-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Tumor Therapy
p-ISSN: 2163-2189 e-ISSN: 2163-2197
2013; 2(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.ijtt.20130201.01
Pentoxifylline: A Potent Inhibitor of Angiogenesis via Blocking STAT3 Signaling in B16F10 Melanoma
Dhumale Pratibha, Nikam Yuvraj, Gude Rajiv
Gude Lab. Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer (ACTREC) Tata Memorial Centre, Sector 22, Kharghar, Navi Mumbai, 410 210, India
Correspondence to: Gude Rajiv, Gude Lab. Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer (ACTREC) Tata Memorial Centre, Sector 22, Kharghar, Navi Mumbai, 410 210, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Pentoxifylline (PTX) has been shown to exert anti-metastatic activity in solid tumor. In the present study the underlying molecular mechanism of the anti- angiogenic activity of PTX was investigated in highly metastatic B16F10 melanoma. PTX suppressed the phosphorylation of Signal transducer activator of Transcription 3(STAT3) and its upstream kinases in B16f10 melanoma at nontoxic dosages. It also reduced the expression of HIF1α, VEGF (potent angiogenic factor), its receptors (VEGFR1, VEGFR2) and pro-inflammatory cytokines which play a significant role in induction of angiogenesis in solid tumors. Moreover, PTX significantly suppressed the microvessel density around tumor induced in mice by injecting B16F10 cells intradermally on shaven ventral site. The inhibition in vasculature around tumor resulted in regression of tumor volume in PTX treated group of animals as compared to untreated group. These findings suggest that PTX exert anti-tumor activity by inhibiting angiogenesis via targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in B16F10 melanoma.
Keywords: Pentoxifylline, STAT3, HIF1α, Angiogenesis, Melanoma
Cite this paper: Dhumale Pratibha, Nikam Yuvraj, Gude Rajiv, Pentoxifylline: A Potent Inhibitor of Angiogenesis via Blocking STAT3 Signaling in B16F10 Melanoma, International Journal of Tumor Therapy, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2013, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtt.20130201.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Melanoma is a complex genetic disease which is invasive by nature. Most deaths from melanoma are due to metastases that are resistant to conventional therapies. Metastasis is a sequential process which consists of interrelated steps such as adhesion, breakdown of basement membrane, angiogenesis, motility and homing to distant target organ of tumor cells[1, 2]. Thus to target the spread of melanoma to distant organs it is necessary to restrict the disease at very early stages. One such early important stage is tumor angiogenesis[3]. It not only facilitates tumor growth but also provides an efficient route of exit for tumor cells to leave the primary site and enter the blood stream Therefore a highly vascular tumor is consider to have more ability to get metastasize[4].Newly formed vasculature in solid tumors differs greatly from that found in normal tissue, typically displaying a broad range of structural & functional abnormalities leading to the condition called as hypoxia[5]. It is regulated by balance between multiple pro and anti angiogenic factors such as VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), Matrix metalloproteases (MMP2, MMP9), and pro-inflammatory cytokines etc. which are secreted either by tumor cell itself or from host tissue in response to activation of metabolic stress[6]. Theses pro-angiogenic factors further activate oncogenic cell survival pathways and one of them is the STAT3 (Signal Transduction & activation of Transcription 3) pathway, which contributes significantly to tumor progression. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT3 gets activated via phosphorylation through receptor associated kinases like JAK2 and Akt and gets dimerized and translocated to the nucleus, where it acts as transcription regulator of genes associated with angiogenesis and spread of cancer. In hypoxic conditions, STAT3 also stabilizes HIF1α, both of which regulate transcription of genes required for cell survival and proliferation[9-11]. Thus there is a pressing need to identify a new agent which will target STAT3 and associated angiogenic factors, which are crucial for angiogenesis & metastasis in melanoma.Pentoxifylline (PTX) is a methyl xanthine derivative which is used in the treatment of peripheral vascular diseases and intermittent claudation. It enhances tumor sensitivity to both radiation and chemotherapeutic agents[12]. Earlier studies from our laboratory has shown that PTX causes cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase at nontoxic dosages. It is a phosphodiestrase inhibitor which elevates cyclic AMP levels and impedes cancer cell migration and it also modulates surface expression of integrins and integrin mediated adhesion of B16F10 cells to extracellular matrix and lung homing[13]. However it remains unknown whether PTX affects any key targets involved in pathological tumor angiogenesis.In the present study we investigated the molecular mechanism of inhibition of angiogenesis by PTX in B16F10 melanoma and observed its effect on in vivo angiogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. We found that PTX inhibits STAT3 signaling and also demonstrates a decrease in expression of VEGF, its receptors and pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in angiogenesis. In vivo experiments in B16F10 melanoma showed inhibition of microvessel density around tumor and regression in tumor volume on treatment with PTX. Our results suggest that PTX can be developed as a good candidate for anti-angiogenic therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
- B16F10, a highly metastatic cell line was derived from C57BL/6 murine melanoma was purchased from national centre for cell science, Pune, India. The cell line was maintained as continuous culture in IMDM (Iscove’s minimum dulbecco’s medium) supplemented with 10% fetal bovin serum (biowest), 100 U/ml penicilline& 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Cells were grown in humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and at 95 % air at 37℃. IC50 value of pentoxifylline on B16F10 cells was found to be 39.2± 1.3 mM for 2 hr drug exposure of PTX, whereas at extended treatment of 24 hrs it is found to be 13.18± 1.8Mm. For all our In Vitro experiment cells were treated with PTX at subtoxic dosage of 1 mM, 2 mM& 4 mM.C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Animal House, Advanced Centre for Treatment Research Education in Cancer (ACTREC), Tata Memorial Centre, Kharghar, Navi Mumbai. All mice were used in accordance with the institutional guidelines of IAEC, ACTREC.Antibodies against STAT3, Phosphorylated STAT3 (tyr 705), JAK2, Phosphorylated JAK2, ERK1/2, Phospho ERK ½, Akt, PhosphoAkt, VEGF, HIF1α and CD31, were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Antobodies against Tubulin was purchased from Sigma Aldrich.
2.2. Western Blotting
- B16F10 cells were grown to 70-80 % confluency& treated with PTX for 24 hrs. The cells were scraped, followed by PTX treatment and washed in ice cold PBS, and then whole-cell extracts were prepared by lysis buffer[50mM Tris, 1% Triton X-100, 150mM NaCl, 5mM EDTA, 10mM EGTA, 50 mM Na fluoride, 1mM Na orthovanadate, 1mM PMSF and protease inhibitor cocktail]. Lysates were spin at 10,000 rpm for 20 minutes to remove insoluble material. Supernatants were collected and kept at -80 C. Protein concentrations were determined with Bradford reagent. Whole cell lysates were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE. After electrophoresis, the proteins were electro-transferred to PVDF membranes. Blocking was performed for 2 h at room temperature in blocking buffer consisting of 5% skim milk powder in TBST (Tris buffer saline, pH 7.4, 0.1% Tween-20). The membrane was blotted with the relevant antibodies, and the proteins were detected by an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (FEMTO).
2.3. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
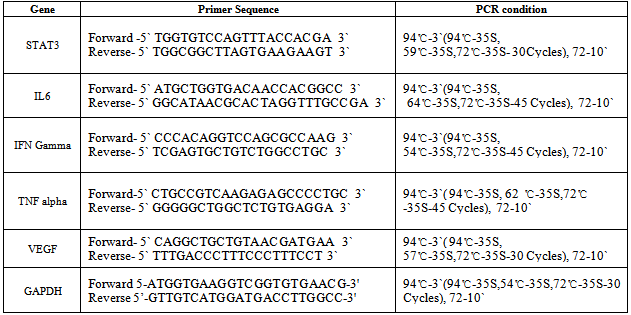
- RNA was extracted by Trizol (Sigma Aldrich) method. cDNA preparation and PCR were performed using kit from Fermentas according to manufacturer’s instructions. Primers were manufactured by Sigma Aldrich and had the following sequences:
2.4. ELISA
- The B16F10 melanoma cell line was maintained in IMDM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin/streptomycin. To prepare supernatants from B16F10 cell line for ELISA, 3 ml of fresh medium were added with or without PTX to established cell line when 60–70% confluent in 60 mm petri dish and collected after 24 h. Supernatants were centrifuged at 1500 × g to remove particles, and aliquots were stored frozen at −80° until use in ELISA. Cell number in the petri dish was determined to standardize the quantity of cytokine secreted per 106 tumor cells. VEGF level in cell culture supernatant was determined using an ELISA kit (Allied Life Science). According to manufacturer’s instruction and analyze using ELISA reader SPECRA MAX 190.The experiment was repeated three times.
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
- The localized tumor along with blood vessels was fixed in buffered formaldehyde and embedded with paraffin. 5 µm sections of tumor tissue were processed to examine blood vasculature inside tumor tissue. Briefly, sections were deparaffinised, washed with PBS, blocked with 5% BSA and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibody against specific endothelial cell marker CD31 .Followed by incubation with fluorescently conjugated secondary antibodies(anti goat conjugated with Alexa 568). Slides were then stained with DAPI for 1 minute in dark. Images were acquired at 10X using Trinocular Motorized Upright Research Microscope (ZEISS)
2.6. Determination of Effect of Pentoxifyllineon invivo Angiogenesis and on Tumor Development
- Angiogenesis was induced in three groups of C57BL/6 mice (5 mice/ group) by injecting B16-F10 melanoma cells (1 x 106) intradermally on shaven ventral skin surface of each mouse. Group I animals received Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and served as control. Group II & III animals were treated with 20 mg/Kg & 40 mg/Kg dose of pentoxifylline respectively by intraperitoneal route for 10 days after tumor injection. On Day 14 all animals were sacrificed, the blood vessel density was observed & inhibition in blood vessel density was counted.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
- Data expressed as Mean + S.D of three independent experiments. Statistical evaluation was done by applying student‘t’ test and One way ANOVA.
3. Results
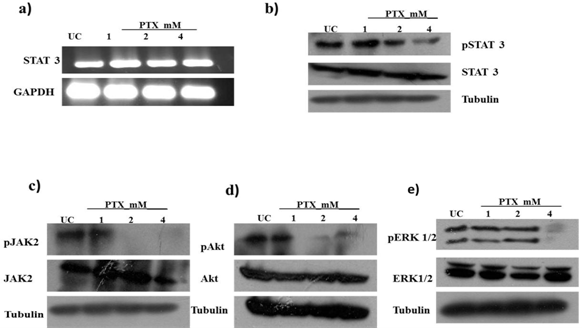
3.1. PTX Suppress STAT3 Signaling Pathway
- STAT3 is implicated in cell survival, tumor development, angiogenesis and metastasis of melanoma[15]. We examined whether PTX has any effect on STAT3 protein in B16F10 melanoma cells. We observed that PTX does not affect STAT3 at transcriptional or translational level but the active form of STAT3 i.e. phosphorylated form of STAT3 gets significantly inhibited on PTX treatment in a dose dependent manner (Fig. 1a, 1b). As STAT3 is activated by upstream kinases such as JAK2, ERK 1/2 or AKT on ligand binding or stimulation of cytokines & growth factors[16-18], we analyzed activation (phosphorylation) of JAK2, ERK 1/2 and AKT in B16F10 cells on PTX treatment by western blotting. PTX suppressed the phosphorylation of JAK2 and AKT (Fig. 1c, 1d). A similar inhibitory effect was observed on ERK 1/2 albeit at a higher concentration i.e. at 4 mM (Fig 1e). These results indicate that PTX inhibits the activation of STAT3 by inhibiting the activation of its upstream kinases.
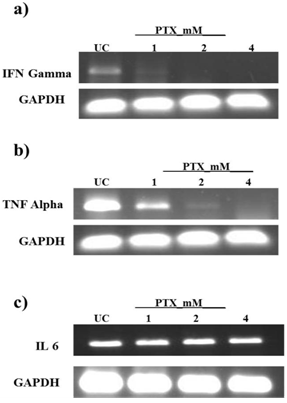
3.2. PTX Modulates the Expression of Cytokines Regulated by STAT3 which are Involved in Angiogenesis
- Cytokines play an important role in tumor development & angiogenesis[19]. We carried out studies to observe the effect of PTX on pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are mainly governed by STAT3, in B16F10 melanoma such as IL6, TNFα and IFN γ by RT PCR[20,21]. The results showed that TNFα, IFNγ are inhibited significantly by PTX treatment in dose dependent manner. (Fig. 2) However no effect was observed on IL6 expression.
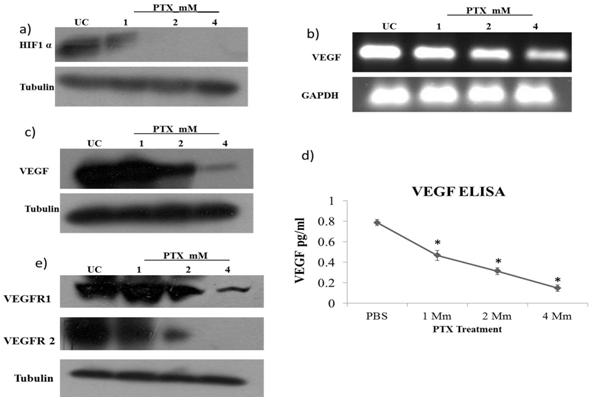
3.3. PTX Inhibits Expression of HIF1α & VEGF
- Hypoxia is one of the many conditions which induce the process of angiogenesis in solid tumors. HIF1α has been shown to carry out this induction when cancer cells reach a hypoxic state. STAT3 modulates the stability & activity of HIF1α and in turn enhances the expression of genes involved in angiogenesis & cell survival. STAT3 also interacts with HIF1α and gets recruited on VEGF promoter region[22]. To determine the effect of PTX on HIF1α we checked the protein levels of HIF1α by western blot. We observed that the expression of HIF1 α was strongly inhibited by PTX at 1mm dose and further at higher doses (Fig.3a). As HIF1α, along with STAT3, acts as a transcriptional factor for expression of VEGF, we checked the effect of PTX on VEGF at mRNA & protein level by RT PCR & western blot respectively. We found a dose dependent decrease in VEGF expression at both transcriptional & translational level (Fig. 3 b, c). To quantify inhibition in VEGF secretion in the culture supernatant of B16F10 cells, ELISA was performed after incubating the cells with PTX. This inhibition was approximately 80% in 2 mM& 90 % in 4 mM (Fig. 3d).
3.4. PTX Inhibits Expression of VEGF Receptors on B16F10 Cells
- Coexpression of VEGF & VEGF receptors such as Flk 1 (VEGFR1), KDR (VEGFR2) on tumor cell implies that autocrine loops exist between VEGF and VEGFR binding. VEGF acts on tumor cells itself and further induces proliferative and angiogenic effect in solid tumors[23,24]. We, therefore, studied the effect of PTX on VEGF receptors such as Flk 1, & KDR which are main receptors of VEGF in angiogenesis. We found that expression of both receptors significantly got inhibited by PTX treatment in a dose dependent manner in B16F10 cells (Fig. 3e).
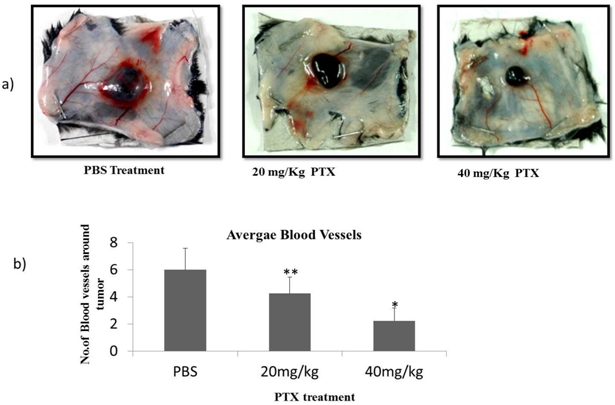
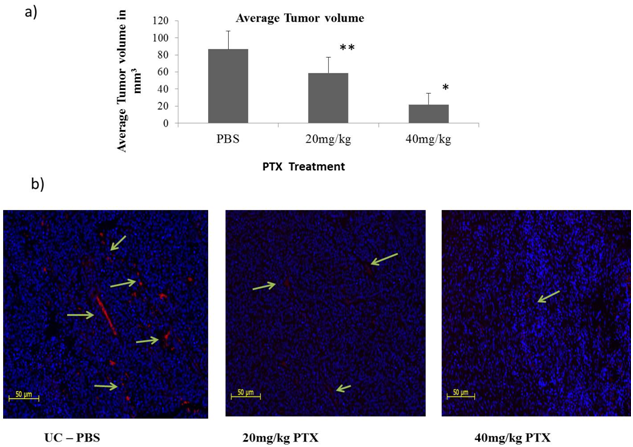
3.5. PTX Inhibits Tumor Induced Microvessels and Induces Regression in Tumor Devlopment
- The ability of PTX to inhibit newly formed vasculature around tumors was studied in intradermaly induced B16F10 melanoma tumor on shaven ventral side of animals[25]. We observed that the number of tumor induced capillaries was significantly reduced after PTX treatment. Control animals had an average no. of 6 ± 1.63 capillaries whereas 4.25 ± 1.25 & 2.25 ± 0.95 average no. of capillaries were observed around the tumor of 20 mg/kg & 40 mg/kg PTX treated group of animals (Fig. 5). To understand the effects of PTX on tumor development; the tumor volume of localized tumor was measured by averaging the diameters using Verniercallipers. The tumor volume was expressed in mm3 using formula 0.4x a x b2. As shown in Figure 5, after 10 days treatment, the volume of tumors in PTX treated groups was much smaller than the control group. To further confirm the effect of PTX on blood vasculature inside the tumor tissue, we performed blood vessel staining of tumor tissue sections with endothelihal cell marker (CD31) antibody[26]. We observed that the average numbers of vessels in PTX treated groups were less than the control group. These results indicate that PTX not only inhibits angiogenesis but also tumor growth in vivo.
4. Discussion
- Melanoma is a malignancy of pigment producing cells. Although melanoma at primary stage is curable through surgery, treatment of advance metastatic melanoma remains difficult and it is associated with poor prognosis. Despite worldwide efforts in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment, cases of melanoma continue to rise. Extensive research and clinical trials involving cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs, immunostimulatory agents such as interferon, Interleukin (IL2) both as single agent & in combination regimen have yielded low response rates against metastatic melanoma. Therefore it is necessary to target the disease before it attains its metastatic ability.As angiogenesis plays a critical role in growth & spread of melanoma, it is a potential target in melanoma therapy. Angiogenesis is characterized by proliferation of endothelial cells in tumor tissue[27, 28]. In recent years several therapeutic approaches aimed at developing anti-angiogenic cytotoxic agents such as inhibitors of endothelial cells e.gAngiostat, GEM220, Inhibitors of matrix metalloprotease COL3, Neovastat and modulators of upstream kinasees cetuxiamb, Herceptin etc have been tried[29, 30 ]. But the major problem associated with use of these anti-angiogenic agents in melanoma therapy is that their use has shown complications in normal physiological function of kidney, heart as well as in wound healing process and also has revealed defects in fetus development[31. 32]. Thus there is a pressing need to develop an anti-angiogenic agent which will target abnormal microvessel density in tumor tissue, and will be less toxic causing no developmental or physiological disorders. One of the promising approaches in this regard is to investigate the anti-angiogenic potential of drugs that already have shown their efficacy in treatment of other diseases. This will facilitate early implementation of that drug into clinical setup as its pharmacokinetic data and side effects are already known.Pentoxifylline (PTX) is a theobromine derivative and its chemical name is 1-(5-oxohexyl) - 3, 7-dimethylxanthine. Clinically this compound is used to treat a peripheral vascular disease and is commercially available in the name of Trental. PTX shows its anti proliferative, anti-adhesive, anti-metastatic properties on melanoma cell line at non toxic dosage[33-36]. Therefore PTX draws attention for its use in antimetastasis therapy. In the present study we report that PTX exerts its anti angiogenic activity by targeting STAT3 signaling in the highly metastatic B16F10 melanoma model.STAT3 is constitutively activated at 50 to 90% frequency in diverse forms of cancer including melanoma. It is a cytoplasmic protein which gets activated by upstream kinases via ligand binding or through cytokines or growth factors[37]. A critical role of STAT3 activation in tumor cell survival, proliferation, angiogensis, metastasis and immune evasion has been well demonstrated. STAT3 contributes to tumor cell survival by regulating the expression of genes that are involved in cell survival[38]. STAT3 promotes metastasis &angiogensis by inducing expression of metastatic genes, MMPs, serine protease uPAand potent angiogenic genes, bFGF and VEGF. STAT3 signaling in dendritic cells leads to immune tolerance[39, 40]. STAT3 is, thus, an attractive target for cancer therapy including advanced metastatic melanoma.Our data demonstrate that PTX significantly inhibits the activation of STAT3 in the highly metastatic B16F10 melanoma. The inhibitory effect is associated with inhibition in activation of the upstream kinase JAK2. Janus associated kinase (JAK) has tyrosine kinase activity, which binds to cytokine receptors and gets activated and further triggers the activation of STAT3. It has been reported by other investigatorsthat inhibition in activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway results in inhibition of tumor growth[42]. ERK 1/2 and Akt are found to be constitutively activated in melanoma and play an important role in tumor development. Inhibition in activation of ERK 1/2 or PI 3/Akt kinase induces cell death[43]. Both of these molecules are involved in activation of STAT3. In our study we show that PTX inhibits the phosphorylation of Akt in a dose dependent manner and a similar inhibitory effect on pERK1/2 is observed at higher concentration of PTX i.e. at 4 mM. This might be one of the ways through which the activity of STAT3 gets inhibited by PTX; but the possibility of other ways of inhibition of STAT3 exists. Altered levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines which are also pro-angiogenic factors are observed in various forms of cancer including melanoma. The cytokines such as IL-6, IFNγ and TNF α act as autocrine growth factors; they are secreted by tumor cells and in turn they activate cell survival by activating STAT3 signaling[43-45]. We observed a significant reduction in expression of IFNγ and TNF α at the transcriptional level on PTX treatment. However no effect was observed on IL6. It is possible that some other transcription factor, along with STAT3, is involved in synthesis of IL6 in B16F10 melanoma.Recently, Niu and colleagues reported that constitutive activity of STAT3 up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis[46]. In hypoxic condition of solid tumors STAT3 stabilizes HIF 1α through delaying protein ubiquitination& accelerating protein synthesis. HIF 1 alpha is also regulated at the level of protein initiation by activation of Akt . HIF 1α along with STAT3 acts as a transcription factor for VEGF expression in tumor cells[47, 48]. Our results suggest that protein levels of HIF 1α get significantly decreased on PTX treatment in B16F10 melanoma. Consistently PTX treatment also causes a remarkable decrease in expression of VEGF at transcriptional & translational level. Co-expression of VEGF and its receptors on the tumor cell implies that VEGF may directly function on tumor cells themselves by enhancing downstream signaling such as STAT3 signaling[49, 50]. PTX treatment shows a remarkable decrease in the expression of VEGF receptors (VEGFR1, VEGFR2). The exact molecular mechanism of this inhibition on VEGF receptors is still unclear. We plan to study this in the future. The above results indicate that PTX can exert its anti-angiogenic effect in B16F10 melanoma by inhibiting expression of VEGF & its receptors.To confirm the anti-angiogenic effect of PTX in vivo we injected B16F10 cells intradermaly on shaven ventral side of C57BL/6 mice. In this in vivo angiogenesis assay we found that PTX inhibits tumor induced new blood vessel formation without any side effects in C57BL/6 mice in a dose dependent manner. This effect was observed with no toxicity in mice which further gives advantage to using PTX in anti-angiogenic therapy of cancer treatment.In summary our results show that PTX downregulates the activation of STAT3 via inhibiting the activation of its upstream kinases. PTX treatment also inhibits HIF1α. Inhibition in activation of STAT3and HIF1α further decreases the expression of the gene VEGF which is involved in angiogenesis. Inhibition in angiogenesis in vivo corroborates our theory that PTX can be used as a potent anti-angiogenic agent. Thus PTX treatment could be beneficial in melanoma therapy and should be taken in serious consideration for its implementation as an anti-angiogenic agent for adjuvant therapy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The Authors would like to express their gratitude to Indian council of medical research (ICMR), New Delhi for funding.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML