-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology
p-ISSN: 2163-2219 e-ISSN: 2163-2227
2024; 13(5): 63-69
doi:10.5923/j.ijvmb.20241305.01
Received: Aug. 12, 2024; Accepted: Sep. 8, 2024; Published: Sep. 19, 2024

Oxidative Stress and Functional Activity of Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease
Saatov T. S., Ikromov S. A., Mustafakulov M. A., Ishankhodzhaev T. M.
Institute of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Ikromov S. A., Institute of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Oxidative stress plays a critical role in the functional activity of cells in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In AD, oxidative stress leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which disrupt cellular processes and contribute to neuronal damage. This oxidative imbalance affects key cellular functions, including signal transduction, protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, and overall cellular homeostasis. The accumulation of ROS exacerbates neurodegeneration by impairing mitochondrial function, inducing protein aggregation, and altering cellular signaling pathways. Understanding the interplay between oxidative stress and cellular function in AD is essential for developing targeted therapeutic strategies to mitigate disease progression and improve cognitive function.
Keywords: Oxidative stress, Alzheimers, Tau protein
Cite this paper: Saatov T. S., Ikromov S. A., Mustafakulov M. A., Ishankhodzhaev T. M., Oxidative Stress and Functional Activity of Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease, International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology, Vol. 13 No. 5, 2024, pp. 63-69. doi: 10.5923/j.ijvmb.20241305.01.
1. Introduction
- Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known to actively participate in the regulation of cellular functional activity under both normal and pathological conditions. This influence of ROS is exerted through their involvement in the functioning of cellular regulatory systems, one of which includes phosphorylation/DE phosphorylation processes. In cell metabolism and functioning, phosphorylation/DE phosphorylation acquires critical importance and depends on the balanced action of enzymes involved in these processes. Phosphorylation involves enzymes belonging to the group of protein kinases, while DEphosphorylation is carried out by protein phosphatases, which cleave phosphate groups. The phosphorylation/DE phosphorylation of proteins is a crucial regulatory link in the processes of cell division, differentiation, proliferation, transformation, and secretion [1].Recently, significant attention has been paid to the disruption of the balance between protein phosphorylation/DE phosphorylation processes. In Alzheimer's disease, this primarily concerns the phosphorylation of tau protein, proteins involved in mitosis, and brain tissue enzymes [2-4].The enhancement of proteolysis and phosphorylation of APP and tau protein in brain tissue leads to an increase in β-amyloid (βA) production and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT), which are a neuronal component of the neuron’s cytoskeleton [4]. The tau protein plays an important role in the polymerization of tubulin and the stabilization of microtubules, which support the neuronal skeleton. Its post-translational modification, driven by phosphorylation, is involved in the regulation of these processes. Consequently, phosphorylation processes regulate the binding function of tau protein in relation to tubulin [5].In the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), an accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles is observed. These tangles are represented as bundles of paired helical filaments composed of phosphorylated and aggregated tau protein associated with neuronal microtubules [5]. Normally, tau protein contains three moles of phosphate per mole of protein, while paired helical filaments of tau protein (PFH) contain 11 moles of phosphate per mole of protein. Aberrant phosphorylation of tau protein may be a critical factor in the formation of PFH [6].Numerous studies have shown that excessive activation of mitotic exit may be associated with hyper phosphorylation of tau protein, leading to disruption of the axonal transport mechanism, loss of cellular shape, degeneration of affected neurons, and the progression of AD [5]. Hyper phosphorylation of proteins is caused by an imbalance between kinase and phosphatase activities.In physiological conditions, peptidyl-prolyl isomerases participate in maintaining the balanced state of these processes in cells [4]. One representative of the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase family is Pin1 (peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase). Pin1 is involved in the regulation of the activity of enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation and DE phosphorylation of the cytoskeletal protein tau and also influences β-amyloid (βA) production by interacting with APP [5]. The action of Pin1 is associated with the isomerization of the peptide bond between pSer/Thr-Pro in proteins, which affects their assembly, folding, and multiple functions, including intracellular transport, intracellular signaling, transcription, mitosis, and apoptosis [4,7,8].Under conditions of oxidative stress (OS) with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a decrease in Pin1 activity has been detected in the hippocampus, caused by its oxidative modification. This leads to the intense phosphorylation of APP at the Thr668-Pro site and an increase in βA production. It has been shown that in AD, neurodegeneration and apoptosis may be associated with the oxidative destruction of nuclear Pin1, which participates in the regulation of phosphorylation and the activity of mitotic and nuclear proteins [4].It is known that the state of oxidative stress (OS) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is accompanied by the intensification of neuronal apoptosis, which is regulated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals, as well as lipid peroxidation (LPO) products, particularly 4-HNE, and β-amyloid peptides (βA1–40 and βA1–42). Their effects are mediated through the influence on key metabolic cascades involved in the induction of apoptosis, including p53 mobilization, induction of Box (which has pro-apoptotic effects), reduction of Bcl-2 (which has anti-apoptotic effects), release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytosol, and activation of caspase-3 [9].
2. Materials and Methods
- One of the central links in triggering these processes is the disruption of the balance between phosphorylation/DE phosphorylation processes and the intensification of protein phosphorylation. Several studies highlight the key role of p53 in oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in neurodegenerative diseases. The action of p53 is explained by its ability to bind to specific DNA regions that regulate the expression of key genes encoding proteins that control cell cycle progression and apoptosis. The regulation of p53's transcriptional activity and its activation depend on the degree of phosphorylation. Both JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase)/SAPK (stress-activated protein kinases) and p38 MAP kinase (mitogen-activated protein kinase) are involved in the phosphorylation process. JNK/SAPK-mediated phosphorylation of the tyrosine residue of p53 occurs at position 81 [10,11].In Alzheimer's disease (AD), there is a sharp intensification of p53 phosphorylation processes due to decreased Pin1 activity resulting from its oxidative destruction. It has been shown that in mild cognitive impairment and AD, p53 levels significantly increase in the inferior parietal lobe [6]. The activation of apoptosis involving p53 leads to the induction of pro-apoptotic Bax genes. Box's influence on apoptosis is linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, which is accompanied by the release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm, the formation of apoptosomes, and the activation of caspases 9 and 3. The disruption of mitochondrial structure and function may be directly caused by the effects of ROS and β-amyloid (βA).It is also possible that Box proteins, which stimulate apoptosis, contribute to the formation of specific channels in the mitochondrial membrane for cytochrome c [10]. The presence of free ceramide around mitochondrial membranes facilitates the formation of mitochondrial pores [12]. Oxidative stress (OS) is associated with the activation of the sphingomyelin-ceramide complex, which is accompanied by the hydrolysis of sphingomyelins and the formation of ceramides. It has been shown that βA, in complex with transition metals, can activate the sphingomyelin-ceramide complex and contribute to the disruption of mitochondrial structure. Treatment of glial cells with the βA peptide (25–35) leads to the activation of the sphingomyelin-ceramide cascade, increasing cellular ceramide levels [13].A higher level of ceramide has been found in the brain tissue of individuals with Alzheimer's disease compared to elderly individuals of the same age, indicating the pathogenic role of ceramides in the development of AD. The intensity of βA peptide-induced neuronal apoptosis is significantly reduced by α-tocopherol and N-acetyl cysteine and is completely eliminated by the administration of a specific inhibitor of stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs), such as JNK and p38 MAPK [13].Thus, the inclusion of oxidative stress mechanisms leads to the activation of apoptosis mechanisms (Picture 1). This represents a type of physiological protective response of the body to the state of oxidative stress, during the initial stages of which the body attempts to eliminate damaged cells through apoptosis. As the disease progresses, it is likely that, alongside the intensification of apoptosis, mechanisms of necrotic neuronal damage are also activated. Academician S. Saatov and others study the mechanisms of lipid and enzyme action in the process of apoptosis.
 | Picture 1. The effect of reactive oxygen species on the apoptosis process in Alzheimer’s disease. MAP kinase - mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK/SAPK - N-terminal protein kinase |
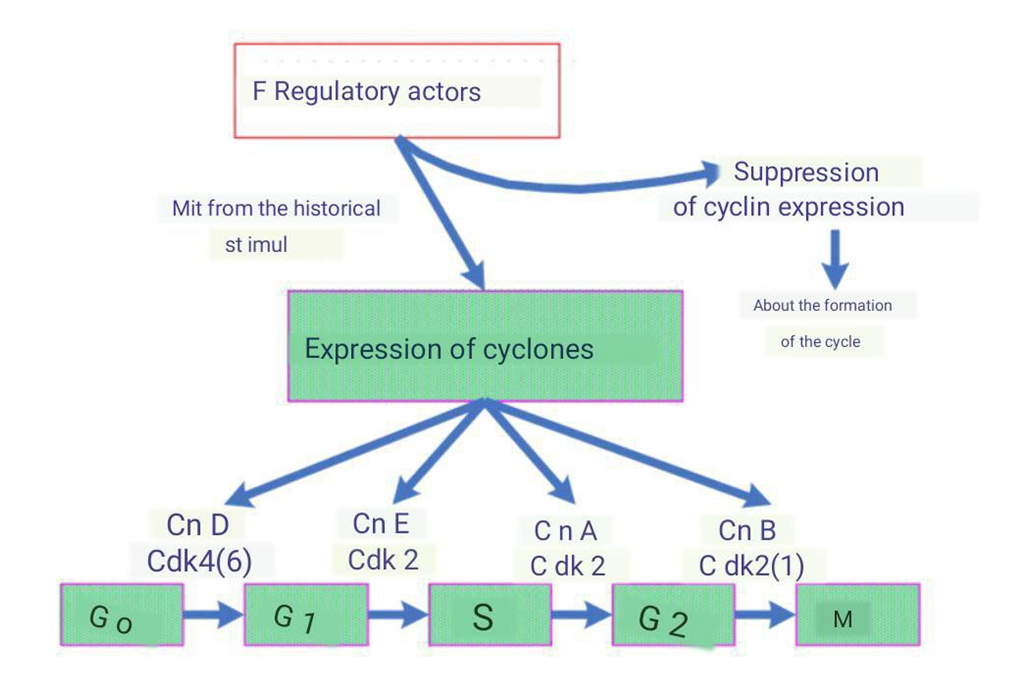 | Picture 2. The role of cyclin expression in cell progression through the mitotic cycle. CnD, CnE, CnA, CnB - Cyclins D, E, A, B; Cdk - Cyclin-dependent kinases |
3. Result and Discussion
- The reduction in the phosphorylation level of pRb protein is caused by the action of ant proliferative stimuli [20]. One of the initial steps in cell transition to the G1 phase is the activation of Cdk4/2 by their mitogen-controlled regulatory subunits, cyclins D1, D2, and A, and the removal of their inhibitors—p21 and p16. The levels of these cyclins decrease under the influence of 4-HNE, which positively affects p21 content. The Cdk4/2-cyclin complex participates in the phosphorylation of pRb, leading to the inhibition of its ability to bind to the E2F transcription factor. E2F is a heterodimeric transcription factor that binds to promoter regions of many genes involved in the cell cycle. E2F is involved in the transcription of specific genes that encode proteins necessary for the next stage of the cell cycle. Consequently, phosphorylation of pRb leads to the expression of E2F-dependent genes required for the transition of the cell into the S phase of the cell cycle, followed by cell division. The regulatory effect of reactive oxygen species, particularly 4-HNE, on the expression of cyclins D1, D2, and A, on the activity of Cdk4/6 and Cdk2, on the regulation of E2F expression, and on the formation of the pRb/E2F complex has been demonstrated [21,22] (Picture 3).
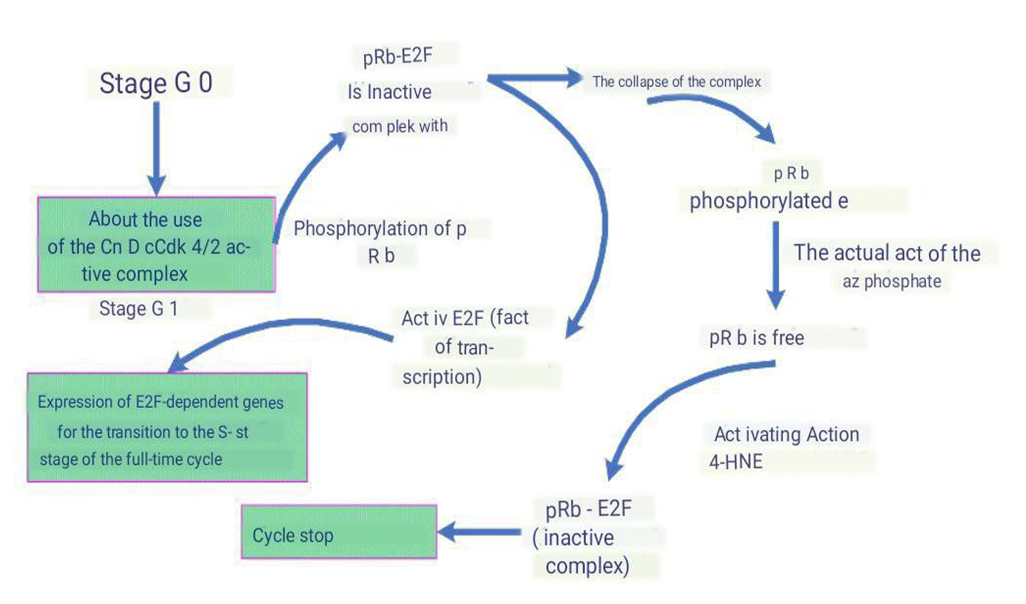 | Picture 3. The Role of Retinoblastoma Protein (pRb) in Cell Cycle Regulation. 4-HNE - 4-Hydroxynonenal |
4. Conclusions
- It is believed that the initiation of abortive cell cycles is a type of cellular adaptation response to stress conditions, including OS. Accordingly, increased levels of inhibitors are seen as a protective reaction against premature activation of cell cycle initiators. Other studies have highlighted the localization of phosphorylated histone H3 in cells, which is one of the nuclear components of nucleosomes and plays a key role in chromosome condensation during division. Compared to the nuclei of actively dividing cells, its quantity in the cytoplasm of hippocampal neurons in AD is significantly increased. The presence of phosphorylated histone H3 in the cytoplasm of neurons indicates mitotic catastrophe, leading to neuronal dysfunction and neurodegeneration [32]. Analyzing the literature, Popov and Stepanichev concluded that cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase is associated with the induction of p53-dependent apoptosis. It is likely that in this case, some essential components ensuring the continuity of the cell cycle are missing, despite the presence of proteins controlling the G2/M transition—cyclins B1, Cdk2, and Cdk1.The cessations of cell arrest in the G2 phase after replication is also accompanied by death involving various mechanisms, including apoptosis. It has been shown that in brain regions affected by neurodegenerative changes, signs of cell activation for re-entry into the cell cycle are observed. In the neurons of the cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease (AD), cells with tetraploid DNA content and cyclin B1 expression have been identified [33].Thus, AD is characterized by the initiation of abortive mitosis, leading to neuronal death caused either by apoptosis or neurodegeneration. It is likely that attempts by neurons to re-enter the cell cycle are primarily driven by external growth factors, while at the cellular signaling level, reactive oxygen species (ROS) act as secondary messengers, leading to abortive re-entry into the cell cycle and subsequent neuronal degeneration.Currently, there is no clear understanding of the causes behind the initiation of abortive mitosis. Given the multifactorial control of the cell cycle, this process may need to be considered from the perspective of the overall metabolic state of the organism during aging. In the context of stress adaptation, oxidative damage in cells may signal the activation of mechanisms aimed at initiating apoptosis and restoring cell numbers through mitosis. However, aging occurs against a background of chronic oxidative stress. Under these conditions, neurons, after differentiation, cannot re-enter a full cell cycle due to initial disruptions in many aspects of this process, the severity of which increases over time. All of this indicates the exhaustion of the body's compensatory abilities during aging, driven by disturbances in oxidative-reductive status.Thus, oxidative stress, associated with the intense generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), depletion of antioxidant defenses, and imbalance of their components, oxidative destruction of lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates, is one of the primary causes of neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease. It is possible that only an integrated approach to studying the state of key metabolic pathways in cells, as well as investigating hormonal and immunological status and functional activity of cells, will reveal the triggering mechanisms of AD development.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML