalytic reactions, such as hydrogenation of various unsaturated organic compounds, [13-15] reduction of carbon dioxide, [16] hydration of acrylonitrile to acrylamide, [17] Heck reaction, [18] coupling reactions, [19] and visible light-induced hydrogen evolution.[20] Therefore, noble metal nanoparticles become an active research subject in some important fields.Chemical reduction is an important reaction and is widely used for the preparation of the metals. In this laboratory experiment, chemical reduction is adopted to synthesize solution dispersible metal nanoparticles (colloidal nanoparticles). The goal of this experiment is to apply a reliable procedure for preparing noble metal nanoparticles to train and lead the undergraduate students understand and master the basic principles, the steps of chemical reduction, and the advanced knowledge in nanoscience. This experiment is suitable for undergraduate students in the study of general chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry.The determination of an optimal set of conditions for the synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles is described below. This easy and convenient method uses dilute aqueous solutions, can be done on the lab bench, and requires simple equipment such as a magnetic stirrer. The characterization of the noble metal nanoparticles by ultraviolet–visible absorption spectrophotometer (UV-Vis absorption), X-Ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), and transmission electron microscope (TEM) benefits the students by exposing them to a few important instruments that often widely used in the future academic research or industrial work.
2. Experiment Description
2.1. Materials
- Poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) (PVP, K-30), silver nitrate (AgNO3, 99.8%), Hexachloroplatinic acid (H2PtCl6·6H2O, 98.5%), chloroauric acid (HAuCl4·3H2O, 99%) and ruthenium chloride hydrate (RuCl3·nH2O, Ru content would be determined through a literature method [21]) are commerical products purchased from Aldrich. Other reagents were of analytical grade and used without further purification.The water used for this experiment was Millipore grade (with >18.2 MΩ cm resistivity); however, good results were attainable with water purified by high-quality reverse osmosis.
2.2. Instruments and Characterization
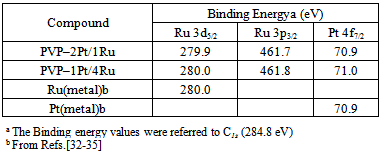
- UV-Vis absorption spectra were recorded on a Varian Cary 500 UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometer; 1 mL of the colloidal nanoparticle solution was diluted to 5 mL with distilled water before measurement.Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photographs were taken by using a JEOL-2100 electron microscope. Specimens were prepared by placing a drop of the colloidal dispersion on a copper grid covered with a perforated carbon film and then evaporating the solvent. The particle diameters were measured from the enlarged TEM photographs. The particle size distribution histogram was obtained on the basis of the measurements of about 300–400 particles.X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was obtained using an Axis Ultra spectrometer (Kratos, UK). A mono Al-Kα (1486.6 eV) X-ray source was used at a power of 225 W (15 kV, 15 mA). To compensate for surface charge effects, binding energies were calibrated using C1s hydrocarbon peak at 284.8 eV. The samples were prepared by drying the colloidal nanoparticle dispersion via rotatory evaporation.
3. Experimental Procedure
3.1. Preparation of Colloidal Metal Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Preparation of PVP–stabilized Pt Colloidal Nanoparticles
3.1.1.1. Preparation of PVP–stabilized Pt Colloidal Nanoparticles by Conventional Heating Method
- In a 100 mL round-bottom flask, 1.00 ×10−4 mol H2PtCl6 and 2.00 ×10−3 mol (as monomeric unit) PVP were dissolved in a mixture of 30 mL methanol and 30 mL water. The solution was heated up rapidly to ebullition and kept on refluxing under vigorous stirring. After the mixture was refluxed for about 25 min, the color of the solution changed from yellow to dark brown instantaneously. The metal colloids (PVP–Pt) were obtained by refluxing the solution for another 2.5 h.
3.1.1.2. Preparation of PVP–stabilized Pt Colloidal Nanoparticles by Microvwave Irradiation
- The preparation was carried out in microwave oven. 0.4 g PVP, 1.00 ×10−5 mol metal precursor H2PtCl6 were dissolved in 20 mL water (PVP-stabilized Au or Ag colloidal nanoparticles were also prepared by using corresponding metal precursors, e.g. HAuCl4 or AgNO3, see supporting information). After microwave irradiation for 3 min, PVP-stabilized metal colloidal nanoparticles were obtained.
3.1.2. Preparation of PVP–stabilized Pt/Ru Bimetallic Colloidal Nanoparticles
- PVP (0.146 g, 1.31 ×10−3 mol as monomeric unit), RuCl3·nH2O and H2PtCl6·6H2O with a total amount of 6.55×10−5 mol were dissolved in a mixed solvent of water and ethanol (the volume ratio was 9:1) in a 100 mL round-bottomed flask to form a dark red homogeneous solution. The total volume of the solution was 56 mL. This solution was heated to ebullition and kept refluxing under vigorous stirring. A homogeneous dark brown solution of colloidal dispersion of PVP–Pt/Ru was obtained after 3 h.
3.2. UV-Vis Spectra of Metal Colloidal Nanoparticles
- Several characterization methods were used to analysis the formation and the morphology of noble metal colloidal nanoparticles. The instructors can choose one or more methods depending on their availability and the related course materials. PVP–Pt/Ru colloidal nanoparticles were used as typical examples in this paper.The color change of these metal nanoparticles in the preparation process was observed. The solution of the corresponding metal salts was heated quickly to ebullition (normally in 5 min) and kept refluxing for 3 h. During the course of heating, we observed a successive color changes for the reaction solution; the final color of the solution of PVP–Pt/Ru colloidal nanoparticles was dark brown. The following color changes were observed in the cases of PVP–2Pt/1Ru (molar ratio of Pt:Ru = 2:1) and PVP–1Pt/2Ru (molar ratio of Pt:Ru = 1:2) nanoparticles (Schemes 1 and 2).
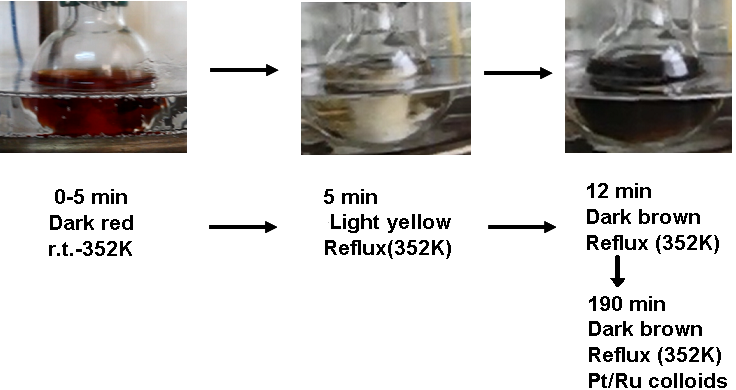 | Scheme 1. Color changes of the reaction solution during the synthesis of PVP–2Pt/1Ru nanoparticles |
 | Scheme 2. Color changes of the reaction solution during the synthesis of PVP–1Pt/2Ru nanoparticles |
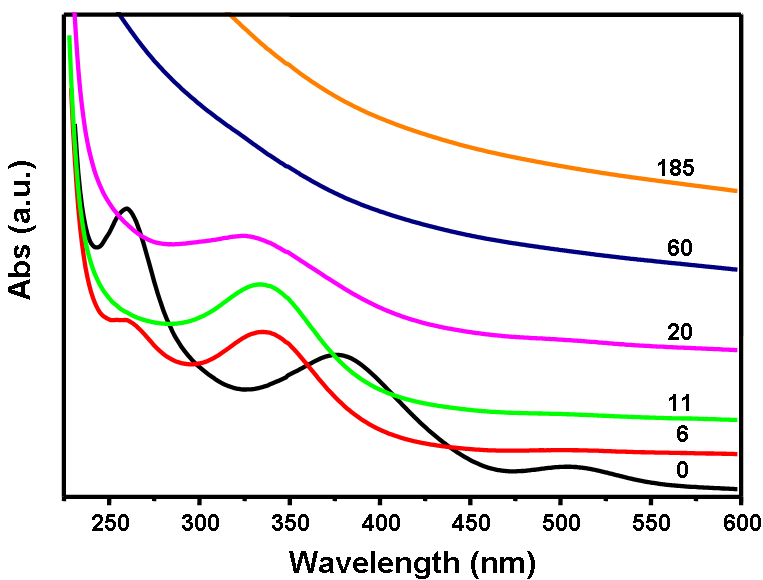 | Figure 1. UV-Vis absorption spectra of the reduction of H2PtCl6 and RuCl3 in an ethanol-water system |
3.3. TEM Characterization of Metal Colloidal Nanoparticles
- The dependence of particle size and morphology on the molar ratio of Pt/Ru was examined by TEM. Table 1 lists the average diameters (d) and standard deviations (σ) of PVP–Pt/Ru colloids. A representative TEM photograph and the corresponding histogram are given in Figure 2. According to the molar ratios of Pt to Ru in the preparation, the obtained colloidal nanoparticles were named as 4Pt/1Ru, 2Pt/1Ru, 1Pt/1Ru, 1Pt/2Ru, and 1Pt/4Ru. The particles had small sizes of 2.1 – 2.8 nm in average and no particle bigger than 4.5 nm was observed. Their standard deviations were 0.35 – 0.47 nm.
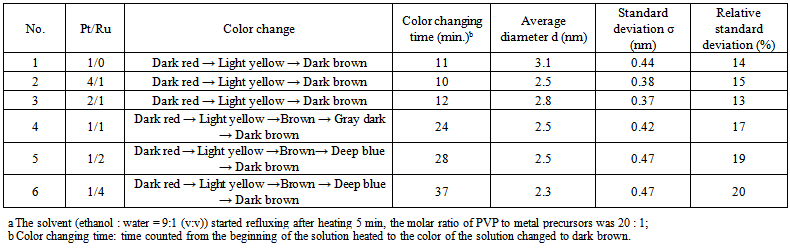 | Table 1. Formation of PVP–Pt/Ru colloidal nanoparticles |
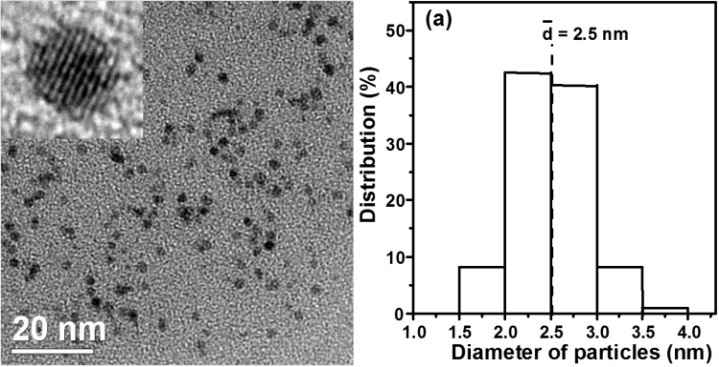 | Figure 2. TEM photograph (left) and the corresponding particle size distribution histogram (right) of PVP-Pt/Ru nanoparticles (inset: HRTEM photograph of a particle) |
|
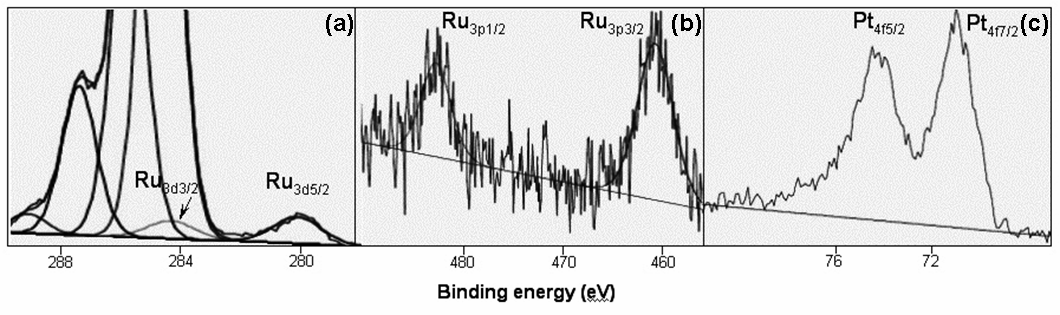 | Figure 3. XPS spectra of PVP-1Pt/4Ru: a) Ru3d5/2 and Ru3d3/2, b) Ru3p3/2 and Ru3p1/2, c) Pt4f7/2 and Pt4f5/2 |
4. Application of the Obtained Metal Nanoparticles
- These metal nanoparticles can be further used as nanocatalysts for converting organic environmental pollutants [31-33] or synthesizing organic intermediates [14, 34-36]. These catalytic experiments are performed at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, making them suitable for physical chemistry and materials chemistry laboratories.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (21301103, 21077062, 51272084, 21105053, 61225018), the Taishan Scholarship, the Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2012FZ007), the 47th Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, the Shandong Province High Education Research and Development Program (J13LA08), and the LSUS Foundation (F57-10-6100).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML