-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Instrumentation Science
2012; 1(4): 41-44
doi: 10.5923/j.instrument.20120104.01
A different Way to Determine the Gamma-ray Linear Attenuation Coefficients of Materials
E. E. Ermis , C. Celiktas
Ege University, Faculty of Science, Physics Department, 35100, Bornova, Izmir, Turkey
Correspondence to: E. E. Ermis , Ege University, Faculty of Science, Physics Department, 35100, Bornova, Izmir, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this work, gamma-ray linear attenuation coefficients of plexiglass, bakelite and Pb materials were determined to offer an alternative method for determining the gamma-ray linear attenuation coefficients of materials. Pulse shape discrimination (PSD) timing method was utilized for this purpose. 662 keV-energy photopeak radiations were used from 137Cs radioisotope. In the experiments, slow energy signals were gated from fast timing signals, coincidently. Pure photopeak signals triggered by timing signals were used in the determination of attenuation coefficients. To check the validity of the obtained experimental results, in addition, the coefficients were also calculated by Xcom code. Obtained experimental coefficients were compared with the calculated values from Xcom code and reference results.
Keywords: Gamma-ray, 137Cs, Linear Attenuation Coefficient, PSD Method, NaI(Tl) Inorganic Scintillation Detector
Cite this paper: E. E. Ermis , C. Celiktas , "A different Way to Determine the Gamma-ray Linear Attenuation Coefficients of Materials", International Journal of Instrumentation Science, Vol. 1 No. 4, 2012, pp. 41-44. doi: 10.5923/j.instrument.20120104.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Gamma-ray linear attenuation coefficient describes the absorption of gamma-rays in unit length of an absorber material. This quantity depends on the energy of the incident gamma-ray beam and the density of the absorptive material.Photon penetration in matter is governed statistically by the probability per unit distance travelled that a photon interacts by one physical process or another. This probability, denoted by µ, is called linear attenuation coefficient and has the dimensions of inverse length (e.g. cm-1)[1]. When an incident gamma beam with the intensity of I0 collide perpendicularly with an absorber with the thickness of x, the intensity (I) passing through the absorber can be evaluated with this equation:
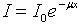 | (1) |
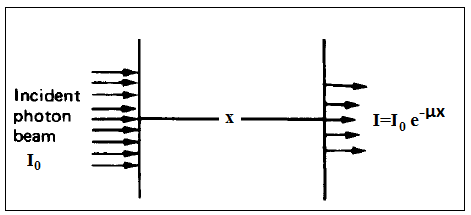 | Figure 1. Monoenergetic photons incident on a slab[4] |
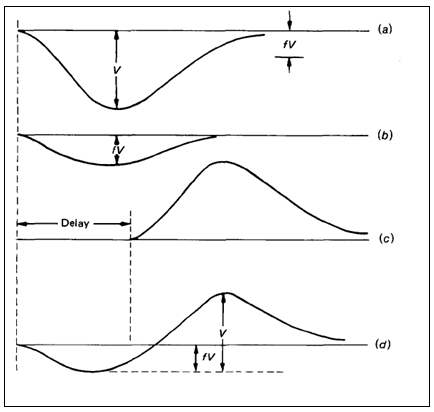 | Figure 2. The timing method [3] |
2. Experiments
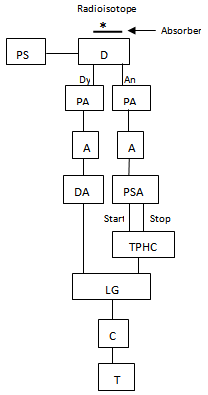
- Fig. 3 illustrates the schematic diagram of the used spectrometer.
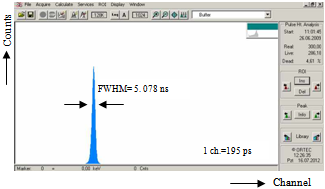 | Figure 4. The obtained time spectrum |
3. Results and Discussions
- The obtained time spectrum, which is the timing output of the TPHC, through the used timing method is shown in Fig. 4.The time resolution value was found as 5.078 ns from this figure. Corresponding time per unit channel of MCA was calculated as 195 ps from this time spectrum by dividing the TPHC range to the conversion gain (1024 ch.) of the MCA. Obtained energy spectrum (black) and the gated energy spectrum with timing signals (blue) are shown in Fig. 5. The energy resolution value was calculated as 4.22%.
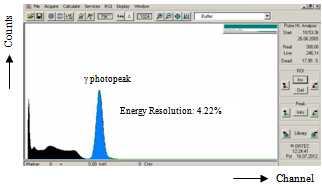 | Figure 5. Source spectrum (black) and the gated spectrum with timing signals (blue) |
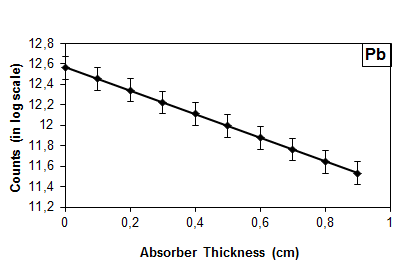 | Figure 6. Gamma-ray attenuation graph for Pb |
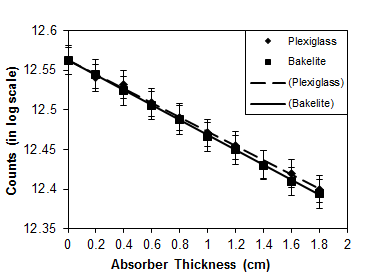 | Figure 7. Gamma-ray attenuation graphs for plexiglass and bakelite absorbers |
4. Conclusions
- Gamma-ray linear attenuation coefficients of Pb, plexiglass and bakelite absorber materials were investigated by using PSD timing method for 662 keV energy.Coefficient values for the absorber materials used in the setup are agreed well with the ones obtained from the Xcom program and the reference values. In addition to gamma attenuation coefficients via timing method, beta attenuation coefficients were obtained in Ref.[19] by using the method. It is concluded from these results that the timing technique can be used for determining both the gamma and beta-ray linear and mass attenuation coefficients of materials. It has been shown in this work that the spectrometers for determination of gamma-ray absorption coefficients using PSD timing method might be an alternative for the conventional gamma absorption setups.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work was supported by TUBITAK, the Scientific and Technological Research Council of TURKEY under project number 197T087 and by EBILTEM, Center of Science and Technology, Ege University under Project No. 99 BIL 001.
References
| [1] | J.E. Turner, ‘Atoms, Radiation and Radiation Protection’, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH&Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2007. |
| [2] | G.F. Knoll, ‘Radiation Detection and Measurements’, John Wiley & Sons. Inc, New York, 2000. |
| [3] | R.W. Leo, ‘Techniques for Nuclear and Particle Physics Experiments’, Springer–Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. |
| [4] | N. Tsoulfanidis, ‘Measurements and Detection Radiation’, Taylor & Francis, USA, 1995. |
| [5] | J. Kalyna and I.J. Taylor, ‘Pulse Shape Discrimination: An Investigation og n-γ Discrimination With Respect to Size of Liquid Scintillator’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth., vol. 88, no. 2, pp. 277-287, 1970. |
| [6] | N. Zaitseva, B.L. Rubert, I. Pawelczak, A. Glenn, H.P. Martinez, L. Carman, M. Faust, N. Cherepy, S. Payne, ‘Plastic Scintillators with Efficient Neutron/Gamma Pulse Shape Discrimination’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth., vol. 668, no. 2012, pp. 88-93, 2012. |
| [7] | P.A. Söderström, J. Nyberg, R. Wolters, ‘Digital Pulse Shape Discrimination of Fast Neutron and γ Rays’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth., vol. 594, no. 2008, pp. 79-89, 2008. |
| [8] | T. Szczesniak, M. Moszynski, A. Syntfeld-Kazuch, L. Swiderski, D. Wolski, M. Grodzicka, G. Pausch, J. Stein, F. Kniest, M.R. Kusner, P. Schotanus, C. Hurlbut, ‘Light Pulse Shapes in Liquid Scintillators Originating from Gamma-Rays and Neutrons’, IEEE Trans. Sci. Symposium Conference Record, pp. 1480-1485, 2009. |
| [9] | R.C. Hochel and D.W. Hayes, ‘Background Reduction and Noise Discrimination in Proportional Counting of Tritium Using Pulse-shape Analysis’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth., vol. 130, no. 1, pp. 183-188, 1975. |
| [10] | S.P. Garg, K.B.S. Murthy, R.C. Sharma, ‘Application of Pulse Shape Discrimantion Technique to ImproveThe Energy Resolution of a Gas Scintillation Proportional Counter’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth. A, vol. 336, no. 1-2, pp. 200-205, 1993. |
| [11] | C. Celiktas, E.E. Ermis, M. Bayburt, ‘Energy Resolution Improvement of NaI(Tl) Scintillation Detectors by Means of a Timing Discrimination Method’, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., vol. 293, no. 2012, pp. 377-382, 2012. |
| [12] | Gy. Mathe and B. Schlenk, ‘Pulse-shape Discrimantion Method for Particle Identification’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth., vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 10-12, 1964. |
| [13] | M. Mutterer, W.H. Trzaska, Y.N. Kopatch, M. Sillanpaa, J. von Kalben, S.V. Khlebnikov, G. Schrieder, G.P. Tyruin, ‘Particle Identification with Time of Flight and Pulse-Shape Discrimination in Neutron-Transmutation-Doped Silicon Detectors’, Nucl. Instrum. and Meth., vol. 608, no. 2009, pp. 275-286, 2009. |
| [14] | A. Poskus, ‘Attenuation of Gamma Rays’,http://www.kkek.ff.vu.lt/uploads/erasmus/no10.pdf, accessed 16 July 2012. |
| [15] | ‘Interaction of Gammas’, Advanced Laboratory, University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin,http://www.hep.wisc.edu/~prepost/407/gamma/gamma.pdf, accessed 16 July 2012. |
| [16] | M.J. Berger and J.H. Hubbell, ‘NBSIR 87-3597’, 1987. |
| [17] | P.S. Rao and E.C. Gregg, ‘Attenuation of Monoenergetic Gamma-rays in Tissues’, Am. J. Roentgenol, vol. 123, no. 3, pp. 631-637, 1975. |
| [18] | B. Goswami and N. Chaudhuri, ‘Measurements of Gamma-ray Attenuation Coefficients’, Phys. Rev. A, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 1912-1916, 1973. |
| [19] | E.E. Ermis and C. Celiktas, ‘Determination of Beta Attenuation Coefficients by Means of Timing Method’, Ann. Nucl. Energy, vol. 41, no. 2012, pp. 115-118, 2012. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML