-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology
p-ISSN: 2163-2219 e-ISSN: 2163-2227
2016; 5(2): 27-33
doi:10.5923/j.ijvmb.20160502.01

Inhibitory Effects of Thiazolide Compounds against Hepatitis C virus: in vitro Study
Iram Amin1, Shagufta Naz2, Muhammad Shahid1, Samia Afzal1, Usman Ashraf1, Asif Rasheed1, Afza Rasul2, Rabia Nawaz1, Sadia Zahid1, Iqra Almas1, Khadija Zahid1, Farkhanda Manzoor2, Muhammad Idrees3
1Division of Molecular Virology, National Centre of Excellence in Molecular Biology (CEMB), University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
2Lahore College for Women University, Lahore, Pakistan
3Hazara University, Mansehra, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Iram Amin, Division of Molecular Virology, National Centre of Excellence in Molecular Biology (CEMB), University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is estimated to infect nearly 200 million individuals globally, including approximately 10 million in Pakistan. The newly approved antiviral medicines belonging to Direct Antiviral Agents (DAA) compounds are very expensive and their access is difficult for poor patients. There is a need to develop the more effective, cheap and less toxic antiviral drugs that can be used along with standard PEG-IFNα and Ribavirin therapy that is still in use in developing countries. In this invitrostudy, we examined the inhibitory effect of Thiazolide derivatives (RM4832 and RM4863) against hepatitis C virus in Huh-7 cell lines. The RNA quantitative results showed a sharp significant antiviral response shown by both of the compounds by decreasing the viral titers after 24 hours of incubation. Compounds showed improved antiviral activity at the dose of 2.0ul (400uM concentration) and 2.5ul (500uM concentration) respectively. This study provides the basis for future work on these compounds especially to determine the specific pathway and mechanism for inhibitory action in the replicon systems of viral hepatitis. Thiazolide derivatives show promising inhibitory effects against HCV genotypes 3a infection, which suggests its possible use as complementary and alternative medicine for HCV viral infection.
Keywords: HCV, Genotypes, Huh-7 cell line, Thiazolides
Cite this paper: Iram Amin, Shagufta Naz, Muhammad Shahid, Samia Afzal, Usman Ashraf, Asif Rasheed, Afza Rasul, Rabia Nawaz, Sadia Zahid, Iqra Almas, Khadija Zahid, Farkhanda Manzoor, Muhammad Idrees, Inhibitory Effects of Thiazolide Compounds against Hepatitis C virus: in vitro Study, International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2016, pp. 27-33. doi: 10.5923/j.ijvmb.20160502.01.
Article Outline
1. Background
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a blood borne virus and its infection is a main cause of chronic liver diseases [1]. About 170 million people are chronically infected with this deadly virus and almost 500,000 deaths occur annually due to hepatitis C related diseases [2]. Like some of the other developing countries Pakistan has also been recognized as one of the countries of the world where hepatitis C virus (HCV) is endemic [3]. Majority of HCV infections direct to chronic hepatitis, which in turns proceed to liver diseases including fibrosis, cirrhosis and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [4-6]. It is estimated that annually there is a risk of 1-4% among patients to develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from cirrhosis [7, 8]. HCC is more widespread in patients of age 60 years and older, especially in males [9]. In Pakistan the frequency of HCC ranges from 3.7% to 16% of malignant tumors and the important and most common cause of HCC is viral hepatitis C [10]. Normally HCV has been classified into six major genotypes and their prevalence diverge from one region to another in the world [11]. In Pakistan a strong relationship between chronic HCV infection and genotype 3a and development of HCC has been reported [12]. Although Pakistan has more than 10 million people carrying HCV infection but unfortunately the disease is normally diagnosed at much delayed stage like other under developed and developing countries because of limited health facilities which then leads to chronic infections later on [13].Treatment of hepatitis C was mainly dependent upon the combination of pegylated interferon alpha (PEG-IFNα) and ribavirin. This treatment was also considered as “standard of care (SOC)” treatment for the past ten years or so. The efficiency of this SOC has been increased by the use of two protease inhibitors mainly telaprevir or boceprevir in hepatitis C genotype 1. In year 2011 FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) approved the use of these protease inhibitors as HCV therapy [14]. Recently some of the approved antiviral medicines with higher sustained virological response (SVR) rates has come into the market for treatment of HCV. These medicines include molecules like sofobuvir, ledipasvir and simeprevir which belongs to direct antiviral agents (DAA) and can treat HCV within 8-12 weeks of dosage with SVR up to 90% or greater [15]. In developing countries like Pakistan, where the combination therapy of PEG-IFNα and ribavirin is still in use, although having moderate anti HCV activity and multiple side effects, because the access to newly synthesized and approved drugs is very low [16]. The main side effects of combination PEG-IFNα and ribavirin therapy directs to thyroid dysfunction especially Hypothyroidism [17]. Hematological disorders mainly considerable fall in haemoglobin, platelets count and total leucocyte count in majority of patients at 24 weeks of Interferon plus ribavirin therapy [18] and weight loss were also reported [19]. The resistance of drug owed to viral mutation, high cost and severe side effects make it necessary to explore some other antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV that may strengthen the therapeutic landscape, especially in low income countries. In this regard, several hundreds of plants, pharmaceutical extracts and synthetic compounds has also been used for the treatment of HCV. Nitazoxanide (NTZ 1), the first and broad spectrum Thiazolide which is considered as anti-infective agent and is approved in the United States for the cure of diarrhea. These small- molecule drugs are also considered as broad-spectrum antiviral agents which target the processes involved in host regulated viral replication [20]. Its effective circulating metabolites such as tizoxanide 2 and some other similar thiazolides are useful for both DNA and RNA viruses [20]. NTZ 1 is an efficient anti-HCV agent in all three conditions whether it is used alone, along with pegylated Interferon or along with combination therapy of both PEG-IFNα and ribavirin [21, 22]. However a major boost occurred in rapid (RVR) and sustained virological response (SVR) if triple therapy of NTZ1, PEG-IFNa and ribavirin used in comparison to combination therapy without NTZ1. If NTZ1 was used alone for 4 weeks and after that pegylated IFN and NTZ1 were used for 36 weeks, without ribavirin, then SVR in 80% of patients was observed [22]. This suggested a guarantee for the treatment of those patients who are incapable to bear ribavirin. These consequences can be compared to direct acting antiviral agent (DAA) such as telaprevir or boceprevir in combination with PEG-IFNα and ribavirin. Recent studies showed that nitazoxanide reduces ATP-sensitive intracellular Ca2+ stores which results in slight endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by the use of bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) as a surrogate for HCV infection [23]. From these studies, it is believed that both NTZ1/tizoxanide2 and the newer thiazolides, present significant assurance in the treatment of HCV especially for those patients who are incapable to bear ribavirin. These consequences can be compared to direct acting antiviral agent (DAA) such as telaprevir or boceprevir in combination with PEG-IFNα and ribavirin. Considering the above-mentioned facts, the purpose of present study was to determine the toxicity of selected Thiazolides derivatives in human hepatoma (Huh7) cell lines and to evaluate their antiviral activity in the Huh-7 cell lines infected with HCV serum.
2. Methods
- Sample Collection and Cell linesSera samples from more than 50 patients chronically infected patients with HCV without any previous history of antiviral treatment were received from Genome Centre for Molecular Diagnostic and Research (GCMD), Lahore, Pakistan. At least 10 Patients of each gender (M/F) were selected with age group of about 20 years to 50 years and with High titer (Viral load) of about 1 million plus of HCV. The participating subjects gave informed consent for the collection of blood samples for this study. The estimated duration of infection varied from 6 months to 15 years and the diagnosis of chronic HCV was based on elevated serum ALT (SGPT) and AST (SGOT) levels at least for six months, histological examination and detection of serum HCV RNA. Children were excluded from the study and all patients were negative for HBs Ag. The Human Hepatoma (HuH-7) cell lines were obtained from Cell bank of Department of Biology, Lahore University for Science & Technology (LUMS), Lahore-Pakistan.Thiazolides Derivatives Two Thiazolide derivatives were used in this study. These were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as solvent to make Stock solution and further working dilutions in DMEM. Dilutions ranging from 10umol-100umol concentration were prepared. Two of these compounds RM4832 and RM-4863 were used for the determination of anti-HCV activity in vitro using Huh-7 cell lines named as compound A and compound B respectively.Cell culturingThe Huh-7 cell line is routinely grown in Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 100 µg/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C with 5% CO2. They are highly permissive for the initiation of HCV replication. The Huh-7 cell line was routinely grown in Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 100 µg/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C with 5% CO2. They are highly permissive for the initiation of HCV replication. The Huh-7 cell line grown in DMEM was split and plated in 6 wells plate for toxicological analysis of Thiazolide derivatives which has been previously optimized using different dilutions to achieve the maximum inhibitory effects of compound against HCV.Toxicological Analysis Huh-7 cells were seeded in DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin and streptomycin at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 in 6 well plate. These cells were treated with different concentrations of compounds of Thiazolide, considering first well as control and added different concentrations of the compound from lowest to highest in the wells. After different intervals the cells were trypsinized and were counted through haemocytometer by using trypan blue dye exclusion method.Anti HCV analysis of Thiazolides derivativesFor in vitro replication of HCV, Huh-7 cell line was used as described previously [24, 25]. For extraction of total RNA from the Huh-7 cells which have been infected with HCV serum Purescript RNA Isolation kit (Life Technologies, USA) was used and HCV REAL-TM Qunat SC kit (Secace Biotechnologies, Italy) was used for Real Time quantification of Extracted HCV RNA according to given protocol.
3. Results
- Toxicity analysis of Compounds Toxicity of Thiazolide Derivatives were initially determined in Huh-7 Cell Lines. These cells were treated with different concentrations of Thiazolide Derivatives. The viability of Huh-7 cells was confirmed at different concentrations by using Trypan Blue Exclusion Test by using cell suspension and trypan blue dye in ratio of 1:1. Cytotoxicity of compounds A & B were evaluated in Huh-7 cells at different doses ranging from 0.5 to 3.0 µl in duplicate and their concentration ranging from 100uM to 600uM respectively. Huh-7 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of Compound A & B for 24 hours and assessed for cytotoxicity by using the cell counting by haemocytometer. The Average number of viable cells per ml in 6 well plates was calculated. It is clear from the results that up to a dose of 2.5µl, the compound-A and 2.0µl, the compound- B were non-toxic to the cells and were toxic at higher concentration. The concentration at which more than 70-80 percent of the cells survived was considered as non-toxic. 1X-PBS was used as a control. Administrations of up to 2.5μl and 2.0μl of the drugs A and B were found to be non-toxic (Figure 1 & 2). At these concentrations cells did not display any significant cytotoxicity during cell passage and trypan blue counting. Cells viability was counted by haemocytometer and trypan blue stain method.
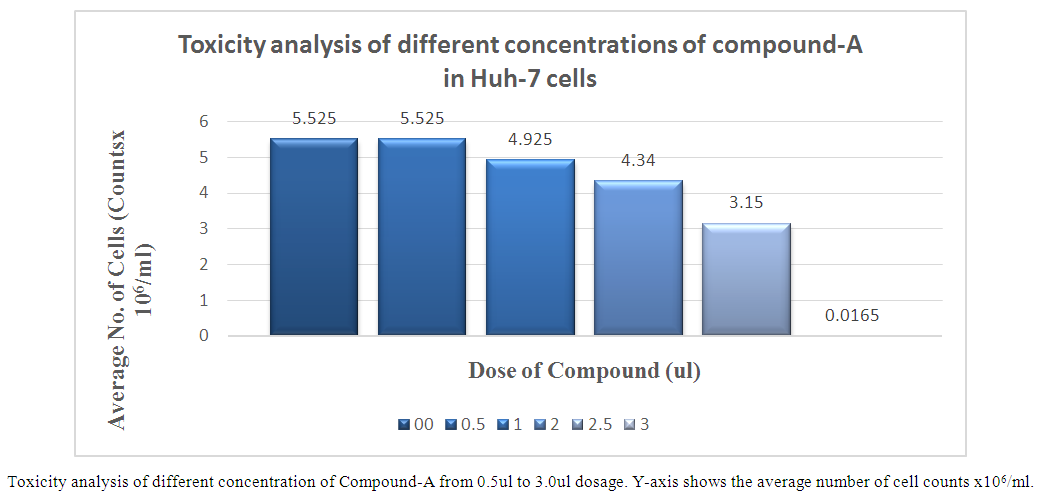 | Figure 1. Toxicity analysis of different concentrations of compound-A in Huh-7 cells |
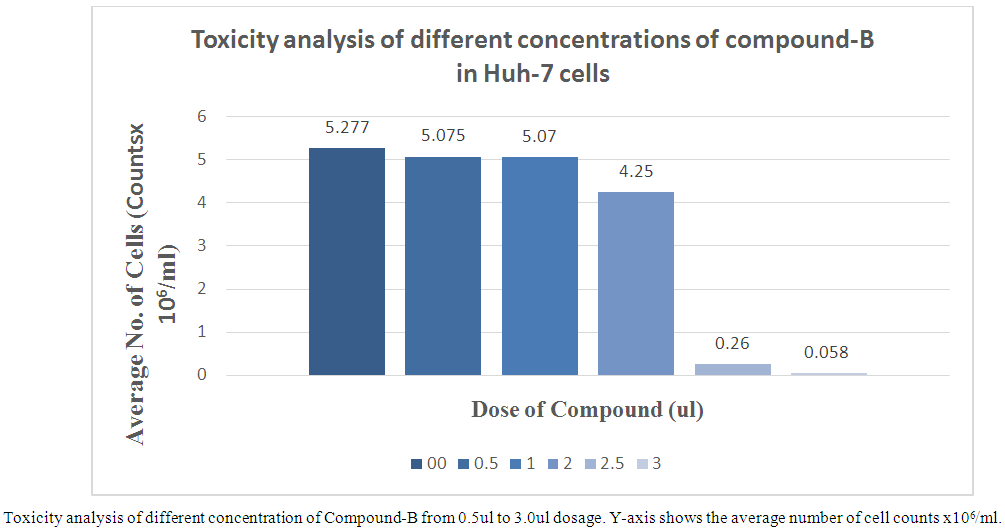 | Figure 2. Toxicity analysis of different concentrations of compound-B in Huh-7 cells |
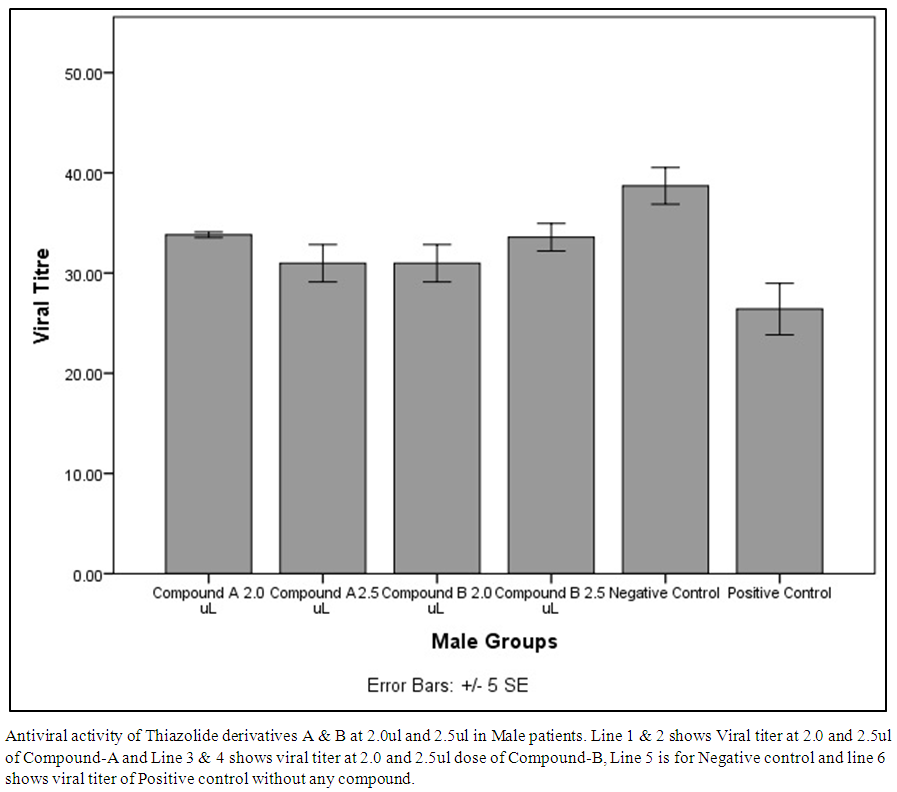 | Figure 3. Antiviral activity of Thiazolide derivatives A & B at 2.0ul and 2.5ul in Male patients |
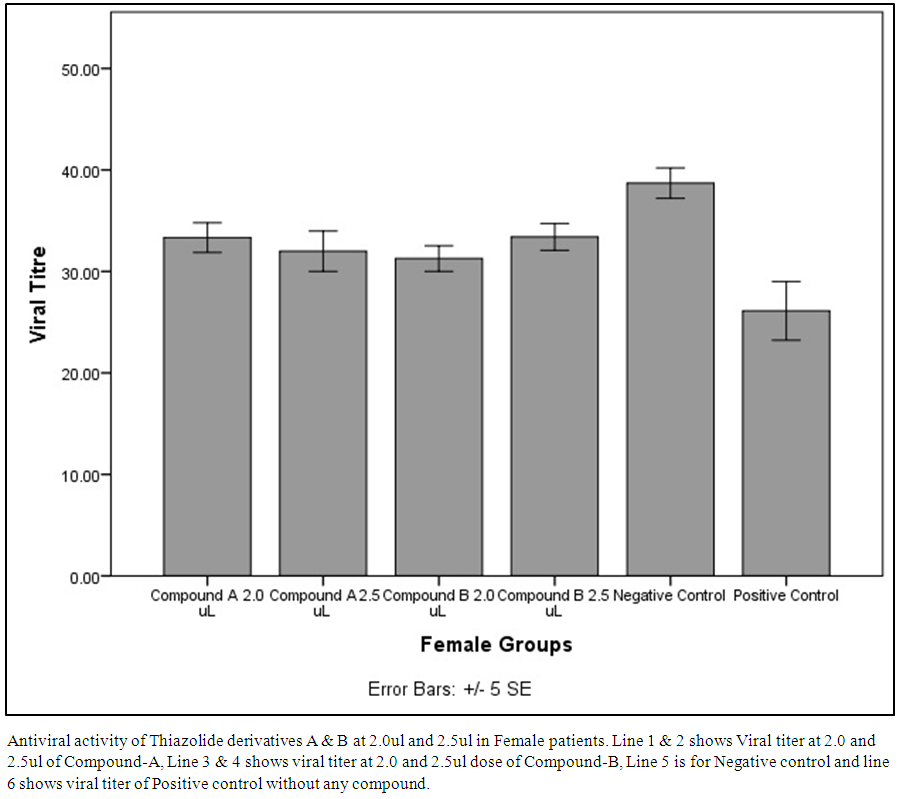 | Figure 4. Antiviral activity of Thiazolide derivatives A & B at 2.0ul and 2.5ul in Female patients |
4. Discussion
- Currently PEG-IFNα in combination with ribavirin is remarkably successful in patients to achieve sustained virological response (SVR) but some severe side effects and high cost of treatment are hurdles to the success of this treatment [26, 27]. Numerous plants and pharmaceutical extracts are also important for the treatment of HCV [28]. Nitazoxanide (NTZ1), an important Thiazolide and its circulating metabolite tizoxanide2 and analogous thiazolides are found to be efficient against both RNA and DNA viruses and a considerable enhancement was observed in Sustained virological response (SVR) as well as Rapid Virological Response when triple therapy of NTZ1/ PEG-IFNα/ribavirin was used in comparison with “SOC” without NTZ1 for the treatment of HCV [22]. The data suggest that two derivatives of Thiazolides (RM4832 and RM4863) could be excellent antiviral agents against HCV. Antiviral effects of NTZ, TIZ and RM4832 against a genotype 1a full length replicon was already reported [29] that were equivalent to those reported for AVA5 cells for genotype 1b [30]. NTZ was an effective inhibitor of an NS5B and two NS3 drug-resistant mutants in Huh7 cells. No significant differences in potency of NTZ relative to that observed for 'wild type' HCV (in AVA5 cells) was observed for any of the drug-resistant mutants tested. Although the mechanism of action of NTZ is not known, the divergence of the intracellular protozoa and viruses inhibited suggests that a cellular, rather than common viral function is being affected. It is conceivable that changes in the intracellular environment induced by NTZ may alter the effect of subsequent treatment with other anti-HCV agents that also act though the induction of cellular pathways, particularly IFNα. Thiazolides may present the opportunity of new or more efficient combination treatments for chronic HCV, whether it is used as additional agent with currently used SOC treatment or in a substitute for ribavirin, or as an ingredient along with the novel combination course of therapy with other anti-HCV drugs [30].
5. Conclusions
- We suggest that there could be excellent therapeutic agents in Thiazolide compounds for the treatment of HCV infections. However, further studies are required to identify the specific active ingredients by using various techniques. This study also provides basis for future work on these compounds especially derivatives A to determine its mechanism of action in the replicon systems and clinical trials for the treatment of the hepatitis C. Moreover, this study will be helpful to explore the new horizons of the discoveries of the Thiazolide derivatives, which shows promising inhibitory effects against HCV.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors wish to thank all the staff of Genome Centre for Molecular Diagnostic and Research (GCMD), Lahore- Pakistan for their cooperation in sample collection and University of the Punjab for providing funding for this study.
Abbreviation
- Pegylated interferon alpha: PEG-IFNα, Hepatitis C virus: HCV, Hepatocellular carcinoma:HCC, Standard of care: SOC, Human Hepatoma: HuH-7, Nitazoxanide: NTZ 1, Sustained virological response: SVR, Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium: DMEM.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML