-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Game Theory
p-ISSN: 2325-0046 e-ISSN: 2325-0054
2014; 3(1): 7-10
doi:10.5923/j.jgt.20140301.02
The RBI Coordination of Exchange Rate Intervention and Foreign Exchange Market
A. Vadivel
Institute of Economic Growth, University of Delhi Enclave, 110007, New Delhi
Correspondence to: A. Vadivel, Institute of Economic Growth, University of Delhi Enclave, 110007, New Delhi.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) explores coordination of exchange rate intervention in the foreign exchange market with other central banks in order to reduce exchange rate volatility. The present study found that the coordinated exchange rate intervention had reduced exchange rate volatility compare than unilateral exchange rate intervention.
Keywords: Exchange Rate, Nash Equilibrium, Coordinate Intervention, Mixed Strategy
Cite this paper: A. Vadivel, The RBI Coordination of Exchange Rate Intervention and Foreign Exchange Market, Journal of Game Theory, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2014, pp. 7-10. doi: 10.5923/j.jgt.20140301.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Official exchange rate intervention in the foreign exchange markets by the monetary authority involved in selling and buying foreign currency assets against its own currency. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been using intervention tools as a foreign currency asset to stabilize exchange rate volatility. The foreign currency assets comprised of US dollars, Pound Sterling, Euro and Japanese Yen. However it is not included gold, special drawing rights (SDR) and IMF trench position (RBI) as an intervention instruments. Basu[2] introduced “schedule intervention” is tried to alter the exchange rate volatility. So this study has proposing the ‘multiple schedule intervention’ is various central banks intervening in the foreign exchange market reduces it volatility. Even though the central banks intervene in the exchange rate it could not stabilize because of external factors (cross border capital flows). However flexible exchange rate system can be sustained indefinitely in the absence of a speculative attack can succumb to adverse market sentiments Obstfeld[17]. The central bank intervened in the foreign exchange market after the break down of the fixed exchange rate system into the flexible exchange rate system. The Plaza and the Louvre agreements early 80’s the developed countries have accepted coordinated intervention in the foreign exchange market. After 90’s secret trade took place by the Federal Reserve Bank and the Bank of Japan. Further, in 2000 the European Central Bank led to coordinated intervention and also in 2004 by the Bank of Japan Ferre and Manzano[8]. The coordination of central bank’s intervention is maximizing its own profit out of intervention Edison[6]. But informal signal gives the exchange rate would fail to stabilize the external currency values Mussa[15]. Often the monetary authority directly or indirectly intervenes in the foreign exchange markets ‘try to trim’ the exchange rate volatility. So there is problem with central bank intervention in the foreign exchange markets. The present study is exploring coordination of game theory in the foreign exchange markets, which explains tradeoff between exchange rate and intervention. The country’s central bank has been actively traded to reduce exchange rate volatility as well to ensure orderly condition of exchange rate. In the context of coordination intervention in the foreign exchange markets achieves payoff matrix. However, coordination of exchange rate intervention of the central bankers actively engaged on selling and buying foreign currency assets. They met coordination pay off between traders since the domestic currency appreciation (depreciation). The global game theory developed by Carlsson and van Damme[3, 4] has taken on course in laboratory experiments with public and private information. There was limited evidence was supporting public information that destabilizes the economy by creating self-fulfilling belief. Morris and Shin[16] they revealed that trader does not have common knowledge that leads to information asymmetric. However, the common knowledge is helpful to have a coordinated intervention strategy among the central banks to stabilize the exchange rate volatility. Beine et.al[1] studied the Bank of Japan and the federal reserve bank was jointly intervenes from January 1, 1989 to May 31, 2003 the duration was 72 days and Bank of Japan was intervenes 227 days. Moreover Fukao[7]; Morris and Shin[16] suggested private information on the state of the economy to maintain the equilibrium and if the traders are attack the exchange rate through speculation might disorder the equilibrium. Morris and shin[16] and Hellwig[14] revealed that the private information has to stabilize markets then the public information. If this information mismatched they met disequilibrium among coordination of exchange rate intervention. Rubinstein[21] suggested that the common knowledge predictions may not be robust because they expecting more rational from the agents. His Email game trading could not hold in real life. Carbrales et.al.[3] The risk dominated equilibrium predicted by the global game theory. There is no such study about the coordination of exchange rate intervention in the foreign exchange market in India. This study uses Nash equilibrium in the foreign exchange markets, which implies that the RBI’s intervention can reduce exchange rate volatility. The remaining of the paper is organized as follows: Section 3 deals with pure strategy for how the RBI deals with intervention strategy; Section 4 explains mixed strategies (for reduce their its own volatility), Section 5 deals with the coordination of exchange rate intervention and Section 6 end up with conclusion.
2. Theory of Nash Equilibrium in RBI’s Exchange Rate Intervention
- The exchange rate shocks occurred on coordination of central bank intervention and speculators trades in the foreign exchange market which is tradeoff between the central bank and traders. However, the exchange rate highly volatile the monetary authority intervenes to stabilize foreign exchange rate. The major factor for this political instability effects on nominal exchange rate. We can address the central bank utility of intervention actual exchange rate and expected exchange rate is
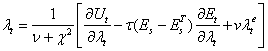 | (1) |
 weight the central bank aversion to deviation from its exchange rate target;
weight the central bank aversion to deviation from its exchange rate target;  intervention expected by speculator at time s;
intervention expected by speculator at time s;  cost of expectation of intervention;
cost of expectation of intervention; 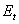 is the nominal exchange rate;
is the nominal exchange rate; 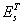 target exchange rate;
target exchange rate; 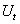 is a generic utility function at time
is a generic utility function at time 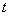 . The reaction function
. The reaction function 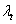 is affects the both utility and the nominal exchange rate, the left implicit
is affects the both utility and the nominal exchange rate, the left implicit 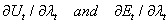 respectively. Intervention is effective during the market based exchange rate regime. Further intervention is not effective influences level of exchange rate Pattanaik and Sahoo (18). The speculator’s loss function defined below.
respectively. Intervention is effective during the market based exchange rate regime. Further intervention is not effective influences level of exchange rate Pattanaik and Sahoo (18). The speculator’s loss function defined below. 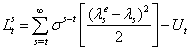 | (2) |
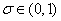 is a discount factor relative to loss of the speculator, the coordination of central bank intervention minimizing his cost to reduce exchange rate volatility. Further the central banks have announced to intervene (signaling) some of them were fail to intervene resulted losing (i.e. no selling/buying operation) with depreciation (appreciation) of exchange rate rates due to misleading of announcements.
is a discount factor relative to loss of the speculator, the coordination of central bank intervention minimizing his cost to reduce exchange rate volatility. Further the central banks have announced to intervene (signaling) some of them were fail to intervene resulted losing (i.e. no selling/buying operation) with depreciation (appreciation) of exchange rate rates due to misleading of announcements. 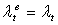 | (3) |
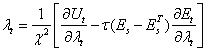 | (4) |
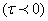 . Further central bank been intervenes to minimize exchange rate volatility without loss of foreign exchange reserves Basu[2]. Since foreign exchange reserves has volatile effect of current account deficit as results the central bank not achieve his goal it is need to repay more foreign exchange reserves for manage exchange rate stability
. Further central bank been intervenes to minimize exchange rate volatility without loss of foreign exchange reserves Basu[2]. Since foreign exchange reserves has volatile effect of current account deficit as results the central bank not achieve his goal it is need to repay more foreign exchange reserves for manage exchange rate stability 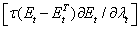 it gives more importance than utility consideration
it gives more importance than utility consideration 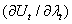 . The RBI’s intervention policy is effective during market based exchange rate system. The empirical literature on investigating this issue was initiated by Friedman[9]. Though the intention of such intervention is to stabilize exchange rate, it yields a return to the intervening authority because of various difficulties encountered in measuring the profitability of intervention [23].
. The RBI’s intervention policy is effective during market based exchange rate system. The empirical literature on investigating this issue was initiated by Friedman[9]. Though the intention of such intervention is to stabilize exchange rate, it yields a return to the intervening authority because of various difficulties encountered in measuring the profitability of intervention [23].3. Pure-Strategy Equilibrium
- The exchange rate has destabilizing since it is variation of external factor such as international crude oil price, gold price, interest rate and instability cross border of capital flows; demand and supply of money and instability food and non-food products. However the central bankers must control the price of food and non-food articles but mainly influences on exchange rate fluctuation above said problem. Further it has follows pure strategies and mixed strategies to intervene in the foreign exchange markets. We explain pure-strategy is an n-player strategies form game is
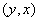 , where
, where 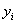 is the set of strategy player
is the set of strategy player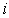 ,
,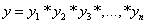 and
and 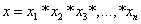 are the payoff function; which is
are the payoff function; which is 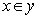 . According to Nash equilibrium strategy for each player, the players to meet pure strategy at least one as high pay off must other players is pure strategy (i.e. one players has sells his currency; at same time someone hold his currency) we can see below illustration[1].
. According to Nash equilibrium strategy for each player, the players to meet pure strategy at least one as high pay off must other players is pure strategy (i.e. one players has sells his currency; at same time someone hold his currency) we can see below illustration[1].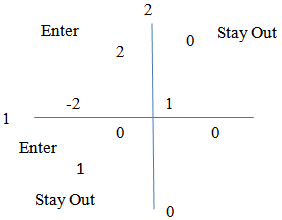 The rivalry of between player one and player two the central bank intervention in the foreign exchange market, the illustration[1] players 1 and 2, which is actively intervene in the foreign exchange markets. The central bank has been intervening and other stay out. Depreciation of domestic currency the monetary authority intervenes in the foreign exchange markets to correct the exchange rate volatility for its own currency. They release the dollar instead of rupee to volatility Re/USD. On 6th September 2011 the Swiss national bank has announced intervention for curbing his currency thus selling foreign exchange reserves. On 5th 2010 the Bank of Japan announced intervention in the foreign exchange market selling his currency against the dollar. It has tried to control his exchange rate volatility Basu[2]. The Currency self-fulfilling is monetary authority has speculates against its currency determines strategies incentive of speculators [Obstfeld[17]; Hellwig et.al,[14]] and also trader participates in the exchange rate market; if the trader expected to hold the results do not attack exchange rate; results of the exchange rate to sustain with minimal values. The agents were expected devaluation of their exchange rate, attack they would meet expenses due all intervention meanwhile single player intervention they don’t attack but he was meets intervention cost Heinemann[12].
The rivalry of between player one and player two the central bank intervention in the foreign exchange market, the illustration[1] players 1 and 2, which is actively intervene in the foreign exchange markets. The central bank has been intervening and other stay out. Depreciation of domestic currency the monetary authority intervenes in the foreign exchange markets to correct the exchange rate volatility for its own currency. They release the dollar instead of rupee to volatility Re/USD. On 6th September 2011 the Swiss national bank has announced intervention for curbing his currency thus selling foreign exchange reserves. On 5th 2010 the Bank of Japan announced intervention in the foreign exchange market selling his currency against the dollar. It has tried to control his exchange rate volatility Basu[2]. The Currency self-fulfilling is monetary authority has speculates against its currency determines strategies incentive of speculators [Obstfeld[17]; Hellwig et.al,[14]] and also trader participates in the exchange rate market; if the trader expected to hold the results do not attack exchange rate; results of the exchange rate to sustain with minimal values. The agents were expected devaluation of their exchange rate, attack they would meet expenses due all intervention meanwhile single player intervention they don’t attack but he was meets intervention cost Heinemann[12]. 4. Mixed Strategy Equilibrium
- The mixed strategy game; we can check four possibilities to intervene in the foreign exchange market such as
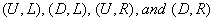 is Nash equilibrium. An each player is choosing of strategy from his out of four strategies i.e. called pure strategies. We look illustration 2 to explains mixed strategies.If player 1 chooses the mixed strategy
is Nash equilibrium. An each player is choosing of strategy from his out of four strategies i.e. called pure strategies. We look illustration 2 to explains mixed strategies.If player 1 chooses the mixed strategy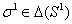 , player 2 chooses the mixed strategy
, player 2 chooses the mixed strategy 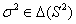 and n players to choose
and n players to choose 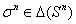 expected pay off to
expected pay off to 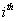 player
player 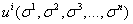
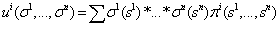 .This part has found that the mixed strategy is among the central bank intervention with mutual interest to reduce volatility. They minimize his cost of intervention further Domniguez[5] revealed that the mixed strategy exchange rate volatility surrounding to exchange rate market. Fatum and Hutchinson[10) studied the Bank of Japan and Federal Reserve Bank coordination their intervention both large scale and coordination of intervention to increase the chances of success. Sertel[22] founds three different kinds of behaviour of the private sector: (a) Cournot-Nash behaviour with free entry from outside, (b) collusive behavior and (c) limit pricing behavior. The public enterprises are threaten private participants or do enter. Since prices at marginal cost, and pushes the private firm out of the market.
.This part has found that the mixed strategy is among the central bank intervention with mutual interest to reduce volatility. They minimize his cost of intervention further Domniguez[5] revealed that the mixed strategy exchange rate volatility surrounding to exchange rate market. Fatum and Hutchinson[10) studied the Bank of Japan and Federal Reserve Bank coordination their intervention both large scale and coordination of intervention to increase the chances of success. Sertel[22] founds three different kinds of behaviour of the private sector: (a) Cournot-Nash behaviour with free entry from outside, (b) collusive behavior and (c) limit pricing behavior. The public enterprises are threaten private participants or do enter. Since prices at marginal cost, and pushes the private firm out of the market. 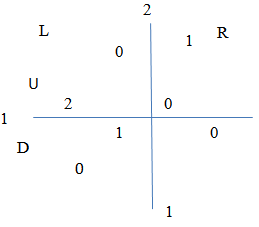
5. Central Bank’s Coordination Intervention
- The central bank coordination intervention agrees with other central banks to intervene in the foreign exchange market without multiple coordination of exchange rate intervention is increase the cost of intervention. They are holding foreign currency assets which are spending without profit while losing of exchange rate appreciation (depreciation). The central bankers have to choose tradeoff (loss/profit) among the central banks since they coordinates then not coordinates. The mixed strategy is plays prime role of exchange rate to reduce exchange rate volatility. It must give proper signals to the market participant otherwise speculator would have maximized his own profit. If the authority agrees with coordinates of intervention on the other hand signals is true; expectation of inflation to fall. The futures monetary policy is implied coordinates of intervention operations have several central banks are not behave homogeneous. For example, India involved in purchasing and selling of foreign currency assets with negligible respective of exchange rate volatility. In practice, over the three year period the G-3 central banks agree to coordination intervention operations on 81 out of 760 trading days. Fatum and Hutchinson[10]. The effects of coordination the central bank intervention in the foreign exchange market has more effective than unilateral intervention but the empirical evidence showed increased exchange rate volatility Pasquariello[19], Galati et al.[11], Frenkel et al. (2005), Payne and Vitale[20], Dominguez[5].
6. Conclusions
- Basically this study addressed different kind of game theory to imply that the RBI intervenes to reduce volatility with other central banks. If it is coordinates reduces exchange rate volatility when other the central banks remain constant. Further the central bankers have been regularly intervening to reduce the exchange rate fluctuations but they are not; basically the developed countries have coordinated intervention whereas the developing countries don’t have coordination operation facility. This study suggests to the Reserve Bank of India to go for the coordination intervention with developing countries in order to reduce the exchange rate volatility without reducing the foreign exchange reserves. Moreover, the RBI reduces the cost of holding the foreign exchange reserves. So that it will enhance the exchange rate stability and enhance the export competitiveness.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML