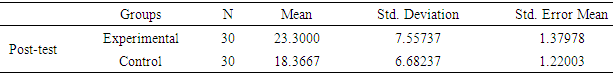-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Learning
2016; 2(1): 8-16
doi:10.5923/j.jalll.20160201.02

The Role of Mind Mapping Soft Ware in Developing EFL Learner's Vocabulary at the Pre-Intermediate Level
Azin Bahadori1, Bahman Gorjian2
1Department of English, Ahvaz Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahvaz, Iran
2Department of English, Abadan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Abadan, Iran
Correspondence to: Bahman Gorjian, Department of English, Abadan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Abadan, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study investigated the role of mind mapping software in using vocabulary among EFL pre-intermediate students. The study was conducted in a pre-university center in Masjedsoleyman. Sixty EFL learners were selected out of 90 learners. They were chosen based on Interchange Language Placement test (Richards & Lesley, 2007) administered as a homogeneity test. Its reliability value was met through calculating KR-21 formula. The learners whose scores were one standard deviation above and one standard deviation below the mean were selected as the participants of the study. Then they were divided into two groups and sat for the vocabulary pre-test designed on the instructed material. Each group includes 30 participants. They included Mind Map (i.e. experimental) and Control groups. The experimental group received vocabularies encompassing the passages taught through the Mind Mapping software 6 (v3.5.3.0) from Xmind.net website as treatment to participants of experimental group. Eight passages of their reading lessons were covered in ten sessions. The control group received conventional instruction on learning vocabularies including definitions, explanation and translation. After 10 sessions of instruction, 50 minutes each, they took the post-test. Independent Samples t-test was used to calculate the data. Results showed that the learners who used the mind mapping software outperformed the control group; however, the both groups showed progress in learning vocabulary. Comparison of the groups' pre and post-test showed that the experimental group performed more strong than the control group (p<0.05).
Keywords: Mind mapping software, Vocabulary, EFL pre-intermediate students
Cite this paper: Azin Bahadori, Bahman Gorjian, The Role of Mind Mapping Soft Ware in Developing EFL Learner's Vocabulary at the Pre-Intermediate Level, Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Learning, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2016, pp. 8-16. doi: 10.5923/j.jalll.20160201.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Vocabulary teaching and learning is a time consuming effort in traditional approaches such as looking up the meaning of new in the printed dictionaries. It has been increasingly argued that computer technologies can support learning in a number of ways and facilitate learning preprocesses (Gorjian, 2008). Teaching vocabulary through Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) activities has been popularly used in English as a foreign/second language learning English as a Foreign Language/English as a Second Language (EFL/ESL) contexts (Son, 2008). Many features of the computer are considered to enhance vocabulary development and reading comprehension. Multimedia is one of them. Multimedia refers to computer-based systems that use various types of content, such as text, audio, video, graphics, animation, and interactivity. The key concepts of multimedia are thus 'computer-based' and 'interactive'. Teachers should pay more attention to the existence of various teaching tools that help in vocabulary development, both traditional, and technology-enhanced. Using CALL approaches to teaching vocabulary, teachers are also freed from long and boring process of teaching vocabulary and are allowed to focus more on other needs of language learners (Gorjian, 2008). Thus, for vocabulary acquisition, teachers could make great use of technology by using multimedia glossed texts, electronic dictionaries, as well as various vocabulary-building software. One of the recent ways in making texts more comprehensible to students is using mind mapping software approaches. According to Budd (2004), Mind Mapping software is a graphic organizer in which the major categories radiate from a central image and lesser categories are portrayed as branches of larger branches. It can be used to generate ideas, take notes, develop concepts and ideas, and improve memory (Buzan, 2000, 2010, 2012). A mind map is a visual and graphic representation that depicts the relationships between facts, terms, and ideas within a learning task (Hall & Strongman, 2002). It is clear that mind mapping software is a category of graphic organizers which have different types for different instructional purposes. "Two commonly used graphic organizers are semantic maps and concept diagrams" (Vaughn & Edmonds, 2006, p.135). Semantic mapping strategy falls under the broad category of graphic organizers (Baleghizadeh & Yousef poori Naeim, 2011). Asadollahfam and Shiri (2012) define semantic mapping as "a graphic representation or picture of one's thoughts, ideas, and attitudes toward a key concept". In addition, Sinatra (1984) defines this as "a graphic arrangement showing the major ideas and relationships in text or among word meanings" (p. 22). Semantic mapping diagram represents the message of the text. It is an excellent strategy to reading comprehension (Schmidt, 1986). Stahl and Vancil (1988) mentioned that semantic mapping represents a diagram of the relationships between words according to their use in a particular text.Based on Hall and Strangman's (2002) view, a descriptive or thematic map works well for mapping generic information, but particularly well for mapping hierarchical relationships, network tree aims to organize a hierarchical set of information, reflecting supper ordinate or subordinate elements, a spider map can help with organization when the information relating to a main idea or theme does not fit into a hierarchy, a problem-solution outline helps students to compare different solutions to a problem, a fishbone map may be particularly useful when cause-effect relationships are complex and non-redundant, a compare-contrast matrix can help students to compare concepts’ attributes, a series of events chain can help students organize information according to various steps or stages. Whiteley (2005) states mind maps expand on spider maps. These maps have a tree structure with one trunk with many branches. They are examples of organic thinking. That is, like a tree, a central idea (the trunk) branches off in many directions.Mind mapping software can have various forms, from representations of objects to hierarchical and cyclical structures. Although their use in learning activities is preferred by people who have a visual style of learning, mind mapping are extremely useful to different learners (Lee & Schallert, 1997). Semantic map, structured overview, web, concept map, semantic organizer, story map, graphic organizer, etc. no matter what the special name, a mind mapping software is a VISUAL representation of knowledge. It is a way of structuring information, of arranging important aspects of a concept or topic into a pattern using labels (Bromley, Irwin-DeVitis, & Modlo, 1995).Mind mapping software have been classified into five major categories according to their structures: star web, chart matrix, tree map, chain, and sketch. Mind mapping software have also been classified into eight categories according to their purposes for teach (Tang, 1992). The eight categories of graphic organizer are KWL(Know, Want and Learned) chart the letters are an acronym for what students in the course of a lesson already know want to know and ultimately learn, history frames, word map, zooming in and zooming out – concepts, zooming in and zooming out –people, Inquiry chart, Venn diagram, column notes. KWL charts can be used as a teacher-led activity to introduce a new topic at any grade level. A history frame allows students to look at historical events and break the information down to understand its significance, the people and places involved and any other pertinent information. A word map helps students analyze a new or complex vocabulary word from many different angles. Zooming in and out – concept graphic organizer allows students to delve deeper into a more complex concept. There is a box in the middle of the page for the concept; then there are five other boxes branching out from the middle, and zooming in and out organizer is similar to the one for concepts, but focuses on people instead. The center box is for the name of a person and the surrounding boxes include spaces for the most and least important information, similar people, related events, surprising facts and a summary statement. An inquiry chart or I-chart is a way to organize information obtained during research. It contains four columns across the top, each for a different question. A Venn diagram is used to compare two ideas, events or people. It contains two overlapping circles. A column notes organizer is simple to set up and versatile in its applications. To organize notes, all a student needs to do is divide a piece of paper into two sections, each with its own heading (Jiang, 2007).Mind mapping software provides teachers with tools to help students on the road to higher achievement in their reading comprehension skills. Mind mapping software that target critical and creative thinking elements help develop students in their ability to comprehend and understand the meaning of a text. The focus of the students in content is improved and they can classify the content into small understandable units. Mind mapping software facilitates classroom communication, as well as deepen the learners' understanding of the passage (Gorjian, 2008).This study aims to investigate the effectiveness of discourse structure-based mind mapping software on EFL students’ vocabulary learning based on selected texts. The findings may be of benefit to classroom teachers include discourse structure-based mind mapping software in their teaching new vocabularies instruction.In many EFL classes, even where teachers have devoted much time to vocabulary teaching, the results have been disappointing, especially where English is not the main medium of communication. Therefore, finding a new way to alleviate this problem and help teachers with vocabulary instruction seems to be crucial. In English classes we use Mind Mapping software, and conventional approaches affecting vocabulary retention. The advance in technology has made it easy to take advantage of modern facilities.The aim of this study is showing that using modern methods such as Mind Mapping software has a significant effect on learning new lexical items of foreign language learners. This study will investigate the following research questions:RQ1. Does the use of mind mapping software affect students' vocabulary development? RQ2. Is there any difference between the learners who use mind mapping software and the conventional method of teaching vocabulary in developing EFL their vocabularies?
2. Literature Review
- In today’s world, being able to read in a proficient manner in both L1 and L2 is of utmost importance because we are bombarded with new vocabularies everywhere we go. The ultimate aim for foreign learners is to understand what information the writer has intended to convey in the specific context they encounter. However, it should not be forgotten that there exist some prerequisites to achieve this, such as exploiting some background knowledge, recognizing main ideas and supporting details, and pinpointing connections between relevant information. Only in this way can readers form meaningful representations of the text content in their minds (Grabe, 2009). It might be simplistic to think of a text as comprising only linguistic elements such as semantics and syntax. Structure, pragmatic nature, intentionality, content and topic have roles to play in the reconstruction of the intended meaning of the author by the learner (Bernhardt, 1998). Grabe (2009) highlights the importance of discourse structure awareness in relation to this reconstruction of meaning. Discourse structures are viewed as knowledge structures, text structures or basic rhetorical patterns in texts. In this thesis, discourse structures and text structures will be used interchangeably. An understanding of these top-level structures might be associated with having an insight into the inter-relatedness of ideas in a text and forming a correct interpretation of what the writer has set out to express (Jiang & Grabe, 2007). Skilled vocabulary learners of L1 and L2 with discourse structure sensitivity are alert to the specific ways in which information is organized and identify the signaling mechanisms for this, as well as able to distinguish main ideas from the minor ones as they read. Moreover, they use their text structure knowledge to guide their comprehension, which in return equips them with an organized, a coherent and a more global understanding of the text (Grabe, 2009). Mind mapping software are defined as “visual and spatial displays designed to facilitate the teaching and learning of textual material through the use of lines, arrows and a spatial arrangement that describe text content, structure and key conceptual relationships” (Kim, Vaughn, Wanzek, & Wei, 2004, p. 105). In educational settings, they have been perceived as valuable instructional tools because “a good graphic representation can show at a glance the key parts of a whole and their relations, thereby allowing a holistic understanding that words alone cannot convey” (Jiang & Grabe, 2007, p. 34). Since there is a manageable number of repeating patterns (description, definition, sequence, procedure, cause-effect, classification, comparison-contrast, problem-solution) in expository texts, they lend themselves to being used along with mind mapping software to direct students’ attention to text structures and help to enhance reading comprehension (Grabe, 2009; Jiang & Grabe, 2007).A review of recent articles indicates that the use of spatial graphic representation of textual information in the construction of reading activities is likely to create positive results in terms of increased comprehension, and the employment of a greater number of strategies (Kools, Van De Wiel, Ruiter, Crüts, & Kok, 2006; Lin & Chen, 2006; Suzuki, 2006; Suzuki, Sato, & Awazu, 2008). The findings of these studies showed that graphical displays can reduce the cognitive burden on students because of their two-dimensional spatial arrangement. Jiang (2007) carried out a longitudinal large-scale study which aimed at understanding the possible effects of mind mapping software completion on learning new vocabulary for better reading comprehension skills. Jiang (2007) found that mind mapping software instruction which lasted for 16 weeks caused a significant improvement in Chinese EFL students 'reading comprehension. The analysis of the participant students’ responses to the short attitude survey, which was given at the end of the instruction period, revealed that the students held positive attitudes towards the use of mind mapping software in reading instruction. Another study by Carrell, Pharis and Liberto (1989) had similar findings in terms of the subject’s reaction to mind mapping software. The effect of visual representation of knowledge has also been explored in content area instruction. Stull and Mayer (2007) found out that the integration of mind mapping software into scientific texts helped students in transferring their understanding of content to problem solving-based tasks. For instance, the following minds maps are presented in Figure 1.
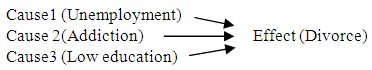 | Figure 1. Cause and Effect Outline |
3. Method
3.1. Participants
- The study was conducted in a pre-university center in Masjedsoleyman. The participants of the study were 60 learners at pre- intermediate level and with age ranging 17-18 years old were selected out of the research population (n=90) after administering a vocabulary test extracted from the Interchange Language Placement Test (Richards & Lesley, 2007). The learners whose scores were one standard deviation above and one standard deviation below the mean were selected as the participants of the study. Then they were randomly divided in to experimental and control groups through systematic random sampling. Each group included 30 participants.
3.2. Instrumentation
- In this study, two tests were used including the vocabulary test was used as the pre-test as well as the homogeneity test to determine the learners’ level of vocabulary knowledge on the selected texts at the beginning of research period and a post-test to determine the effect of mind mapping software on developing students' vocabulary of selected texts. This test was a modified version of the pre-test. Some items were replaced to prevent reminding the items of the pre-test. The reliability of the pre and post tests were calculated through KR-21 formula as (r= .72, and r= .79 respectively).
3.3. Materials
- The materials used in this study were eight reading passages (i.e., Importance of Exercise, Presentation of a good Speech, Global Warming, Earthquakes, Child Labor, Space Exploration, IT and it’s Services, Great Men and Women) that were chosen from a Pre-Intermediate Textbook, Connect (Richards, Barbison & Sandy, 2009). While selecting the reading passages, the researcher made an effort to create a combination of texts that had different discourse structures as the aim was to expose the students to as many discourse patterns as possible during the course of the study. The text structures of the eight reading passages that were used in the study included description, definition, sequence, procedure, cause-effect,and classification.
3.4. Procedure
- The present study intended to investigate the effects of using mind mapping software on the development of vocabulary skills of Iranian learners. In other words, the researcher attempted to have a deep look at how mind mapping software can improve learners' vocabulary. In this respect, after homogenizing learners, they were randomly divided to two groups: experimental and control group. Learners in experimental group were exposed to mind mapping software and worked on the lessons of their books. However, learners in the control group were exposed by traditional teaching and worked on them. Pre- and post-test were administrated before and after the intervention. The data were collected for further analysis.As mentioned previously, the text structures of the eight reading passages that were used in the study included description, definition, sequence, procedure, cause-effect, classification, comparison-contrast, and for & against. In each text, two or three of these structures were nested within one another. The researcher used the mind mapping software 6 (v3.5.3.0) from Xmind.net website that directly reflected the discourse structures of the selected texts. In order to understand whether this software was appropriately designed, the opinions of five teachers were sought. They all agreed on the appropriateness of the mind mapping software developed by the researcher. In order to test the practicality of the graphic organizers, eight reading teachers from the pre- intermediate level were asked to sit down and complete the graphic organizers with the texts, they all successfully completed the mind mapping software.Before the experiment started, the participant teacher had tried to make the students familiar with the procedure of the study by using several samples of text structure-based mind mapping software for some texts in their course books and by asking the students to fill them in. Both the selection of the texts and the development of the related mind mapping software were done by the researcher. The participants of the study participated in both the mind mapping software and the conventional treatments so it can be claimed that they acted as their own experimental and control groups. After the preparation sessions, in the first week of the experiment, a homogeneity test, that was used as pre-test was administered. Such test was 40 open -ended questions that got from reading texts, the test material was designed based on the scope of the study. It was made up of eight passages, totaling 40 vocabulary items classified into four types of vocabulary items – (1) Identifying the definition, (2) matching, (3) understanding vocabulary and (4) making definitions. Each category included 10 items: each item was worth 1 mark and the sum total of the test was 40, students answered these questions during 100 minutes. The learners who got the scores within one standard deviation below and above the mean were accepted as the participants of the study. Then two experimental and control groups were selected through systematic random sampling. During 10 sessions of instruction, 90 minutes each, the texts were worked. In the experimental group at the beginning of the instruction, the researcher familiarized the students with what mind mapping software are and how to use them effectively while reading new vocabulary of a text. The students were also trained to use different organizers for different types of passages. The students learned a variety of existing mind mapping software and they also started creating their own designs. In the following 10 sessions the participants in the experimental group structured their own mind mapping software for reading texts studied in the class hour and presented them to their classmates in groups. Some of the mind mapping software was also presented by the students to the whole class by drawing on the board. Then, new vocabulary questions were answered by the participants and checked by the instructor. The instruction material and content provided for both the experimental and control groups were the same but the control group was not exposed to the use of mind mapping software and implementing the same in learning new vocabulary process. The control group adopted conventional methods where students were made to read the new vocabulary again and again to understand the content and answer the comprehension questions. They were able to understand the meaning conveyed in the paragraph or passage but they could not classify a paragraph into main idea, topic sentence, supporting details, etc. In the last section after10 session’s treatment, a post-test was administered; pre-test was modified for the post- test. It was 40 open-ended questions from new vocabulary of reading texts for each group .they replied those questions during 100minutes. The reliability of the tests were calculated through KR-21 formula Then the data was statistically analyzed.
3.5. Data Analysis
- In this study, data were collected through the administration of post-tests. In the analysis of this quantitative data, the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 17 was used. In order to examine the effects of the discourse structure-based mind mapping software on students’ developing vocabulary, parametric statistical methods were used for the analysis as the data were normally distributed. Independent Samples t-test conducted in order to explore how mind mapping software affected the participant students’ comprehension of each text as well as the students’ overall reading performance in the study.
4. Results
- This section describes the process of analyzing the collected data, statistical computations, results and figures obtained. Focusing on the role of using mind mapping strategy on vocabulary learning and retention, the statistical calculation and results are presented and then the results of the study will be discussed.
4.1. The First Research Question
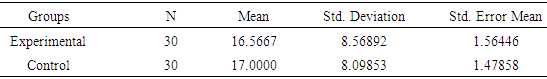
- The first research question of the study explored whether the use of mind mapping software can improve learners' vocabulary skills. The experimental and control learners' descriptive statistics in pre- and post-tests are presented in Table 4.1.Table 1 shows there is a slight difference between the pre-tests vocabulary test among the experimental and control groups' pre-tests. Findings denote that the learners have somehow similar means. However, Independent samples t-test can show the significant difference between the groups' pre-tests. Moreover, to have a clear picture of learners’ improvement, an independent sample t-test was run between post-assessments of experimental and control groups. The results were presented in Table 2.
|
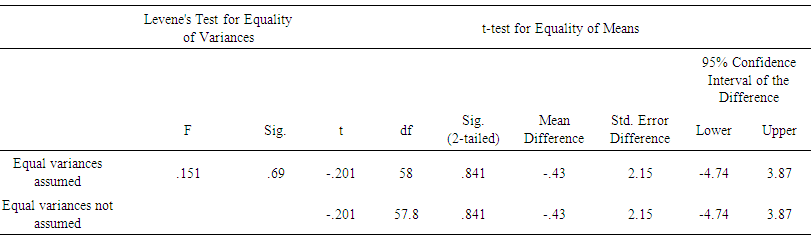 | Table 2. Independent Samples Test (Pre-test, Experimental and Control Groups) |
4.2. The Second Research Question
- The second research question of the study explored the possible differences between learning by mind mapping software or traditional instruction with regard to their vocabulary abilities. The descriptive statistics of learners’ vocabulary ability in the post-test are presented in Table 3.
|
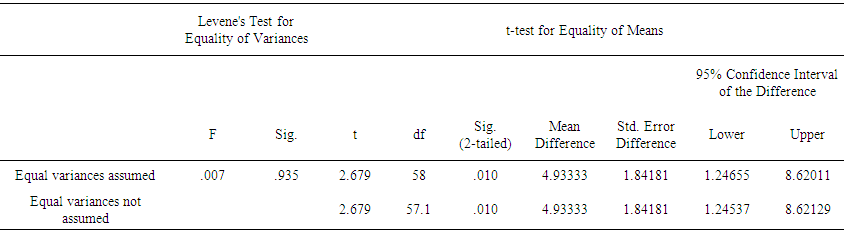 | Table 4. Independent Samples Test (Post-test, Experimental and Control Groups) |
5. Discussion
- The findings of the current study regarding the effects of discourse structure-based mind mapping software on students’ vocabulary development of selected texts will be presented and discussed with reference to the literature. Then, the findings related the differences between using mind mapping software and the conventional comprehension method will be presented and discussed.Question One: Does the use of mind mapping software affect students' vocabulary development? The quantitative data gathered from the students’ performance which were administered at the end of each procedure during the ten session treatment shed some light on the use of the mind mapping software for improving vocabulary. The post-test scores of the two groups for both the mind mapping software and the conventional performances were calculated and compared with each other to see the effects of the mind mapping software treatment. This comparison indicated that the learners performed better on post-tests when they completed discourse structure-based mind mapping software as a pedagogical tool in teaching in comparison to those that took part in a conventional method. The success of the mind mapping software treatment was consistent across the eight texts used in the study. This finding supports what the literature indicates about the use of mind mapping software in developing vocabularies.Since the mind mapping software used in the present study included lines, arrows and spatial arrangement, the students had an opportunity to store the contents of the texts in the form of both verbal information and visual images. This might be one of the reasons that led to the higher scores in the post-tests given after the students had been involved in mind mapping software activities.To this end, learners were undertaken a treatment and pre- and post-test were administrated. According to the findings, there are statistical significant differences before and after the intervention in experimental learners’ vocabulary development. It denotes that, mind mapping software as a pedagogical tool are significant instructional means which effectively promote learners’ vocabulary as a reading skill. The results highlight the importance of multimedia in language acquisition, promotion of learning skills and strengthen of cognitive abilities.The literature has also reported the same significant effect of multimedia on learners’ language functioning. Teaching vocabulary through Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) activities has been popularly used in English as a foreign/second language learning (English as a Foreign Language/English as a Second Language) contexts (Son, 2008). Many features of the computer are considered to enhance vocabulary development and reading comprehension. Multimedia is one of them. Multimedia refers to computer-based systems that use various types of content, such as text, audio, video, graphics, animation, and interactivity. The key concepts of multimedia are thus 'computer-based' and 'interactive'. Teachers should pay more attention to the existence of various teaching tools that help in vocabulary development, both traditional, and technology-enhanced. Using CALL approaches to teaching vocabulary, teachers are also freed from long and boring process of teaching vocabulary and are allowed to focus more on other needs of language learners (Gorjian, 2008).Generally, creating a meaningful environment by the help of mind mapping software promotes the vocabulary skills of learners and overcome limitations of a successful comprehension. Moreover, this helps to strengthen the imaging systems which are an indispensable part of learners’ lives. The second research question of the study is: Question Two: Is there any difference between the learners who use mind mapping software and the conventional method of teaching vocabulary in developing EFL their vocabularies?Focus of mind mapping software is on interrelationships of ideas rather than isolated ideas, mind mapping software get away from the linearity of the text and approximate the macrostructure of the text. Texts are not list like sequences-they have rhetorical structures that organize information and serve writers’ purposes (Grabe, 2009). They allow a holistic understanding that words alone cannot convey (Jiang & Grabe 2007). They have powerful construct validity (Grabe, 2009).Conventional method is concerned with the teacher being the controller of the learning environment. Power and responsibility are held by the teacher and they play the role of instructor (in the form of lectures) and decision maker (in regards to curriculum content and specific outcomes). They regard students as having 'knowledge holes' that need to be filled with information. In short, the traditional teacher views that it is the teacher that causes learning. Learning is chiefly associated within the classroom and is often competitive. The lesson's content and delivery are considered to be most important and students master knowledge through drill and practice (such as rote learning). Content need not be learned in context.Some disadvantages of the conventional method are, places students in a passive rather than an active role, which hinders learning, encourages one-way communication; therefore, the lecturer must make a conscious effort to become aware of student problems and student understanding of content without verbal feedback, requires a considerable amount of unguided student time outside of the classroom to enable understanding and long-term retention of content. In contrast, interactive methods (discussion, problem-solving sessions) allow the instructor to influence students when they are actively working with the material and require the instructor to have or to learn effective writing and speaking skills.The findings of this study are matched with Tang (1992) who carried out an experiment that explored the effect of graphic representation of knowledge structure of classification on intermediate level ESL students’ comprehension of content knowledge. The subjects dealt with the same passage in two different groups: the graphic and the non-graphic group. The written recall protocols, which were used as post-tests, showed that the graphic group performed significantly better than the non-graphic group in terms of the information recalled from the text. Similarly, in the current study, the post-test summaries indicated that the mind mapping software group was able to produce a higher number of macro and micro level ideas when compared with the discussion group. This finding also supports the conclusions of a study conducted by Kools. (2006). The results of their study showed that mind mapping software as a graphic organizers had a strong effect on text comprehension at both macro and micro levels.A study by Carrell, Pharis and Liberto (1989) attempted to test the effect of using semantic mapping as a post-reading activity. After reading the passage, one of the students in the experimental group was asked to develop a class post-reading map on the board by gathering input from the rest of the class. When the students were required to answer open- ended questions as part of a post-test, the semantic mapping group did significantly better than the control group. In the present study, after the students completed the mind mapping software on their worksheets in pairs, individual students took turns to fill in the same mind mapping software on the board. This activity might have facilitated more exposure to and more involvement with the eight texts. The aforementioned possibility could be taken into consideration while explaining the higher post-test scores gained after the mind mapping software performances.According to these findings, it can be concluded that using mind mapping software increase students’ curiosity and it can motivate them to follow the new way of teaching vocabulary in reading skill. In this regard, It is a well-accepted fact that learning new vocabulary in reading is of utmost importance. Findings of the study further proved that there is a meaningful differences between vocabulary ability of experimental and control groups after the intervention. In our modern world, where we are inundated by print, having large volume of vocabulary is a prerequisite to deal with large amounts of information that is made available to us. In short, possessing reading skills is a means of survival. However, being a skilled L1 reader is not enough to be an active and successful participant of society if he does not know vocabulary. Most school systems around the world demand that their students learn English because it is a global language that could guarantee the capacity for economical and professional competition (Grabe, 2009).Vocabulary teaching and learning is a time consuming effort in traditional approaches such as looking up the meaning of new in the printed dictionaries. It has been increasingly argued that computer technologies can support learning in a number of ways and facilitate learning preprocesses (Gorjian, 2008).
6. Conclusions
- This study has attempted to explore the use of discourse structure-oriented mind mapping software in reading comprehension. The results of the study revealed that the students did significantly better on post-test after filling in mind mapping software when their post-test scores obtained after the mind mapping software performances were compared with those obtained after the conventional method performances. The success of the experimental group was consistent across the four texts used in the study. The results of the study and the pedagogical implications discussed in this section might assist teachers in organizing the tasks in their reading classes and helping learners to better comprehend reading texts.Since the mind mapping software was used with pre-intermediate students enrolled in their first learning vocabulary course in school, who were practicing learning at the limited new words only, use of Free Mind was not used to generate complex ideas at complex vocabularies. Therefore, the present study recommends that a follow up study be conducted in the subsequent learning vocabulary courses to see whether the subjects are continuing to use the mind mapping techniques in generating and organizing ideas. Use of the mind mapping software should be also extended to other advanced level writing courses and other language courses at COLT such as reading, writing building and grammar. When using the mind mapping software, it is recommended that students use it to construct mind maps collaboratively. Kwon and Cifuentes (2009) found that students who collaboratively constructed concept maps created significantly higher quality concept maps than those who individually constructed concept maps indicating deeper conceptual understanding. For Effective use of the mind mapping software, it is recommended that language instructors at COLT need to be trained in using Free Map as well.Based on the findings of the present study, various important areas can be suggested for further research related to the use of discourse-structure oriented mind mapping software in reading instruction. First of all, the study was limited to 60 students from pre- intermediate level. It is necessary to conduct the study with a larger number of students from different levels, such as elementary, intermediate and upper-intermediate levels, to investigate any differences between the aforementioned levels. In addition, structured interviews might be conducted with the participant learners in order to have a deeper insight into their perceptions regarding the exploitation of graphic organizers in reading classes.Second, because this study lasted for only three weeks due to time constraints and institutional restraints, it is essential to conduct this study over a longer period of time so more texts and a higher number of mind mapping software can be included. Third, this study used only one type of reading method (conventional) to compare with the effectiveness of discourse structure-oriented mind mapping software. Further studies are necessary to determine whether the students still do better on post-tests after completing graphic organizers when the mind mapping software activities are compared with post-reading tasks other than discussion. Future studies could also address the effects of student-created mind mapping software on text comprehension.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML