-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering
p-ISSN: 2325-0062 e-ISSN: 2325-0070
2017; 6(2): 36-42
doi:10.5923/j.ijtte.20170602.03

Satellite Boroughs Connection
Vladimír Strakoš1, Michal Novák2, 3
1Supervisor of Doctoral Studies, College of Logistics, Commercial Benefit Corporation, Přerov, Czech Republic
2Combined Studies Doctoral Student of the Faculty of Transportation Sciences, Department of Logistics and Management of Transport, Czech Technical University in Prag, Czech Republic
3Dispatcher Passenger Traffic for the Region Bohemia, Czech Railways, Inc., General Directorate, O 11 – Department of Control Operation of Personal Transport, Czech Republic
Correspondence to: Michal Novák, Combined Studies Doctoral Student of the Faculty of Transportation Sciences, Department of Logistics and Management of Transport, Czech Technical University in Prag, Czech Republic.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of this article is to introduce to the non-professional and professional public the use of monorail as a vehicle for connection of the satellite city districts. The issue of the article is to show how can be different routes monorail boroughs connected with a uniform system of public transport between residents and work places. The combination of satellite boroughs via monorail provides its potential users quality and fast transport between the residences and work places. The system relieves congested roads; it also provides the availability of more urban parts of one or more cities and, ultimately contributes significantly to the environmentally friendly solution for public transport in cities. With the use of solar energy it will also ensure environmental friendliness over each individual point of the line’s length. The main contribution of the paper is to draw out a possible solution for public transport by using the existing modes of transport known today to resolve the temporal and convenient access to employment in urban areas without the inefficient solutions to individual automobile transport.
Keywords: Monorail, Satellite city district, Uniform system mass transport in the cities
Cite this paper: Vladimír Strakoš, Michal Novák, Satellite Boroughs Connection, International Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2017, pp. 36-42. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtte.20170602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- From the historical development of the town developed, especially in the second half of the last century so that it was the character and amenities of the city in the past and on the outskirts of the settlements were built of prefabricated buildings with many residents in a relatively small space. It is due to advances in engineering and the desire of young people to live as early as possible in their own homes. Therefore, manufacturing companies and the historic core with a smaller population often left middle marginal settlements.There was, however a different time, a different trend, which began to be built on the outskirts of cities such production less demanding on heavy machinery or logistics warehouses for temporary storage of delivered goods before shipping it to stores for residents.With rising living standards are increasingly developing in people the desire for a private house with a beautiful garden and swimming pool and if possible away from the bustling city. But this is in contrast with the length of transportation to work and therefore are increasingly growing number of cars used for commuting to work. Thus overloads road links around the villa area and the city center with authorities and companies which provide employment opportunity.The journey to and from work often form a significant part, to some extent working hours and thus decreasing the time for fulfillment of activities related to human life in the family and also a time for recreation and relaxation.These effects on human life in society still increasing important factor and that is that it increases the speed of cars, increases the speed of public transport, but these benefits is virtually impossible to use due to the necessity of limiting the speed of movement of vehicles moving on roads.After considering all of these options comes to the fore the fact that the distance between the residence and place of work is evaluated mainly by the time that citizen spends on the way to and from work, and practically it does not matter the distance. On the basis of this conclusion emerges the question of how humans organize transportation to and from work and still allow him to live in his house with its garden and swimming pool.Virtually the only option for cases where a person has come every day to work, to ensure rapid transport. Of course, we can also consider the possibility of speeding traffic passenger cars, but it is not against protecting the environment that we have all the best. The following is one of several proposals for equipment transport links so that the guy spent the shortest time getting to and from work.
2. Monorail
- Monorail is a single-track railway line where vehicles run on only one rail. Usually the rail is mounted on an artificially elevated place and concrete columns. The term monorail is a combination of English words mono (single) and rail (rail transport) and used since 1897, when this idea came up German engineer Eugen Langen. His idea was to hang over the tram in the street and a project called Einschieniges Hängebahnsystem Eugen Langen. Based on this idea started English engineers simply use the name of the monorail.In today's colloquial word monorail used for any form of elevated railways both for transporting passengers in vehicles or factories for the transport of materials and supplies in the suspended state, so. suspended transport. Monorail for passenger transport is mainly used for rapid transport from the city center to the airport, which replaces the bus or metro.Vehicles monorail (Monorail) appear mostly as light rail vehicles and drivers can be occupied or vacant and remote controlled computer. The actual usage is multiple. Transportation cab may be used either alone as a light rail vehicle in the manner of a bus, or as separate units articulated, or combine to form a train of multiple units. This advanced transportation system used as a rapid transit monorail system is driven by a linear induction motor mounted in the chassis, which also serves as a support element of skeletal fixation element booths and the whole kit Monorail.
 | Figure 1. Classic monorail and underslung monorail |
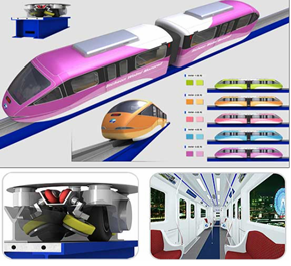 | Figure 2. Chassis monorails (left) and the interior cabin space (right) |
 | Figure 3. Monorail completely frees up space in the streets and in the parks |
2.1. History
- The first monorail was made in Russia in 1820 (Ivan Elman). Attempts have been made to create a monorail as an alternative to conventional rail. Probably the earliest was patented monorail (Henry Palmer) in the UK in 1821 and for the transportation of stone from the quarry.One of the first systems put into practical use was the proposal of the French engineer Charles Lartigue transport between Ballybunion and Listowel in Ireland in 1888th. High speed monorail using the Lartigue system was designed in 1901 and between Liverpool and Manchester.In 1910, Alaska was proposed in Brennan gyroscopic monorail and was considered for the transportation of the coal mine.The first half of the 20th century brought many other proposed projects that either never left the drawing board, or implement short prototypes. One of the first monorails in the United States was built in New York at the beginning of the year. In 1930, but the high cost of the operation was halted relatively soon.In Japan Iron style was built by Lockheed Monorail (Odakyu Mukogaoka - Yuen Monorail, Kawasaki, 1966-2001). In the second half of the 20th century, is more extended another monorail. In 1950, a prototype system was designed for speeds of 200 mph on the straights and 90 mph in the arches and was built in Germany. In the same year it designed an innovative system called ALWEG and later the French system SAFEGE. ALWEG technologies are used by the two largest manufacturers of single tracks Hitachi and Bombardier.In 1956, he was put into operation the first monorail in the United States and started trial operation in Houston, Texas. Later in the period, they were installed additional monorail, eg. At Disneyland in California, Walt Disney World in Florida, Seattle, and many others. From this period monorail received some support in comparison to conventional transport systems.Monorail and began to be perceived as a shuttle from the densely populated areas in shopping centers, as it was in the beginning in Las Vegas, where the monorail linking the city with the Las Vegas Convention Center.In the second half of the 20th century it was seen as competition monorail passenger cars, which were operational while, but it meant and still mean disaster environment.Several single track uses for its survival in this period, revenue from tourism, which benefits from the unique perspectives offered largely increased traffic routes.
2.2. The Turning Point in the Preview to the Monorail
- Since 1980, the increased density of car traffic and congestion and began tossing construction in urban centers and the monorail are experiencing a revival of interest for the use of public transport. Furthest to use the monorail as Japan and now also adds Malaysia. Monorail in Tokyo is one of the busiest routes in the world. On average, carries 127,000 passengers a day and the total since the start of operation carried more than 1.5 billion passengers since 1964. Monorails have also meteoric emergence in specialized theme parks.Modern public means of transportation-track system used beam ALWEG and tires. The monorail is also a type of magnetic levitation maglev in Shanghai. The city of Chongqing in China has adopted a unique ALWEG with a much larger fleet than for other monorails and capacity is comparable to heavy rail. It's because Chongqing is in the environment many hills, mountains and rivers, and therefore tunneling is quite expensive. In India Monorail Project in several cities and is used for mass and rapid transportation of passengers. Mumbai Monorail is the first one.
 | Figure 4. Monorail in Xi'an in China |
 | Figure 5. Example depot in Osaka, where it is possible to move the track into several branches. They move to a bright long stretches |
3. Satellite Links Cities
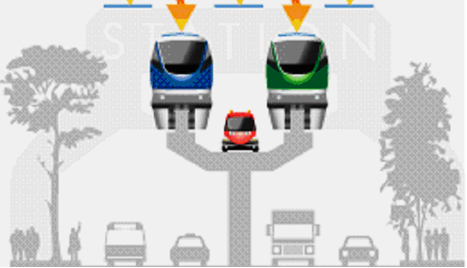
- Further described the design is not entirely original, because China is also considering speed trains in which the passengers being picked up or without stopping the main transport unit. This proposal is also based on the same idea.
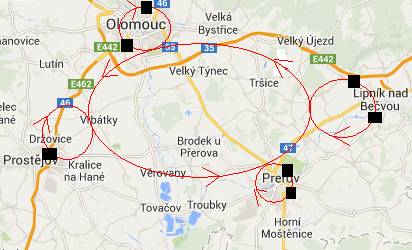 | Figure 6. Example circuit in a landscape with cities |
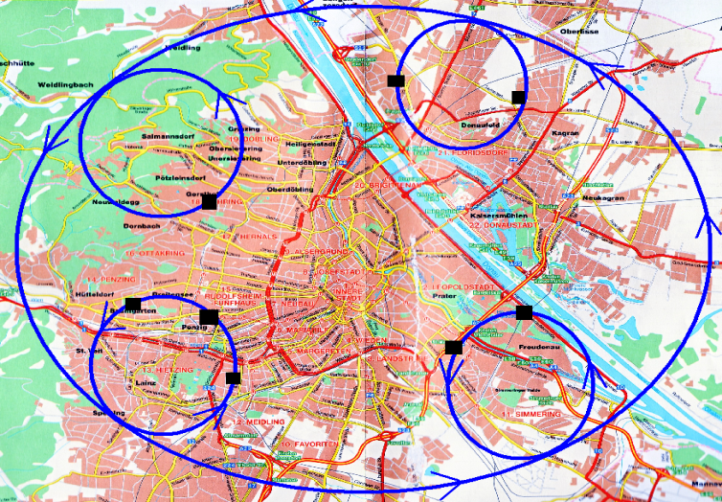 | Figure 7. Example circle around one city |
3.1. Construction and Design Solutions
- The structural design of the entire system supertrain is a very difficult matter, both from a construction and in terms of energy consumption and economic terms and also in terms of traffic organization. Therefore, the aim of this chapter only indicate real possibilities in all the aforementioned areas to allow for a less informed reader to get an idea how such a device might look like and how it could affect the lives of several nearby towns or in a separate city with more stops that every day people are displaced. E.g. They are more housing estates and technology centers at the periphery of the central part of the city.To achieve maximum speed and maintaining it is good to use for vehicle design monorail high-strength steel in the most exposed and most loaded connections, as well as light aluminum alloy to ground and the casing or can use the knowledge of the airline industry, which is also trying to make the individual components of the aircraft as light and durable. Another important design element for monorail ride is that all the "hard" components necessary for smooth operation, were placed under the floor monorail. This achieves a low center of gravity, which affects the stability of the assembly and its driving characteristics. To ensure proper operation of the kit monorail is good to install into the chassis battery backup power from solar panels on the roof. These batteries will ensure that in case of sudden power failure electricity monorail will be able to transport people to the nearest transfer point and remains on track in the dark.Own supertrain and minitrain must have the same length sets 20m, width is sufficient around 1.5 meters, where half a meter on either side of the vehicle inside the benches and in the middle half-meter walk-through lane. The actual set consists of two equally long parts, wherein each part has a door either outside or inside depending on what type of circuit is determined. An important measure of the transfer of the width of doors, allowing the fastest possible transfer of people between the set and minitrain to supertrain. Consider one wing width of 1 meter. When using double doors open out from ourselves toward the wall (the side of the set as the Metro), we get a transfer hole two meters wide. When the layout sets two equally long parts is good to use in one part of the kit door to exit to minitrain - supertrain and in the second part sets the door to exit to supertrain - minitrain.Supertrain connections and minitrain for safe access of people from one set to another is provided by electromagnets placed in corners from top to bottom with double doors (total 4). After speed supertrain and minitrain electromagnets are activated and form a stable two sets, then the door opens and people in transgresses rest between sets. After the transfer, the door closed, the solenoids are deactivated and each kit goes on its way to the next station and all must catch one minute. Therefore, the wide door for the transfer, because if the door closer, could cause crowding and panic that misses transfer between sets. Conversely, when the door wider problem may arise with the speed of opening and closing even after the transfer, when it is necessary disproportionately large amount of time, which can be used for secure transfer.Technical design should minimize impact on other traffic in a certain area. If supertrain ride along the ground, either on the track or road and would have a negative influence on the existing traffic. If it was a yard as part of the existing railroad, would significantly increase the intensity of traffic along this track, and it is practically unacceptable.If you would create a separate circuit around the railway, it would not be at the level of the surrounding landscape, as it would again significantly reduce traffic, especially in places where the S-Bahn crossed another road.From these simple considerations that the only sensible option is a rail track on poles above ground. Because at a certain section connects two parallel sets and moving it sutertrain and minitrain and double-railroad would be too broad. Therefore, it is most likely a single-track railway - monorail.From the foregoing, it minitrain leaving the site with higher population density, makes a few kilometer radius along the way for some time to connect to the eater supertrain, where passengers transgresses. Then he returns to the same place. One of the interesting questions is whether the entire circuit will be in one plane, a plane supertrain or the circuit will connect the street level in the city, and still remains in the same amount and the difference in height to compensate passengers have escalators.If you think about this carefully think about, so if it goes, it would be better to transport route minitrain remained in the plane supertrain because it saves the energy needed to overcome heights. In addition, they could be moving stairs up to the level of the route used eg. To enter the upper floor of the shopping center, which would probably be very interesting for traders.What could be the path minitrain and what could be arches. After his trip to minitrain must start from stop to supertrain speed and acceleration that it is for the transport of ordinary people is acceptable. If the acceleration at start-up was such. 1G, so he started up the car about 3 sec., while it missed the runway about 40 m long. The track minitrain it is quite easy to implement.So that passengers are able to change, so we consider that both associated trains travel together for 1 minute and still cover a distance of about 1.5 km track. After driving this distance minitrain disconnects and starts to slow down and veer toward the settlement. If will return to the center of an arc with a radius of about 200 m, and its average speed decreases to 50 km.hod-1, while the passenger will operate the centrifugal force of about 75 N. When the arc radius 100 m passengers will also cause a greater centrifugal kit strength of about 150 N. In order to compensate the centrifugal forces on the passengers during curve of radius 100 m vehicle tilt of about 110. However, if the path could go minitrain curve radius of 200 m at 50 km.hod-1 and in the arc will tilt 50. The only purpose of this account is not processing specific proposal, but to get an idea about the feasibility of the proposed project.Connecting the circuit to the place of settlement would therefore be symbolic of an ellipse with a length of about 2 km. Based on these considerations Loop minitrain his career for about 3 minutes and eg. If there will be 2 stops in 1 minute and total travel time minitrain will take approximately 5 minutes. This also means very flexible transportation even between stops minitrain. It can also be used for crossing from one station to another without passengers transferred to supertrain and went to another part of the city or conurbation.Yet we will do when passengers go from one station to the farthest part of the city to stop in another part of town. In such a case, the path to minitrain transgression lasted about 5 min., Supertrain journey to the farthest place to transfer to another minitrain would take about 15 minutes, and another 5 minutes to the finish. Total could transport to the farthest pier last 25 minutes.It is theoretically possible that a private car would be quicker, but it is unlikely, because the journey by car will congested roads or streets and waiting in a queue of other cars would have lost a lot of time. Moreover, it is not insignificant that waiting in queues when we do not know how long it will constipation take or attend driving at low speed with our powerful car, a man mentally exhausted and the finish comes already very nervous while in transit "Train" is still on the move and lose a little time.
3.2. Energetic
- Will such transport energy intensive? Not because the train - super long train rides without stopping and thus requires only little energy. Consider that the two cars supertrain will have a weight of 20 t, so that when starting at speed 130 km / h consumes about 13 meters.If the start-up time of 60 seconds and the required engine performance without the loss of 216 kW and if he was starting for 2 minutes, then it would be only 108 kW. If we calculate the effectiveness of 0.8, so will the power output of 130 kW. Anything we add to the friction and the power needed for the launch of 150 kW.After starting it now only overcomes friction and air resistance which currently estimate to 50 kW.Within an hour circling it is 50 kWh which eg. At a cost of CZK 5 per kWh will be CZK 250 per hour. If the train rounded the circuit in 15 minutes and an hour passes 4 circuits and that would mean about 160 passengers, in the case when the TRAIN ride only 40 passengers.If the price for a ticket to the estimate of CZK 10, so the fare chosen CZK 1,600 per hour. It's not a big income, but it is quite possible that the operation of pay, and the rest would be used for other expenses.Minitrain starts off every 15 min., i.e. according supertrain driving circuit, which in our case is 15 min., which are obviously additional costs of operating the system.Variant ground rail linkParallel to such a proposal, I think that almost everyone can think of such a connection on the ground, such as the third single track railway. Such a solution is of course possible and without major complications. But it has one or more obstacles.Railroad track led on the ground inevitably intersects with other roads and that means the speed limit for all vehicles involved, quality finishes crossing for crossing vehicles rigorous security crossing, maintaining the level crossing sites, auto light and audible alarm and stop other vehicles of transport, which will run through crossing while driving supertrain.The kit supertain must go much lower rate than that which is on track on poles, because transportation on land connects populated areas where they move both adults and children, where they can illegally cross the track, which may be on the track any obstacle, whether there fell from a passing car, or were intentionally placed on the track. Moreover, even suicide can not be excluded, because in such a case of death is certain and in very short time.If supertrain go through the land, so his journey without stopping problematic and almost meaningless. I think it's almost certain that it will go lower speeds and in appropriate locations will stop. That is obstructing the kinetic energy of moving masses and in turn greater energy consumption during start-up and above would be greatly extended travel times and this leads again to use their own cars.If the travelling kit without stopping joined module for transferring and populated area can be a closed track inside or outside the closed track as it is shown in Fig. 6th.If the connecting lines are inside the oval track supertrain would have to be almost too long and the flexibility and importance of such a merger would be completely lost.The situation with external circuits is not much better, because the oval should arcs of smaller radius.
4. Conclusions
- Monorail offers countless variations of its use. One option is the use of the above-described method of transport people into employment or for travel. Using it is necessary to take into account the focus on efficiency, capacity, speed, quality and safety. For example, construction of a monorail in Japan proved that the investments in the construction and operation will return in a few years and the experience gained will help society as a whole to ensure all the needs for development in the future.ResumeWith the development of human society there is a passenger transport problem between locations in the city. Development of villages into cities and urban agglomerations brought the problem of how to ensure the fastest and better transportation between boarding and departure points. The modern city has preserved historical center and gradually has penetrated into the neighbourhood where district is formed. The current system of the road transport on the streets is already insufficient into its capacity to meet the person transport requirements, because the streets in cities are clogged by all modes of transport. Large cities today have two ways how to develop transport services. Either by underground transport in the form of underground or over ground transport in the form of a monorail. Monorail is over ground transport, which is structurally incorporated into the streets. In building process is used elevated beams, which is used as a track. Monorail is a monorail transport system, which uses light units (sets). These units (sets) are powered by electricity which is produced in power stations or is supplied by solar panels. Unit (set) is moved along a rail which is used for the power supply. Unites are driven by electric motors located in the wheels. Wheels are fitted with tires and carry the entire weight of the kit. Monorail meets the 21st century requirements for environmental and economical form of transport between neighbourhoods. All monorail lines today are built as a separate line on the busiest road passenger transport directions. Monorail is not connected to the public transport system. This aspect is a limiting factor for passengers to use, because it reduces the quality of the availability for different areas.This article shows the increasing efficiency of passenger transport between neighbourhoods or districts. When using multiple lines Monorail, which in some sections run in parallel, can be used to change between different driving sets. Each monorail is equipped with door magnets, which are activated by parallel line approach at the some point. Sets are magnetically connecting it the driving process, the door are opened and passengers can change the mode of transport in the driving process. After the transfer of the doors are closed , the magnets are deactivated and the individual sets goes on at other points on board, departure or transfer.This proposed principle shows that in today's knowledge and use of the famous monorail technology is able to provide highly effective, fast, high quality and environmentally friendly form of transport. The principle of transfer between sets for monorail ride can provide for big city, which is built around the perimeter of the main circuit and it is connected to the internal circuits. The internal circuit’s stops ensure the transfer to other modes of transport. Monorail can also be used to link Twin Cities and urban parts of the large circle. Big circle touches the city borders. This circuit connects an accumulation of small circuits monorail tracks that are passing in urban areas. In urban areas is again linked to the other modes. Other modes of transport in this instance, the monorail for the collection and distribution of passengers.These two principles monorail lines indicate that by the expenditure of money and the right project, it is easy to reach public transport in densely populated areas.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML