-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology
p-ISSN: 2163-2219 e-ISSN: 2163-2227
2024; 14(4): 58-61
doi:10.5923/j.ijvmb.20241304.03
Received: Aug. 3, 2024; Accepted: Aug. 23, 2024; Published: Aug. 28, 2024

"Microzim-2" - Biologically Active Product for Improving the Growth and Development of Cotton in the Difficult Climatic Conditions of the Bukhara Region
Bakhtiyor Aripov1, Gulandon Gazieva1, Zakhro Akhmedova2
1Department of Zoology and General Biology, Bukhara State University, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
2Department of Microbiology, Institute of Microbiology of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Bakhtiyor Aripov, Department of Zoology and General Biology, Bukhara State University, Bukhara, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study explores the application of the enzyme-organic fertilizer Mikrozim-2 as a biologically active agent aimed at enhancing the growth and development of cotton under the challenging climatic conditions of the Bukhara region, Uzbekistan. Conducted on the farm Latif-Sharif-Ergash in the Jondor district, the research focuses on the Bukhara-6 cotton variety, grown in soils with varying degrees of salinity. The study involved pre-sowing seed treatment and subsequent fertilization with Mikrozim-2. Key parameters such as seed germination rates, the development of vegetative organs, and phenological indicators were meticulously measured to assess the product's effectiveness. The findings provide insights into the potential of Mikrozim-2 to mitigate the adverse effects of harsh environmental conditions on cotton cultivation, contributing to improved agricultural outcomes in the region.
Keywords: Enzyme-organic fertilizer, Saline soil, Microzim-2, Plant development, Germination, Physiological development of the plant, Phenological indicators
Cite this paper: Bakhtiyor Aripov, Gulandon Gazieva, Zakhro Akhmedova, "Microzim-2" - Biologically Active Product for Improving the Growth and Development of Cotton in the Difficult Climatic Conditions of the Bukhara Region, International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology, Vol. 14 No. 4, 2024, pp. 58-61. doi: 10.5923/j.ijvmb.20241304.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Globally, one of the most pressing challenges in agriculture is the enhancement of soil fertility, the enrichment of organic matter, and the maintenance of a positive nutrient balance. Soil, as a biologically diverse and dynamic environment, plays a critical role in supporting plant growth. Its fertility is primarily influenced by the rate and direction of microbiological processes, which are, in turn, affected by factors such as irrigation, salinity, and aridity. These factors are particularly pronounced in the Bukhara region of Uzbekistan, where diverse soil types, varying degrees of salinity, and harsh climatic conditions significantly impact agricultural productivity.In the Bukhara region, the challenges of maintaining soil fertility are compounded by extreme environmental conditions. The region's soils are characterized by high salinity levels, arid conditions, and limited water resources, which together create a formidable environment for crop cultivation. The structural and functional characteristics of the soil microbiome in this area are not only indicative of the ongoing metabolic processes but also serve as valuable indicators of soil fertility. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for developing effective agricultural practices tailored to the region's specific needs.In modern crop production, the role of fertilizers, plant growth regulators, and beneficial microorganisms cannot be overstated. Intensive farming practices heavily rely on these inputs to optimize plant growth and protect crops from pests. However, there is a growing recognition of the advantages of biologically synthesized substances over their chemical counterparts. Organic substances and metabolites derived from living organisms, such as animals, plants, and microorganisms, offer a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers.The benefits of using organic products and biological metabolites are multifaceted. These substances often exhibit a broader spectrum of positive effects on plant health and soil quality, coupled with higher efficiency even at minimal doses. Unlike chemical treatments, which can have detrimental effects on the environment and human health, biologically active products contribute to long-term soil fertility and sustainable agricultural practices. In this context, the enzyme-organic fertilizer "Mikrozim-2" represents a promising solution for addressing the unique challenges faced by cotton growers in the Bukhara region.
2. Materials and Methods
- This article will use an environmentally friendly biological product created in accordance with the State Program for Biologization of Agricultural and Industrial Branches, namely in the cultivation of a strategically important cotton crop in the harsh climatic conditions of the Bukhara region.The extreme environmental situation caused by salinity has undoubtedly led to environmental deterioration. Consequently, there is a need to help nature restore its natural balance, reduce the degree of soil salinity, water pollution, vegetation, and agricultural crops, helping to improve the health of the soil and obtain a high-quality cotton harvest.Biologically active metabolites of microorganisms at the first stage of action disinfect crop seeds from seed coat pathogens, then promote rapid germination, increasing the energy of seed germination, promote the rapid development and growth of plants, increase their productivity and reduce morbidity.The accumulation of toxic chemical compounds in the soil, used in agriculture as fertilizers, leads to a sharp deterioration not only in its fertility, but also in environmental pollution, which raises the problem of providing agriculture with biologically pure, active fertilizers.In relation to cotton cultivation, the main attention is paid to the creation of an environmentally friendly biological product for the environment and human health, and their use in soils of varying degrees of salinity in our region. In particular, the high efficiency of biostimulants created on the basis of enzymatic activity and metabolites of fungi isolated from local conditions and soil sources has been studied. One of these microbiological preparations is the biological preparation “Mikrozim-2”, created at the Academy of Sciences of the Institute of Microbiology of the Republic of Uzbekistan.The biological product “Mikrozim-2” was used in the crop fields of the Bukhara region of the Republic of Uzbekistan. During the observations, the condition of the soil of the sown fields was determined before and after the use of “Microzyma-2”, as well as microbiological indicators, enzymatic activity, humus content, absorbed substances containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, soil pH, porosity, water absorption, electrical conductivity, the amount of salts in them composition.It is known that the main components of human and animal nutrition are agricultural products, among which one of the main types of raw materials for the food industry is environmentally friendly and high yield obtained from annually planted plants. To obtain a high and high-quality crop yield, first of all, it is necessary to create and widely use biological preparations that accelerate the development of plants, provide them with nutrients, and protect them from various pests.During the research, we conducted a number of laboratory and field experiments. The purpose of the study was to develop methods for using the enzyme-organic fertilizer “Microzim-2” in the cultivation of cotton on various types of saline soils in the Bukhara region. Based on this, the following tasks were set: improving the protein component composition of “Microzim-2” and preparing a biological product for testing in the field conditions of the Bukhara region. Agrochemical and microbiological analysis of the soil of cultivated areas intended for cotton in order to observe the biorecovery process before and after the use of “Microzim-2”.Determination of the consumption rate of the drug and seeds depending on fertility, soil type, degree of salinity and seed variety. Observation of the growth and development, fruiting of cotton in various farms in the region. Creation of methods for reusing the drug in order to reduce the rate of application of mineral fertilizers using “Mikrozim-2”. The yield of cotton was also studied, and the effectiveness of Microzim-2 was assessed in comparison with reference preparations when introducing cotton cultivation. We calculated the economic efficiency of using “Microzim-2” in the conditions of the Bukhara region. A scientific and practical recommendation was drawn up for the cultivation of cotton in the saline soils of the region.The initial and after use of Microzim-2 soils, their microbiological characteristics, enzymatic activity, humus content, activated nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium substances, soil pH, porosity, water absorption, electrical conductivity, the amount of salts in their composition have been studied [1,3,6].To assess the real state of the soil in the experimental fields, we carried out an agrochemical analysis of the types of salinity, soil elements, as well as agrochemical indicators of the soil in which cotton is grown; the degree of salinity of the soil samples is 1.12, the pH value is -8.1 and belongs to the chloride type. Sulfate type, medium alkaline, which exceeds the norm -7.0. Analysis of the content of salts and macroelements in the soil composition showed that the complex of salts Ca(HCO3)2, CaSO4, MgSO4, Na2SO4, NaCl, MgC2 is relatively low in concentration, non-toxic salts within 0.058%.A study of the fertility of soil samples showed that the humus content is 0.828%, the C content is 0.48, and the gross forms of N are 0.063%. Assessment of the supply by the content of humus, C and N, that is, nutrients turned out to be poor, which requires an increase in these criteria with the help of nutrients and biofertilizers.In the fields of the “Latif-Sharif-Ergash” farm in Jondor region, cotton seeds of the Bukhara-6 variety were sown on 30 hectares. Before planting, the seeds were treated with the biological preparation “Mikrozim-2” and planted in an amount of 30 kg/hectare. For sowing seeds of the Bukhara-6 variety, an experimental plot of the “Latif-Sharif-Ergash” farm was selected and agrotechnical services were provided. On April 23, 2023, for a 4-hectare experimental field, seeds of the bare variety Bukhara-6 120 kg, 15 liters of water and 4 liters of the biostimulant mixture “Microzim” were used during planting. Then the energy of seed germination, seedling growth, leaf size. All phenological observations were carried out. In the control and experimental variants, changes, microbiology, enzyme activity results, the content of humus, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other macro-microelements, pH indicators and salts were determined [4,5,9].In order to reduce the consumption of mineral fertilizers, foliar fertilization of cotton in experimental fields was carried out in selected volumes of the biological preparation “Mikrozim-2”.
3. Results
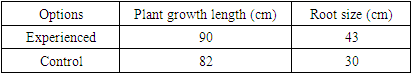
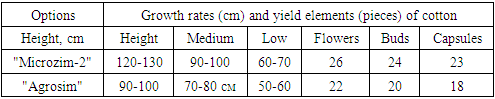
- As noted above, the introduction of the biological product "Microzim-2" in the cultivation of cotton was carried out in the farm "Latif-Sharif-Ergash" in the Jondor district of the Bukhara region, on fields with an area of 8.0 hectares with a strong contamination of sulfate-chloride salinity. For the experiments, bare cotton seeds of the “Bukhara-6” variety were used, and the Turkish drug “Agrozim” was used as a control. Pre-treatment of seeds with "Mikrozim-2" was carried out at a rate of 30 l/t, and with the drug "Agrozim" at a rate of 10 l/t in accordance with the instructions. Seed treatment and planting on an area of 4.0 hectares were carried out on April 24, 2023. In this case, 120 kg of seeds, 40 liters of water and 5 liters of the biostimulating composition "Microzim-2" and 120 kg of seeds were pre-sowing treated with the preparation "Agrozim", and the soaked seeds were mixed for 6 hours. So, after sowing seeds into the soil, every 48 hours in experimental and control fields, the energy of seed germination, further growth of cotton seedlings, the degree of germination, the appearance of true leaves and their sizes, the length of stems, roots and other indicators were assessed. It was noticed that the growth rates of seeds sown by treatment with the biological preparation "Mikrozim-2" were 0.4-0.5 cm longer than the control, the size of the roots was also larger than the control option.The study of the state of seedlings and the further growth of seedlings showed significant differences in the sizes of stems, leaves and roots of cotton plants. The size of the leaves of seedlings of the "Bukhara-6" variety showed that under the influence of "Mikrozim-2" it was 4x4.5 cm, while in the experimental varieties it was 5.0 x 6.0 cm. By the end of August it was found that the surface of the leaves of the experimental variants reaches 9.0-17.0 cm. During this period, strong growth of the stem and root and an increase in the formation of branches were observed [6,9,10]. The growth indicators of the Bukhara-6 variety in the farms of the Jondor region are shown in the table (Table 1).
|
|
4. Discussion
- When observing the germination of seeds in the experimental field treated with Mikrozim-2, compared to the control field, germination was 3-4 days earlier. Germination in the control variant was 78%, and in the experimental variants - 95-96%.As a result, it was noted that in cotton plants treated with Microzim-2, the rate of growth and development changed in comparison with the control. And also in the experimental varieties of cotton, flowering is much faster and there were 7-8 more bolls than in the control version. Salt tolerance of cotton was noted. Water was irrigated once at the beginning of July [7,8,10].It was noted that the yield collected to date in the experimental version was 42-45 kg/hectare, and in the control version - 35-37 kg/hectare. The results obtained showed that in the fields where Microzim-2 was applied, increased and early yields were observed, and soil fertility indicators also improved. It is advisable to use this agrobiotechnology over large areas because it is environmentally friendly and cost-effective. Based on the above positive results, the first harvest began on August 16, ripening reached 89-90%, which proves the early ripening of the cotton crop. Thus, on cotton fields with a volume of 2.0 hectares, it was found that Mikrozim-2 is an effective biological product. Despite the strong salinity of the soil, the increase in cotton yield was 3.0-4.3 kg/hectare compared to the “Agrozim” control.And so, it was found that by introducing the organic fertilizer-biostimulator "Mikrozim-2" for growing cotton on the saline soils of the Bukhara region, the scientific foundations of agrobiotechnology were created, allowing to achieve high yields and economic efficiency, suitable for widespread implementation in other regions and regions of the Republic.
5. Conclusions
- The application of the biological product "Mikrozim-2" in the cultivation of cotton under the harsh climatic conditions of the Bukhara region has demonstrated significant potential in improving crop yields and soil health, even in areas with high soil salinity. The study revealed that "Mikrozim-2" effectively enhanced seed germination, accelerated plant growth, and increased cotton productivity compared to the control treatment with the chemical product "Agrozim."Key observations included a noticeable improvement in the growth rate of cotton plants, with earlier germination and stronger development of vegetative organs. The treated cotton plants not only exhibited better resistance to salinity but also produced a higher number of bolls, leading to an increased yield of 42-45 kg/hectare, compared to 35-37 kg/hectare in the control group. Additionally, the use of "Mikrozim-2" contributed to early ripening of the cotton crop, with the first harvest beginning on August 16, and ripening rates reaching 89-90%.The study also highlighted the environmental benefits of using "Mikrozim-2," which led to improved soil fertility indicators, including enhanced microbial activity, increased humus content, and better nutrient availability. The results suggest that "Mikrozim-2" is not only effective in boosting cotton yields but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices by reducing the reliance on chemical fertilizers and mitigating soil degradation.Given the positive outcomes observed in this study, it is recommended that "Mikrozim-2" be adopted more widely in cotton cultivation, particularly in regions with similar environmental challenges. The integration of this biostimulant into existing agricultural practices could provide a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution for enhancing cotton production in saline soils, thereby contributing to the long-term sustainability of agriculture in the Bukhara region and beyond.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The heading of the Acknowledgment section and the References section must not be numbered.SAP Productions wishes to acknowledge all the contributors for developing and maintaining this template.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML