-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Civil Engineering Research
p-ISSN: 2163-2316 e-ISSN: 2163-2340
2020; 10(2): 29-38
doi:10.5923/j.jce.20201002.01
Received: July 20, 2020; Accepted: August 19, 2020; Published: August 29, 2020

Partial Replacement of Cement with Glass Bottle Waste Powder in Concrete for Sustainable Waste Management: A Case Study of Kumasi Metropolitan Assembly, Ashanti Region, Ghana
Emmanuel Kwesi Nyantakyi1, Abena Obiri-Yeboah2, Ghadafi Abdullai Mohammed2, Martin Kyereh Domfeh1, Nana Kwame Obeng-Ahenkora1
1Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Energy and Natural Resources, Sunyani, Ghana
2Department of Civil Engineering, Kumasi Technical University, Kumasi, Ghana
Correspondence to: Emmanuel Kwesi Nyantakyi, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Energy and Natural Resources, Sunyani, Ghana.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The objective was to investigate partial replacement of single and mixed coloured waste glass bottle powder for cement in concrete technology. Ordinary Portland cement in concrete mix was replaced with bottle glass waste powder of 30%, 50% and 70% respectively during mixing. A mix design ratio of 1:2:4 with water-to-cement ratio of 0.6 and design strength of 20MPa was used. Concrete cubes of sizes 150mmx150mmx150mm were cast and slump tested. Compressive strength density and percentage of water absorption test for concrete curing ages at 7- and 28-days were determined respectively. The slump test results showed decreasing slump values with increasing proportions of glass bottle waste powder. Further tests on the concrete specimen showed decreased compressive strength, density and percentage of water absorption values as glass bottle waste powder in concrete increased as compared to the control concrete mix. Replacement of glass bottle powder of 30% for cement in the concrete showed an enhanced performance when compared with the other percentage ratios used as well as the control mix. The study therefore recommends a 30% glass bottle waste powder to replace cement. The study recommends a study of the replacement over a longer period to verify the properties obtained.
Keywords: Replacement, Glass Bottle Waste Powder, Concrete Technology, Sustainable Waste, Kumasi
Cite this paper: Emmanuel Kwesi Nyantakyi, Abena Obiri-Yeboah, Ghadafi Abdullai Mohammed, Martin Kyereh Domfeh, Nana Kwame Obeng-Ahenkora, Partial Replacement of Cement with Glass Bottle Waste Powder in Concrete for Sustainable Waste Management: A Case Study of Kumasi Metropolitan Assembly, Ashanti Region, Ghana, Journal of Civil Engineering Research, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 29-38. doi: 10.5923/j.jce.20201002.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Sustainable construction practice means creation and responsible management of a healthy built environment considering resource efficiency and ecology (Plessis, 2007). Being versatile and economical, concrete became prime construction material over the world, however, it has impacts on the environment (Naik, 2008). Manufacturing of cement (key ingredient used for the production of concrete) is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions (Imbabi et al., 2012).Being non-biodegradable in nature, glass disposal on landfill sites has many severe environmental implications and could also be quite expensive. Sustainable construction practices mean creation and responsible management of a healthy built environment considering resource efficiency and ecology (Plessis, 2007). Manufacturing of cement (key ingredient used for the production of concrete) is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions (Imbabi et al., 2012). Waste glass when not properly disposed leads to environmental problems. Landfill is the conventional approach to solid waste management, but space for landfill is becoming scarce in many parts of Ghana as the need for land for other projects become imminent. Final disposal of waste glass in Ghana is normally on dump and landfill sites and on nearby undeveloped lands. These practices create problems for authorities where land scarcity exists. Using glass powder to replace cement in concrete production is advantageous by reducing waste glass that ends up on our landfill site thereby reducing construction cost. For instance, in brick manufacturing, substituting waste glass for clay in red mixture reduces the heat required to fire the body to maturity (Diaz et al., 1982). Moreover, the substitute could result in about thirty percent (30%) increase in the quantity of red bricks produced without additional kiln capacity. Many authors have worked on the use of glass material in concrete production in construction industry as a way of managing generated bulk waste glass in society. Their works established solid grounds for further investigation into waste glass management (Bashar and Ghassan, 2009). In the late sixties, researchers devoted their study on the use of waste glass as coarse and fine aggregates in concrete production (Pike et al., 1960, Schmidt et al., 1963). Recent works by (Pike et al., 1960, Schmidt et al., 1963) rekindle the ideas but concentrate on usage of glass material as either fine or coarse aggregate replacement in concrete, moulding of blocks and road construction material. It is against this background that investigations are ongoing to further exploit new ways of reusing glass waste for sustainable management of solid waste.Research indicates that glass has a chemical composition and phase comparable to traditional supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) (Ryou et al., 2006; Binici et al., 2007; Nassar and Soroushian, 2012). It is abundant, can be of low economic value and often landfilled (Byars et al., 2003). Milling of glass to micro-meter scale particle size, can enhance reactions between glass and cement hydrates, bring energy and offer environmental and economic benefits when cement is partially replaced with it for production of concrete (Rashed, 2014). Some studies also focused on the use of waste glass as aggregate in concrete production (Rashed, 2014; Taha and Nounu, 2009). A study on durability of concrete with waste glass pointed to better performance against chloride permeability in the long term but there is concern about alkali-silica reaction (Rashed, 2014). The pozzolanic properties of glass were first notable at particle sizes below approximately 300 ml, and below 100 ml, glass can have a pozzolanic reactivity at low cement replacement levels after 90 days of curing (Shi et al., 2005). This size can be achieved by using a grinding operation with the help of ‘‘Ball Mill” which is generally used in cement industry to grind cement clinker. Several researches show that, at a higher age recycled glass concrete (15% to 20% of cement replaced) with milled waste glass powder provides compressive strengths exceeding those of control concrete (Nassar and Soroushian, 2011). However, review study by Rashed (2014) showed previous studies with glass addition were not conclusive considering workability and strength while the chloride resistance of glass added concrete was found to be similar with control condition. Moreover, glass waste generation have several environmental challenges. Disposal of glass waste bottles in landfills reduces their life span thus creating land use problems. Apart from limited space challenges, waste glass bottles found in the open gutters of our cities choke and clog gutters thereby causing perennial flooding in our cities amidst even light rains. This is the biggest environmental problem faced by managers of big cities in Ghana. Glass bottles and plastic polythene bags are major components of solid waste dump along the shores of beaches posing threat to users of the beaches and marine organisms across the country. Interestingly, waste glass has proven to be a good substitute for one or two ingredients of concrete in the construction industry for concrete production. Furthermore, cost of production of concrete for building infrastructure would decrease, and the industry would become more environmentally friendly. We can guarantee a cleaner and greener environment if we make reuse and recycling of waste glass a priority. This study examined the potential of replacing cement with waste glass powder for sustainable concrete technology. Experimental work was carried out on the performance of glass in mortar and concrete. Concrete samples were prepared to evaluate strength properties. Fig. 1 below shows a map of the study area.
 | Figure 1. Map of the study |
2. Materials and Methods
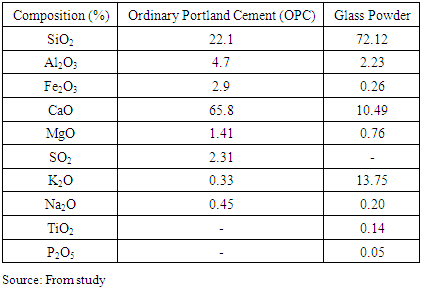
- The experiment was undertaken at the Materials Laboratory of the Ghana Highway Authority (GHA), Kumasi in January 2020. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) 42.5R, fine aggregates (2.36mm-75µm) and coarse aggregates (9.5mm-25mm) used in this study were obtained locally from markets in Kumasi. Glass bottle powder, gathered and sorted to single colour groups (white, green, brown) from a landfill site, was obtained by manually grinding bottles in the GHA materials laboratory and had sized between 425µm and 600µm. Figs. 2 and 3 show pictures of broken glass and glass powder respectively. The chemical composition of OPC is presented in the Table 1. Potable water from standpipes was used throughout the experimental process. The size distributions of ground GP and cement used in this study are shown in Fig. 4. Both cement and GP show the same median particle size of around 10 µm. The chemical compositions of GP and OPC are displayed in Table 1. The specific gravities of cement and GP are 3.16 and 2.55, respectively. The surface appearance of GP and OPC are compared in Figs. 5a and 5b.
|
 | Figure 2. A picture showing broken glass |
 | Figure 3. A picture showing glass powder |
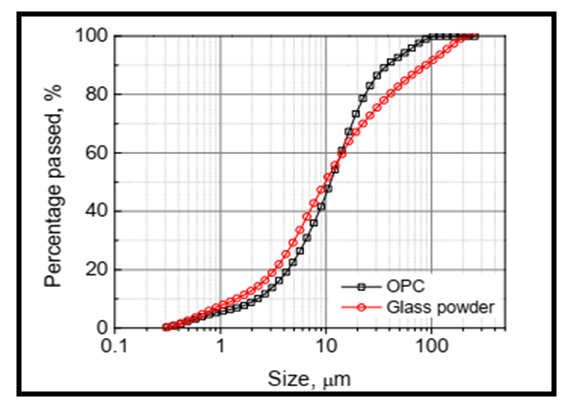 | Figure 4. Particle size distribution of OPC and glass powder |
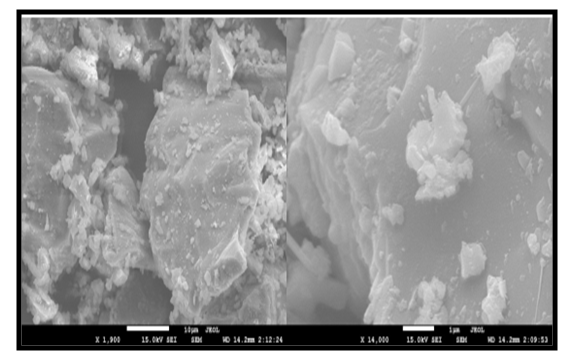 | Figure 5a. OPC particles morphologies using SEM |
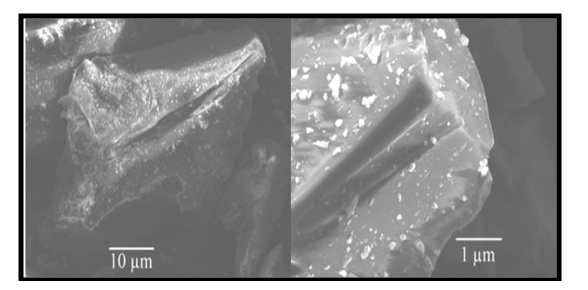 | Figure 5b. Finely ground glass powder morphologies using SEM |
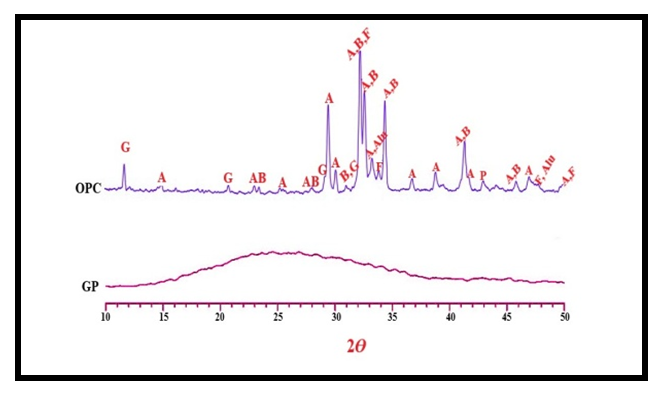 | Figure 6. XRD patterns for OPC and GP |
2.1. Mixing and Casting of Concrete Cube Specimen
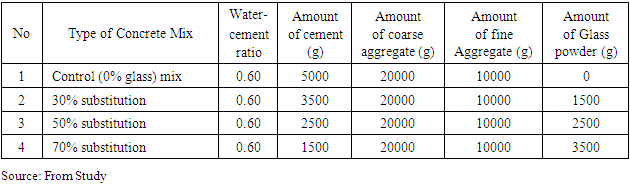
- Coarse and fine aggregates, cement, water and glass bottle powder were measured using a beam balance and mixed by hand. A mix proportion of 1:2:4 by weight was used for all mixes and molded in 150mm x 150mm x 150mm cubes. Concrete cubes placed in curing tanks and cured for 7- and 28-days. Four types of concrete mix proportions were prepared for testing. Controlled concrete mix (0% glass bottle powder), which comprises sea sand (11000g), granite stones (18000g), cement (5000g) and water (3200g) resulted in water-cement ratio 0.60. The glass concrete mixes contained waste glass bottle powder of 30%, 50% and 70% by weight as a partial substitution for cement using ASTM C109 (ASTM, 2016c). This is presented in Table 2. Slump test was conducted on fresh mortar after mixing to measure the workability of the fresh concrete whereas destructive and non-destructive tests (water absorption, density and compressive strength, rebound hammer test, ultrasonic pulse velocity test and split tensile test) were conducted on the hardened concrete using standard procedures.
|
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. XRD Tests
- Paste samples were taken from the center of 50 mm cube specimens for the purpose of XRD. The paste samples were cured in 105°C oven for 24 hours and then finely ground to be less than 75 µm. Shimadzu XRD-6000 diffractometer was employed to qualitatively determine the influence of GP on the chemical composition of the hydrated production. The XRD scan was between 10° and 60° with a speed of 0.5°/min. The content of CH could be obtained from two different intervals in the weight loss curve, corresponding to the decomposition of Portlandite and calcite, respectively.
2.2.2. Water Absorption Test
- Water absorption (such as BS1881 part 122) is an absorption test that measure water absorption by an immersed of the sample. These tests are more relevant for an application in which concrete is exposed to low or no hydrostatic pressure.Procedure:1) The fine aggregate passing through IS 4.75mm sieve is taken about 1kg and dried in an oven at a temperature of 110°C±5°C for 24 hours and cooled to room temperature.2) Its weight is taken as (w1 g).3) The dried fine aggregate is immersed in clean water at a temperature 27°C±2°C for 24 hours.4) The fine aggregate is removed from the water.5) Within three minutes from the removal of water, the weight of fine aggregate w2 is found out.6) The above procedure is repeated for various samples. Formula used:
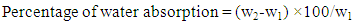 | (1) |
2.2.3. Rebound Hammer Test
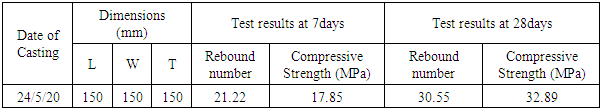
- The rebound hammer test was performed on cubes of size 150mm×150mm×150mm by pressing a plunger of a rebound hammer against the surface of concrete vertically downward as specified in IS 13311 (Part 2): 1992. The rebound was read off along a graduated scale and was designated as the rebound number. Table 3 shows the test results.
|
2.2.4. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test
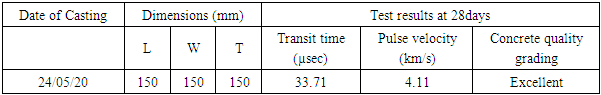
- Mix proportion used in making, compacting and curing of concrete is very important as they affect the density and modulus of elasticity of concrete. The ultrasonic pulse velocity of concrete is related to these. Concrete quality was checked as per specifications given in IS 13311 (Part 1): 1992. The ultrasonic pulse was produced by transducer which was held in contact with one surface of the concrete member. After travelling a known path length in the concrete, the pulse of vibration was converted into an electrical signal by the second transducer held in contact with the other surface of the concrete member and the transit time of the pulse was measured. Table 4 shows the test results.
|
2.2.5. Split Tensile Test
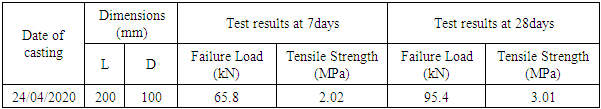
- Split tensile test on cylinders of size 100mm diameter and 200mm height was conducted on the compressive testing machine (Aimil, 2000kN) as per specifications given in IS 5816:1999. The load was applied at a rate of 1.8kN/s up to failure of specimen. The average split tensile strength of 3 cylinders was taken after 7 and 28 days. Table 5 shows the test results.
|
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of Constituents
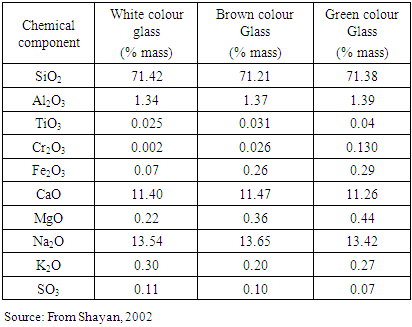
- Chemical composition of coloured glass used for the experiment in shown in Table 6.
|
3.2. XRD
- The XRD patterns for cement with glass powder at age of 7 and 28 days are shown in Fig. 7. The compositions of the hydration product for Portland cement paste are C-S-H and CH and their principal peaks do not change from 7 to 28 days. CH peaks tend to be weakened with increasing glass powder and longer curing time, especially for 70% glass powder paste at 28 days in which the CH peaks almost disappear. The XRD results directly reveal that CH is consumed to form the additional C-S-H in paste with glass powders. At 28 days, peaks corresponding to CH can be obviously seen for OPC and 30GP paste, which means that CH remains even after 28 days of pozzolanic reaction with glass powder. However, it is not true for paste with 70% glass powder in which the CH seems to be insufficient for glass powder to be fully reacted.
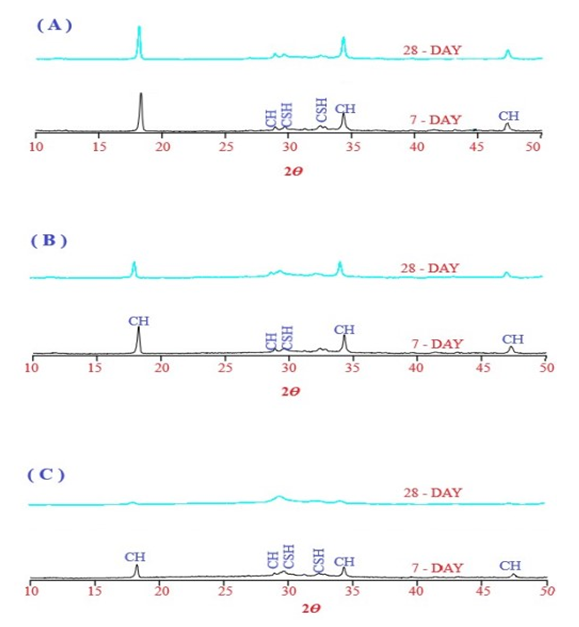 | Figure 7. XRD patterns of cement with different contents of glass: (a) OPC, (b) 30GP and (c) 70GP |
3.3. Test on Fresh Concrete
- Slump test: The results show slump values of 30%, 50% and 70% for both mixed and single colour glass concrete were slightly lower compared to the control concrete mix (0% glass) (Fig. 8). Decrease of slump values could be due to an increase in percentage of glass bottle powder in concrete mix. Park et al (2004) and Adaway and Wang (2015) observed that increasing ratio of glass bottle powder in concrete led to decrease in slump of concrete made with glass bottle powder. It was further observed that mixed colour glass bottle concrete had higher slump values for all the ratios as compared with ratios of single colour glass bottle concrete. This implies that colour does have an effect on the pozzolanic properties of glass. One of the factors that affected the slump was chemical admixtures when added during colouring of glass.
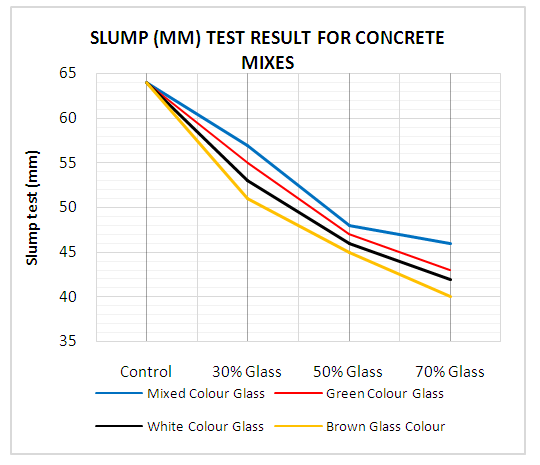 | Figure 8. Slump test result for Concrete mixes |
3.4. Test on Hardened Concrete
- Dry Density: Test results for concrete mix for 7- and 28-days of curing are shown in Figs. 9 and 10. The results show that dry density of glass bottle concrete mix decreased as percentage ratio (30%, 50% and 70%) of glass bottle powder in concrete increased compared to the control concrete (0% glass bottle powder) mix for 7- and 28-days of curing. Both single colour glass bottle concrete and mixed colour glass bottle concrete mixes recorded lower drier densities compared with control concrete mix. This was generally due to lower mass of glass bottle concrete mix as compared to control concrete mix. Also, unit weight of glass bottle powder concrete is lower than that of control concrete mix. This is consistent with Abdallah (2011) who observed that dry density of glass concrete decreased as percentage ratio of glass material in concrete increased. Zero/No (0%) substitution of glass has higher density than that of 70% substitution of glass powder. It is observed that values for dry density of concrete mixes increased consistently from 7 through to 28day curing. For instance, 0% glass concrete increased from 2395.2 kg/m3 to 2463.7 kg/m3, 30% Green glass (2392.2kg/m3 to 2456.6kg/m3), 30% white glass (2392.8kg/m3 to 2454.8kg/m3), 30% Brown glass (2391.1 kg/m3 to 2455.1kg/m3) and 30% Mixed colour glass (2393.1kg/m3 to 2456.8kg/m3). Comparing mixed colour glass concrete to that of single colour concrete, the mixed colour had slightly higher density values in the 30% glass concrete than the other ratios at 7- and 28-days curing ages. Again, mixed colour glass has preferred results than single colour glass.
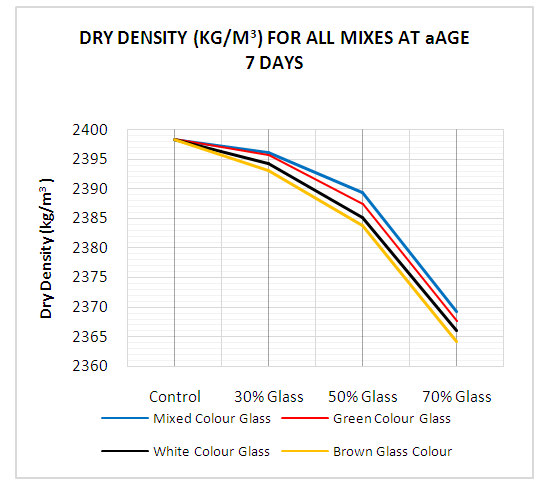 | Figure 9. Dry Density for all concrete mixes at 7 Days |
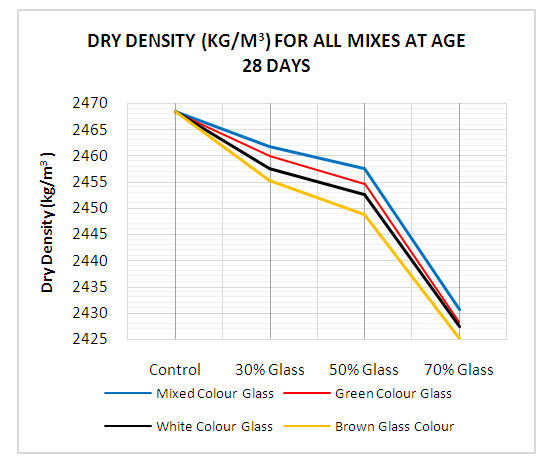 | Figure 10. Dry Density for all Mixes at age 28 day |
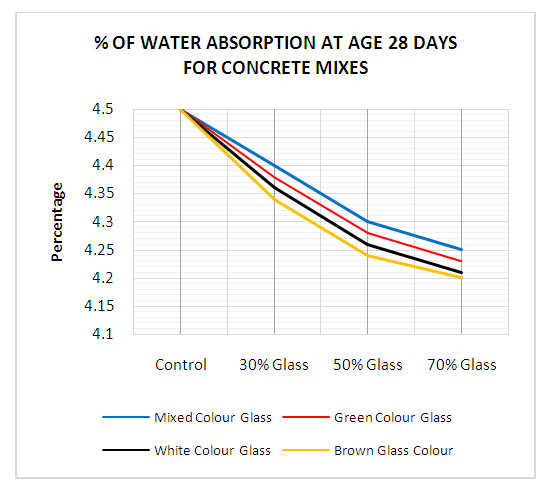 | Figure 11. Percentage of Water Absorption at 28 days for Concrete mixes |
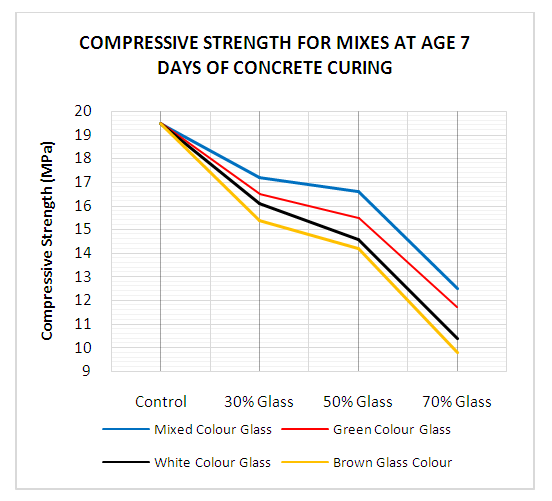 | Figure 12. Compressive Strength for mixes at age 7 Days of concrete curing |
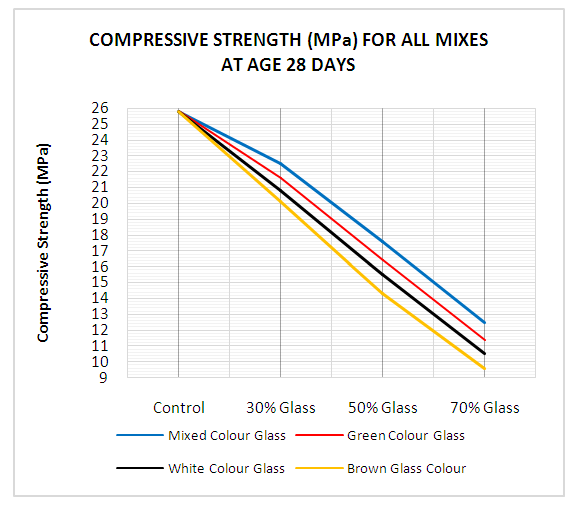 | Figure 13. Compressive Strength for all mixes at age 28 Day |
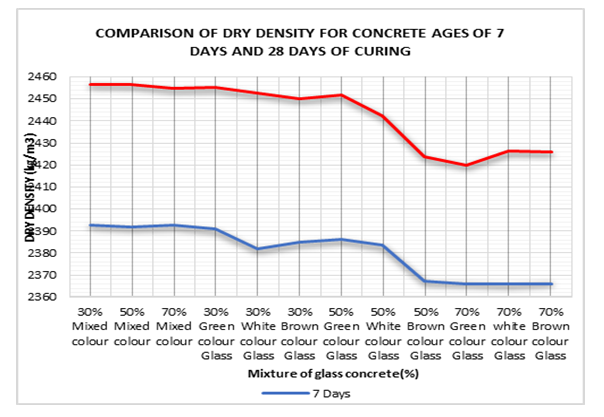 | Figure 14. Comparison of Dry Density for concrete ages of 7- and 28-days of Curing |
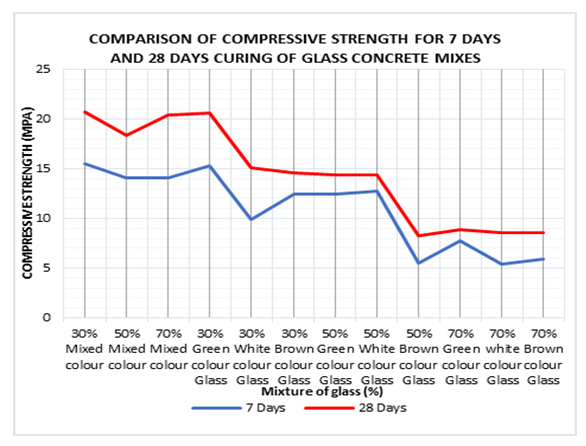 | Figure 15. Comparison of Compressive Strength for 7- and 28-days Curing of Glass Concrete mixes |
3.5. Other Tests
3.5.1. Rebound Hammer
- From the rebound hammer test results as shown in Fig. 16, the compressive strength of cube at 7 and 28 days is coming 17.85MPa and 33.66MPa corresponding to and 31.66 rebound Number respectively.
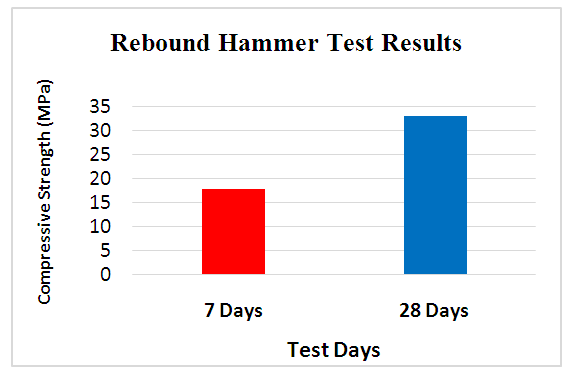 | Figure 16. Rebound Hammer test results for 7- and 28-days Curing of Glass Concrete mixes |
3.5.2. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test
- The results of ultrasonic pulse velocity shown in Table 4 indicate that quality of concrete was excellent as ultrasonic pulse velocity is 4.11km/s.
3.5.3. Split Tensile Test
- Fig. 17 shows that the split tensile strength of cylinders at 7 and 28 days are 2.02MPa and 3.01MPa respectively. The increase in strength is about 49.0% between 7 and 28days.
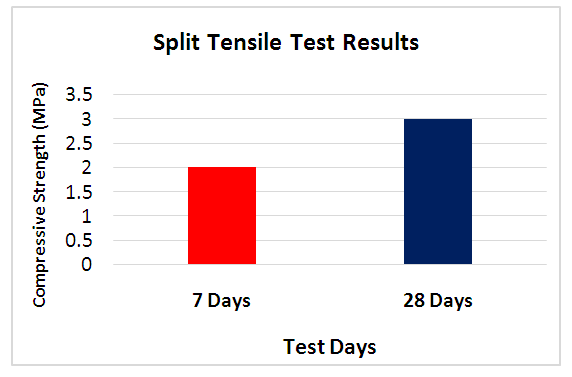 | Figure 17. Split Tensile test results for 7- and 28-days Curing of Glass Concrete mixes |
3.6. Independent Sample T- Test for Comparing Dry Density and Compressive Strengths
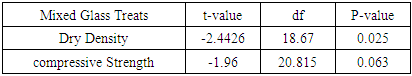
- Test results for compressive strengths and dry densities of concrete with glass waste powder were further assessed using independent sample test to determine whether there is difference in the values obtained for the different concrete curing ages of 7- and 28-days. The results from Table 7 indicate that there exists significant statistical difference among dry densities of concrete curing ages of 7- and 28-days. However, no significant statistical difference was observed for compressive strengths of glass bottle waste powder concrete at different ages of 7- and 28-days at 0.05 significant levels.
|
4. Conclusions
- This study used knowledge of material engineering and solid waste management to solve the ever-increasing rate of waste glass bottles generation in our society with the main objective of replacing cement with glass bottle powder in concrete technology for sustainable waste management. Slump for fresh concrete made with glass bottles powder as substitute for cement decreased as percentage of glass bottle powder in concrete increased. Even though there is reduction of slump values for concrete containing glass bottle powder, they have good workability. The 30%, 50% and 70% glass bottle powder replaced with cement in concrete showed a decrease value for slump of fresh concrete made with glass bottle powder as compared with control concrete mix (0% glass). Compressive strength of concrete made with glass bottle powder decreased as glass content in concrete increased when compared with control concrete mix (0% glass). Concrete containing glass bottle powder indicated an improved compressive strength at the later ages. Thirty (30%) waste glass replacement of cement in concrete had the highest value of 20.75MPa compressive strength for curing age of 28 days when compared with other concrete mix ratios of 50% and 70%. Water absorption decreased with an increase of percentage ratio of waste glass bottle powder as replacement of cement in concrete. All glass mixes (mixed colour mix, green colour mix, clear colour mix and brown colour mix) showed a decrease value of water absorption when compared with the control mix (0% glass). Densities of all mixes increased with increased percentage of glass powder when compared with the control (0% glass mix) concrete for both 7- and 28-days curing.
5. Recommendations
- The study recommends a 30% glass bottle waste powder to replace cement for use in concrete production for sustainable solid waste management. It is also recommended that the effects of different colours (white, green and brown) be studied independently to see the impact of the different colours on the pozzolanic effect of the glass. The study further recommended the study of the replacement over a longer period of time to verify the properties obtained.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to acknowledge the management of Ghana Highway Authority, Kumasi, Ashanti Region, Ghana for using their laboratory to undertake this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML