-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering
p-ISSN: 2325-0062 e-ISSN: 2325-0070
2015; 4(1): 8-15
doi:10.5923/j.ijtte.20150401.02
Utilization of Infrastructure Gateway System (IGS) as a Transportation Infrastructure Optimization Tool
Koorosh Gharehbaghi, Maged Georgy
School of Property, Construction and Project Management, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia
Correspondence to: Koorosh Gharehbaghi, School of Property, Construction and Project Management, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Developing and maintaining transportation infrastructures (TI) have notable impacts on communities and industry alike. Sizable investments are thus made throughout the asset’s life cycle to maintain its performance up to expectations. Operation and maintenance of existing TI particularly consume sizable monetary resources. For instance in countries with fully developed TI systems, such as Australia, maintenance activities can consume approximately 75% of the overall TI budget. To streamline the life cycle decision-making process, various optimization tools can be utilized as part of a Transportation Infrastructure Management System (TIMS); yet, their application in real world practice has been limited due to different reasons. The use of Infrastructure Gateway System (IGS) proposed in this paper is envisioned to enhance the overall process of TI development and maintenance management. An IGS establishes a number of control points (or gates) throughout the life cycle of the TI asset to regulate its development and provide basis for the life cycle management decisions. Methods such as Dynamic Programming (DP) and Markov Chain process are used in collaboration to help establish optimized maintenance strategies. Example TI cases/scenarios are presented to illustrate the fundamental concepts in the proposed IGS approach. In conclusion, the IGS with its complementary optimization components can provide TI agencies with proper and well-founded approach for assets development and maintenance.
Keywords: Decision-making, Infrastructure gateway system (IGS), Infrastructure management, Optimization, Transportation infrastructure management system (TIMS)
Cite this paper: Koorosh Gharehbaghi, Maged Georgy, Utilization of Infrastructure Gateway System (IGS) as a Transportation Infrastructure Optimization Tool, International Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2015, pp. 8-15. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtte.20150401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The construction and maintenance of public infrastructures have long-term impacts on the environment, the competitiveness of industries, as well as the development of communities (Bryce et al. 2014, Crawford 2011, Hastings 2010, Kabir et al. 2014). Countries make sizable investments in developing these public assets and continue to pour funds throughout their life cycles to maintain services up to the end customer expectations. For instance, under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, a whopping US$131 billion were set aside for infrastructure projects. Yet, as questioned by Jimenez and Pagano (2012), could these investments make a lasting contribution to improving the nation’s public infrastructure! Both Hastings (2010) and Jimenez and Pagano (2012) emphasize that a successful infrastructure program comes down to the quality of managing the whole life cycle of these infrastructure assets.Out of the different asset types into existence, transportation infrastructures (TI), e.g. roads, railways, bridges, etc., constitute critical elements of any nation’s public infrastructures. While the construction of new TI tends to attract most public attention, it is important to recognize that the operation and maintenance (O&M) of existing TI consume more monetary resources and have broader long-term impacts than the construction activity itself. In countries with fully developed TI systems, such as Australia, O&M activities can consume up to 75% of the overall TI budget (Franks and Stewart, 2008). Moreover, the O&M process has been identified by commentators as the main key to enhancing physical sustainability of existing infrastructure assets (Sohail et al. 2005).Managing the construction, operation and maintenance of TI assets has been the focus of attention of many researches. Various types of decision-making models utilizing the likes of AHP, TOPSIS, ELECTRE, fuzzy logic, and others, have been developed for TI management. A comprehensive review of such models can be found in Kabir et al. (2014). Optimization models were also developed to streamline and hence improve the whole-service-life of TI assets e.g. Durango-Cohen and Sarutipand (2009), Medury and Madanat (2013), Morcous and Lounis (2005), Robelin and Madanat (2008), Zhang and Gao (2012), etc. In practical terms, the optimization models typically functions from within a broader Transportation Infrastructure Management System (TIMS). According to Alberta Transportation (2014), TIMS is a unique knowledge system designed to ensure that highway assets and the annual capital investments are managed for optimum lifetime performance by measures of safety, economics, environmental sustainability and innovativeness.Despite the plethora of researches, the optimization models have not been widely employed due to the needed computational time and its applicability in real life scenarios (Chen et al. 2014). To improve the context in which optimization models are utilized, the paper introduces Infrastructure Gateway Systems (IGS). IGS are believed to have potential in streamlining the process of TI asset management. Paper will first introduce the IGS and its decision making process. The specific IGS adopted in this research is then examined with clarification of the different gates it has. Afterwards, the elements of TIMS are explored to help understand how it supports IGS in TI decision-making. Finally a set of example projects are introduced and the application of the IGS is briefly discussed to demonstrate the potential of the proposed approach in optimizing the TI delivery and maintenance process.
2. Infrastructure Gateway Systems (IGS): A Review of the Literature
- The IGS is founded on the principles of stage-gate project management. For a more comprehensive coverage of this project management approach, the reader is advised to review publications such as Chao et al. (2014), Cooper et al. (2002), etc. In the context of the current research, an IGS establishes a number of control points (or gates) throughout the life cycle of the TI asset to regulate its development and provide basis for the life cycle management decisions. As per CIDB (2011), a standardized IGS organizes the work flow (sequence of connected activities) according to stages of the delivery and maintenance of infrastructure assets. It simply groups logically related activities in the infrastructure cycle together into discrete stages in such a manner that the end of the stage culminates in a major milestone in the form of documented information which requires approval or acceptance before a stage can be regarded as being complete. These stages create decision gates (control points) at the end of each stage which can be used to provide assurance that the proposed work (CIDB 2011): ● Remains within agreed mandates;● Aligns with the purpose for which it was conceived; and ● Can progress successfully from one stage to the next.A gateway system designed around a set of gates (control points) that are strategically located within an infrastructure asset management cycle has the potential to (CIDB 2010, Watermeyer 2012):● Enable projects to be more accurately scoped and costed at an earlier stage in the asset life cycle;● Reduce time and cost overruns;● Improve alignment of service delivery with available funds;● Improve procurement discipline;● Manage risks more effectively;● Reinforce responsibility and accountability for decisions; and● Enable projects to be better aligned with policies objectives.The information upon which a decision is based at a gate and the decisions made can be audited to ensure that projects remain within an organization’s mandate, are justifiable and realize value for money. The opportunity to audit the life cycle of projects also (CIDB 2010):● Improves transparency which, in turn, reduces the opportunity for mismanagement and corruption in planning and implementation;● Enables the procurement strategy adopted for a portfolio, program or project to be reviewed and improved upon when delivering similar projects in the future;● Enables post implementation reviews to take place to examine whether planned benefits are achieved and risks are being effectively managed; and● Removes perverse incentives relating to the promotion of one project or a solution over another.Watermeyer (2011 and 2014) reviewed the IGS used in South Africa to manage the country’s infrastructure assets. The IGS in reference allows the delivery and maintenance of works to be planned and implemented in a controlled, logical and methodical manner. The model allows workflow of activities by the national, provincial and local governments. Considering IGS from a procurement perspective, Watermeyer (2011) pointed out that the deliverables by the end of every IGS stage form the basis for the scope of work of a contracting strategy and accordingly enable the contractor to be procured to take the work forward. Watermeyer et al. (2013) further elaborated on the functionality of the South African IGS in connection with a broad infrastructure delivery management system (IDMS). Within the context of IDMS, the IGS interacts with 4 systems, namely, infrastructure planning system, program and project management system, construction procurement system (CPS), and lastly operations and maintenance system. However, in order to deliver the intended outcomes in an efficient way, the IDMS externally interacts with 3 more generic management systems; they are financial management system, internal audit system, and risk management system.
3. The Proposed Infrastructure Gateway Systems (IGS)
- Structuring the IGS requires the utilization of a System Engineering (SE) approach. System engineering views a system as a combination of interacting elements organized to achieve one or more stated purposes (Hitchins 2007, Kossiakoff 2011). Furthermore it integrates the set of elements into sub-systems or assemblies that accomplish a defined objective. As we proceed with the use of IGS in optimizing the life cycle decisions of TI assets, it is important to fully appreciate the pivotal role of the Transportation Infrastructure Management System (TIMS). Figure 1 illustrates the IGS designed by the paper’s authors for TI management. This particular IGS has been revised after the original work of the first author in 2009. As seen, the proposed IGS has 4 main gates; they are:1.Analysis: At the analysis gate, pre-analysis considerations, such as, TIMS applications, sub-systems and possible system elements need to be established. These system components are key aspects of the TIMS Hard System development. Furthermore, at this stage, the main problems together with the proposed alternatives are considered.2. Configuration: For the configuration gate, all system components including the sub-systems and system elements require to be configured. At the gate, the actual TIMS is configured.3. Development: At the development gate, the full integration of the TIMS system occurs. TIMS specifications are further reviewed and assessed against its main desired outputs.4. Implementation & Evaluation: At this gate, TIMS is launched and assessed. System testing and refinement are also conducted here to ensure successful output.
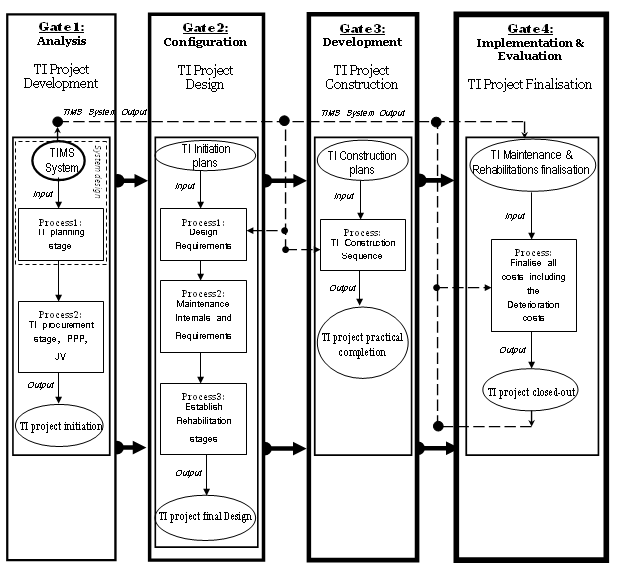 | Figure 1. 4-Stage IGS for Transportation Infrastructure Management (Revised after Gharehbaghi, 2009) |
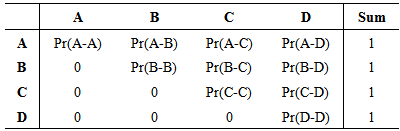
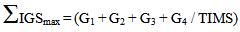 | (1) |
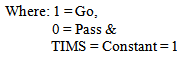 Accordingly:
Accordingly: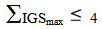 | (2) |
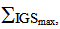 it can be concluded how the IGS gates are utilized, where 1 represents low utilization, and 4 represents extreme utilization. Furthermore, projects may start with a low
it can be concluded how the IGS gates are utilized, where 1 represents low utilization, and 4 represents extreme utilization. Furthermore, projects may start with a low 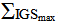 value that can gradually be increased. This will occur on projects where the system conception maybe weak or not well defined. In such cases, and after being pointed out by the IGS, it will be required to either increase the system’s input requirements (via Gate 1: Analysis), or prolong the system’s processing stage (Gates 2: Configuration and Gate 3: Development) to ensure that project is well mobilized. Following such process thus ensures that the project will at least produce high
value that can gradually be increased. This will occur on projects where the system conception maybe weak or not well defined. In such cases, and after being pointed out by the IGS, it will be required to either increase the system’s input requirements (via Gate 1: Analysis), or prolong the system’s processing stage (Gates 2: Configuration and Gate 3: Development) to ensure that project is well mobilized. Following such process thus ensures that the project will at least produce high 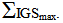 This is the final and most important feature of the proposed IGS as a transportation infrastructure optimization tool.
This is the final and most important feature of the proposed IGS as a transportation infrastructure optimization tool.4. TIMS: The Foundational Concepts and Components
- As seen in figure 1, TIMS has a controlling role over the 4 gates of the IGS utilized in this research. TI typically includes roads, bridges, tunnels, airports, railways, and seaports. As a result, a TIMS usually covers many subsystems, among which Pavement Management System (PMS) and Bridge Management System (BMS) are the most important (Chen et al. 2014, Hoel et al. 2007). TIMS with all its constituent components, figure 2, will perform tasks necessary for the IGS presented in the previous section to function properly. Details on the TIMS constituent components and their functioning in the broader context of IGS are discussed hereinafter.
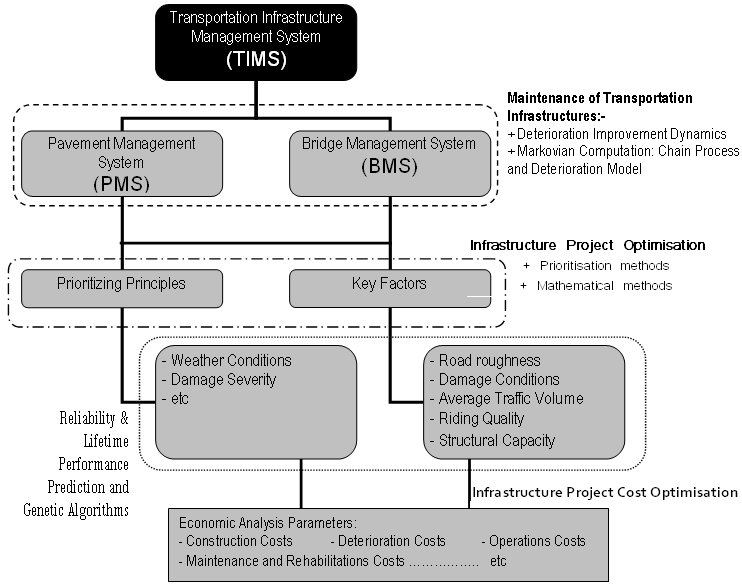 | Figure 2. TIMS and Its Primary Sub-Systems |
4.1. Infrastructure Project Optimization
- As part of any TIMS, life-cycle project optimization is a key element in the TI decision-making process. In PMS, project optimization primarily concerns finding an optimal maintenance strategy with maximized benefits for the road network. Meanwhile, in BMS, the structural capacity and integrity of bridge assets are the primary points of interest for any project optimization process. Currently, there are two main categories for project optimization in TIMS; they are prioritization and mathematical methods (Chen et al. 2014). A prioritization method is employed to help compare a number of proposed maintenance strategies for the TI in concern. The selection is based on some pre-screened principles that are used to aid in deciding the maintenance strategy for each year in the planning period (Chen et al. 2014). Frank and Stewart (2008) summarized the characteristics of different prioritization methods. The two most popular approaches for such purpose are based on TI performance parameters and economic analysis parameters (Chen et al. 2014). Mathematical optimization for TIMS, on the other hand, falls into two categories: static and dynamic. The latter is made possible via Dynamic Programming (DP) (Gharehbaghi and Hughes, 2006). The static and dynamic categories usually use the maintenance strategy as the decision variable, and constraints from budget, manpower, machine, and material. While the static category incorporates certain constant variables, the dynamic category is the most important and includes maintenance activities. For this category, the Markov decision processes are utilized. The separation of these two categories has the positive effect of minimizing the overall costs.
4.2. Decision-Making for TI Maintenance
- TI maintenance management can be organized as a hierarchy of activities that belong to two main categories: (i) periodic rehabilitation and (ii) routine day-to-day operations. While the activities within and between the two categories differ from each other in terms of their costs, characteristics, and the extent of their impacts, they all contribute to the overall service level of the TI system and compete for resources from the same budget. For the latter, various resource allocation models are utilized (Gharehbaghi and Raso, 2011). In principle, a systematic and transparent decision support tool within TIMS permits trade-offs among multiple objectives and integrate analyses across several assets and operations (Gharehbaghi and Hughes, 2006). Decisions concerning the maintenance of TI generally falls into two different levels (Gharehbaghi and Raso, 2012): (i) the programming level, where the focus is on the life-cycle analysis of individual assets and, more specifically, the selection of those actions that will be funded through annual maintenance and repair programs; and (ii) the network level, where the focus is on the aggregate quality distributions of assets and services, and the purpose is to guide the allocation of resources among different maintenance activities, asset types, road districts, or other sub-networks. The network-level decisions are inherently more strategic because they set the budgets for the optimization of programming-level decisions. Network-level decisions are also more challenging because they must address longer time horizons and a broader range of objectives. In effect, they are essential to the sustainable development of the whole network (Hoel et al., 2012).
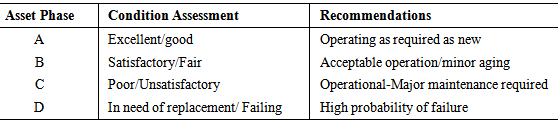
4.3. Infrastructure Deterioration Modeling
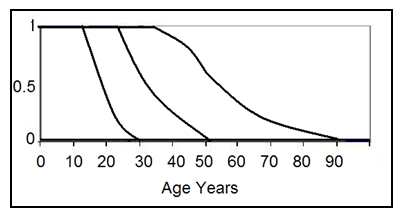
- According to Hoel et al. (2012), infrastructure deterioration accounts for both condition- and criticality-based failure of assets. Analysis takes into account the likelihood that an asset would fail, based on the health, applied type of use, time in use, and typically-accepted life expectancy of that asset. These components can help to construct the declining functionality of a TI asset, as represented by the curve in figure 3. As observed, the relationship between the deterioration curve and the probability of failure (P-F) is critical. Combining the condition and criticality components helps define the risks associated with TI assets, where numeric scales may be utilized to quantify the risk level (Goodman and Hastak, 2006).
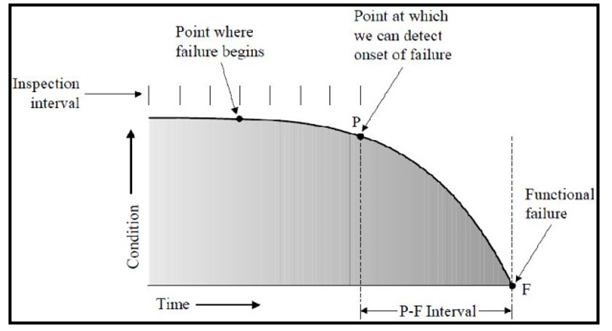 | Figure 3. An Asset’s Probability of Failure (“P-F”) over Its Lifespan (ABS, 2014) |
|
|
 | Figure 4. Asset state probability curve |
5. Illustrative Application in TI Management
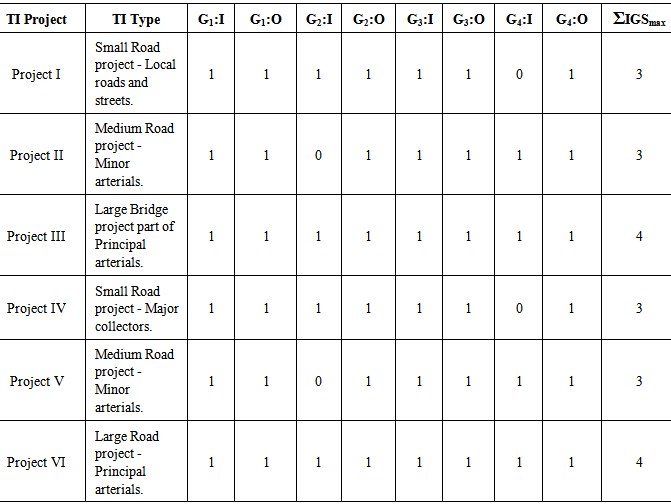
- To better understand and validate the proposed IGS, sample TI projects have been examined, table 3. The table summarizes the application of the 4-stage IGS onto six TI Projects, where Gx refers to Gate x, I is the gate’s input, and O is the gate’s output. The projects in reference were selected from the states of Victoria and New South Wales in Australia. For confidently reasons, the names and exact locations of these projects cannot be disclosed.As it can be noticed, projects III and VI are the only two projects that have utilized all gates. Meanwhile, the rest of projects have at some stage by-passed some gates. This is mainly due to the independent utilization of the TIMS, which provides a basis to by-pass some gates via the optimization process. In this particular application, the resultant
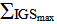 varies between 3 (high utilization) to 4 (extreme utilization). A value of 3 indicates that majority of IGS gates has been used, whereas a value of 4 denotes that all IGS gates were utilized. To further explain, in the case of Project VI, vigorous project design specifications were present, and hence no gate could have been by-passed. Project III was part of a mega PPP project and had special requirements for site including unique excavation technique and different soil chemical composition specifications. Again all gates had to be processed. However, for the normal routing types of TI projects, some gates were by-passed without any negative impact. When many projects are increasingly constrained in time and/or cost, the added flexibility offered by the gateway system not only reduces project duration but also enhances the whole-life-cycle delivery of the TI project pool. The examples in this section clearly demonstrate the potential of using the gateway system as a capable apparatus for the life cycle optimization of a given TI project pool. Further details regarding the application of IGS are planned for other future publications by the authors.
varies between 3 (high utilization) to 4 (extreme utilization). A value of 3 indicates that majority of IGS gates has been used, whereas a value of 4 denotes that all IGS gates were utilized. To further explain, in the case of Project VI, vigorous project design specifications were present, and hence no gate could have been by-passed. Project III was part of a mega PPP project and had special requirements for site including unique excavation technique and different soil chemical composition specifications. Again all gates had to be processed. However, for the normal routing types of TI projects, some gates were by-passed without any negative impact. When many projects are increasingly constrained in time and/or cost, the added flexibility offered by the gateway system not only reduces project duration but also enhances the whole-life-cycle delivery of the TI project pool. The examples in this section clearly demonstrate the potential of using the gateway system as a capable apparatus for the life cycle optimization of a given TI project pool. Further details regarding the application of IGS are planned for other future publications by the authors.
|
6. Conclusions
- Countries invest sizable funds in the development and maintenance of TI assets. The operation and maintenance of existing TI, in particular, have far reaching implications on their serviceability. As such, diverse research into TI asset management has been conducted over the years. Van der Lei (2012) summarized the most recent research trends in this domain. These trends were the result of a special session held at the WCEAM 2010 conference in Brisbane, Australia. One of the key trends was decision making for infrastructure asset management. This is the theme under which this paper is classified.The paper proposes employing IGS to streamline the decision-making and life-cycle management of TI assets. The proposed system comprises 4 gates, namely, analysis, configuration, development, and implementation & evaluation. As seen, the functioning of this IGS requires the use of variety of tools and techniques not uncommon in the subject domain. This includes the likes of Dynamic Programming, Markov chain analysis, and others. Six case studies were briefly reviewed as the basis for endorsing the proposed IGS. However more should follow. Achieving the ultimate goal of having an effective and successfully operative IGS in real world practice dictates the collection of sizable data relating to the condition of the various TI assets into consideration. This is imperative to be able to carry out the TI optimization process. Furthermore, TI performance models need to be constantly developed and maintained to assist with the development of priorities. In addition, in determining TI performance enhancement, the four gates of the proposed IGS need to be carefully analyzed and integrated. In conclusion, the IGS approach has potential to streamlining the TI decision-making process; yet more effort is needed for the transition into fully operative system in reality.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML