-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Civil Engineering Research
p-ISSN: 2163-2316 e-ISSN: 2163-2340
2014; 4(1): 14-24
doi:10.5923/j.jce.20140401.03
Bauxite Industry in Guinea and Value Opportunities of the Resulting Red Mud as Residue for Chemical and Civil Engineering Purposes
Traoré D. L.1, Traoré S.2, Diakité S.1
1Department of Civil Engineering, Polytechnic Institute University of Conakry, UGANC, Conakry, Guinea
2Department of Chemical Engineering, Polytechnic Institute University of Conakry, UGANC, Conakry, Guinea
Correspondence to: Traoré S., Department of Chemical Engineering, Polytechnic Institute University of Conakry, UGANC, Conakry, Guinea.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract Because of the importance and the diversity of its mineral resources, Guinea is referred to as geological scandal. Whatever assessing system, experts highlight the country’s bauxite potential with superlatives. Several geological surveys concede that Guinea is home to 33% of the world’s known bauxite reserves. An inconsistency exists in the manner in which the content of a deposit is defined and in different statistical data, the concepts and definitions are confused. Hence, an expert making comparisons among various bauxite deposits has to recognize the terms in use and has to adjust them in his assessment for consistency. The huge bauxite potential offers a serious option to the country to become a frontrunner in the bauxite and aluminum industry and to develop a subsequent red mud valorization opportunities. This paper describes the bauxite potential and the local alumina industry in Guinea and reviews the valorization technologies of the resulting the red mud.
Keywords: Bauxite, Reserve, Alumina, Red mud, Residue, Product
Cite this paper: Traoré D. L., Traoré S., Diakité S., Bauxite Industry in Guinea and Value Opportunities of the Resulting Red Mud as Residue for Chemical and Civil Engineering Purposes, Journal of Civil Engineering Research, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 14-24. doi: 10.5923/j.jce.20140401.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In a resource-constrained world, the struggle for raw materials will continue. Minerals are valuable, finite and largely non-renewable natural resources. They provide raw materials for many industries and play a central role in the evolution of human society.Because of its particularly suitable mineralization geo-climatic conditions, Guinea conceals enormous mining resources. Bauxite, Iron, gold, diamond, and several metal ores have been identified by different and tallying surveys. This is the reason why the country is referred to as a geological scandal [1].Presently the aluminum industry in Guinea is still at the mining stage of bauxite, the main raw material that is refined and smelted into aluminum. Guinea is home to 33% of the world’s known bauxite reserves and is the only country in Africa that produces more than 1 % of global production. The refining of bauxite into alumina has taken place in Guinea since 1959 at the ACGbauxite and alumina plant in Fria. The capacity of the plant, the only alumina refinery in Sub-Saharan Africa, is 700.000 tons of alumina per year; 1.1% of global output and 1.9 million tons of bauxite. Approximately 13 % of the country’s bauxite production has been refined into alumina at this plant each year since 2001with the remainder being exported [2].The bauxite and alumina sector is responsible for the largest direct contribution to GDP in Guinea. The conversion of bauxite into alumina releases a considerable amount of waste generally known as red mud which requires a proper management in order to prevent or mitigate the severe environmental implications with regard to human health, water quality, biodiversity protection, etc. Despite government regulations laws, up to date the red mud and bauxite waste have not been properly managed on the standpoint of technology in Guinea [3].The gigantic bauxite potential offers a serious option to the country to become a leader in the bauxite and aluminum industry. However several constrictions such as power scarcity and environmental concerns should be abridged. As to the treatment of red mud, the first choice of most companies from all over the world would bestoring it in an open yard or marine dumping. Since there is a great deal of industrial alkali, fluoride and heavy metals and other potential pollutants in red mud, long-term stockpiling of red mud would not only occupy scarce land resources, but also easily lead to serious pollution of the surrounding soil, air and groundwater. On the other hand, treatment by marine dumping may destroy the ecological balance of the ocean.This paper presents the bauxite and alumina industry in Guinea and examines the technological options to reuse the subsequent red mud as waste. It describes the progress of experimental research and production practice of safe storing and the methods of comprehensive utilization. The paper reviews the existing technological solutions to valorize the red mud resulting from the Bayer process in order to develop another engineering activity.The objective is to provide information on the enormous bauxite and alumina industry in Guinea and assist in economic and technical planning by scientists, industry-leaders, high level policy makers.
2. Method
- The work is a compilation of information on the geology, occurrence, distribution and amount of Guinea’s reserves and potential resources of bauxite that is possible sources of alumina. An attempt was made to review most of the weighty articles on the country bauxite deposits published since the 1960’s and those of the present-day. In addition, authorities and experts of the Guinean Mining sectors (Ministère des Mines et de la Géologie, Direction Nationale des Mines, Centre de Promotion et de Développement Minier, etc.) as well as those of the main bauxite Companies CBG, ACG and CBK were interviewed.Basing on data gathered a succinct analysis was made about how can Guinea develop and play a key role in the of bauxite sector worldwide and resulting products. As standard tool, the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis was used. With regard to the environment impact of bauxite and alumina industry, an attention was paid to the dust sources of the bauxite extraction, transport and handling and to the current practice in red mud management.
2.1. Concepts Definitions
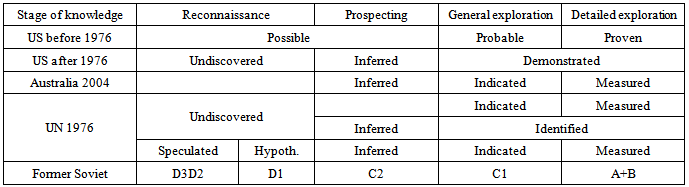
- A very definite inconsistency exists in the manner in which the content of a deposit is defined. Often statistics on a given deposit report “reserve” as the only category without further explanation. From the 70’s the concept of resources has been introduced [4] but not everywhere. Further, in different statistical data, the concepts and definitions are confused and not always correctly used. Hence, a geologist making comparisons among various bauxite deposits has to recognize the terms in use and has to adjust them in his assessment for consistency. As it is clearly worded in the JORC code of 1992 as follows: Resource: is quantified on the basis of geological data and an assumed cut-off grade only. There is an implication that there are reasonable prospects of eventual economic exploitation.Reserve: it is that part of the resource which, after application of mining factors, results in an estimated tonnage and grade which can be the basis of a viable project after taking account of all relevant metallurgical, marketing, environmental, legal, social and governmental factors.Bauxite reserves: that is that part of the reserve base which could be extracted economically at the time of discovery [5]. Ore reserves and resources are classified into categories which express the geological knowledge and confidence levels that can be attributed to both grade and tonnage. There have been a lot of changes in the definition and determination of each the categories, Tab.4 shows the evolution of the knowledge in mineral resources survey.At the point of view of chemistry or geochemistry, in order to portray bauxite quality rather than quantity, the reserve figures are presented as the tonnage of recoverable Al2O3. Recoverable Al2O3 is defined as the amount of alumina contained in the bauxite reserves that can be extracted in solution by the Bayer process. Also taken into account is the efficacy of the process which is controlled by the relative abundance of the alumina minerals gibbsite, boehemite, and diaspore and the presence of deleterious minerals such as kaolinite. Numerically, recoverable Al2O3 is equal to average Al2O3 multiplied by the percentage recovery of alumina in the Bayer process. For example, alumina recovery from gibbsitic ore with low (<3%) Boehemite content is 98%, whereas the yield from Boehemite-rich bauxite is reduced to 90%.
|
2.2. Bauxite Potential of Guinea
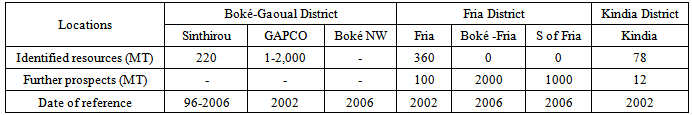
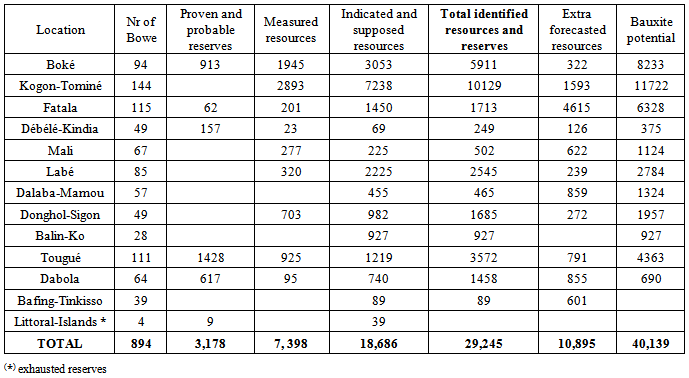
- Whatever concepts and definitions used, it appears from all studies that Guinea is the country the most endowed with bauxite in the world.One of widest portray of the bauxite potential of Guinea was published in the early 1960’s [6]. The data of this study are year after year established by further investigations by means of better methods and equipment. Large mainland deposits are in the Boké, Dabola, Kindia, Friguiagbé, Badi-Konkouré (Fria), and Tougué-Dabola regions. Nearly all mainland deposits occur on plateaus characterized by open or brushy, gently rolling uplands incised by wooded stream valleys. This type of land relief is known “fouga” in mandingo language or “bowés”. The “fouga” are at altitudes ranging from 900 feet at Boké to about 3,500 feet near Dabola [7]. Badi-Konkouré(Fria): Large bauxite deposits occur near the junction of the Badi and Konkouré Rivers, Laterite deposits 25-30 feet thick formed on a dolerite sill that overlies schist along the Konkouré River. The laterite consists of red gibbsitic earth containing hard lumps and crusts and is underlain by a red clay zone. This clay is underlain by yellow clay in which the structures of the dolerite are preserved; residual dolerite boulders occur in the lower part of this zone. Gibbsite is the only bauxite mineral in these deposits. Goethite is the most abundant iron mineral, but hematite is common. Particularly in the uppermost part, kaolinite is the principal clay mineral, but chlorite also occurs in the least weathered part of the laterite.Boké: The depositis located on the tidal Nunez River. The very large bauxite deposits of the region are on both sides of the Cogon River, and their center is about 55 miles northeast of Boké: The bauxite occurs in the capping laterite layer of “bowés” at altitudes of 900-1000 feet. The lower slopes of stream valleys between the “bowés” are generally covered by soil and forest, but laterite extends down into the valleys locally. A typical section of the bauxite and laterite is 40-50 feet thick and consists of an upper iron-rich crust underlain by a softer bauxitic laterite that grades downward into a ferruginous bauxite layer.The bauxite consists primarily of gibbsite and hematite with minor amounts of goethite, boehmite, quartz, and kaolinite. Boehemite makes up as much as 4-5% of the bauxite at the surface. The minor quartz in the laterite commonly, but not everywhere, decreases in quantity with depth. Kaolinite is most abundant in the lower parts of the laterite and presumably is a major constituent of the clay-rich layer below the laterite.Dabola: Bauxite deposits in this region are on “fougas” at altitudes of about 3,500 feet, between the Niger and Tinkisso Rivers. The deposits on the Ouroussa "fouga" near Dabola formed on diabase; elsewhere in this region laterite formed on mica schist. Extensive drilling on the Oursa (Ouroussa) and Sinseri “bowes” has revealed very large deposits of bauxite. Kindia-Friguiagbé: The bauxite deposits in this area cover nearly 2,000 acres, and their average thickness is 4-8 meters. This bauxite is 40-45 % Al2O3 and 5-6 % SiO2, and about one-third of the silica is in kaolinite [8].One sample of bauxite weathered from sericite schist was taken 3 meters below the surface on a plateau a few kilometers southwest of Kindia. This sample is approximately 80% gibbsite and contains identifiable quantities of Boehemite and quartz and a moderate amount of hematite. The gibbsite occurs in both concretions and light-colored matrix. The concretions are dark red, pale red, yellowish pink, and white with red bands. Many of the concretions consist of alternate irregular bands of pure crystalline gibbsite and iron-impregnated material. The matrix consists largely of unoriented aggregates of gibbsite crystals that are less than 10 microns in size. Quartz grains are scattered throughout the bauxite, and some grains are loose and occupy round holes. The quartz has either formed secondarily or the matrix has shrunk away from grains during dehydration.Tougué-Dabola: Extensive bauxite deposits occur between Tougué and Dabola. Bauxite of good grade is present in both areas. Only a few of the plateaus have been prospected. Total potential bauxite resources are also very large. They include the marginal and submarginal deposits in the five regions containing reserves, as well as the very large deposits in the Tougué-Dabola region and other parts of the country which have not been adequately prospected.Recent investigations covering 3 districts [4] come to an even firmer statement with regard to the potential: “In Guinea the bauxite potential, in practice, is not limited.Taking into account its identified bauxite deposits both in tonnage and grade, its further prospects, and its geographical position, Guinea is the number one bauxite country of the world. Accessibility of the bauxitic “fougas” located on savannah zone is relatively easy. Ore concentration is high. Number of ore bodies contain >100 Mt of bauxite. The relatively high mono content (>5%) at some places is a disadvantageous factor; nevertheless, it concentrates in more or less definite layers which can be selectively mined.
|
|
2.3. The Alumina Industry in Guinea
- The most important bauxite mining establishments in Guinea are Compagnie des Bauxites de Guinée (CBG), Compagnie des Bauxites de Kindia (CBK); and Alumina Company of Guinea (ACG). The refining of bauxite into alumina has taken place in Guinea since 1959 at the ACG/Friguia bauxite and alumina complex in Fria. The capacity of the plant, the only alumina refinery in Sub-Saharan Africa, is 7 million tons of alumina per year, i.e. 1.1 % of global output. Approximately 13 % of the country’s bauxite production has been refined into alumina at this plant each year with the remainder being exported. In conjunction with the Sangarédi Refinery Project, a nine million tons per year bauxite mine is being planned, which would increase the production capacity of the country by almost 50 % and could move it back to second place on the global production table.At first glance, Guinea seems the most likely place to locate an aluminum smelter in West and Central Africa, if not all of Africa; it has large bauxite reserves, considerable hydroelectric potential with limited domestic demand, and one alumina refinery with another under construction [10].Moreover, much of the transport infrastructure is already being developed in the context of the new alumina refinery, which would greatly reduce the extractive industries for capital costs of a new smelter. However, much of the hydroelectric potential of Guinea is scattered around the country in small projects, with over two thirds of the reported 6,000 MW being associated with installations of less than 200 MW, many of which would not be viable in the 8th month dry season.Aluminum smelting has never taken place in Guinea, while the country is currently deficient in power generation capacity. From an economic stand point bauxite and alumina have historically been by far the most important exports of Guinea [11], accounting for 64% of total exports in 2006. In addition, direct tax revenues from the bauxite and alumina industries have typically accounted for more than 15 % of government finances. Both exports and fiscal revenues have likely increased both absolutely and relatively in recent years.The bauxite and alumina sector is responsible for the largest direct contribution to GDP in Guinea; in 2005, mining (dominated by bauxite and alumina) accounted for 20 % of GDP versus 12,9 % for agriculture as shows Fig.1.
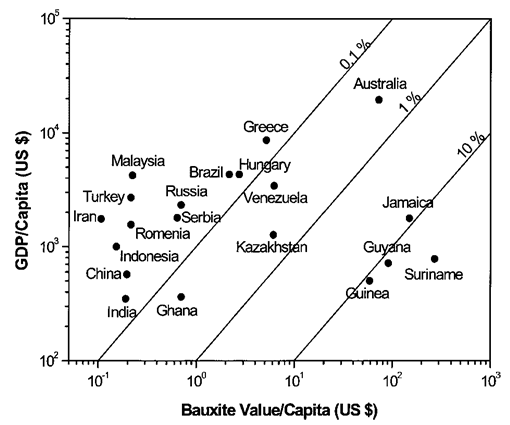 | Figure 1. Plot of gross domestic product (GDP) per capita versus potential bauxite value per capita in 2000 US dollars, Data source: CRC database; EIA, 2003; Kelly and others, 2003 |
2.3.1. Origin of Bauxite Waste
- Bauxite mining and processing have had a strong and varied impact on the environment because they entail modifications not only of the landscape but also because they provoke severe pollution by rejecting wastes into the biosphere (soil, the atmosphere and the water) [12].In Guinea, the terminology used by the 3 main bauxite mining industries CBG, ACG and CBK with regard to main waste is “bauxite mud” and in that of alumina extraction, “red mud”.Bauxite mud is found in quarries as well as in the installations of the plants treating bauxite. Studies advocate that wherever there is dust in the dry season, there will be mud during the winter season. The bauxite mud comes most habitually from washing the machines (conveyor belts, feeding chains of the crushing mill) and from the meeting points of the feeding conveyors for the dryers. The most significant problem is experienced at the plant at Kamsar because of the large quantity of bauxite which is treated there each day. Clearing and excavation work done with the help of bulldozers usually entails complete destruction of vegetation. This type of destruction not only modifies the landscape but threatens the fauna and causes physical destruction as a result of soil erosion. The major danger is that of the chemical degradation of the soils because nutritive elements have been washed away. This can cause loss of productivity to the detriment of agriculture and grazing [13]. An estimate suggests that the total surface area affected by the mining activities of the three companies present, from the time of their establishment to the middle of 1990’s represented approximately 1118 hectares.Dust represents a major pollution factor in the bauxite industry. Among sources of dust the quarries where the setting off of explosives and the movement of trucks loaded with the mineral along dirt roads produces vast quantities of dust particularly in the dry season.Another source of dust comes from the transformation of bauxite (crushing and drying). In the course of the crushing stage especially in the dry season, cyclones transport the dust in chimneys and release it into the air. A last but no fewer source of dust particles is that which results from alumina refining at the Friguia plant and from loading operations at the mining port [14]. The clients of this Company require grains of alumina which have a diameter of at least 45 microns so as to permit saving energy in the high furnaces during the production of aluminum. Even if clients accept grains of a diameter that is less than 45 microns, these must not exceed 12% of the quantity supplied.
2.3.2. Red Mud from Alumina Processing in Guinea
- There are different aluminum production processes for different bauxites that subsequently produce different types of red mud. The red mud, according to the production process of the aluminum, can be divided into Bayer process red mud, sintering process red mud and combined process red mud. It was reported that 0.8~1.5 t of red mud is produced by each 1 t alumina produced.Red mud is mainly composed of coarse sand and fine particles of mud. Its composition, property and phase vary with the origin of the bauxite and the alumina production process, and will change over time when stocked. The amount of alkali in red mud fluid is about 2 to3 g/L (calculated by Na2O), which results in a pH value between 13 and 14.
2.3.2.1. Chemical and Mineral Compositions of Red Mud
- Chemical analysis shows that red mud contains silicium, aluminium, iron, calcium, titanium, sodium as well as an array of minor elements namely K, Cr, V, Ba, Cu, Mn, Pb, Zn, P, F, S, As, and etc. The variation in chemical composition between red muds worldwide is high. Typical composition of red mud from the Guinean bauxite is given in Tab.4 and Tab.5.
|
|
2.3.2.2. Physical Properties
- The properties of red mud vary significantly from different bauxites and different methods of generation. In general, red mud is a very fine material in terms of particle size distribution, having an average particle size <10 μm. Typical values would account for 90% of the volume below75 μm. The specific surface area (BET) of red mud is as large as 64–187 m2·g−1, which indicates that red mud has a high degree of mineral particle dispersion. Red mud has large water content, up to 700to 1000 kg/m3, accounting for 79%–93% of the total weight. This water will be desorbed when the red mud gets shocked, which may lead to a decrease of mechanical properties of red mud.Red mud is a very fine- grained material. Typical values for particle size distribution are 90 weight % below 75 microns. It has a porous structure with a void ratio of 2.5–3.0, a high compressibility (Eg = 28–40 MPa) and low shear strength (C = 9.6–74.3 kPa; φ = 13.5–21.0°). Despite red mud’s properties of high porosity and water content, it will not shrink or expand after drying [18].It is estimated that approximately 35 % - 40 % per ton of bauxite treated ends up as waste via the Bayer process. Furthermore, about 70 million tons of bauxite residue or RM are produced yearly worldwide and are not utilized [19].
2.3.2.3. Red Potential of Guinean Alumina Industry
- About 1 tonne of alumina is produced from 3 tonnes of bauxite and about 1 tonne Aluminum is produced from 2 tons of alumina. Depending on the raw material processed, 1-2.5 tons of red mud is generated per ton of alumina produced.If one calculates on the basis of the production of 600000 metric tons of alumina per year, the plant at Friguia generates an equal quantity of red mud. Over the company’s 30 years of existence, the quantity of red mud produced may very well exceed 20 million metric tons, It should be mentioned that up until the end of the 1980’s this mud was simply dumped in the Konkouré river which flows not far from the plant. It has now been established that the mud resulting from the extraction of alumina is very caustic. Investigations suggest that until recently, the Konkouré River also received oil residues and polluted water coming from the ACG alumina plant and the caustic soda or red mud, which had previously been stocked in the Doté valley. The Lakoy River was the recipient of the liquid wastes which contained soda and hydrocarbon channeled by the plant’s principal sewage canal. Fig.2. represents the quantity of NaOH, and the pH at different points of Konkouré River. The pH varying between 9 and 11 with an average of 10.45 is high. It is related to the quantity of soda coming from bauxite attack with NaOH during the Bayer process.
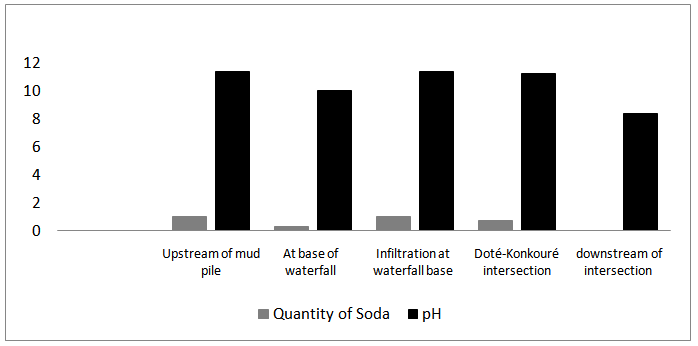 | Figure 2. Soda content and PH of the Konkoure River |
2.3.2.4. Value Opportunities of the Red Mud
- The question of what to do with bauxite residue arose with the development of the Bayer process for alumina refining and the recognition that it generated a large amount of waste material. Regardless of over 50 years of research and hundreds of publications on the subject, little evidence exists of any significant utilization of bauxite residue at any time.The global inventory of bauxite residue stored on land currently is estimated to be over 2.7 billion tonnes, with an annual growth rate of over 120 million tonnes.With regard to bauxite there are two broad utilization classes for the red mud that have the potential to create value. These are: (i) construction materials and chemicals; (ii) environmental and agronomic use and (iii) metallurgical applications. Environmental and agronomic aspects are out the scope of this study.
2.3.2.4.1. Construction and Chemical Applications
- Construction and Chemical Applications includes the following three application areas: Civil and Building Construction, Catalyst and Catalyst Support or Adsorbent, and Ceramics, Plastics, Coatings or Pigments.
2.3.2.4.1.1. Civil and Building Construction
- Building materials stand out as an application which could consume significant residue volume. Concrete is the dominant construction material in the world today, so the addition of residue to cement and/or concrete in any significant amounts, or as a geopolymer replacement, presents a value opportunity. For example annual crushed stone aggregate consumption in the US amounts to 1.63 billion tonnes per annum [20] with worldwide consumption in the order of 20 billion metric tonnes, compared to some 120M tpa bauxite residue estimate. CementAvailability of raw material required for manufacturing of cement and production of concrete are limited in nature. This increased demand will lead to fast depletion of natural resources and will cause big threat to environment. The iron and alumina contents of thered mud can be beneficial to the setting and strength properties of the cement, but the soda is detrimental. Replacement of the soda with calcia improves the performance of the residue as an additive. It should be noted that in this application the residue has to be calcined to temperatures in the order of 1000oC, either as a pre-treatment or in combination with the production of quicklime [21].Residue was chosen as a source of alumina and iron in preference to other industrial by-products because of its low silica content, and it was found to perform better than fly-ash. By optimizing the firing temperature and the composition of the mix it was possible to prepare cements with superior setting strengths to ordinary Portland cement, with red mud additions in the range 20 to 50% by dry weight. The titanium content of the mud was found to be beneficial to concrete strength. Bauxite is commonly used directly in cement-making as a source of alumina and iron for the production of both Portland and calcium aluminate cements. The global usage of bauxite in this application in 1999 was estimated at 1.0-1.2M tpa, making its use asa cement additive the largest non-metallurgical use of bauxite have examined the feasibility of using residue as a minor additive to Portland cement in the local cement industry [22]. A pilot-scale study has demonstrated that Portland cement with acceptable properties can be prepared containing up to 5%residue, which if incorporated into the cement production. The cost of processing the residue for incorporation into the cement was estimated at €10/tonne of dry residue [23].Blended cement samples, were prepared with replacement of cement by neutralized red mud with increment of 5 percent (i.e. 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% & 25%). setting time with different percentage of NRM in cement. With the increase in neutralized red mud in the mix, the water required for standard consistency also increases and the relationship between the standard consistency and requirement of water for that is linear. As the red mud having small grain size, due to which surface area was increased and also the water required was increased. Beyond 10% replacement of cement by red mud the setting times are increased [24]. For each grade of concrete design mix i.e. M 30, M 40 and M 50, there was an initial decrease in the compressive strength for 5% replacement of cement by NRM. But from the next replacements i.e. 10 % and 15% the compressive strength are increased with the increase in the % replacement of cement by NRM.Scientists conducted a series of studies into the production of cement using red mud, fly ash, lime and gypsum as raw materials. Use of red mud cement not only reduces the energy consumption of cement production, but also improves the early strength of cement and resistance to sulfate attack.AggregateAggregates consist of a variety of materials; they are classified as either coarse or fine. The coarse aggregate is natural gravel or a coarse fraction of crushed rock and similarly, fine aggregate is native or synthetic sand. There are many studies on the production of coarse aggregates from the finer red mud fraction. The production of aggregates from red mud requires many processing steps such as: drying, pelletizing and calcining. The published work on this as a residue utilization option appears contradictory. For example residue could replace the aluminosilicate fractions for geopolymers, but base this on work combining a synthetic alkali waste stream (8.9 % w/w Na2O, 28.7% w/w SiO2 and 62.5 % w/w H2O) with fly-ash [25].Whilst the test materials only required mixing and curing at 85°C for 2 hours and could exhibit (depending on sodium, silicate and aluminate ratios) compressive strengths of almost 50 MPa; this is not the same as actually testing residue. Compressive strength is one of the key attributes for aggregate substitution. For comparison the compressive strength of a natural marble might range over 100-180 MPa, so a geopolymer of up to50 MPa would have limited applications. Composites based on lime, silica and limestone to Jamaican residue only managed compressive strengths of 22 MPa [26]. Compressive strengths of gravels used in concrete manufacture vary widely depending upon source, typically ranging 165-235 MPa, with >94% of aggregate used for gravels having over 70 MPa compressive strength. Drying and firing of residues may produce acceptable synthetic aggregates. Firing conditions of 220°C for 40 min, then 1200°C for 2.5 hours a product was obtained with compressive strength comparable to or better than gravel [27].The issue of calcination cost should be taken into account. One of the key aspects of cement production is that because calcining to high temperatures (1400-1500°C for long periods) is a major part of the process it can provide a very good guide to the likely costs of heating a material on a large scale. For cement production, fuel costs are the main cost for calcining to clinker and power costs for grinding the clinker to cement. Bricks and blocksThere are two approaches to brick and block manufacture from the fine fraction of red mud depending on whether the material is kiln fired or not. Conventional clay bricks are fired at around 1000°C to achieve the required strength.Unfired bricks are made by including cement or other inorganic or organic binders. Residue can be added to the mix as either a major or minor component [28]. It has been shown that bricks of comparable quality to commercial clay bricks can be prepared from bauxite residue mixed with natural materials such as clay or shale. Other waste products such as fly ash and coke dust may also be added. Lightweight bricks can be manufactured by including other additives such as ferrosilicon and foaming agents. Unfired bricks can be prepared with bauxite residue as either a major or minor component by including setting agents, which may be inorganic (gypsum, lime, cement) or organic (polymethylmethacrylate, polyvinyl acetate, etc.) [29].
2.3.2.4.1.2. Geopolymers
- Geopolymerization is an emerging technology being developed for the utilization of industrial by-products including fly-ash, slags, metakaolin, rice husk, etc. [27]. Geopolymers have a number of advantages over the established ordinary Portland cement-based concrete technology, in particular an 80% reduction in overall CO2 emissions intensity. They can be prepared with excellent mechanical properties.For several considerations, the geopolymers appears to be apotential alternative to the classic hydraulic binders. Nevertheless, their chemical composition is very different from that of cementsor lime. Cements owe their mechanical properties to the formation of the hydrated calcium silicates (C–S–H) while the exothermic reaction of geopolymerisation generates a structure closer to zeolites or aluminosilicate gels. This alkaline aluminosilicate material, generally amorphous is mainly produced from metakaolin (source of Si and Al) reacting with hydroxides or alkaline silicate solutions [30]. The geopolymerization mechanism involves Si and Al dissolution from the starting materials generates to make available poly sialate units (e.g., sialate [-Si-O-Al-O], sialatesiloxo [Si-O-Al-O-Si-O] or sialatedisiloxo [-Si-O-Al-O-Si-O], de-ending on the Si/Al ratio) cross-linked [AlO4]- and [SiO4] tetrahedral units, with charge balance ensured by Na+ or K+ ions.Two different geopolymers GP were synthesized from metakaolin MK and the admixture of red mud RM and their mechanical properties, composition, and microstructure were characterized, respectively [31]. In general, for a given Si/Al ratio, the MK-GP exhibits much higher compressive strength, stiffness, and failure strain than the RM-GP. For the studied geopolymer samples, the MK-GP achieved strength of 31 MPa, while the RM-GP had strength of 13 MPa. The MK-GP can be cured completely as less as 9 days, while the RM-GP takes more than 21 days for complete curing.
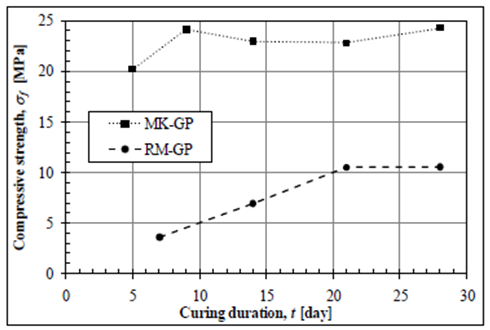 | Figure 3. Effect of curing duration on the compressive strength of the MK-GP (Si/Al = 1.75) and RM-GP (RM/FA = 50/50) [33] |
2.3.2.4.1.3. Catalysts or Adsorbents
- Catalytic applications of red mud have been widely touted, mainly because of its Fe2O3 and also TiO2 content and high surface area [32], but also because it is viewed as a cheap and disposable source of fine sized raw material. The catalytic applications were reviewed for hydrogenation, hydro-dechlorination, exhaust gas clean-upand other areas [33]. It was concluded that the performance of unmodified residue was poor compared to straight iron oxides or commercial catalysts. Most applications require some prior treatment, or “activation”, of the residue to improve catalytic efficiencies. Such activation procedures include size reduction, heat treatment (usually to 400°C to convert hematite to magnetite), sulphidization, and even acidaddition to dissolve the iron and other minerals that are then believed to precipitate in a more active form. Removal of Ca and Na is also desirable, because Na in particular promotes sintering and corresponding loss of specific surface area at elevated temperatures. Other researchers also agree with the generally poor performance of residue [34].
2.3.2.4.1.4. Ceramics, Coatings, Plastics and Pigments
- The most frequently used applications are: refractories, ceramics, cement; production and refining of metals other than iron; inorganic pigments and non-fibrous fillers, and inks, paints, polishes.For PVC (polyvinyl chloride), red mud is not only a filler that has a reinforcing effect, but is also an efficient and cheap thermal stabilizer, providing the filled PVC products with an excellent anti-aging property. Its lifetime is 2 to 3 times that of ordinary PVC products. At the same time, the fluidity of red mud is better than other fillers, which makes it plastic with good processing properties. And the red mud PVC composite plastics have fire retardant property, and can be made into red mud plastic solarwater heaters and plastic construction profiles. [35].
2.3.2.4.2. Metallurgical Applications
- Metallurgical Applications, includes the following areas: Recovery of Major Metals, Steel Making and Slag Additive, and Recovery of Minor Metals. The metallurgical applications inparticular illustrate utilization drivers based on overly simplistic interpretations of metal value and processing costs.
2.3.2.4.2.1. Recovery of Major Metals
- The major metals referred to are iron, aluminum, titanium and sodium. Theoretically, it is difficult to see how bauxite residue containing 40% Fe2O3 incombination with aluminum, silicon, soda and a number of other elements and with at least 20% free moisture content could compete with virgin iron ore containing>99% Fe2O3 and <5% free moisture. Likely the only way in which processing of red mud for the production of iron or alumina could possibly be viableis through the creation of additional value by producing several metals in a single integrated process.The aims of the recovery of multiple major metals are to simultaneously maximize the value created and minimize the residual solids produced [36].Recovery of high value minor components, such as titanium, plays a potentially important role in adding value. To be successful, any processing scheme for metals recovery would have to be designed and evaluated for specific residues to maximize opportunities arising from the compositions. For instance, some alumina residues from India have been found to have up to 28% w/w TiO2, so Ti recovery may be of particular interest there. It is technically feasible to recover the TiO2 by treatment with a hydrochloric and then sulphuric acid producing 97.5% TiO2 (white), somewhat above a typical synthetic rutile grade.
2.3.2.4.2.2. Steel Making and Slag Additive
- The red mud is recorded as one of a number of possible additives used as a source of aluminum, silicon and calcium to modify the properties of the slag to improve separation, setting and other qualities. Its use in these applications presumably depends on its relative cost, availability and performance in comparison to other possible additives that include clay, slate and sand. It is not possible to gauge the likely extent of usage of bauxite residue in these applications from the scientific literature, and this area of use has not been discussed to any significant extent in the literature. Henceit would seem that this is not a majorarea of actual or potential application of bauxite residues, however it may be useful to confirm this.
3. Conclusions
- The immense endowment with mineral resources offers a possibility to Guinea to yield a key position in the mineral and metal industry. The conversion of the 2/3 of the world bauxite reserves into aluminain Guinea or elsewhere will produce a huge volume of red mud with serious environment concerns. However this amount of residue may be processed into valuable products suitable for application in engineering sectors.Converting the red mud into a new product is not only the development of technological solutions. Arguably a choice of technologies already exists to fully utilize bauxite residue. However, to make a significant impact on the amount of residue stored, applications that will consume large quantities of residue on an ongoing basis are required. The performance of residue in any particular application must be competitive with the alternatives in relation to quality, cost and risk. The economic viability for any utilization option must be demonstrated on a case-by-case basis. The overall lack of progress on utilization suggests that no strong economic case has been established to date.For any given application, it must to be demonstrated that the risk associated with it is less than the risk associated with continued storage. Moreover, utilization will probably also require incentives to initiate change on a case-by-case basis.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML