-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Virology and Molecular Biology
p-ISSN: 2163-2219 e-ISSN: 2163-2227
2012; 1(2): 12-17
doi: 10.5923/j.ijvmb.20120102.01
Seroproteomics Reveals Cross-reactivity of Anti-Enterovirus 71 Antibodies with Cytoplasmic Actin
Jia Jun Lee 1, 2, Yong Zher Koh 2, Seng Hock Quak 1, Vincent Tak Kwong Chow 3, Chee Wah Tan 4, Chit Laa Poh 5, Justin Jang Hann Chu 3, Eng Lee Tan 1, 2
1Department of Paediatrics, University Children’s Medical Institute, National University Hospital, Singapore
2Centre for Biomedical and Life Sciences, Singapore Polytechnic, Singapore
3Department of Microbiology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore
4Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Malaysia
5School of Health and Natural Sciences, Sunway University, Selangor, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Eng Lee Tan , Department of Paediatrics, University Children’s Medical Institute, National University Hospital, Singapore.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Antibodies generated against Enterovirus 71 (EV71), the major etiological agent for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD), were reported to cross-react with other enteroviruses and host proteins. Coxsackieviruses, which is serologically similar to EV71, was reported to mimic actin. Therefore, we hypothesized and successfully demonstrated the cross-reactivity of anti-EV71 antibody to cytoplasmic β-actin using seroproteomics approach. Using 3-dimensional modelling, the cross-reactivity might be due to the structural similarity between the previously reported immunodominant VP1 linear epitope and a homologous motif of cytoplasmic β-actin. Protein-protein docking simulation revealed a large surface of EV71 VP1 was able to bind to a region of the myosin VI cargo binding domain overlapping the cargo binding site. Myosin molecules was also identified to be co-precipitated with EV71 VP1, suggesting the possibility of EV71 VP1 to exploit its similarities to cytoplasmic β-actin so as to bind to myosin for viral shuttling in host cell. Our findings that antibodies against EV71 VP1 cross-react with cytoplasmic β-actin led us to proposed that EV71 may exploit the actin-myosin transport machinery for viral transport in host cells. Further experiments on the interaction of EV71 VP1 with cytoplasmic β-actin and myosin VI may elucidate the mechanism of EV71 infection.
Keywords: Hand, Foot And Mouth Disease, Potentially Fatal Enterovirus 71, Seroproteomics, Cross Reactivity, Cytoplasmic Β-Actin
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is a non-enveloped, single positive-sense RNA virus belonging to the Enterovirus genus, under the Picornaviridae family. It is grouped under the same genus as poliovirus and coxsackieviruses[1]. EV71 was first isolated in 1969 in California from the faeces of an infant who was afflicted by encephalitis[2]. Together withCoxsackieviruses, EV71 is known to cause Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD), which mainly affects infants and children of age 6 and lower. Though most HFMD cases are caused by Coxsackieviruses and are self-limiting, HFMD caused by EV71 are associated with severe complications such as aseptic meningitis, brainstem encephalitis, monoplegia and acute flaccid paralysis[3]. EV71 outbreaks of varying severity have been reported throughout the world, with recent epidemics occurring primarily in the Asia Pacific region countries such asMalaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong and Taiwan[3-6].It has been well established that when an individual is infected with pathogens such as viruses or bacteria, antibodies are generated by the host immune system to eliminate them. However, autoimmunity may arise due to molecular mimicry, cryptic or new antigenic determinants, or superantigens[7]. Neutralizing antibodies generated against EV71 were almost exclusively targeted to its VP1 capsid protein which was exposed to the external environment and participate in viral attachment and entry[8-12]. Over the past few years, there have been reports showing antibodies having cross-reactivity between different kingdoms of species such as antibodies to Streptococcus pyogenes can cross-react with enteroviruses like poliovirus and coxsackievirses and human cardiac myosin,and antibodies to EV71 can cross-react with human brain tissue[13, 14]. Furthermore, coxsackievirus was reported to mimic human actin molecules, thus antibodies to this virus was able to cross-react with actin[15]. Antibodies of enterovirusescross-reacting between each other were also documented as well[16-18]. Apart from the harmful effects of autoimmunity, cross-reactivity can also be beneficial, as shown by Hagiwara et al., who reported that infants initially lacking any EV71 antibodies developed antibodies against EV71, after recovery from HFMD caused by Coxsackievirus A16[17].Since coxsackievirusescross-react with EV71 serologically due to high nucleotide (77%) and amino acid (89%) homologies, we postulated that antibodies against EV71 may also cross-react with actin molecules[19, 20]. To date, there is no report of EV71 antibodies cross-reacting with actin proteins. In this study, we successfully demonstrated the presence of serological cross-reactivity between EV71 and host actin protein by seroproteomics in EV71 infected Rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cell line.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Cell Culture
- The EV71 strain used in this study was Enterovirus 5865/sin/000009 strain (accession number 316321; designated as Strain 41), isolated from a fatal case during the outbreak in Year 2000 in Singapore. Rhabdomyosarcoma (RD, ATCC® catalogue no. CRL-2061™) cells were cultured in 75cm2 culture flasks using Minimum Essential Medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 2% penicillin-streptomycin (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) at 37℃ with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator.
2.2. Patient Sera
- Pooled sera with different antibody titre was obtained from patients admitted to Department of Paediatrics, National University Hospital and were diagnosed with EV71 infections.
2.3. Infection and Protein Extraction
- When cells reached 95% confluency, they were infected with EV71 with a MOI of 10 and incubated for 4 h before being harvested. Total protein extraction was done with the ProteoExtract Complete Mammalian Proteome Extraction Kit (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Briefly, cell pellets were resuspended in ice-cold resuspension buffer and lysed with the extraction buffer. Reducing agent and benzonase nuclease were added to disrupt disulfide bonds and degrade nucleic acids respectively. The solution was then incubated with gentle agitation for 30 min and the protein extract supernatant was collected by centrifuging at 16,000g for 30 min. The proteins were stored at -70℃.
2.4. Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2DE)
- The concentrations of proteins were measured with the NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, USA) and then diluted to 100 mg/ml with rehydration buffer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA). The proteins were then applied to 7cm, pH4-7 ReadyStrip IPG Strips (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA) and rehydrated for 12 h in passive mode. The absorbed proteins in the IPG strips were then focused on the Protean IEF cell (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA) with the following conditions; 250V for 20 min with linear ramp, followed by 4,000V for 2 h with linear ramp and finally 4,000V for 10,000 v-hours with rapid ramping. After equilibration with equilibration buffers (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA), SDS-PAGE was carried out on the IPG strips using 10% Mini Protean TGX gels (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA) for 110 min at 90V. The gel was then stained with 0.1% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, USA) for 1 h and subsequently de-stained until background staining was negligible. Gel images were then captured with a GS-800 calibrated densitometer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA).
2.5. Seroproteomics
- The gel was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane using iBlot® Transfer Stack and iBlot® gel transfer device (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Western blot was done using the WesternBreeze® Chromogenic Kit–Anti-Mouse according to the manufacturer’s instruction (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA). Briefly, the membrane was blocked for 1 h using 10 ml of blocking solution. The membrane was then incubated with 10 ml of pooled sera (diluted 100 to 200 times) for 3 h with shaking. The membrane was subsequently washed four times with wash solution. The membrane was then incubated with 10 ml of mouse anti-human IgG conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, USA) for 1 h. After washing with wash solution, 5ml of the appropriate chromogenic substrate was added to the membrane. Excess substrate was washed away after colour development and the membrane was air dried. The image of the membrane was then captured with a GS-800 calibrated densitometer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, USA). All experiments were repeated thrice to ensure reproducibility.
2.6. Transfection of TAP-tagged VP1 into Mammalian Cell Line
- The VP1 region (891bp) of EV71 was first amplified by PCR and was subsequently cloned into InterPlay® C-terminal Mammalian TAP vector (Agilent, Santa Clara, USA). The clones were then transfected into RD cells using Lipofectamine 2000 CD Transfection Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Successfully transfected cells were subsequently maintained using Geneticin® (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) as the selective antibiotic at 0.8mg/ml.
2.7. Co-precipitation of TAP-Tagged VP1
- RD cells from ten 175cm2 cell culture flasks were pooled and collected by centrifugation. Co-precipitation of VP1 was done with InterPlay® TAP Purification Kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were resuspended in lysis buffer and lysed by three successive rounds of freeze-thaw. The supernatant was incubated with streptavidin resin for 2h. After that, the resin was wash twice with streptavidin binding buffer and the tagged VP1 was eluted with streptavidin elution buffer. The supernatant was then added to the calmodulin resin and incubated for another 2h. The resin was then washed with calmodulin binding buffer and the proteins eluted by boiling at 95℃ for 5 min.
2.8. In-gel Digestion and MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS/MS
- Protein spots of interest were excised from the gel and washed twice with water. Destaining of the gels was done thrice in 100 μl of 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate/50% (v/v) acetonitrile for 5 min, followed by addition of 50 µl acetonitrile. The gels were then dried down with a vacuum centrifuge followed by reduction in freshly prepared 100mM ammonium bicarbonate containing 10mM DTT. After incubation at 56℃ for 1 h, alkylation was done with 55mM iodoacetamide (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, USA) in 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate. The gel was then incubated at room temperature for 1 h and then washed three times with 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate. The gels were then dehydrated with acetonitrile and dried with a vacuum centrifuge. Tryptic digestion was done with 12.5 ng/µl of sequencing grade modified trypsin (Promega, Wisconsin, USA) in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate and incubated for 30 min at 4℃. Extraction of the peptides was then repeated thrice using 25 µl of 5% formic acid in 50% aqueous acetonitrile. The extract were incubated for 10 min and concentrated by centrifugation. The digested peptides were mixed with freshly prepared matrix solution (10 mg of CHCA in 1 ml of 0.5% TFA and 50% acetonitrile) in a 1:1 (v/v) ratio. Analysis of the peptides was then performed on the ABI 4700 Proteomics Analyzer with TOF/TOF™ optics (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). Peptide tolerance was set at 100ppm with fixed modification of cysteine carbamidomethyl, variable modification of methionine oxidated and permitted missed cleavage of up to 1. Trypsin cleavage of the protein was at the C-terminal side of KR unless next residue is P. The proteins were identified by searching in the National Center for Biotechnology Information nonredundant (NCBInr) database using MASCOT program (http://www.matrixscience.com).
2.9. Multiple Sequence Alignment and 3D Modeling
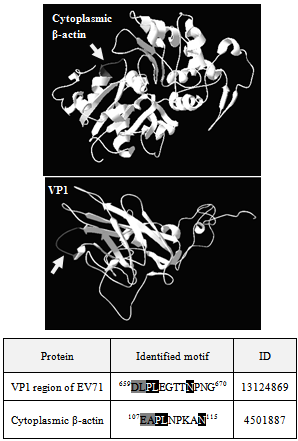
- DNAStarLasergene 7.1 was used to align different actin isoforms; actin cytoplasmic 2 (cytoplasmic β-actin,gi | 4501887), actin alpha 1 skeletal (gi | 60832848), actin alpha cardiac (gi | 4885049), actin alpha 2 smooth muscle aorta (gi | 54696572) and actin gamma 2 smooth muscle enteric (gi | 54696576) with EV71 (gi | 13124869) using Clustal V method. Three dimensional modelling of cytoplasmic β-actin and the VP1 region of EV71 were done with GENO3D Release 2[21]. The protein sequence of cytoplasmic β-actin (UniProtKB P63261 ACTG_HUMAN) was modelled using the template pdb2y83O-0 and for VP1 region of EV71 (UniProtKB Q993S1_9ENTO) the template was pdb1d4m1-0. Protein-protein docking simulation was done with 3DGARDEN server version 1.4[22]. Structure of myosin 6 cargo binding domain bound to cargo were obtained from RCSB PDB database (PDB ID 3H8D). The parameters used for the simulation were as follows; patch union identifier was set as global, number of facet pairs was 5000, number of azimuthal steps for each facet pair was 15, number of predictions for the complex structure to generate was 10, average number of angular steps per refined dihedral was set to 3.
3. Results
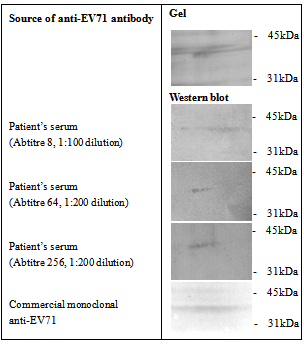
- The ability of anti-EV71 antibody to cross-react with host actin proteins was demonstrated by seroproteomics on EV71-infected RD cell line, using pooled sera from EV71 infected patients. Two proteins were observed; one of approximately 60kDa (data not shown) and another protein size of roughly 42kDa. The band intensities increased with increasing antibody titre (Figure 1). Analysis by mass spectrometry identified the first protein to be EV71 VP1 protein and the second protein was cytoplasmic β-actin (mascot score 228, sequence coverage 24%).
4. Discussion
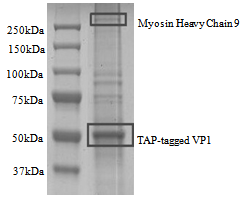
- In this study, we hypothesized that anti-EV71 antibodies cross-react with actin isoforms. The seroproteomic results using EV71-infected patient sera and western blotting using commercially available monoclonal anti-EV71 antibodies confirmed our hypothesis. The identified actin in both cases was found to be cytoplasmic β-actin, an isoform found in all mammalian non-muscle cells responsible for cytoskeleton maintenance and intracellular motility[23,24]. The other protein found from the western blot was the homodimer form of EV71 VP1, which was previously demonstrated by Lalet al.[25]. Surprisingly, another cytoplasmic actin, γ-actin, which always co-exists with cytoplasmic β-actin, was not identified to cross-react with anti-EV71 antibody in this study[26]. Although it was well known that the protein sequence of actin isoforms were highly similar, reports have shown that cells were able to differentiate the different isoforms, so as to compartmentalized them for different functions[23,24]. In this case, the antibodies generated by the host may be able to discriminate the different actin isoforms as well.It was also found that there was structural similarity between the corresponding homologous motif of cytoplasmic β-actin with the immunodominant VP1 linear epitope identified previously, evident though both the sequence alignment as well as the secondary structures of both the VP1 region and the cytoplasmic β-actin[9, 10].Structural similarity suggests that antibody generated against this immunodominant VP1 linear epitope might also bind to cytoplasmic β-actin. Generating EV71 cross-reactive antibodies might be common as report had shown EV71 antibodies can cross-react with human brain tissues, causing neurological complications[14]. Nevertheless, generating cross-reactive antibodies to cytoplasmic β-actin may not cause autoimmunity, since it only exists intracellularly.The rationale for VP1 region to mimic cytoplasmic β-actin might be cryptic or more importantly have an evolutionary advantage on viral survival and thus lead us to propose that VP1 region of EV71 might also interact with myosin and use it for intracellular transport of viral proteins and genome. This is observed in many viruses, including adenovirus and HIV, which enters host cell in an actin-dependent manner[27]. Our hypothesis was confirmed by the co-precipitation of myosin heavy chain 9 (non-muscle) with TAP-tagged VP1. Modelling simulation of protein-protein docking was used to predict the binding of EV71 VP1 to myosin VI cargo binding domain. Myosin VI was chosen for the simulation as it is found in apical brush border of polarized non-muscle cells such as intestinal cells was shown to move towards the minus end of actin filaments and function to transport clathrin-coated vesicles[28]. The simulation predicted that a large surface of VP1 region can bind to a region on myosin VI cargo binding domain overlapping the cargo binding site. This suggest that VP1 region might compete and displace the cargo for binding to myosin VI and gets itself shuttle within the host cell. Moreover, the ability of myosin VI to move towards minus end on actin filament allows the virus to transport its genome from organelles such as smooth endoplasmic reticulum to the perinuclear region for RNA translation. Hence, it is possible that EV71 might exploit myosin VI to transport itself in the host cytoplasm.
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, we demonstrated the cross-reactivity of EV71 antibody to cytoplasmic β-actin. The cross-reactivity may arise due to sequence and structural similarity between the immunodominant VP1 epitope and a homologous motif of cytoplasmic β-actin. We also further proposed that EV71 VP1 might bind to the cargo binding domain of myosin VI and exploit the actin-myosin transport machinery to enter host cell and initiate infection. Further experiments on the interaction of EV71 VP1 with cytoplasmic β-actin and myosin VI may elucidate the mechanism of EV71 infection.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We thank MrsPhoonMeng Chee from the Department of Microbiology, National University of Singapore for providing the EV71 strain 5865/SIN/00009. This research was supported by a grant funded by National Medical Research Council (Grant number R-178-000-176-275).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML